Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Combined reactive magnetron sputtering and plasma decomposition of non-volatile precursors to grow luminescent thin films
Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 222 (2013) 144-150
Show abstract ▽
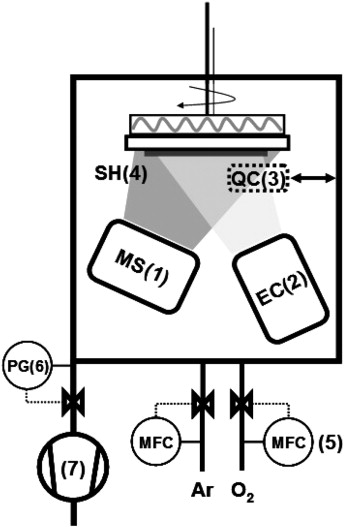
This paper reports a new procedure of the preparation of mixed oxide thin films that combines the traditional reactive magnetron sputtering deposition with the plasma activated decomposition of non-volatile precursors sublimated by means of an effusion cell. The possibilities of this new experimental procedure are illustrated with the preparation of luminescent thin films consisting of rare earth (RE) cations (Tb3 +, Eu3 +) incorporated in an oxide matrix (TiO2 and SiO2). The oxide matrix component was supplied by reactive magnetron sputtering from metallic Ti or Si targets, while the RE cation was dosed by sublimation of acetylacetonate compounds of the selected elements. The obtained mixed oxide thin films have been fully characterized by different methods and their luminescent properties studied as a function of the matrix type and concentration of the RE element present in the film. The advantages of the synthesis procedure are highlighted with regard to its versatility and the possibility of tailoring the properties of complex luminescent materials.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.02.016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis and characterization of kanemite from fluoride-containing media: Influence of the alkali cation
Corredor, JI; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 98 (2013) 1000-1007
Show abstract ▽
Kanemite belongs to the group of naturally occurring sodium silicate minerals that was first found in Kanem, at the edge of the Lake Chad, and has been synthesized in different ways from NaOH-SiO2 mixtures and used as precursor for the design of microporous and mesoporous materials. The fluoride route to the synthesis of microporous materials is based on the substitution of OH− anions by fluoride anions, which may subsequently also play a mineralizing role, and gives rise to materials with higher hydrophobicity and thermal and hydrothermal stability. Moreover, F− plays an important role in the incorporation of framework heteroatoms, thereby affecting the activity of the final material. The aim of this study was to synthesize fluorokanemite using different synthetic routes and different F− source. The final product was characterized by a combination of methods that provided information regarding the incorporation of fluorine into the framework and the short- and long-range structural order of the fluorosilicate. Kanemite with water content close to ideal was obtained in all cases. The washing process was found to have no effect in the long- or short-range structural order of the layer framework, although it did affect the structure of the cation in the interlayer space of kanemite. The mineralizing agent therefore appears to be the key to the synthesis. Furthermore, it governs the resulting kanemite structure by controlling the formation of hydrogen bonds in the framework, and therefore the degree of lamellar structure condensation.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4372
Materiales Avanzados
Estudio in-situ de la transformación térmica de limonita utilizada como pigmento procedente de Perú
Romero-Gomez, P; Gonzalez, JC; Bustamante, A; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 52 (2013) 127-131
Show abstract ▽
Se ha realizado un estudio cinético de la transformación térmica de limonita [FeO(OH).nH2O] mediante análisis térmico gravimétrico (TGA), termodifracción de rayos X (DRX) y espectroscopía μ-Raman. La muestra estudiada fue extraída de un yacimiento en el distrito de Taraco, provincia de Huancané, Región de Puno (Perú). La técnica DRX en polvo identificó la fase goetita como el principal componente mineralógico, además de cuarzo. La muestra se sometió a un tratamiento térmico
in-situ en un intervalo de temperaturas de 100 a 500 °C en atmósfera de aire e inerte (nitrógeno) y se estudió por DRX. Los resultados han mostrado que la fase goetita permanece estable desde la temperatura ambiente hasta 200 °C. A partir de los 250 °C se produce una transformación de fase α-FeO(OH)→α-Fe2O3
con un cambio cromático, es decir, el paso de la fase
hidroxilada goetita (amarillo) a la fase oxidada hematites (rojo) con una pérdida de peso de un 8 %, teniendo como evidencia la evolución de los perfiles de difracción y los resultados de ATG. Los espectros μ-Raman del tratamiento térmico in-situ corroboran que se produce también una transición de fase a la temperatura de 290 °C a través de la transformación de las bandas Raman características de la fase goetita hacia la fase hematites en el rango de frecuencias de 200 a 1800cm-1.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.3989/cyv.162013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Liquid-phase sintering of Ti(C,N)-based cermets. The effects of binder nature and content on the solubility and wettability of hard ceramic phases
Cordoba, JM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 559 (2013) 34-38
Show abstract ▽
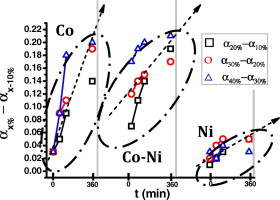
Different commercial TiC–TiN/Co/Ni mixtures were used as raw materials for Ti(C,N) cermets, and the effects of the sintering parameters (binder content, binder nature, sintering time and additives) on the final hard ceramic phase were studied at the sintering temperature of 1400 °C. When Co is used as the binder medium, it is possible to completely convert the starting commercial TiC–TiN mixture into TiCxN1−x. When Ni is used, which exhibits lower solubilising capacity than Co, the total conversion can never be reached and the metallurgical reactions between TiC and TiN during the liquid-phase sintering are more dependent on the sintering time than on the binder content. However, the use of Co–Ni mixtures, showing a synergic effect between the wettability capacity of Ni and the solubilising capacity of Co, enhances the metallurgical reactions at short sintering times.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.01.046
Reactividad de Sólidos
Limitations of model-fitting methods for kinetic analysis: Polystyrene thermal degradation
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMResources, Conservation and Recycling, 74 (2013) 75-81
Show abstract ▽
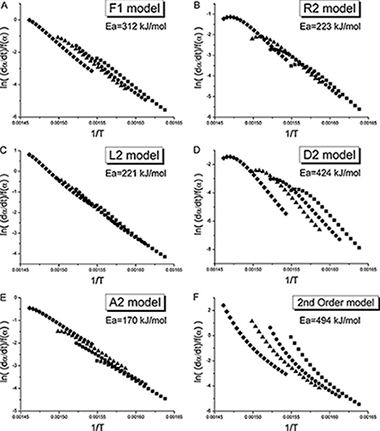
In this paper, some clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis are provided in response to the lack of plot linearity and dispersion in the activation energy values for the thermal degradation of polystyrene found in the literature and some results proposing an nth order model as the most suitable one. In the present work, two model-fitting methods based on the differential and integral forms of the general kinetic equation are evaluated using both simulated and experimental data, showing that the differential method is recommended due to its higher discrimination power. Moreover, the intrinsic limitations of model-fitting methods are highlighted: the use of a limited set of kinetic models to fit experimental data and the ideal nature of such models. Finally, it is concluded that a chain scission model is more appropriate than first order.
Mayo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.02.014
- ‹ anterior
- 304 of 422
- siguiente ›














