Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites: mechanochemical synthesis, properties, and the role of capping agent
Balaz, M; Balaz, P; Tjuliev, G; Zubrik, A; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kostova, NJournal of Materials Science, 48 (2013) 2424-2432
Show abstract ▽
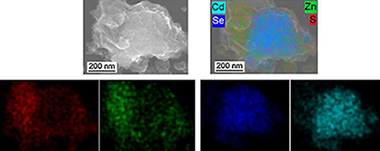
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were synthesized mechanochemically with the aim to prepare a material which could be used in medicine for biosensing applications. Although synthesized CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were capped with l-cysteine, cystine was formed from l-cysteine during the milling process. It was proven that water plays the key role in this oxidative transformation. The novel material was characterized by the complex of physico-chemical methods (FTIR, XPS, SEM, EDX, surface area measurements) and CHNS analysis. The leakage of Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions into physiological solution was also studied.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-012-7029-3
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Behaviour of Au-citrate nanoparticles in seawater and accumulation in bivalves at environmentally relevant concentrations
Garcia-Negrete, C. A.; Blasco, J.; Volland, M.; Rojas, T. C.; Hampel, M.; Lapresta-Fernandez, A.; Jimenez de Haro, M. C.; Soto, M.; Fernandez, A.Environmental Pollution, 174 (2013) 134-141
Show abstract ▽
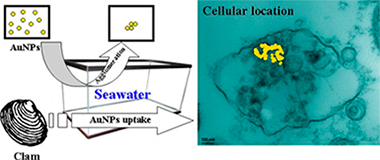
The degree of aggregation and/or coalescence of Au-citrate nanoparticles (AuNPs, mean size 21.5 ± 2.9 nm), after delivery in simulated seawater, are shown to be concentration-dependent. At low concentrations no coalescence and only limited aggregation of primary particles were found. Experiments were performed in which the marine bivalve (Ruditapes philippinarum) was exposed to AuNPs or dissolved Au and subsequently, bivalve tissues were studied by Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy and chemical analyses. We show that the bivalve accumulates gold in both cases within either the digestive gland or gill tissues, in different concentrations (including values of predicted environmental relevance). After 28 days of exposure, electron-dense deposits (corresponding to AuNPs, as proven by X-ray microanalysis) were observed in the heterolysosomes of the digestive gland cells. Although non-measurable solubility of AuNPs in seawater was found, evidence is presented of the toxicity produced by Au3+ dissolved species (chloroauric acid solutions) and its relevance is discussed.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.014
Materiales Coloidales
Solvent-Controlled Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Uniform Eu:YVO4 Nanophosphors with Different Morphologies
Nunez, N; Sabek, J; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cantelar, E; Escudero, A; Ocañaa, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 8 (2013) 1301-1309
Show abstract ▽
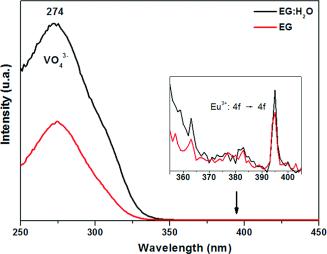
A facile solvothermal route has been developed for the preparation of tetragonal europium-doped yttrium orthovanadate nanoparticles (Eu:YVO4) and is based on a homogeneous precipitation reaction at 120 °C from solutions of rare earth precursors (yttrium acetylacetonate and europium nitrate) and sodium orthovanadate in ethylene glycol or ethylene glycol/water mixtures. The nature of the solvent has a dramatic effect on the morphology and crystallinity of the resulting nanoparticles. Polycrystalline nanoellipsoids (130 × 60 nm) were obtained in pure ethylene glycol, whereas quasispherical nanoparticles (100 nm) with monocrystalline character precipitated in ethylene glycol/water (7:3 by volume) mixtures. To explain these different morphological and structural features, the mechanism of particles formation was investigated. The effects of the doping level on the luminescence properties (emission spectra and luminescence lifetime) were also evaluated to find the optimum nanophosphors. Finally, it is shown that the luminescent efficiency of the quasispherical nanoparticles was higher than that of the nanoellipsoids; this can be related to differences in crystallinity and in impurity content.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201201016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Joining and interface characterization of in situ reinforced silicon nitride
Asthana, R; Singh, M; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 552 (2013) 137-145
Show abstract ▽
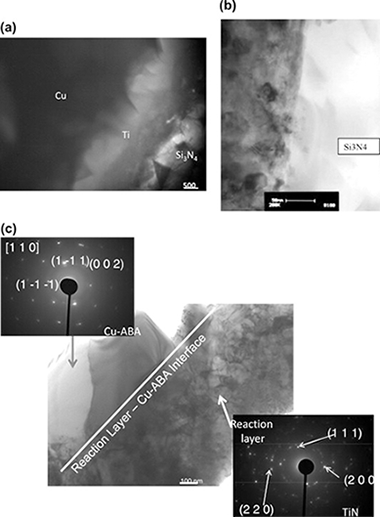
Copper-base active metal interlayers were used to bond in situ reinforced silicon nitride (Honeywell AS800) at 1317 K for 5 and 30 min in vacuum. The joints were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A Ti-rich interaction zone (∼3.0–3.5 μm thick) formed at the Si3N4/braze interface. This reaction layer grew toward the inner part of the joint with a featureless microstructure, creating a strong bond. Regions of a Ti-rich phase were frequently found next to the reaction layer but surrounded by the Cu alloy. Extensive Ti and Si enrichments were noted at the interface but there was no evidence of interfacial segregation of Y, La, and Sr (from Y2O3, La2O3 and SrO, added as sintering aids). The reaction layer thickness and composition did not change when brazing time increased from 5 min to 30 min suggesting rapid growth kinetics in the early stages of reaction. The joints were crack-free and showed features associated with plastic deformation, which indicated that the metal interlayer accommodated strain associated with CTE mismatch. The inner part of the joint consisted of highly textured large grains of the braze alloy.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.09.104
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The distribution of elements in sequentially prepared MgB2 on SiC buffered Si substrate and possible pinning mechanisms
S. Chromik; A. Nishida; V. Strbik; M. Gregor; J.P. Espinós; J. Liday; R. DurnyApplied Surface Science, 269 (2013) 29-32
Show abstract ▽
MgB2 thin films are prepared by sequential evaporation of boron and magnesium bilayers on SiC buffered Si substrates followed by an in situ annealing. Precursor Mg–B bilayers are deposited by electron beam evaporation at room temperature. The amount of B is varied so as to result in different thickness (15 nm and 50 nm) of stoichiometric MgB2 final film after an in situ reaction with the excess Mg top layer in the vacuum. We show the distribution of the elements through the film.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses have shown that carbon is not free in the films (except the surface of the film) and silicon is in the compound form, too. In the case of the 15 nm thick films we see a strong interdiffusion of the elements (C, B) and we observe a suppression of TC of the film to 20 K. We register different slope of the HC2(T)HC2(T) dependence – the lowest temperature value of HC2HC2 for the 15 nm thick film exceeds the one for the 50 nm thick film in spite of lower TC. We suppose that δl pinning mechanism is dominant for the 15 nm thick film.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.10.019
- ‹ anterior
- 309 of 422
- siguiente ›














