Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Plasticized, greaseproof chitin bioplastics with high transparency and biodegradability
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Porras-Vazquez, JM; Tedeschi, G; Morales, Y; Fernandez-Ortuno, D; Athanassiou, A; Guzman-Puyol, SFood Hydrocolloids, 145 (2023) 109072
Show abstract ▽
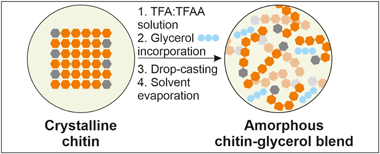
A mixture of trifluoroacetic acid:trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFA:TFAA) was used to dissolve chitin from shrimp shells. Free-standing films were prepared by blending the chitin solution and glycerol at different percentages, followed by drop-casting, and the complete evaporation of the solvents. After this process, the chitin matrix showed an amorphous molecular structure, as determined by X-ray diffraction. Optical, mechanical, thermal, and antioxidant properties were also thoroughly investigated. The incorporation of glycerol induced a plasticizing effect on the mechanical response of films and improved their transparency. In addition, hydrodynamic and barrier properties were determined by contact angle and water vapor/oxygen transmission rates, respectively, and revealed typical values of other polysaccharides. These bioplastics also presented an excellent greaseproof behavior with the highest degree of oil repellency as determined by the Kit test. Moreover, the overall migration was evaluated by using Tenax & REG; as a dry food simulant and levels were compliant with European regulations. Their antifungal properties were tested using Botrytis cinerea as a model. Biodegradability was also determined by measuring the biological oxygen demand in seawater. Degradation rates were high and similar to those of other fully-degradable materials.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109072
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Spherosilicate-modified epoxy coatings with enhanced icephobic properties for wind turbines applications
Kozera, R; Zietkowska, K; Przybyszewski, B; Boczkowska, A; Sztorch, B; Paku, D; Przekop, RE; Trzcinski, J; Borras, AColloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 679 (2023) 132475
Show abstract ▽
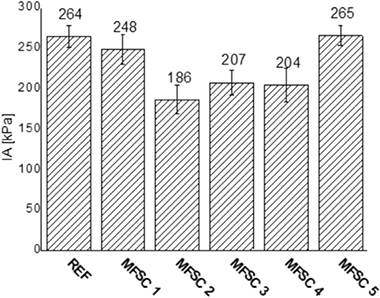
Industries around the world use active methods, which include thermal, mechanical and chemical approaches, to reduce icing on aerodynamic surfaces such as wind turbines and aircraft. However, they are often inefficient, costly, and pollute the environment. For years, new coatings with anti-icing properties (so-called icephobic coatings) have been developed to either replace or work in tandem with active systems. In this study, coatings were designed based on an epoxy gelcoat commonly used for wind turbines through chemical modification with spherosilicate derivatives. Di- and tri-functional spherosilicates have both groups that increase the degree of hydro-/icephobicity of composites , groups capable of interacting with epoxy resin and amine hardener. The icephobicity of the surface was determined using ice adhesion. The lowest value of this parameter reached a value of 186 kPa, a 30 % reduction compared to the unmodified coating. In addition, the hydrophobicity of the surface was determined (the highest water contact angle was equal to 103 degrees). A correlation was observed, proven in many works, that as the surface roughness increases, the anti-icing properties deteriorate. For individual modifications, it was also shown that hydrophobicity has a positive effect on ice adhesion. The work also examined the surface zeta potential and determined the durability of the properties after 100 icing/deicing cycles.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132475
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Alkane metathesis over immobilized pincer-ligated iridium complexes: Effect of support nature
Megías-Sayago, C; Centeno-Vega, I; Bobadilla, LF; Ivanova, S; Rendon, N; Suarez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 338 (2023) 123002
Show abstract ▽
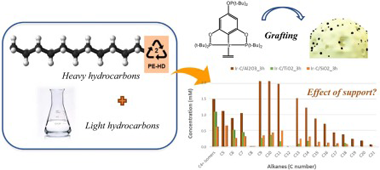
In this work, catalytic alkane metathesis has been evaluated as a suitable approach to upcycle hydrocarbons (polyolefins) at moderate temperatures. To this end, a pincer-ligated iridium complex (dehydrogenation catalyst) has been combined with a rhenium-based (metathesis) catalyst, being the effect of immobilizing the Ir complex over different supports deeply investigated. FTIR spectroscopy has been used to confirm the complex grafting and to elucidate the anchoring site to the support. Additionally, the supports have been dehydroxylated at different conditions to evaluate its possible impact in both the complex grafting and the catalytic activity. The influence of the support nature and its participation in the catalytic reaction have been clearly evidenced.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123002
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Incorporation of bioactive compounds from avocado by-products to ethyl cellulose-reinforced paper for food packaging applications
Acquavia, MA; Benitez, JEJ; Bianco, G; Crescenzi, MA; Hierrezuelo, J; Grife-Ruiz, M; Romero, D; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia-Guerrero, JAFood Chemistry, 429 (2023) 136906
Show abstract ▽
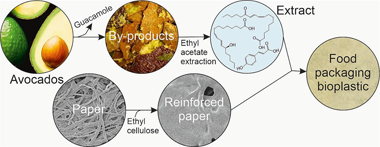
Reinforced films were fabricated by impregnating paper in ethyl cellulose solutions. After solvent evaporation, the infused ethyl cellulose acted as binder of the paper microfibres and occupied the pores and cavities, thus improving the mechanical and barrier properties. To prepare active films, avocado by-products from guacamole industrial production were extracted in ethyl acetate. Then, the extract (optimized to be rich in phenolic compounds and flavonoids and mainly composed by lipids) was incorporated to the paper reinforced with the highest content of ethyl cellulose. In general, the addition of the avocado by-products extract decreased the water uptake and permeability, improved the wettability, and increased the biodegradability in seawater and the antioxidant capacity. In addition, these films acted as barriers and retainers for Escherichia coli and Bacillus cereus. The potentiality of these materials for food packaging was demonstrated by low overall migrations and a similar food preservation to common low-density polyethylene.
Diciembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136906
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhancement of upconversion photoluminescence in phosphor nanoparticle thin films using metallic nanoantennas fabricated by colloidal lithography
Ngo, TT; Viaña, JM; Romero, M; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Miguez, HMaterials Advances, 4 (2023) 6381-6388
Show abstract ▽
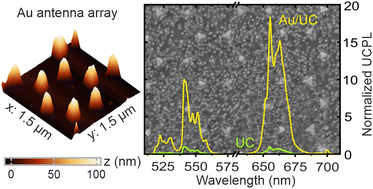
Lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), as multifunctional light sources, are finding utility in diverse applications ranging from biotechnology to light harvesting. However, the main challenge in realizing their full potential lies in achieving bright and efficient photon upconversion (UC). In this study, we present a novel approach to fabricate an array of gold nanoantennas arranged in a hexagonal lattice using a simple and inexpensive colloidal lithography technique, and demonstrate a significant enhancement of UC photoluminescence (UCPL) by up to 35-fold through plasmon-enhanced photoexcitation and emission. To elucidate the underlying physical mechanisms responsible for the observed UCPL enhancement, we provide a comprehensive theoretical and experimental characterization, including a detailed photophysical description and numerical simulations of the spatial electric field distribution. Our results shed light on the fundamental principles governing the enhanced UCNPs and pave the way for their potential applications in photonic devices.
Noviembre, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/D3MA00775H
- ‹ anterior
- 7 of 410
- siguiente ›














