Artículos SCI
2021
2021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Advanced parametrisation of phase change materials through kinetic approach
Lizana, J; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Energy Storage, 44 (2021) 103441
Show abstract ▽
Phase change materials (PCM) have been widely investigated for heat storage and transfer applications. Numerous numerical simulation approaches have been proposed for modelling their behaviour and predicting their performance in thermal applications. However, simulation approaches do not consider the kinetics of the phase transition processes, compromising the accuracy of their predictions. The phase change is a kinetically driven process in which both the reaction rate and the reaction progress depend on the heating schedule. This work evaluates and parametrises the influence of kinetics in the melting and crystallisation behaviour of a well-known PCM, PEG1500, and compares potential discrepancies with common phase change parametrisation alternatives. The kinetic dependence was experimentally evaluated through differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The kinetic parameters required for modelling the kinetics of the processes were determined by both model-free and model-fitting procedures following ICTAC (International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry) recommendations. Then, the phase transition was parametrised through a kinetic model and compared with three conventional phase transition models: linear without hysteresis, non-linear without hysteresis, and non-linear with hysteresis. The statistical comparison between models demonstrates the higher accuracy of the kinetic approach to correctly represent the partial enthalpy distribution of latent heat storage materials during alternative phase change rates, obtaining a coefficient of determination (R-2) of 0.80. On the other hand, the accuracy of kinetic-independent models is limited to the range from 0.40 to 0.61. The results highlight the high discrepancies of conventional models compared to the kinetic approach and provide criteria and guidelines for efficient kinetic modelling of phase change in heat transfer evaluations.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103441
Reactividad de Sólidos
Fabrication and characterization of FeCoNiCrMn,(Al) high entropy alloy based (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) cermet
Real, C; Alcala, MD; Trigo, I; Fombella, I; Cordoba, JMInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 101 (2021) 105694
Show abstract ▽
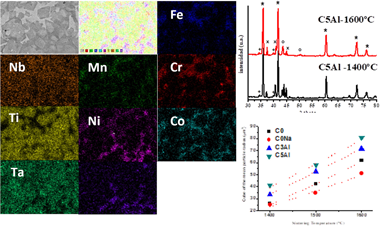
From nanostructured mechanically synthesized powder a set of FeCoNiCrMn,(Al) based (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) cermets were fabricated and sintered by a pressureless procedure. Highly dense cermets were obtained, and the nature of chemical change, microstructure, mechanical properties and coarsening kinetic of ceramic phase were characterized by image analysis, microindentation, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The design of the material was performed using a set of three different chemical cermet composition and three different sintering temperatures, or comparative purposes.
Diciembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2021.105694
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
K-Promoted Ni-Based Catalysts for Gas-Phase CO2 Conversion: Catalysts Design and Process Modelling Validation
Gandara-Loe, J; Portillo, E; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 785571
Show abstract ▽
The exponential growth of greenhouse gas emissions and their associated climate change problems have motivated the development of strategies to reduce CO2 levels via CO2 capture and conversion. Reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction has been targeted as a promising pathway to convert CO2 into syngas which is the primary reactive in several reactions to obtain high-value chemicals. Among the different catalysts reported for RWGS, the nickel-based catalyst has been proposed as an alternative to the expensive noble metal catalyst. However, Ni-based catalysts tend to be less active in RWGS reaction conditions due to preference to CO2 methanation reaction and to the sintering and coke formation. Due to this, the aim of this work is to study the effect of the potassium (K) in Ni/CeO2 catalyst seeking the optimal catalyst for low-temperature RWGS reaction. We synthesised Ni-based catalyst with different amounts of K:Ni ratio (0.5:10, 1:10, and 2:10) and fully characterised using different physicochemical techniques where was observed the modification on the surface characteristics as a function of the amount of K. Furthermore, it was observed an improvement in the CO selectivity at a lower temperature as a result of the K-Ni-support interactions but also a decrease on the CO2 conversion. The 1K catalyst presented the best compromise between CO2 conversion, suppression of CO2 methanation and enhancing CO selectivity. Finally, the experimental results were contrasted with the trends obtained from the thermodynamics process modelling observing that the result follows in good agreement with the modelling trends giving evidence of the promising behaviour of the designed catalysts in CO2 high-scale units.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.785571
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of helium incorporation on growth process and properties of aluminum thin films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering
Ibrahim, S; Lahboub, FZ; Brault, P; Petit, A; Caillard, A; Millon, E; Sauvage, T; Fernandez, A; Thomann, AlSurface & Coatings Technology, 426 (2021)
Show abstract ▽
The effect of helium content on the morphology, crystallinity, and composition of aluminum films was investigated by depositing He-loaded Al films onto Si substrates via direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering in different Ar/He plasma mixtures. Three different plasma regimes were identified depending on the percentage of He in the gas phase. For a low He to total gas ratio (ΓHe ≤ 70%), the plasma is dominated by argon, where Ar+ ions contribute to sputter out the target atoms. The films deposited in this regime exhibited the classical dense columnar structure and contain very low amount of He (below 2%). Then, as ΓHe increases, helium ions begin to be formed and more fast He neutrals reach the substrate, affecting the film growth. As He amount increased in the gas phase up to 95%, the proportion of He inserted in the films rised up to ⁓15 at. %. Moreover, bubbles/porosity were formed inside the films; those obtained in pure He plasma presented a highly porous fiberform nanostructure. All results confirmed that the modification of the film characteristics was related to the change of the deposition conditions when Ar was replaced by He and to the insertion/release mechanisms of He during the growth.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127808
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
By-products revaluation in the production of design micaceous materials
Mouchet, A; Raffin, F; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAplied Clay Science, 214 (2021) 106292
Show abstract ▽
One of the main objectives of a sustainable development and circular economy is the recycling of by-products generated in industrial and agricultural production processes. One of the possible solution is the use of such by-product materials in the synthesis of environmental adsorbents. In the current research, we present the synthesis of a high charge swelling mica with enhance adsorbent properties from blast furnace slag and rice husk ash. Moreover, to ensure the sustainable synthesis a natural bentoniteis used as Si and Al source. Thus, the current study investigated the fabrication of swelling high charged micas, Na-Mn (n (layer charge) = 2 or 4), from FEBEX bentonite, blast furnace slag and rice husk ash thorough the NaCl melt method. The reaction yield, cation framework distribution and structural characteristic of micas have been studied thorough X-ray Diffraction and Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. The yields of Na-Mn synthesis and degree of purity of the mica depends on the nature of these precursors. Thus, a sustainable, non-expensive and environmental friendly process has been evaluated.
Noviembre, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106292
- ‹ anterior
- 63 of 410
- siguiente ›














