Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 over CuO/CeO2 catalysts: Characterization and performance as a function of the exposed face present in the CeO2 support
Gamarra, D; Camara, AL; Monte, M; Rasmussen, SB; Chinchilla, LE; Hungria, AB; Munuera, G; Gyorffy, N; Schay, Z; Corberan, VC; Conesa, JC; Martinez-Arias, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 130-131 (2013) 224-238
Show abstract ▽
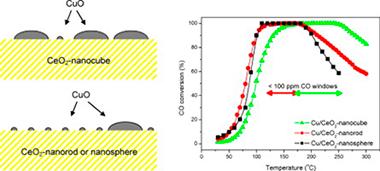
A series of oxidised copper-cerium nanostructured catalysts prepared by impregnation of copper over ceria supports synthesized by different methods (hydrothermal with varying preparation parameters, microemulsion/precipitation), in order to achieve different specific morphologies (nanocubes, nanorods and nanospheres), have been examined with respect to their catalytic properties for preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 (CO-PROX). The catalysts have been characterized in detail by XRD, Raman, SBET measurement, HREM, XPS, TPR and EPR, which allows establishing a model of structural characteristics of the catalysts. The characterization results have been correlated with analysis of CO-PROX catalytic properties by means of catalytic activity measurements complemented by operando-DRIFTS. Structural dependence of the CO oxidation reaction on the dispersed copper oxide entities as a function of the exposed face present at the surface of the different ceria supports is revealed. An important overall enhancement of the CO-PROX performance is detected for the sample supported on ceria nanocubes which is proposed to be a consequence of the interaction between copper oxide and (1 0 0) faces of the ceria support.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.008
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Valence band electronic structure characterization of the rutile TiO2 (110)-(1 x 2) reconstructed surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Garnier, MG; Aebi, P; Blanco-Rey, M; de Andres, PL; Martin-Gago, JA; Lopez, MFSurface Science, 608 (2013) 92-96
Show abstract ▽
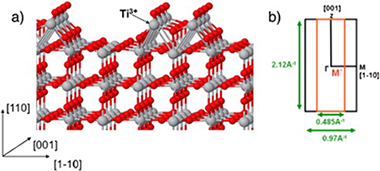
The electronic structure of the TiO2 (110)-(1 × 2) surface has been studied by means of angular resolved ultraviolet photoemission spectroscopy (ARUPS). The valence band dispersion along the high symmetry surface directions, [001] and [1–10], has been recorded. The experimental data show no dispersion of the band-gap Ti 3d states. However, the existence of dispersive bands along the [001] direction located at about 7 eV below the Fermi level is reported. The existence of two different contributions in the emission from the defects-related state located in the gap of the surface is univocally shown for the first time.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.09.019
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Biocompatible Europium-Doped Calcium Hydroxyapatite and Fluoroapatite Luminescent Nanospindles Functionalized with Poly(acrylic acid)
Escudero, A; Calvo, ME; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MLangmuir, 29 (2013)
Show abstract ▽
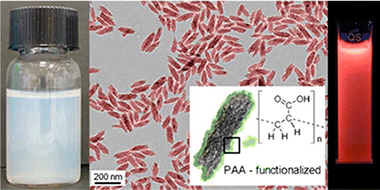
Europium-doped calcium hydroxyapatite and fluoroapatite nanophosphors functionalized with poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) have been synthesized through a one-pot microwave-assisted hydrothermal method from aqueous basic solutions containing calcium nitrate, sodium phosphate monobasic, and PAA, as well as sodium fluoride in the case of the fluoroapatite particles. In both cases a spindlelike morphology was obtained, resulting from an aggregation process of smaller subunits which also gave rise to high specific surface area. The size of the nanospindles was 191 (32) × 40 (5) nm for calcium hydroxyapatite and 152 (24) × 38 (6) nm for calcium fluoroapatite. The luminescent nanoparticles showed the typical red luminescence of Eu3+, which was more efficient for the fluoroapatite particles than for the hydroxyapatite. This is attributed to the presence of OH– quenchers in the latter. The nanophosphors showed negligible toxicity for Vero cells. Both PAA-functionalized nanophosphors showed a very high (up to at least 1 week) colloidal stability in 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid (MES) at pH 6.5, which is a commonly used buffer for physiological pH. All these features make both kinds of apatite-based nanoparticles promising tools for biomedical applications, such as luminescent biolabels and tracking devices in drug delivery systems.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/la304534f
Allochthonous red pigments used in burial practices at the Copper Age site of Valencina de la Concepción (Sevilla, Spain): characterisation and social dimension
Rogerio-Candelera, MA; Herrera, LK; Miller, AZ; Sanjuan, LG; Molina, CM; Wheatley, DW; Justo, A; Saiz-Jimenez, CJournal of Archaeological Science, 40 (2013) 279-290
Show abstract ▽

The use of red pigments linked to burial practices is widely documented in the Iberian prehistoric record and very often it has been traditionally interpreted as a ritual practice entailing the utilisation of local raw materials (iron oxides). Some research works, nevertheless, have also detected the use of red pigments which can only be interpreted as allochthonous. The red pigments spread over a single inhumation in a monumental Megalithic tomb surrounding Valencina de la Concepción Copper Age settlement was studied by means of X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray microfluorescence, micro-Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopies. This approach allowed characterising the red pigments as cinnabar, mixed with tiny amounts of iron oxides. The presence of cinnabar, a product that was necessarily imported, in a context of an exceptional set of grave goods, suggests that the use of cinnabar was linked not only to ritual but also to practices related to the display of social status.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2012.08.004
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Efficient and affordable hydrogen production by water photo-splitting using TiO2-based photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Mendez, AO; Lopez, CR; Suarez, MN; Rodriguez, JMD; Navio, JA; Hevia, DF; Pena, JPInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 2144-2155
Show abstract ▽
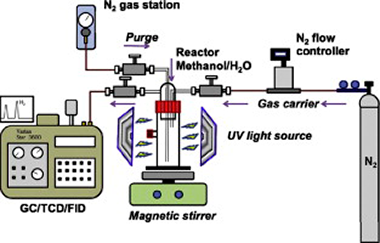
TiO2-based photocatalyst materials were synthesized through a sol–gel method, followed either by: (1) hydrothermal treatment (150 °C/24 h), or (2) heat treatment (calcination) in a temperature range between 400 and 900 °C. The resulting materials were characterized through BET, XRD, TEM, FTIR, RAMAN, laser diffraction and UV–Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. Photoactivity of the various materials was checked against photocatalytic water-splitting for hydrogen production and a relationship between TiO2 structure and hydrogen production capacity was identified. Optimum results were obtained for anatase-rutile mixtures in a ratio of 87:13. The activity of the home-made photocatalysts was also compared (under the same conditions) with the best commercially available materials which have been widely described in the literature: Hombikat UV100, Millenium PC100, Kronos vlp7000,Degussa P25and Kemira 625.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.005
- ‹ anterior
- 311 of 422
- siguiente ›














