Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites: mechanochemical synthesis, properties, and the role of capping agent
Balaz, M; Balaz, P; Tjuliev, G; Zubrik, A; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kostova, NJournal of Materials Science, 48 (2013) 2424-2432
Show abstract ▽
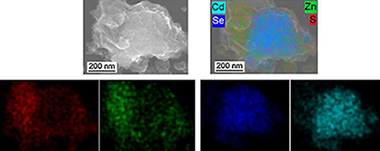
Cystine-capped CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were synthesized mechanochemically with the aim to prepare a material which could be used in medicine for biosensing applications. Although synthesized CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites were capped with l-cysteine, cystine was formed from l-cysteine during the milling process. It was proven that water plays the key role in this oxidative transformation. The novel material was characterized by the complex of physico-chemical methods (FTIR, XPS, SEM, EDX, surface area measurements) and CHNS analysis. The leakage of Cd2+ and Zn2+ ions into physiological solution was also studied.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-012-7029-3
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Behaviour of Au-citrate nanoparticles in seawater and accumulation in bivalves at environmentally relevant concentrations
Garcia-Negrete, C. A.; Blasco, J.; Volland, M.; Rojas, T. C.; Hampel, M.; Lapresta-Fernandez, A.; Jimenez de Haro, M. C.; Soto, M.; Fernandez, A.Environmental Pollution, 174 (2013) 134-141
Show abstract ▽
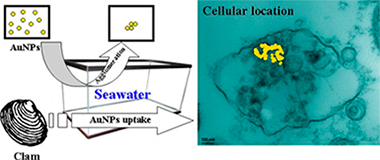
The degree of aggregation and/or coalescence of Au-citrate nanoparticles (AuNPs, mean size 21.5 ± 2.9 nm), after delivery in simulated seawater, are shown to be concentration-dependent. At low concentrations no coalescence and only limited aggregation of primary particles were found. Experiments were performed in which the marine bivalve (Ruditapes philippinarum) was exposed to AuNPs or dissolved Au and subsequently, bivalve tissues were studied by Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy and chemical analyses. We show that the bivalve accumulates gold in both cases within either the digestive gland or gill tissues, in different concentrations (including values of predicted environmental relevance). After 28 days of exposure, electron-dense deposits (corresponding to AuNPs, as proven by X-ray microanalysis) were observed in the heterolysosomes of the digestive gland cells. Although non-measurable solubility of AuNPs in seawater was found, evidence is presented of the toxicity produced by Au3+ dissolved species (chloroauric acid solutions) and its relevance is discussed.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth of silver on ZnO and SnO2 thin films intended for low emissivity applications
Alvarez, R; Gonzalez, JC; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Cueva, A; Villuendas, FApplied Surface Science, 268 (2013) 507-515
Show abstract ▽
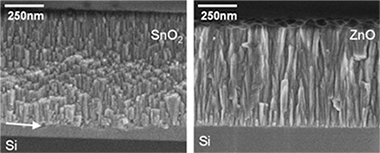
In the present work we have investigated the relationships existing between the optical properties and the growth mechanism, microstructure and surface roughness of SnO2 and ZnO oxide films prepared by magnetron sputtering under conditions resembling those utilized in industry. Thin films of these oxides with different thicknesses were characterized by atomic force microscopy, glancing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), X-ray reflectometry and spectroscopic ellipsometry. The roughness evolution of the film properties (density, surface roughness and refraction index) as a function of their thickness has been evaluated within the concepts of the Dynamic Scaling Theory of thin film growth. Zinc oxide films were rougher than tin oxide films of similar thickness, indicating a different growing mechanism for the two materials. Silver was evaporated onto the surface of the two oxide thin films and its earlier stages of nucleation studied by background analysis of the X-ray photoemission spectra. A different nucleation mechanism was found depending on the nature of the oxide acting as substrate. The superior performance of the zinc oxide based low emissive coatings is related with a better wetting of silver on the surface of this oxide despite the comparatively lower roughness of the tin oxide layers.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.156
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Impact of Ce–Fe synergism on the catalytic behaviour of Au/CeO2–FeOx/Al2O3 for pure H2 production
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Idakiev, V; Delgado, JJ; Ivanov, I; Tabakova, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 3 (2013) 779-787
Show abstract ▽
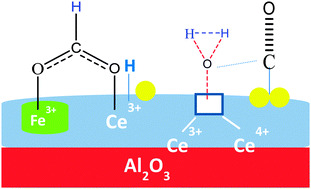
In this work the development of a series of gold catalysts, essentially based on γ-alumina promoted with a small superficial fraction of Ce–Fe mixed oxides, is reported. The catalytic behaviour is evaluated in the water gas shift reaction. The formation of a Ce–Fe solid solution is evidenced by XRD and related to the catalytic activity where the importance of the Ce–Fe interaction is demonstrated. The best catalyst reached CO conversions very close to the equilibrium limit. A long-term stability test is performed and the loss of activity is observed and attributed to reaction intermediates. Almost complete recovery of the initial conversion is achieved after oxidation treatment, suggesting that the problem of stability could be overcome by a suitable change in the reaction parameters thus leading to a highly efficient catalyst for future applications in H2 production and clean-up.
Marzo, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C2CY20537H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Valence band electronic structure characterization of the rutile TiO2 (110)-(1 x 2) reconstructed surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Garnier, MG; Aebi, P; Blanco-Rey, M; de Andres, PL; Martin-Gago, JA; Lopez, MFSurface Science, 608 (2013) 92-96
Show abstract ▽
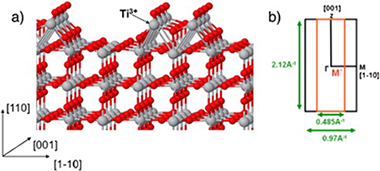
The electronic structure of the TiO2 (110)-(1 × 2) surface has been studied by means of angular resolved ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (ARUPS). The valence band dispersion along the high symmetry surface directions, [001] and [1–10], has been recorded. The experimental data show no dispersion of the band-gap Ti 3d states. However, the existence of dispersive bands along the [001] direction located at about 7 eV below the Fermi level is reported. The existence of two different contributions in the emission from the defects-related state located in the gap of the surface is univocally shown for the first time.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.09.019
- ‹ anterior
- 310 of 422
- siguiente ›














