Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis and characterization of alkali-activated materials containing biomass fly ash and metakaolin: effect of the soluble salt content of the residue
Jurado-Contreras, S; Bonet-Martínez, E; Sánchez-Soto, PJ; Gencel, O; Eliche-Quesada, DArchives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 22 (2022) 121
Show abstract ▽
The present study investigates the production and characterization of alkali-activated bricks prepared with mixing metakaolin (MK) and biomass fly ash from the combustion of a mix of pine pruning, forest residues and energy crops (BFA). To use this low cost and high availability waste, different specimens were prepared by mixing MK with different proportions of BFA (25, 50 and 75 wt%). Specimens containing only metakaolin and biomass fly ash were produced for the purpose of comparison. Effects of the alkali content of biomass fly ash, after a washing pretreatment (WBFA), as well as the concentration of NaOH solution on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of the alkali-activated bricks were studied. It was observed that up to 50 wt% addition of the residue increases compressive strength of alkali-activated bricks. Alkalinity and soluble salts in fly ash have a positive effect, leading materials with the improved mechanical properties. Concentration of NaOH 8 M or higher is required to obtain optimum mechanical properties. The compressive strength increases from 23.0 MPa for the control bricks to 44.0 and 37.2 MPa with the addition of 50 wt% BFA and WBFA, respectively, indicating an increase of more than 60%. Therefore, the use of biomass fly ash provides additional alkali (K) sources that could improve the dissolution of MK resulting in high polycondensation. However, to obtain optimum mechanical properties, the amount of BFA cannot be above 50 wt%.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1007/s43452-022-00444-2
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Versatile Ni-Ru catalysts for gas phase CO2 conversion: Bringing closer dry reforming, reverse water gas shift and methanation to enable end-products flexibility
Merkouri, LP; le Sache, E; Pastor-Perez, L; Duyar, MS; Reina, TRFuel, 315 (2022) 123097
Show abstract ▽
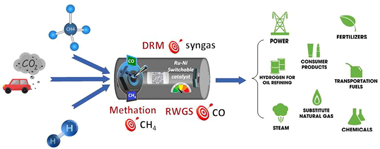
Advanced catalytic materials able to catalyse more than one reaction efficiently are needed within the CO2 utilisation schemes to benefit from end-products flexibility. In this study, the combination of Ni and Ru (15 and 1 wt%, respectively) was tested in three reactions, i.e. dry reforming of methane (DRM), reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) and CO2 methanation. A stability experiment with one cycle of CO2 methanation-RWGS-DRM was carried out. Outstanding stability was revealed for the CO2 hydrogenation reactions and as regards the DRM, coke formation started after 10 h on stream. Overall, this research showcases that a multicomponent Ni-Ru/CeO2 -Al2O3 catalyst is an unprecedent versatile system for gas phase CO2 recycling. Beyond its excellent performance, our switchable catalyst allows a fine control of end-products selectivity.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.123097
Materiales Coloidales
Neodymium doped lanthanide fluoride nanoparticles as contrast agents for luminescent bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Cantelar, E; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; De la Fuente, JM; Ocaña, MBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 61 (2022) 540-549
Show abstract ▽
The synthesis of uniform neodymium-doped lanthanum trifluoride nanoparticles with lenticular shape and a mean diameter around 45 nm by using a homogeneous precipitation method is reported. The luminescent properties of the synthesized samples in terms of their emission spectra and emission lifetime are analyzed as a function of the Nd content to find the optimum phosphor and its suitability for luminescent imaging in the second biological window. The X-ray attenuation properties of the optimum phosphor are evaluated to investigate their additional ability as contrast agent for X-ray computed tomography. Finally, the colloidal stability of the obtained nanoparticles in physiological medium and their cytotoxicity are also analyzed to assess their aptness for in vivo bioimaging applications.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.07.004
Effect of sintering under CO+N-2/H-2 and CO2+air atmospheres on the physicochemical features of a commercial nano-YSZ
Colomer, M.T.; Simenas, M.; Banys, J.; Vattier, F.; Gagor, A.; Maczka, M.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 904 (2022) 163976
Show abstract ▽
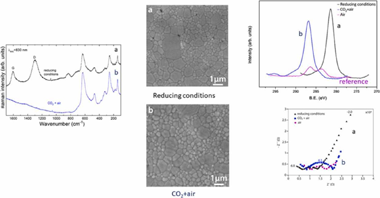
Given the need to process anodes and composites based on nano-YSZ in reducing or in air containing additional CO2 atmospheres for the fabrication of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs), we have studied the effect of the exposure to CO+N2/H2 or CO2+air mixtures during sintering of YSZ green pellets, prepared from commercial nanopowders, on their structure, microstructure, chemical composition and their electrical properties. The reduced sample shows Raman bands at 1298 and 1605 cm−1 that are assigned to the D and G bands of carbon, respectively. The bands intensity ratio ID/IG indicates a larger content of disordered carbon. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) shows that C is present in the reduced samples as reduced carbon. However, the samples sintered in CO2+air present C as carbonate-type. Impedance spectroscopy reveals that the highest total conductivity is for the reduced samples in the whole range of studied temperatures. In addition, sintering in CO2+air causes a detrimental effect on the grain boundary conductivity and therefore, on the total electrical conductivity of YSZ. It can be due to the presence of impurities such as carbonates and oxidised or even, polymerised carbonaceous species located at those areas.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163976
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High temperature mechanical properties of polycrystalline Y2SiO5
Cabezas-Rodríguez, R; Ciria, D; Martínez-Fernandez, J; Dezanneau, G; Karolak, F; Ramirez-Rico, JBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 61 (2022) S60-S68-228
Show abstract ▽
The high temperature mechanical properties of polycrystalline Y2SiO5 were studied in compression at temperatures in the range of 1200-1400 degrees C, both in constant strain rate and constant stress experiments. To examine the effect of grain size on the plastic deformation, two routes were used for the synthesis and sintering of Y2SiO5: one of solid state reaction followed by conventional sintering in air, and one of sol-gel synthesis followed by spark-plasma sintering, resulting in starting grain sizes of 2.2 and 0.9 mu m, respectively. Ceramics obtained by these routes exhibited different high-temperature compression behavior: while the conventionally processed ceramic exhibited grain growth during mechanical testing and a stress exponent close to one, compatible with diffusional creep, the spark-plasma sintered ceramic showed no grain growth but significant cavitation, a stress exponent close to two and partially superplastic behavior. These results have implications for the design and lifetime assessment of rare earth silicate-based environmental barrier coatings.
Mayo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.09.008
- ‹ anterior
- 51 of 410
- siguiente ›














