Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Coloidales
From structure to luminescence investigation of oxyfluoride transparent glasses and glass-ceramics doped with Eu3+/Dy3+ ions
Walas, M; Lisowska, M; Lewandowski, T; Becerro, AI; Lapinski, M; Synak, A; Sadowski, W; Koscielska, BJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 896 (2019) 1410-1418
Show abstract ▽
Glasses and glass-ceramics with nominal composition 73 TeO2- 4BaO-3Bi(2)O(3)-18SrF(2)-2RE(2)O(3) (where RE = Eu, Dy) have been synthesized by conventional melt-quenching technique and subsequent heat treatment at 370 degrees C for 24 h in air atmosphere. Various Eu3+ to Dy3+ molar ratio have been applied to investigate luminescence properties in both glass and glass-ceramic matrices. Especially, white light emission through simultaneous excitation of Eu3+ and Dy3+ has been studied in detail. Influence of crystalline SrF2 phase on luminescence kinetics has been determined by luminescence decay time measurements. Presence of crystalline SrF2 phase has been confirmed by X-ray diffraction technique XRD and transmission electron microscopy TEM. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy XPS and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy FTIR have been applied to get further insight into structural properties of glass and glass-ceramic materials. Color tunable white light emission has been obtained using UV excitation. Influence of the SrF2 crystallization on luminescence properties of prepared materials have been described in detail. Moreover, luminescence properties and especially emission color dependence on the Eu3+ to Dy3+ molar ratio have been exhaustively studied. Color-tunable white light emission has been observed as a result of simultaneous radiative transition of both, Eu3+ and Dy3+ ions when applying UV excitation. Judd - Ofelt and other optical parameters have been calculated based on luminescence emission spectra. Achieved results confirm that tellurite glass-ceramics containing SrF2 nanocrystals are good hosts for RE3+ ions and they can be considered as new phosphors for white light emitting diodes WLEDs.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.07.017
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Casimir-Lifshitz Force Based Optical Resonators
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 10 (2019) 5856-5860
Show abstract ▽
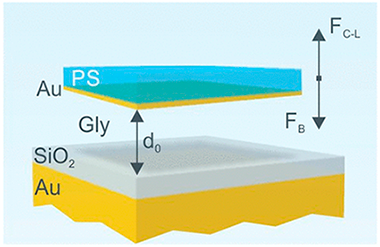
We theoretically investigate the building of optical resonators based on the levitation properties of thin films subjected to strong repulsive Casimir-Lifshitz forces when immersed in an adequate medium and confronted with a planar substrate. We propose a design in which cavities supporting high Q-factor optical modes at visible frequencies can be achieved by means of combining commonly found materials, such as silicon oxide, polystyrene or gold, with glycerol as a mediating medium. We use the balance between flotation and repulsive Casimir-Lifshitz forces in the system to accurately tune the optical cavity thickness and hence its modes. The effects of other forces, such as electrostatic, that may come into play are also considered. Our results constitute a proof of concept that may open the route to the design of photonic architectures in environments in which dispersion forces play a substantial role and could be of particular relevance for devising novel microfluidic optical resonators.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b02030
Reactividad de Sólidos
A QTAIM and DFT study of the dizinc bond in non-symmetric [CpZn2Ln] complexes
Ayala, R; Galindo, AJournal of Organometallic Chemistry, 898 (2019) UNSP 120878
Show abstract ▽
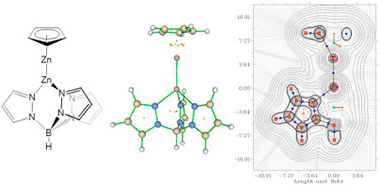
Several [Zn2L2] and [CpZn2Ln] dizinc compounds have been studied by density functional theory (DFT) and quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) in order to compare the nature and topology of the Zn-Zn bond in symmetrical and non-symmetrical complexes. The stability of these complexes have been evaluated on the basis of the formation energies. The disproportionation reaction has also been analysed indicating that symmetric complexes are less stable than non-symmetric ones. To certain extent, the properties of the [CpZn2Ln] complexes are between those of the [Zn2L2] and [Zn2Cp2] compounds. The asymmetry of the [CpZn2Ln] compounds is illustrated in terms of the topological properties, especially in the Source Function (SF) and Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) analysis.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2019.120878
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of pre-deformation on the precipitation hardening in Cu-Ni-Si alloy
Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JMRevista de Metalurgia, 55 (2019) e157
Show abstract ▽
The effects of pre-deformation on the precipitation processes in a Cu-2.8 Ni-1.4 Si (at.%) alloy were studied using differential scanning calorimetric (DSC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and microhardness measurements. The calorimetric curves shows the presence of one exothermic reaction attributed to the formation of delta-Ni2Si precipitates in the copper matrix that was confirmed by TEM. In addition it can be observed that the temperature of the maximum of the DSC peak decreases with the increase of the pre-deformation to the aging treatments. The activation energies calculated for the precipitation of by the Kissinger method, were similar to those calculated by an Arrhenius function, from the maximum hardening of the matrix due to aging treatments (saturation of the hardness during isothermal aging). The analysis of the microhardness measurements together with the calorimetric curves and the TEM micrographs confirm, on the one hand, that the formation of the delta-Ni2Si phase, during the aging treatments, are responsible for the hardening of the copper matrix, and on the other hand that the deformation prior to the aging treatment partially inhibits the formation of the precipitates.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.3989/revmetalm.157
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Spatially Resolved Analysis of Defect Annihilation and Recovery Dynamics in Metal Halide Perovskite Single Crystals
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HACS Applied Energy Materials, 2 (2019) 6967-6972
Show abstract ▽
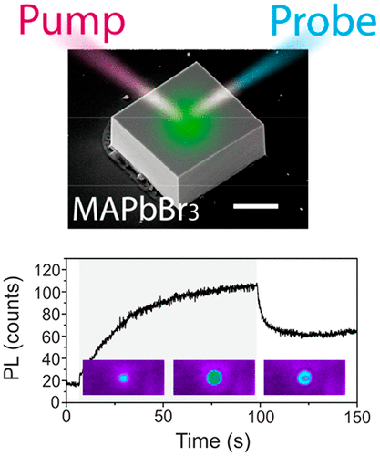
The spectacular advances in efficiency of optoelectronic devices based on lead-halide perovskites have been accompanied by detailed structural and optical studies regarding the instability presented by these materials, which constitute their main bottleneck for commercialization. Following a pump and probe scheme in a laser scanning confocal microscope, we resolve the photoinduced emission activation/deactivation dynamics in CH3NH3PbBr3 single crystals with millisecond and sub-micrometer resolution. This is complemented with a study of spectral variations and interpreted in the framework of light-induced ion migration and associated defect passivation. Our results point to the presence of photoinduced structural changes accompanying the migration of ions.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.9b01335
- ‹ anterior
- 115 of 410
- siguiente ›














