Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of the effective refractive index on the radiative decay rate in nanoparticle thin films
Romero, M; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Lozano, G; Míguez, HNanoscale, 15 (2023) 15279-15287
Show abstract ▽
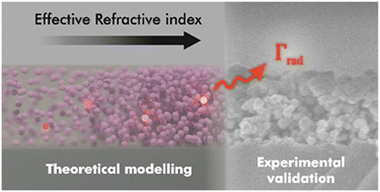
In this work, we theoretically and experimentally study the influence of the optical environment on the radiative decay rate of rare-earth transitions in luminescent nanoparticles forming a thin film. We use electric dipole sources in finite-difference time-domain simulations to analyze the effect of modifying the effective refractive index of transparent layers made of phosphor nanocrystals doped with rare earth cations, and propose a correction to previously reported analytical models for calculating the radiative decay rate. Our predictions are tested against an experimental realization of such luminescent films, in which we manage to vary the effective refractive index in a gradual and controllable manner. Our model accurately accounts for the measurements attained, allows us to discriminate the radiative and non-radiative contributions to the time-resolved photoluminescence, and provides a way to rationally tune the spontaneous decay rate and hence the photoluminescence quantum yield in an ensemble of luminescent nanoparticles.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/d3nr03348a
Materiales Coloidales
Lanthanide vanadate-based trimodal probes for near-infrared luminescent bioimaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Nunez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Becerro, AI; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 646 (2022) 721-731
Show abstract ▽
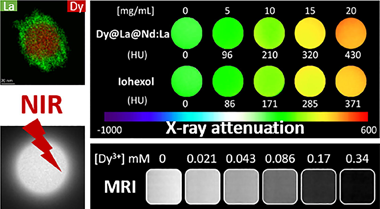
We have developed a trimodal bioimaging probe for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography using Dy3+ as the paramagnetic component and Nd3+ as the luminescent cation, both of them incorporated in a vanadate matrix. Among different essayed architectures (single phase and core-shell nanoparticles) the one showing the best luminescent properties is that consisting of uniform DyVO4 nanoparticles coated with a first uniform layer of LaVO4 and a second layer of Nd3+-doped LaVO4. The magnetic relaxivity (r2) at high field (9.4 T) of these nanoparticles was among the highest values ever reported for this kind of probes and their X-ray attenuation properties, due to the presence of lanthanide cations, were also better than those of a commercial contrast agent (iohexol) commonly used for X-ray computed to-mography. In addition, they were chemically stable in a physiological medium in which they could be easily dispersed owing to their one-pot functionalization with polyacrylic acid, and, finally, they were non-toxic for human fibroblast cells. Such a probe is, therefore, an excellent multimodal contrast agent for near-infrared luminescent imaging, high-field magnetic resonance imaging, and X-ray computed tomography.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.05.078
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones - Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Alkaline Salts on Pyrolyzed Solid Wastes in Used Edible Oils: An Attenuated Total Reflectance Analysis of Surface Compounds as a Function of the Temperature
Romero-Sarria, F; Real, C; Córdoba, JM; Hidalgo, C; Alcalá, MDSpectroscopy Journal, 1 (2023) 98-110
Show abstract ▽
Biochars obtained via the pyrolysis of biomass are very attractive materials from the point of view of their applications and play key roles in the current energy context. The characterization of these carbonaceous materials is crucial to determine their field of application. In this work, the pyrolysis of a non-conventional biomass (solid wastes in used edible oils) was investigated. The obtained biochars were characterized using conventional techniques (TG, XRD, and SEM-EDX), and a deep analysis via ATR-FTIR was performed. This spectroscopic technique, which is a rapid and powerful tool that is well adapted to study carbon-based materials, was employed to determine the effect of temperature on the nature of functional groups on the surface. Moreover, the water washing of the raw sample (containing important quantities of inorganic salts) before pyrolysis evidenced that the inorganic salts act as catalysts in the biomass degradation and influence the degree of condensation (DOC) of PAH. Moreover, it was observed that these salts contribute to the retention of oxygenated compounds on the surface of the solid.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.3390/spectroscj1020009
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Preparation, characterization and activation of Pd catalysts supported on CNx foam for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid
Arzac, GM; Rojas, TC; Real, C; Fernández, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 31899-31613
Show abstract ▽
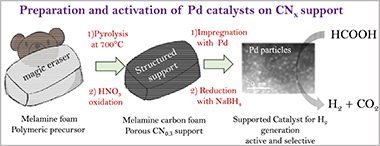
In this work, we have prepared a series of Pd catalysts on a CNx support for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid. The structured CNx support was obtained through thermal pyrolysis of melamine foam and the pyrolysis conditions were optimized to achieve high surface area. The resulting support contains high amount of nitrogen with a contribution of pyridinic component. Several Pd catalysts were prepared and under optimized condi-tions, we were able to obtain small (2.7 +/- 0.9) nm Pd particles by using the oxidized support in powdery form. The activity of the optimized catalyst was studied under different con-ditions in the fresh and the used form. The fresh catalyst did not show significant activity. However, we found that the catalyst activated after use. Activation was understood in terms of the variation of surface Pd oxidation states under the effect of formic acid/sodium formate solutions. We found that the best activity is achieved under an optimal proportion of Pd0/PdII surface states according to previous reports. Under the best conditions, the activity of the best catalyst (8.6Pd/CN0.3) was as high as 9245 h-1, attributable to the small particle size, the Pd0/PdII ratio, the amount of pyridinic nitrogen, and the testing conditions, which included the preadsorption of sodium formate
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.04.244
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Cobalt Stabilization through Mesopore Confinement on TiO2 Support for Fischer-Tropsch Reaction
Platero, F; Todorova, S; Aoudjera, L; Michelin, L; Lebeau, B; Blin, JL; Holgado, JP; Caballero, A; Colón, GACS Applied Energy Materials, 6 (2023) 9475-9486
Show abstract ▽
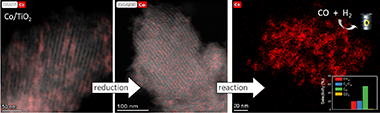
Cobalt supported on mesostructured TiO2 catalysts has been prepared by a wet-impregnation method. The Co/TiO2 catalytic system showed better catalytic performance after support calcination at 380 °C. Co nanoparticles appeared well distributed along the mesopore channels of TiO2. After reduction pretreatment and reaction, a drastic structural change leads to mesopore structure collapse and the dispersion of the Co nanoparticles on the external surface. Along this complex process, Co species first form discrete nanoparticles inside the pore and then diffuse out as the pore collapses. Through this confinement, a strong metal–support interaction effect is hindered, and highly stable metal active sites lead to better performance for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction toward C5+ products.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.3c01432
- ‹ anterior
- 13 of 410
- siguiente ›














