Scientific Papers in SCI
2024
2024
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Evaluation of Pt/TiO2-Nb2O5 systems in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2 from industrial effluents
Lara Sandoval, AE; Serafin, J; Murcia Mesa, JJ; Rojas Sarmiento, HA; Hernandez Niño, JS; Llorca, J; Navío Santos, JA; Hidalgo Lõpez; MCFuel, 363 (2024) 130932
Show abstract ▽
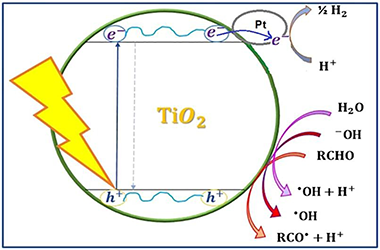
Different Pt-TiO2-Nb2O5 systems were synthesized and studied in the photocatalytic reforming of glucose for the generation of H2. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized photocatalysts were analyzed using different characterization techniques from which it was found that fluoridation and sulphation have different effects on the oxides under study such as a protective effect on the crystalline phase in anatase, and greater response in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The addition of fluorine or sulfates favors the reduction of platinum species on the surface of the semiconductor oxides and a better homogeneity of size and distribution of the particles of this metal. Studies were carried out in the gas phase that allowed the monitoring and quantification of the hydrogen produced from aqueous glucose solutions and it was determined that Pt-F-Nb2O5 and Pt-F-TiO2 are the most efficient materials for the production of hydrogen from this substrate. Similarly, liquid phase studies were carried out with a real sample from a confectionery industry where it was determined that with the material Pt-F-Nb2O5 the highest transformation of glucose is obtained, without the formation of any other sugar or intermediate compound, indicating the preferential production of hydrogen during the photocatalytic reaction. The foregoing demonstrates the potential of the evaluated process in obtaining this gas from the recovery of polluting residues derived from the samples under study.
May, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2024.130932
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Exciton-carrier coupling in a metal halide perovskite nanocrystal assembly probed by two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy
Rojas-Gatjens, E; Tiede, DO; Koch, KA; Romero-Perez, C; Galisteo-López, JF; Calvo, ME; Míguez, H; Kandada, ARSJournal of Physics-Materials, 7 (2024) 025002
Show abstract ▽
The surface chemistry and inter-connectivity within perovskite nanocrystals play a critical role in determining the electronic interactions. They manifest in the Coulomb screening of electron-hole correlations and the carrier relaxation dynamics, among other many-body processes. Here, we characterize the coupling between the exciton and free carrier states close to the band-edge in a ligand-free formamidinium lead bromide nanocrystal assembly via two-dimensional coherent spectroscopy. The optical signatures observed in this work show: (i) a nonlinear spectral lineshape reminiscent of Fano-like interference that evidences the coupling between discrete electronic states and a continuum, (ii) symmetric excited state absorption cross-peaks that suggest the existence of a coupled exciton-carrier excited state, and (iii) ultrafast carrier thermalization and exciton formation. Our results highlight the presence of coherent coupling between exciton and free carriers, particularly in the sub-100 femtosecond timescales.
April, 2024 | DOI: 10.1088/2515-7639/ad229a
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Reforming of biomass-derived producer gas using toluene as model tar: Deactivation and regeneration studies in Ni and K-Ni catalysts
Azancot, L; González-Castaño, M; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Research, 247 (2024) 118210
Show abstract ▽
Within the syngas production from biomass gasification, tar removal constitutes a chief issue to overcome for advanced catalytic systems. This work investigates the performance of Ni and Ni-K catalysts for reforming of derived-biomass producer gas using toluene as model tar. At 750 degrees C and 60Lg(-1)h(-1), the stability test (70 h) revealed stable performances (CO2, CH4 and C7H8 conversions of 60, 95 and 100%, correspondingly) uniquely for the Ni-K catalyst. Although the efficient protection towards coking let by K was demonstrated, TPO studies over the post-reacted systems still evidenced the presence of carbon deposits for both samples. Conducting three successive reaction/regeneration cycles with different gasifying agents (air, steam and CO2) at 800 C for 1h, the capability towards regeneration of both catalytic systems was assessed and the spent catalysts were characterized by XRD, SEM and TEM. While none of the regeneration treatments recovered the performance of the unpromoted catalyst, the Ni-K catalysts demonstrated the capability of being fully regenerated by air and CO2 and exhibited analogous catalytic performances after a series of reaction/regeneration cycles. Hence, it is proved that the addition of K into Ni catalysts not only enhances the resistance against deactivation but enables rather facile regenerative procedures under certain atmospheres (air and CO2).
April, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118210
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
A profitability study for catalytic ammonia production from renewable landfill biogas: Charting a route for the next generation of green ammonia
González-Arias, J; Nawaz, MA; Vidal-Barrero, F; Reina, TRFuel, 360 (2024) 130584
Show abstract ▽
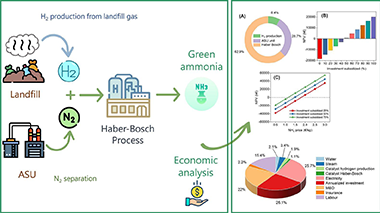
This study introduces a novel techno-economic approach to renewable ammonia production using landfill biogas. The proposed process involves bio-hydrogen generation from landfill biogas, nitrogen production via air separation, and the Haber-Bosch process. Building on our prior research, which demonstrated the economic competitiveness of renewable hydrogen production from landfill gas, we extend our investigation to analyze the feasibility of producing renewable ammonia from biogas-derived bio-hydrogen. However, the economic analysis for the baseline scenario reveals the current lack of profitability (net present value of −18.3 M€), with ammonia prices needing to quadruple to achieve profitability. Major costs, including investment, maintenance, overhead expenses, and electricity, collectively account for over 70%, suggesting the potential efficacy of investment subsidies as a political tool. Only cases with subsidies exceeding 50% of total investment costs, under current ammonia market prices, would render the green ammonia route profitable. Our findings underscore the significant techno-economic challenges in realizing renewable ammonia production, emphasizing the need for innovation in process engineering and catalytic technologies to enable competitive and scalable green ammonia production.
March, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130584
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Optimizing biogas methanation over nickel supported on ceria-alumina catalyst: Towards CO2-rich biomass utilization for a negative emissions society
González-Arias, J; Torres-Sempere, G; Arroyo-Torralvo, F; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAEnrironmental Research, 242 (2024) 117735
Show abstract ▽
Biogas methanation emerges as a prominent technology for converting biogas into biomethane in a single step. Furthermore, this technology can be implemented at biogas plant locations, supporting local economies and reducing dependence on large energy producers. However, there is a lack of comprehensive studies on biogas methanation, particularly regarding the technical optimization of operational parameters and the profitability analysis of the overall process. To address this gap, our study represents a seminal work on the technical optimization of biogas methanation obtaining an empirical model to predict the performance of biogas methanation. We investigate the influence of operational parameters, such as reaction temperature, H2/CO2 ratio, space velocity, and CO2 share in the biogas stream through an experimental design. Based on previous research we selected a nickel supported on ceria-alumina catalyst; being nickel a benchmark system for methanation process such selection permits a reliable data extrapolation to commercial units. We showcase the remarkable impact of studied key operation parameters, being the temperature, the most critical factor affecting the reaction performance (ca. 2 to 5 times higher than the second most influencing parameter). The impact of the H2/CO2 ratio is also noticeable. The response surfaces and contour maps suggest that a temperature between 350 and 450 degrees C and an H2/CO2 ratio between 2.5 and 3.2 optimize the reaction performance. Further experimental tests were performed for model validation and optimization leading to a reliable predictive model. Overall, this study provides validated equations for technology scaling-up and techno-economic analysis, thus representing a step ahead towards real-world applications for bio-methane production.
February, 2024 | DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117735
- ‹ previous
- 2 of 410
- next ›














