Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photoreforming of glycerol to produce hydrogen from natural water in a compound parabolic collector solar photoreactor
Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Sowik, J; Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Colón, G; Peral, J; Malato, SJournal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11 (2023) 111216
Show abstract ▽
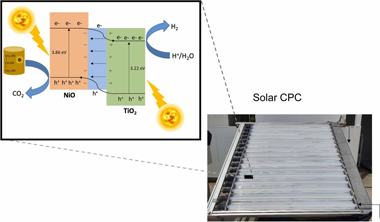
To improve TiO2 for H2 generation, one strategy for the separation of photogenerated charges is the formation of heterostructures with other materials. In particular, NiO is a photocatalyst known for its good stability and low cost. However, no studies at pilot scale using solar energy have been described. Consequently, an evaluation of a physical NiO:TiO2 mixture at pilot scale (25 L) with natural irradiation (2.10 m2 of sun-exposed surface) and with simultaneous glycerol photoreforming was explored. NiO:TiO2 50 mg & sdot;L- 1 resulted in the highest hydrogen production, showing an STH = 1.44%, considering only the UV fraction of the solar irradiation. H2 and CO2 production were analysed by on-line GC; Glycerol, dissolved organic carbon, carboxylic acids and nickel leaching were also evaluated. The NiO:TiO2 mixtures rendered a systematically lower H2 production in natural water than in high-purity water. The increase of ionic strength increased the mean size of particle clusters, promoting rapid sedimentation. All this indicates the importance of testing under real field conditions for attaining reliable solar to hydrogen (STH) efficiency.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111216
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of zeolite topological structure in bifunctional catalyst on direct conversion of syngas to light olefins
Meng, FH; Gong, ZY; Yang, LL; Wang, Q; Xing, MQ; Nawaz, MA; Li, ZMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 362 (2023) 112792
Show abstract ▽
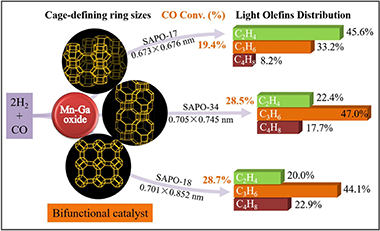
Bifunctional catalyst composed of metal oxide and zeolite (OX-ZEO) is a promising strategy for the direct conversion of syngas to light olefins (STO), where the structure of zeolite plays a vital role in determining the selectivity of product. Herein, three kinds of silicoaluminophosphate zeolites with different topological structures, i.e., the ERI(SP17), AEI(SP18) and CHA(SP34), were hydrothermally synthesized, after the combination with Mn-Ga oxide, the prepared OX-ZEO was applied for STO reaction. The variation in the crystallization time for SP17 synthesis has a great impact on the generation of impurity phase of SAPO-5, where a crystallization time of 48-96 h is found to be beneficial in synthesizing SP17 zeolite with pure phase. SP17 zeolite with a crystallization time of 96 h, possesses the micropores and columnar morphology, where the small cage-defining 8-ring size of SP17 shows the olefins selectivity of 87.0% at a low CO conversion of 19.4%, significantly deviating towards the major fraction of ethylene (45.6%) than that of butene (8.2%). In a contrast, SP18 and SP34 zeolites with the same and large cage-defining 8-ring size, are richer in propylene and butene fractions than that of ethylene in overall similar olefins selectivity of 87.0% and 87.1% at CO conversion of 28.7% and 28.5%, respectively. Interestingly, it is further interpreted that the SP17 sample generated more carbon species during the reaction due to the small 8-ring size, while those amounts of carbon species were restricted in the hierarchical pore structure and plate-like morphology in SP18 and SP34 samples.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2023.112792
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Plasticized, greaseproof chitin bioplastics with high transparency and biodegradability
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Porras-Vazquez, JM; Tedeschi, G; Morales, Y; Fernandez-Ortuno, D; Athanassiou, A; Guzman-Puyol, SFood Hydrocolloids, 145 (2023) 109072
Show abstract ▽
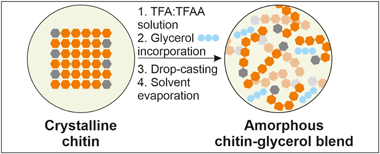
