Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Hydration properties of synthetic high-charge micas saturated with different cations: An experimental approach
Pavon, E; Castro, MA; Naranjo, M; Orta, MM; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 98 (2013) 394-400
Show abstract ▽
An understanding of the interaction mechanisms between exchangeable cations and layered silicates is of interest from both a basic and an applied point of view. Among 2:1 phyllosilicates, a new family of swelling high-charge synthetic micas has been shown to be potentially useful as decontaminant. However, the location of the interlayer cations, their acidity and the water structure in the interlayer space of these silicates are still unknown. The aim of this paper was therefore to study the hydration state of the interlayer cations in the interlayer space of high-charge expandable micas and to evaluate the effect that this hydration has on the swelling and acidity behavior of these new materials. To achieve these objectives, three synthetic micas with different charge density total layer charges (ranging between 2 and 4 per unit cell) and with five interlayer cations (Na+, Li+, K+, Mg2+, and Al3+) were synthesized and their hydration state, interlayer space, and acidity analyzed by DTA/TG, XRD, and 1H MAS NMR spectroscopy. The results showed that the hydration state depends on both the layer charge and the nature of the interlayer cation. A high participation of the inner-sphere complexes in the highly charged confined space has been inferred and proposed to induce Brønsted acidity in the solid.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4217
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Competing Misfit Relaxation Mechanisms in Epitaxial Correlated Oxides
Sandiumenge, F; Santiso, J; Balcells, L; Konstantinovic, Z; Roqueta, J; Pomar, A; Espinos, JP; Martinez, BPhysical Review Letters, 110 (2013) 107206
Show abstract ▽
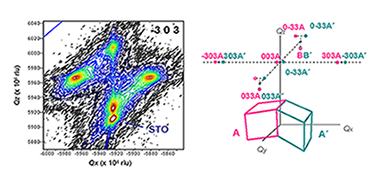
Strain engineering of functional properties in epitaxial thin films of strongly correlated oxides exhibiting octahedral-framework structures is hindered by the lack of adequate misfit relaxation models. Here we present unreported experimental evidence of a four-stage hierarchical development of octahedral-framework perturbations resulting from a progressive imbalance between electronic, elastic, and octahedral tilting energies in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 epitaxial thin films grown on SrTiO3 substrates. Electronic softening of the Mn-O bonds near the substrate leads to the formation of an interfacial layer clamped to the substrate with strongly degraded magnetotransport properties, i.e., the so-called dead layer, while rigid octahedral tilts become relevant at advanced growth stages without significant effects on charge transport and magnetic ordering.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.107206
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
High-performance Er3+–TiO2 system: Dual up-conversion and electronic role of the lanthanide
Obregon, S; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Colon, GJournal of Catalysis, 299 (2013) 298-306
Show abstract ▽
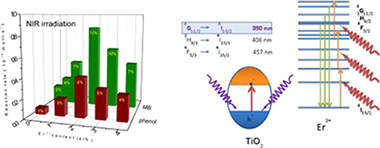
Erbium-doped TiO2 materials are synthesized by means of a surfactant-free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the liquid-phase degradation of phenol and MB and the gas phase of toluene. From the structural and morphological characterization, it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a progressive anatase cell expansion due to its incorporation in the TiO2 lattice. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 2 at% of Er3+ irrespective of the chemical degradation reaction essayed. From activity and optical studies under different irradiation excitation conditions, a dual-type mechanism is proposed to be at the origin of the photocatalytic activity enhancement. On one hand, the improvement observed under UV irradiation occurs by the effective charge separation promoted by Er3+ species which would act as electron scavenger. Besides, the up-conversion luminescence process of Er3+ allows profiting the NIR range of the lamp and transferring energy in the UV range to the TiO2. The dual action of Er ions located at anatase networks will open up a wide roadway for the developing of an integral solar active photocatalyst.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2012.12.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Colored and Transparent Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering: The Glass Blower Approach
Gil-Rostra, J; Chaboy, J; Yubero, F; Vilajoana, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5 (2013) 1967-1976
Show abstract ▽

This work describes the reactive magnetron sputtering processing at room temperature of several mixed oxide MxSiyOz thin films (M: Fe, Ni, Co, Mo, W, Cu) intended for optical, coloring, and aesthetic applications. Specific colors can be selected by adjusting the plasma gas composition and the Si–M ratio in the magnetron target. The microstructure and chemistry of the films are characterized by a large variety of techniques including X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and infrared spectroscopy, while their optical properties are characterized by UV–vis transmission and reflection analysis. Particularly, XAS analysis of the M cations in the amorphous thin films has provided valuable information about their chemical state and local structure. It is concluded that the M cations are randomly distributed within the SiO2 matrix and that both the M concentration and its chemical state are the key parameters to control the final color of the films.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/am302778h
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the O2/CO ratio and the presence of H2O and CO2 in the feed-stream during the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX) over a CuOx/CeO2-coated microchannel reactor
Laguna, OH; Dominguez, MI; Oraa, S; Navajas, A; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Centeno, MA; Montes, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 203 (2013) 182-187
Show abstract ▽
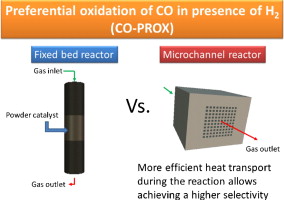
The catalytic performance of a CuOx/CeO2 powder catalyst and that of a microchannel reactor or microreactor (MR) coated with the same solid was determined and compared. The catalytic activity measurements were carried out with varying O2/CO molar ratios in the feed-stream. In addition, the influence of the presence of CO2 and H2O in the reaction mixture was studied. Some discrepancies were observed between the performances of the powder catalyst and the MR depending on the O2/CO ratio. The MR presented a very good performance with a superior selectivity for CO conversion. This behaviour was due to a more efficient heat removal in the case of the MR that inhibited the H2 oxidation reaction and the r-WGS. The isothermicity of the microreactor during the process was demonstrated through the monitoring of the MR inlet and outlet temperatures.
Concerning the presence of CO2 or H2O in the feed-stream, both compounds gave rise to a decrease of the CO conversion. The negative effect on the catalytic performance was more marked when both compounds were fed together, although the principal inhibitor effect was associated to the CO2. This seems to be related with the formation of stable carbonates at the catalyst surface.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.04.021
- ‹ anterior
- 308 of 422
- siguiente ›














