Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Process design and utilisation strategy for CO2 capture in flue gases. Technical assessment and preliminary economic approach for steel mills
Navarro, JC; Baena-Moreno, FM; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Almagro, JF; Odriozola, JARenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 184 (2023) 113537
Show abstract ▽
The steel industry is the most relevant sector in emerging economies due to its application in numerous fields. However, steel manufacturing involves large energy investment and produces significant greenhouse gas emissions. The current world economic and environmental scenario therefore necessitates that improvements in the footprint of the steel industry be made without affecting its viability. Considering the present challenge, we report two possible processes for Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). The first process is the competitive capture of CO2-SO2, followed by CO2 valorisation to methane. However, the CO2 capture capacity and lifetime for the adsorbent after multiple cycles could be improved through preliminary desulphurization of the gas current. The improved system demonstrates net profitability in a typical stainless steel plant. Therefore, it can be implemented in an industrial setting without profitability loss to steelmaking operations, fulfilling bot the goal of reducing CO2 emissions while protecting the mainstay of the plant.
Septiembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113537
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Measurement principles for quantum spectroscopy of molecular materials with entangled photons
Moretti, L; Rojas-Gatjens, E; Uboldi, L; Tiede, DO; Kumar, EJ; Trovatello, C; Preda, F; Perri, A; Manzoni, C; Cerullo, G; Kandada, ARSJournal of Chemical Physics, 159 (2023) 084201
Show abstract ▽
Nonlinear spectroscopy with quantum entangled photons is an emerging field of research that holds the promise to achieve superior signal-to-noise ratio and effectively isolate many-body interactions. Photon sources used for this purpose, however, lack the frequency tunability and spectral bandwidth demanded by contemporary molecular materials. Here, we present design strategies for efficient spontaneous parametric downconversion to generate biphoton states with adequate spectral bandwidth and at visible wavelengths. Importantly, we demonstrate, by suitable design of the nonlinear optical interaction, the scope to engineer the degree of spectral correlations between the photons of the pair. We also present an experimental methodology to effectively characterize such spectral correlations. Importantly, we believe that such a characterization tool can be effectively adapted as a spectroscopy platform to optically probe system-bath interactions in materials.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0156598
Reactividad de Sólidos
Touch-free reactive flash sintering of dense strontium hexaferrite permanent magnet
Jalali, SIA; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Chacartegui, R; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Raj, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society (2023)
Show abstract ▽
This work presents an extension of the touch-free flash sintering technique. In the proposed technique, chemical reaction and sintering occur in a single step, without the use of electrodes, in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. We show that a dense, single-phase strontium hexaferrite magnet can be produced from a mixture of commercial carbonate and oxide powders in a single step in a little more than a minute. This new technique implies significant reduction in energy and time consumption (primarily because of ultrafast processing) relative to conventional sintering.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.19389
Ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized by 1,2,3-triazolylidene ligands in the hydrogen isotope exchange of E-H bonds (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) using deuterium gas
Molinillo, P; Puyo, M; Vattier, F; Lacroix, B; Rendon, N; Lara, P; Suarez, ANanoscale
Show abstract ▽
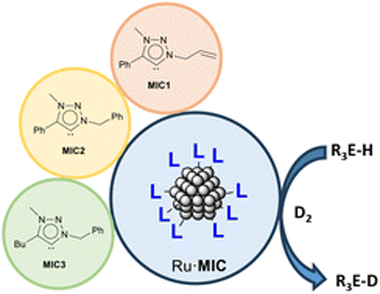
A series of ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru & BULL;MIC) stabilized with different mesoionic 1,2,3-triazolylidene (MIC) ligands were prepared by decomposition of the Ru(COD)(COT) (COD = 1,5-cyclooctadiene; COT = 1,3,5-cyclooctatriene) precursor with H-2 (3 bar) in the presence of substoichiometric amounts of the stabilizer (0.1-0.2 equiv.). Small and monodisperse nanoparticles exhibiting mean sizes between 1.1 and 1.2 nm were obtained, whose characterization was carried out by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), including high resolution TEM (HRTEM), inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). In particular, XPS measurements confirmed the presence of MIC ligands on the surfaces of the nanoparticles. The Ru & BULL;MIC nanoparticles were used in the isotopic H/D exchange of different hydrosilanes, hydroboranes, hydrogermananes and hydrostannanes using deuterium gas under mild conditions (1.0 mol% Ru, 1 bar D-2, 55 & DEG;C). Selective labelling of the E-H (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) bond in these derivatives, with high levels of deuterium incorporation, was observed.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/d3nr02637j
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Plasmas and acoustic waves to pattern the nanostructure and chemistry of thin films
Rico, V; Regodon, GF; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alcaide, AM; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rojas, TC; Alvarez, R; Palomares, FJ; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARActa Materialia, 255 (2023) 119058
Show abstract ▽
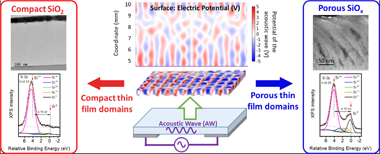
In this work, piezoelectric AWs and plasmas have been brought together during the growth of a thin film as a novel methodology of plasma-assisted thin film structuration. The ensuing effects have been investigated on a model system where SiO2 and SiOx (x<2) thin films have been deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles (MS-OAD) on an electro-acoustically excited LiNbO3 piezoelectric substrate under resonant conditions. The microstructure of the resulting films was 2D patterned and depicted submillimeter size intermingled zones with different optical characteristics, compositions (SiO2 and SiOx) and porosity, from highly porous to dense and compact regions. The 2D nanostructural pattern mimics the AW distribution and has been accounted for by means of a specific simulation model. It is concluded that the morphological and chemical film pattern replicates the distribution of polarization potential on the surface of the AW activated substrate immersed in the plasma. Moreover, we show that the main mechanism responsible for the appearance of domains with different morphology and chemical composition is the focused impingement of Ar+plasma ions on certain regions of the substrate. The general character of this patterning process, the underlying physics and its possibilities to tailor the composition and microstructure of dielectric thin film materials are discussed.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.119058
- ‹ anterior
- 15 of 410
- siguiente ›