A mixture of trifluoroacetic acid:trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFA:TFAA) was used to dissolve chitin from shrimp shells. Free-standing films were prepared by blending the chitin solution and glycerol at different percentages, followed by drop-casting, and the complete evaporation of the solvents. After this process, the chitin matrix showed an amorphous molecular structure, as determined by X-ray diffraction. Optical, mechanical, thermal, and antioxidant properties were also thoroughly investigated. The incorporation of glycerol induced a plasticizing effect on the mechanical response of films and improved their transparency. In addition, hydrodynamic and barrier properties were determined by contact angle and water vapor/oxygen transmission rates, respectively, and revealed typical values of other polysaccharides. These bioplastics also presented an excellent greaseproof behavior with the highest degree of oil repellency as determined by the Kit test. Moreover, the overall migration was evaluated by using Tenax & REG; as a dry food simulant and levels were compliant with European regulations. Their antifungal properties were tested using Botrytis cinerea as a model. Biodegradability was also determined by measuring the biological oxygen demand in seawater. Degradation rates were high and similar to those of other fully-degradable materials.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109072
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Spherosilicate-modified epoxy coatings with enhanced icephobic properties for wind turbines applications
Kozera, R; Zietkowska, K; Przybyszewski, B; Boczkowska, A; Sztorch, B; Paku, D; Przekop, RE; Trzcinski, J; Borras, AColloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 679 (2023) 132475
Show abstract ▽
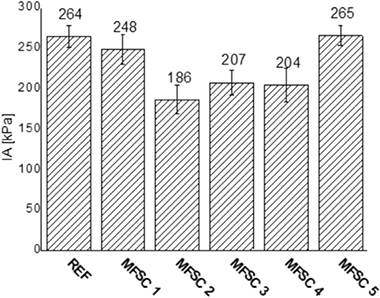
Industries around the world use active methods, which include thermal, mechanical and chemical approaches, to reduce icing on aerodynamic surfaces such as wind turbines and aircraft. However, they are often inefficient, costly, and pollute the environment. For years, new coatings with anti-icing properties (so-called icephobic coatings) have been developed to either replace or work in tandem with active systems. In this study, coatings were designed based on an epoxy gelcoat commonly used for wind turbines through chemical modification with spherosilicate derivatives. Di- and tri-functional spherosilicates have both groups that increase the degree of hydro-/icephobicity of composites , groups capable of interacting with epoxy resin and amine hardener. The icephobicity of the surface was determined using ice adhesion. The lowest value of this parameter reached a value of 186 kPa, a 30 % reduction compared to the unmodified coating. In addition, the hydrophobicity of the surface was determined (the highest water contact angle was equal to 103 degrees). A correlation was observed, proven in many works, that as the surface roughness increases, the anti-icing properties deteriorate. For individual modifications, it was also shown that hydrophobicity has a positive effect on ice adhesion. The work also examined the surface zeta potential and determined the durability of the properties after 100 icing/deicing cycles.
December, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132475
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Coal Chemistry Industry: From Production of Liquid Fuels to Fine Chemicals to Carbon Materials
Zhang, YY; Li, HT; Reina, TR; Liu, JEnergy & Fuels, (2023)
Show abstract ▽
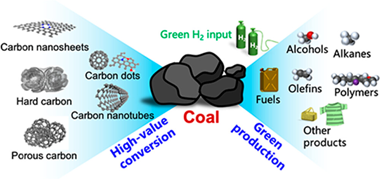
Coal resources are one of the key energy sources and essential for modern economic development. Despite the traditional coal industries having made considerable contributions to chemical production and energy storage, the accompanying environmental pollution and high energy consumption have also arisen that cause significant influence of the ecological balance. Hence, there is an urgent need to exploit feasible approaches to the sustainable utilization of coal resources. This review begins with a comprehensive summary of the representative coal chemistry technologies with critical discussions. Subsequently, a novel strategy coupled with green hydrogen is discussed for sustainable conversion of coal and highly efficient manufacture of downstream products. Moreover, the unique role of coal in terms of high-value-added carbon material production is highlighted as a low-cost resource for distinct applications. Finally, we propose several future directions for advanced coal chemistry development.
November, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02661
- ‹ previous
- 7 of 410
- next ›














