Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Direct mechanosynthesis of pure BiFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles: reaction mechanism
Perejon, A; Murafa, N; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Subrt, J; Dianez, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 1 (2013) 3551-3562
Show abstract ▽
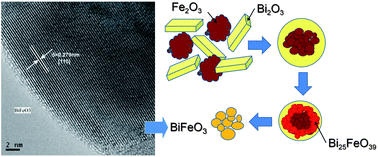
In this work, a mechanochemical procedure is proposed as a simple and fast method to synthesize the pure BiFeO3 perovskite phase as a nanostructured material without the need for purification treatments, while the mechanochemical reaction mechanism has been investigated and correlated with that of the conventional solid-state reaction. Thus, different milling conditions have been used as a tool for tailoring the crystallite size of the resulting BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The materials prepared by the mechanochemical reaction could be annealed or sintered without the formation of undesirable phases. Both the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic transitions were observed by DSC. Finally, the dielectric constants of the prepared material at different frequencies as a function of the temperature have been measured, showing that the material is clearly an isolator below 200 °C, characteristic of a high quality BiFeO3 material.
Junio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings in the temperature range of 25–700 °C
Shtansky, DV; Bondarev, AV; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, PV; Rojas, TC; Godinho, V; Fernandez, AApplied Surface Science, 273 (2013) 408-414
Show abstract ▽
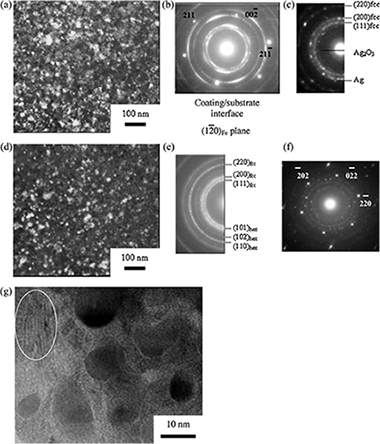
The preparation of hard coatings with low friction coefficient over a wide temperature range is still a challenge for the tribological community. The development of new nanocomposite materials consisting of different metal-ceramic phases, each of which exhibiting self-lubricating characteristics at different temperatures, may help to solve this problem. We report on the structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings deposited by magnetron co-sputtering of Mo and C (graphite) targets and simultaneous sputtering of an Ag target either in pure nitrogen or in a gaseous mixture of Ar + N2. The structure and elemental composition of the coatings were studied by means of X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy. The tribological properties of the coatings against an Al2O3 ball were investigated first at discrete temperatures of 25, 500, and 700 °C, and then during continuous heating in the temperature range of 25–700 °C. The coating structure and their respective wear tracks were also examined to elucidate their phase transformations during heat treatments. The lowest friction coefficients (<0.4) were observed in the temperature ranges of 25–100 °C and 400–700 °C and can be explained by the presence of a free amorphous carbon phase, which served as a lubricant at low temperatures, and by a positive role of silver and two phases forming at elevated temperatures, molybdenum oxide and silver molybdate, which provided lubrication above 400 °C. In the temperature range between 100 and 400 °C, the friction coefficient was relatively high. This problem is to be addressed in future works.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.055
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Solution Properties of the System ZrSiO4–HfSiO4: A Computational and Experimental Study
Cota, Agustin; Burton, Benjamin P.; Chain, Pablo; Pavon, Esperanza; Alba, Maria D.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 10013-10019
Show abstract ▽

ZrSiO4 and HfSiO4 are of considerable interest because of their low thermal expansions, thermal conductivities, and the optical properties of HfSiO4. In addition, silicate phases of both are studied as model radioactive waste disposal materials. Previous first principles calculations reported near ideal mixing in the Zr1–xHfxSiO4 system, with a very weak propensity for phase separation. Density functional theory (DFT)/cluster-expansion first principles calculations presented in this work indicate near ideal mixing with a very weak propensity for ordering. Zr1–xHfxSiO4 samples (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0) were synthesized from intimate stoichiometric mixtures of constituent-oxides and annealing at 1823 K for 20 days in a platinum crucible. Samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD; Rietveld analysis) and 29Si MAS NMR. The XRD data exhibited a pronounced negative deviation from Vegard’s law in the excess volume of mixing, and the 29Si MAS NMR spectra also suggest nonideal mixing. Given the very weak energetics that favor cation ordering, it is clear that there must be some other cause(s) for the observed deviations from ideal mixing behavior.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/jp401539g
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Resonant Photocurrent Generation in Dye-Sensitized Periodically Nanostructured Photoconductors by Optical Field Confinement Effects
Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Luque-Raigon, JM; Miguez, HJournal of the American Chemical Society, 135 (2013) 7803-7806
Show abstract ▽
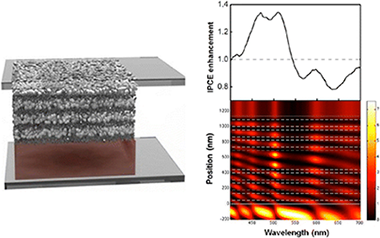
Herein we show experimental evidence of resonant photocurrent generation in dye-sensitized periodically nanostructured photoconductors, which is achieved by spectral matching of the sensitizer absorption band to different types of localized photon modes present in either periodic or broken symmetry structures. Results are explained in terms of the calculated spatial distribution of the electric field intensity within the configurations under analysis.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/ja401096k
Materiales Coloidales
Energy transfer efficiency in YF3 nanocrystals: Quantifying the Yb3+ to Tm3+ infrared dynamics
Quintanilla, M; Nuñez, NO; Cantelar, E; Ocaña, M; Cussó, FJournal of Applied Physics, 113 (2013) 174308 (6 pages)
Show abstract ▽
In this work, we report on the determination of the infrared Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer efficiency in YF3:Yb3+/Tm3+ nanocrystals through the study of Yb3+ dynamics. The obtained results are compared to those previously reported in macrocrystals to analyze possible changes related to size reduction. Luminescence lifetimes are much shorter in the nanoparticles than in bulk samples, a behavior that can be related to Yb3+ → Yb3+ migration and the enhanced surface/volume ratio of the nanoparticles. On the other hand, Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer macroparameter remains unaltered, demonstrating that spectroscopic intrinsic parameters such as radiative and non-radiative probabilities are not affected by size reduction. Finally, a formula that describes Yb3+ lifetime dependence with Yb3+ and Tm3+ concentration is proposed, considering both the effects produced by migration between Yb3+ ions and energy transfer from Yb3+ to Tm3+ ions.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1063/1.4803540
- ‹ anterior
- 303 of 422
- siguiente ›














