Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Evaluation of rare earth on layered silicates under subcritical conditions: Effect of the framework and interlayer space composition
Chain, P; Cota, A; El Mrabet, S; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDChemical Geology, 347 (2013) 208-216
Show abstract ▽
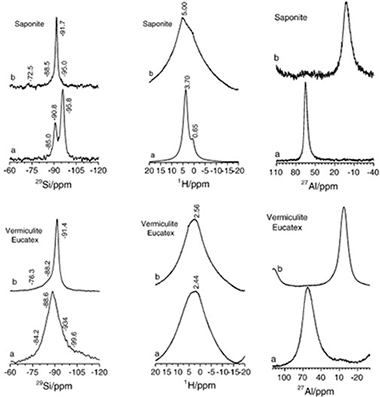
Clay-based minerals are considered to be an important component in backfill barriers due to both their ability to seal and adsorb radioactive waste and to interact chemically with it under subcritical conditions. Herein, we describe a systematic study of the properties of layered silicates that could affect their hydrothermal reactivity, namely type of layers, octahedral occupancy, origin and total amount of the layer charge, and nature of the interlayer cation. The silicates studied were selected on the basis of their different characteristics associated with these properties and were treated hydrothermally at 300 °C for 48 h in a 7.3 · 10− 2 M Lu(NO3)3 · 3.6H2O solution. The final products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction and solid-state NMR spectroscopy. All the layered silicates studied were found to be able to generate a Lu2Si2O7 phase after hydrothermal treatment under subcritical conditions, thereby confirming the participation of a chemical mechanism of the clay barrier generating phases being stables with temperature and pH conditions. However, the extent of this reaction depends to a large extent on the physicochemical properties of the framework and the interlayer space composition, such as the presence or absence of an octahedral sheet, the degree of occupancy of this sheet, and the origin and total layer charge. Therefore, this study allows tuning the clay mineral framework characteristic that favors the rare earth cations (as trivalent actinide simulator) immobilization.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.03.006
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Selective UV Reflecting Mirrors Based on Nanoparticle Multilayers
Smirnov, JRC; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 2805-2811
Show abstract ▽
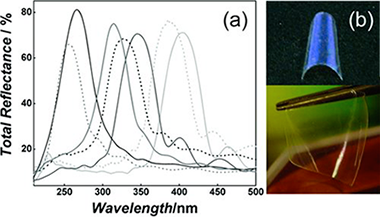
A new type of nanostructured selective ultraviolet (UV) reflecting mirror is presented. Periodic porous multilayers with photonic crystal properties are built by spin-coating-assisted layer-by-layer deposition of colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles of ZrO2 and SiO2 (electronic band gap at λ < 220 nm). These optical filters are designed to block well-defined wavelength ranges of the UVA, UVB, and UVC regions of the electromagnetic spectrum while preserving transparency in the visible. The shielding against those spectral regions arises exclusively from optical interference phenomena and depends only on the number of stacked layers and the refractive index contrast between them. In addition, it is shown that the accessible pore network of the as-deposited multilayer allows preparing thin, flexible, self-standing, transferable, and adaptable selective UV filters by polymer infiltration, without significantly losing reflectance intensity, i.e., preserving the dielectric contrast. These films offer a degree of protection comparable to that of traditional ones, without any foreseeable unwanted secondary effects, such as photodegradation, increase of local temperature or, as is the case for organic absorbers, generation of free radicals, all of which are caused by light absorption.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201202587
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Cyclohexane photocatalytic oxidation on Pt/TiO2 catalysts
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Vaiano, V; Sannino, D; Ciambelli, PCatalysis Today, 209 (2013) 164-169
Show abstract ▽
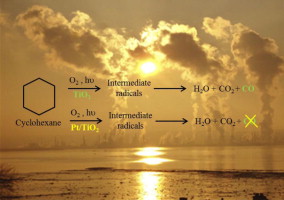
Gas-solid heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) of cyclohexane in humidified air over TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 catalyst was studied.
Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by photodeposition method at different Pt loadings (0.5–2 wt.%). The addition of 0.5 wt.% Pt does not significantly modify the TiO2 properties. The increase in Pt loading induces to an aggregation of metallic particles on TiO2 surface.
The cyclohexane PCO was performed in a fluidized bed photoreactor at 60 and 100 °C. Pure TiO2 was more active than 1 and 2 wt.% Pt/TiO2 samples at 60 °C. Nevertheless, the conversion level increases with temperature on Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts. The cyclohexane was mineralized into CO2, water and low amount of CO. A beneficial effect of Pt addition was found, since total CO2 selectivity was obtained. The Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by photodeposition provide the total cyclohexane PCO without CO production. Photocatalysts deactivation was not observed in any performed test. Evidence of an opportune tuning of temperature is highlighted.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.11.018
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Exploring the benefits of depositing hard TiN thin films by non-reactive magnetron sputtering
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 275 (2013) 121-126
Show abstract ▽
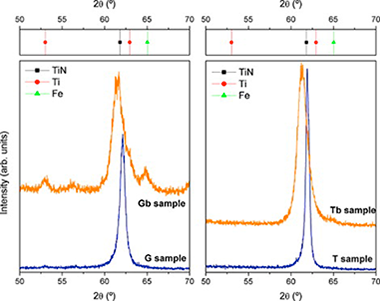
The aim of this paper is to compare the mechanical and tribological properties of TiN coatings prepared in a conventional magnetron sputtering chamber according to two different routes: the usual reactive sputtering of a Ti target in an Ar/N2 atmosphere vs. the comparatively more simple sputtering of a TiN target in a pure Ar atmosphere. Improved properties in term of hardness and wear rates were obtained for films prepared by non-reactive sputtering route, due to the lower presence of oxynitride species and larger crystalline domain size. Additionally, a significant hardness enhancement (up to 45 GPa) is obtained when a −100 V d.c. bias is applied during growth. This behaviour is explained by non-columnar growth and small grain size induced by effective ion bombarding. These results demonstrate that non-reactive sputtering of TiN target appears a simple and efficient method to prepare hard wear-resistant TiN films.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.01.098
Reactividad de Sólidos
Direct mechanosynthesis of pure BiFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles: reaction mechanism
Perejon, A; Murafa, N; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Subrt, J; Dianez, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 1 (2013) 3551-3562
Show abstract ▽
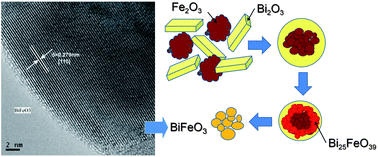
In this work, a mechanochemical procedure is proposed as a simple and fast method to synthesize the pure BiFeO3 perovskite phase as a nanostructured material without the need for purification treatments, while the mechanochemical reaction mechanism has been investigated and correlated with that of the conventional solid-state reaction. Thus, different milling conditions have been used as a tool for tailoring the crystallite size of the resulting BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The materials prepared by the mechanochemical reaction could be annealed or sintered without the formation of undesirable phases. Both the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic transitions were observed by DSC. Finally, the dielectric constants of the prepared material at different frequencies as a function of the temperature have been measured, showing that the material is clearly an isolator below 200 °C, characteristic of a high quality BiFeO3 material.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
- ‹ anterior
- 302 of 422
- siguiente ›














