Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Segregation to the grain boundaries in YSZ bicrystals: A Molecular Dynamics study
Gonzalez-Romero, RL; Melendez, JJ; Gomez-Garcia, D; Cumbrera, FL; Dominguez-Rodriguez, ASolid State Ionics, 237 (2013) 8-15
Show abstract ▽
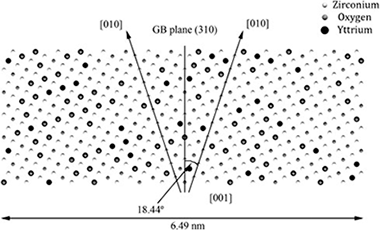
A Molecular Dynamics study about the segregation of yttrium at 1500 K to a Σ5 grain boundary in 8 mol% YSZ has been performed. Segregation has been induced by explicitly taking into account the excess energy associated to the elastic misfit effect for yttrium cations located nearby the grain boundary planes. After an initial transient, a steady regime is reached, in which the number of yttrium cations does not increase with time. Accumulation of yttrium cations is accompanied by that of zirconium ones and oxygen vacancies at some distance of the grain boundary planes. The changes in the radial distribution functions for different ionic pairs are discussed, as also the effect of segregation on oxygen diffusion along the grain boundaries and in volume. Finally, the possibility that segregated yttrium located at available free sites at the grain boundaries is pointed out.
Abril, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2013.02.002
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Light induced hydrophilicity and osteoblast adhesion promotion on amorphous TiO2
Terriza, A; Diaz-Cuenca, A; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Caballero, JLG; Vilches, J; Salido, MJournal of Biomedical Materials Research A, 101A (2013) 1026-1035
Show abstract ▽
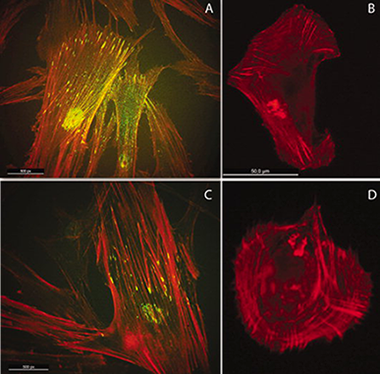
We have studied the effect of the UV induced superhydrophilic wetting of TiO2 thin films on the osteoblasts cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization on its surface. To assess any effect of the photo-catalytic removal of adventitious carbon as a factor for the enhancement of the osteoblast development, 100 nm amorphous TiO2 thin layers were deposited on polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a substrate well known for its poor adhesion and limited wettability and biocompatibility. The TiO2/PET materials were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy and their wetting behavior under light illumination studied by the sessile drop method. The amorphous TiO2 thin films showed a very poor photo-catalytic activity even if becoming superhydrophilic after illumination. The illuminated samples recovered partially its initial hydrophobic state only after their storage in the dark for more than 20 days. Osteoblasts (HOB) were seeded both on bare PET and on TiO2/PET samples immediately after illumination and also after four weeks storage in darkness. Cell attachment was much more efficient on the immediately illuminated TiO2/PET samples, with development of focal adhesions and cell traction forces. Although we cannot completely discard some photo-catalytic carbon removal as a factor contributing to this cell enhanced attachment, our photodegradation experiments on amorphous TiO2 are conclusive to dismiss this effect as the major cause for this behavior. © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. J Biomed Mater Res Part A, 2013.
Abril, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34405
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Angular response of photonic crystal based dye sensitized solar cells
López López, C.; Colodrero, S.; Calvo, M.E. and Míguez, H.Energy & Environmental Science, 6 (2013) 1260-1266
Show abstract ▽
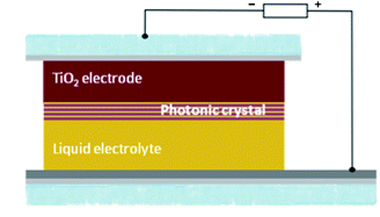
Herein we report an experimental analysis of the performance of photonic crystal based dye solar cells (PC-DSCs) as the incident light angle moves away from the normal with respect to the cell surface. Nanoparticle multilayers operating at different wavelength ranges were coupled to the working electrode of a dye solar cell for this study. The interplay between optical and photovoltaic properties with the incident light angle is discussed. We demonstrate that an efficiency enhancement is attained for PC-DSCs at all angles measured, and that rational design of the photonic crystal back mirror leads to a reduction of the photocurrent losses related to the tilt angle of the cell, usually labeled as cosine losses. Angular variations of the cell transparency are also reported and discussed. These angular properties are relevant to the application of these solar devices in building integrated photovoltaics as potential window modules.
Abril, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3EE23609A
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effects of thermal and mechanical treatments on montmorillonite homoionized with mono- and polyvalent cations: Insight into the surface and structural changes
Fernandez, M; Alba, MD; Sanchez, RMTColloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 423 (2013) 1-10
Show abstract ▽
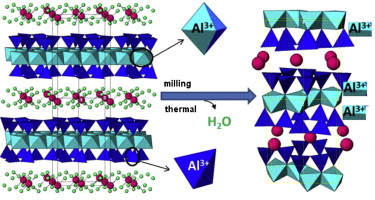
Smectite is a family of clay minerals that have important applications. In the majority of these clay minerals, the hydrated interlayer cations play a crucial role on the properties of the clay. Moreover, many studies have revealed that both thermal and grinding treatments affect the MMT structure and that interlayer cations play an important role in the degradation of the structure, primarily after mechanical treatment. In this study, the effects of these treatments on MMTs homoionized with mono (Na+, Li+ or K+) or polyvalent (Ca2+ or Al3+) cations were analyzed by the combination of a set of techniques that can reveal the difference of bulk phenomena from those produced on the surface of the particles. The thermal and mechanical (in an oscillating mill) treatments affected the framework composition and structure of the MMT, and the thermal treatment caused less drastic changes that the mechanical one. The effect of the interlayer cations is primarily due to the oxidation state and, to the size of the cations, which also influenced the disappearance of aluminum in the MMT tetrahedral sheet. These treatments caused a decrease in the surface area and an increase in the particle agglomeration and the isoelectric point. Both treatments caused the leaching of the framework aluminum. Furthermore, the mechanical treatment induced structural defects, such as the breakup of the particles, which favored the dehydroxylation and the increase of the isoelectric points of the montmorillonites.
Abril, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.01.040
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tuning Dichroic Plasmon Resonance Modes of Gold Nanoparticles in Optical Thin Films
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Ferrer, J; Garcia-Gutierrez, MC; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 1655-1663
Show abstract ▽
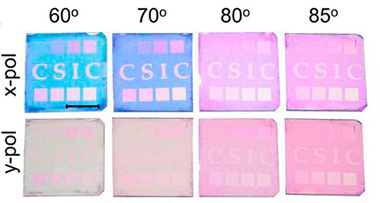
A simple method is presented to tune the gold surface plasmon resonance (SPR) modes by growing anisotropic nanoparticles into transparent SiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. In this type of composite film, the anisotropy of the gold nanoparticles, proved by gracing incidence small angle X-ray scattering, is determined by the tilted nanocolumnar structure of the SiO2 host and yields a strong film dichroism evidenced by a change from an intense colored to a nearly transparent aspect depending on light polarization and/or sample orientation. The formation in these films of lithographic non-dichroic SPR patterns by nanosecond laser writing demonstrates the potentialities of this procedure to develop novel optical encryption or anti-counterfeiting structures either at micrometer- or macroscales.
Abril, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201201900
- ‹ anterior
- 306 of 422
- siguiente ›














