Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Reactividad de Sólidos
In Situ Synthesis of Ceramic Composite Materials in the Ti-B-C-N System by a Mechanically Induced Self-Sustaining Reaction
Aviles, MA; Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 95 (2012) 2133-2139
Show abstract ▽

The synthesis of multicomponent ceramic materials in the titanium-diboride-carbide-nitride-carbonitride system by the mechanochemical process known as the mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was investigated. Ceramic composite powders containing TiB 2and TiC, TiN or TiC xN 1-xwere prepared from a blended mixture of the elements by exploiting the highly exothermic nature of the formation reactions. The synthesis of the composite materials was made possible by the ability of the MSR to simultaneously induce independent self-sustaining reactions, generating a mixture of ceramic phases. The composition of the ceramic composites was designed using the initial atomic ratio of the reactants, and the achieved microstructure was characterized by TiB 2particles in the micrometric range, surrounded by submicrometric and nanometric TiC, TiN, or TiC xN 1-xcrystals.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05174.x
Reactividad de Sólidos
Rapid carbothermic synthesis of silicon carbide nano powders by using microwave heating
Moshtaghioun, BM; Poyato, R; Cumbrera, FL; de Bernardi-Martin, S; Monshi, A; Abbasi, MH; Karimzadeh, F; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 32 (2012) 1787-1794
Show abstract ▽
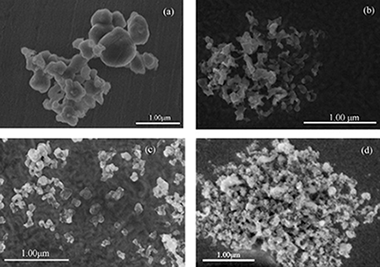
This paper reports an improved procedure for synthesis of silicon carbide nanopowders from silica by carbothermic reduction under fast microwave-induced heating. The powders have been prepared by direct solid-state reaction in a 2.45 GHz microwave field in nitrogen atmosphere after 40 h milling. For the first time, the formation of silicon carbide (beta-SiC) as a major phase can be achieved at 1200 degrees C in 5 min of microwave exposure, resulting in nano sized particles ranging from 10 to 40 nm under optimized synthesis condition. The Rietveld quantitative phase-composition analysis confirmed that the major SiC polytype is cubic SiC (beta-SiC) with 98.5(4) weight fraction and the remained is minor hexagonal SiC polytypic (alpha-SiC) phases. Therefore this method is the most efficient one for SiC powder synthesis in terms of energy and time saving as well as preparation of SiC nano powders.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.12.021
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Sub-ambient CO oxidation over mesoporous Co3O4: Effect of morphology on its reduction behavior and catalytic performance
Alvarez, A; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 431 (2012) 9-17
Show abstract ▽
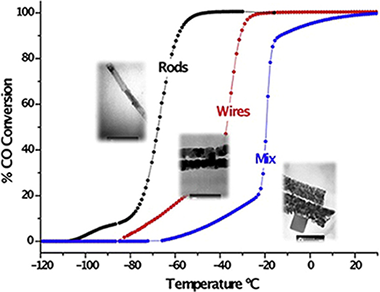
The influence of the Co 3O 4 morphology on its redox behavior and catalytic performance in the CO oxidation reaction is studied. Three different Co 3O 4 morphologies were synthesized by precipitation and hydrothermal methods. TEM and SEM observations clearly show the different obtained morphologies: rods, wires and a mixture of plates and cubes. The textural properties depend on the morphology and the redox ones on the particle size. XRD analysis reveals a spinel structure in all solids with a preferential exposition of the [1 1 0] plane in the Co 3O 4 rods sample. This preferential exposition, along with its higher specific surface area provides the rods with more efficient oxygen storage capacity resulting in an excellent catalytic performance compared to the other two morphologies.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.04.006
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the shape of Ni catalysts in the glycerol steam reforming
Bobadilla, L. F.; Alvarez, A.; Dominguez, M. I.; Romero-Sarria, F.; Centeno, M. A.; Montes, M.; Odriozola, J. A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 379-390
Show abstract ▽
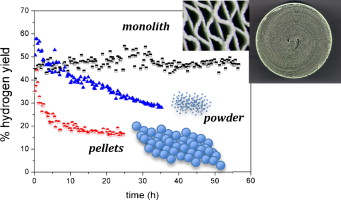
Biomass is an alternative to replace the use of fossil fuels. Glycerol, a byproduct in the biodiesel production, can be used for obtaining hydrogen. The most efficient method for obtaining hydrogen from glycerol is the steam reforming (SR). So far all the published papers report the use of conventional catalyst. In this paper, a structured catalyst has been prepared and compared with the conventional ones (powder and spherical pellets). Results show that the structured catalyst (monolith) is more stable as formation of coke was not observed.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.05.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cu-modified cryptomelane oxide as active catalyst for CO oxidation reactions
Hernandez, Willinton Y.; Centeno, Miguel A.; Ivanova, Svetlana; Eloy, Pierre; Gaigneaux, Eric M.; Odriozola, Jose A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 27-35
Show abstract ▽
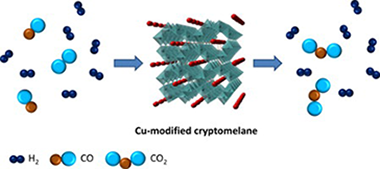
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (cryptomelane structure) were synthesized by a solvent-free method and tested in the total oxidation of CO (TOX), and preferential oxidation of CO in presence of hydrogen (PROX). The influence of Cu in the cryptomelane structure was evaluated by several characterization techniques such as: X-ray fluorescence (XRF), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), hydrogen temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H2) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Cu-modified manganese oxide material (OMS-Cu) showed very high catalytic activity for CO oxidation in comparison to the bare manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (OMS). The improved catalytic activity observed in OMS-Cu catalyst was associated to a high lattice oxygen mobility and availability due to the formation of Cusingle bondMnsingle bondO bridges. In addition, under PROX reaction conditions the catalytic activity considerably decreases in the presence of 10% (v/v) CO2 in the feed while the same amount of water provokes an improvement in the CO conversion and O2 selectivity.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.024
- ‹ anterior
- 328 of 422
- siguiente ›














