Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Applications and potentialities of Atomic Force Microscopy in fossil and extant plant cuticle characterization
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAReview of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 268 (2019) 125-132
Show abstract ▽
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) is a versatile technique of surface characterization, providing accurate information about the topography and other wide variety of magnitudes at submicron scale. It is extensively utilized in materials science, but its use in other disciplines such as paleobotany is infrequent. In this review, we introduce the main concepts of AFM to paleobotanists, comparing the characteristics of this technique to common electronic and optical microscopies. Then, main works with extant plants, in particular plant cuticles, are described. Finally, realistic applications with fossils are reviewed and their potential use in the characterization of plant fossils discussed. AFM is proposed as a complementary technique to common microscopies to characterize plant cuticle fine details at nanoscale.
Septiembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2019.06.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
SiOx by magnetron sputtered revisited: Tailoring the photonic properties of multilayers
Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alvarez, R; Espinos, JP; Rico, V; Gil-Rostra, J; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARApplied Surface Science, 488 (2019) 791-800
Show abstract ▽
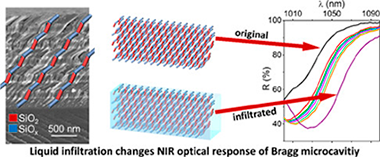
Traditionally porous silicon based photonic structures have been prepared by electrochemically etching of silicon. In this work, porous multilayers of nanocolumnar SiOx and SiO2 thin films acting as near infrared (NIR) 1D-photonic nanostructures are prepared by magnetron sputtering deposition at oblique angles (MS-OA). Simultaneous control of porosity and stoichiometry of the stacked films is achieved by adjusting the deposition angle and oxygen partial pressure according to a parametric formula. This new methodologoy is proved for the synthesis of SiOx thin films with x close to 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6 and nanostructures varying from compact (at 0 degrees deposition angle) to highly porous and nanocolumnar (at 70 degrees and 85 degrees deposition angles). The strict control of composition, structure and nanostructure provided by this technique permits a fine tuning of the absorption edge and refraction index at 1500 nm of the porous films and their manufacturing in the form of SiOx-SiO2 porous multilayers acting as near infrared (NIR) 1D-photonic structures with well-defined optofluidic responses. Liquid tunable NIR Bragg mirrors and Bragg microcavities for liquid sensing applications are presented as proof of concept of the possibilities of this MS-OA manufacturing method as an alternative to the conventional electrochemical fabrication of silicon based photonic structures.
Septiembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.273
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Extraordinary visible photocatalytic activity of a Co0.2Zn0.8O system studied in the Remazol BB oxidation
KarimTanji; J.A.Navio; Jamal Naja; M.C.Hidalgo; Abdellah Chaqroune; C.Jaramillo-Páez; Abdelhak KherbecheJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 382 (2019) 111877
Show abstract ▽
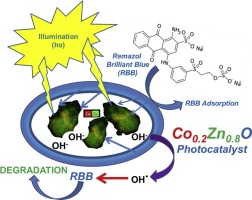
Nanoparticles of CoxZn1-xO system with a nominal composition of x=0.2 were synthesized by the Solution Combustion Method (SCM). Structural and morphological studies as well as the chemical composition of the material were widely investigated by different techniques. Photocatalytic activity under UV and Visible illumination was studied by means of the Remazol Brilliant Blue dye (RBB) oxidation reaction. The effect of different experimental parameters, such as the initial dye concentration, photocatalyst mass, pH or hydrogen peroxide concentration on the RBB discoloration under UV irradiation was studied. Optimal experimental conditions were found to be a photocatalyst mass of 1 g.L-1, dye concentration of 20 mg.L-1 and solution pH of 11. Hydrogen peroxide addition was found to have no effect in the photocatalytic behavior of the material in the range of concentration studied (0 to 6•10-4 M). The optimal parameters were chosen to investigate the degradation of RBB under UV-illumination and just visible illumination. It was observed that the UV-photocatalytic property of pristine ZnO for the RBB removal was scarcely improved after cobalt-incorporation, whereas the effect of cobalt incorporation into ZnO greatly enhanced the RBB conversion under visible illumination. Even more interesting is that, under same experimental conditions, the visible efficiency of the Co-ZnO system is the same that the one showed under UV illumination, i.e. the system does not loose efficiency when illuminated only with visible light.
Septiembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.111877
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Insoluble and Thermostable Polyhydroxyesters From a Renewable Natural Occurring Polyhydroxylated Fatty Acid
Benitez, JJ; Guzman-Puyol, S; Cruz-Carrillo, MA; Ceseracciu, L; Moreno, AG; Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 7 (2019) art. 643
Show abstract ▽
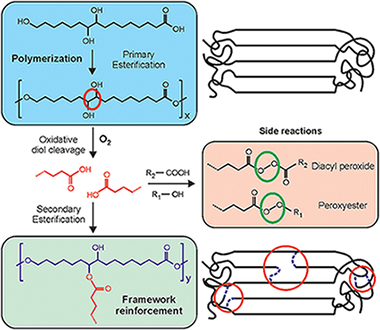
To explore the potential of long chain polyhydroxyalkanoates as non-toxic food packaging materials, the characterization of polyesters prepared from a natural occurring polyhydroxylated C16 carboxylic acid (9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic or aleuritic acid) has been addressed. Such monomer has been selected to elucidate the reactivity of primary and secondary hydroxyl groups and their contribution to the structure and properties of the polyester. Resulting polyaleuritate films have been produced using an open mold in one-step, solvent-free self-polycondensation in melt state and directly in air to evaluate the effect of oxygen in their final physical and chemical properties. These polymers are amorphous, insoluble, and thermostable, being therefore suitable for solvent, and heat resistant barrier materials. Structurally, most of primary hydroxyls are involved in ester bonds, but there is some branching arising from the partial participation of secondary O-H groups. The oxidative cleavage of the vicinal diol moiety and a subsequent secondary esterification had a noticeable effect on the amorphization and stiffening of the polyester by branching and densification of the ester bond network. A derivation of such structural modification was the surface compaction and the reduction of permeability to water molecules. The addition of Ti(OiPr)(4) as a catalyst had a moderate effect, likely because of a poor diffusion within the melt, but noticeably accelerated both the secondary esterification and the oxidative processes. Primary esterification was a high conversion bulk reaction while oxidation and secondary esterification was restricted to nearby regions of the air exposed side of cast films. The reason was a progressive hindering of oxygen diffusion as the reaction progresses and a self-regulation of the altered layer growth. Despite such a reduced extent, the oxidized layer noticeably increased the UV-vis light blockage capacity. In general, characterized physical properties suggest a high potential of these polyaleuritate polyesters as food preserving materials.
Septiembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00643
2018
2018
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Elusive super-hard B6C accessible through the laser-floating zone method
Moshtaghioun, BM; Cumbrera, FL; Gomez-Garcia, D; Pena, JIScientific Reports, 9 (2019) art. 13340
Show abstract ▽
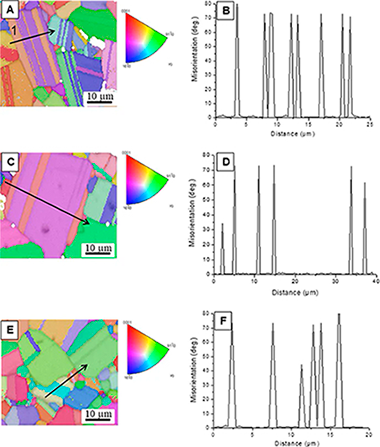
Boron carbide is among the most promising ceramic materials nowadays: their mechanical properties are outstanding, and they open potential critical applications in near future. Since sinterability is the most critical drawback to this goal, innovative and competitive sintering procedures are attractive research topics in the science and technology of this carbide. This work reports the pioneer use of the laser-floating zone technique with this carbide. Crystallographic, microstructural and mechanical characterization of the so-prepared samples is carefully analysed. One unexpected output is the fabrication of a B6C composite when critical conditions of growth rate are adopted. Since this is one of the hardest materials in Nature and it is achievable only under extremely high pressures and temperatures in hot-pressing, the use of this technique offers a promising alternative for the fabrication. Hardness and elastic modulus of this material reached to 52 GPa and 600 GPa respectively, which is close to theoretical predictions reported in literature.
Septiembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49985-2
- ‹ anterior
- 117 of 410
- siguiente ›














