Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Cu-modified cryptomelane oxide as active catalyst for CO oxidation reactions
Hernandez, Willinton Y.; Centeno, Miguel A.; Ivanova, Svetlana; Eloy, Pierre; Gaigneaux, Eric M.; Odriozola, Jose A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 27-35
Show abstract ▽
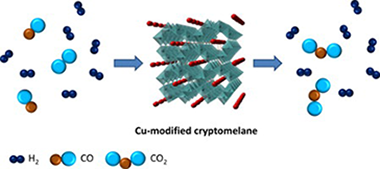
Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves (cryptomelane structure) were synthesized by a solvent-free method and tested in the total oxidation of CO (TOX), and preferential oxidation of CO in presence of hydrogen (PROX). The influence of Cu in the cryptomelane structure was evaluated by several characterization techniques such as: X-ray fluorescence (XRF), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), hydrogen temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H2) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Cu-modified manganese oxide material (OMS-Cu) showed very high catalytic activity for CO oxidation in comparison to the bare manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieve (OMS). The improved catalytic activity observed in OMS-Cu catalyst was associated to a high lattice oxygen mobility and availability due to the formation of Cusingle bondMnsingle bondO bridges. In addition, under PROX reaction conditions the catalytic activity considerably decreases in the presence of 10% (v/v) CO2 in the feed while the same amount of water provokes an improvement in the CO conversion and O2 selectivity.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.024
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
LaNiO3 as a precursor of Ni/La2O3 for CO2 reforming of CH4: Effect of the presence of an amorphous NiO phase
Rosa Pereñiguez , Victor M. Gonzalez-delaCruz, Alfonso Caballero, Juan P. Holgado,Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 123-124 (2012) 324-32
Show abstract ▽
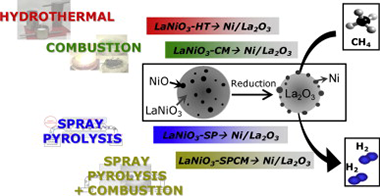
The objective of the present work has been the study of the physico-chemical and catalytic properties of Ni/La2O3 catalysts obtained by reduction of four LaNiO3 samples prepared by different methods. The LaNiO3 precursors as well as the resulting Ni/La2O3 catalysts, were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), temperature programmed reduction and oxidation (TPR, TPO). The catalytic performances of these systems for dry reforming of methane (DRM) were also tested. These samples show different physico-chemical properties resulting from the synthesis method used. The XAS and TPR measurements show that in all four LaNiO3 samples there is, in addition of the crystalline LaNiO3 rhombohedrical phase, a significant amount of an amorphous NiO phase, not detectable by XRD but evidenced by XAS. The amount of this NiO amorphous phase seems to play, together with some other microstructural parameters, an important role in the performance of the Ni/La2O3 samples for the DRM reaction.
Julio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.04.044
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Three-dimensional fabrication and characterisation of core-shell nano-columns using electron beam patterning of Ge-doped SiO2
Gontard, LC; Jinschek, JR; Ou, HY; Verbeeck, J; Dunin-Borkowski, REApplied Physics Letters, 100 (2012) 263113
Show abstract ▽
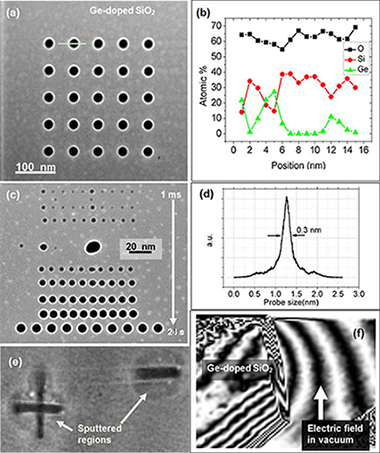
A focused electron beam in a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) is used to create arrays of core-shell structures in a specimen of amorphous SiO2 doped with Ge. The same electron microscope is then used to measure the changes that occurred in the specimen in three dimensions using electron tomography. The results show that transformations in insulators that have been subjected to intense irradiation using charged particles can be studied directly in three dimensions. The fabricated structures include core-shell nano-columns, sputtered regions, voids, and clusters.
Junio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1063/1.4731765
Weakly Interacting Molecular Layer of Spinning C60 Molecules on TiO2 (110) Surfaces
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Lanzilotto, V; Gonzalez, C; Verdini, A; de Andres, PL; Floreano, L; Lopez, MF; Martin-Gago, JAChemistry-A European Journal, 18 (2012) 7382-7387
Show abstract ▽
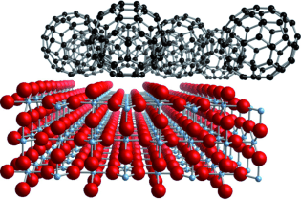
The adsorption of C60, a typical acceptor organic molecule, on a TiO2 (110) surface has been investigated by a multitechnique combination, including van der Waals density functional calculations. It is shown that the adsorbed molecules form a weakly interacting molecular layer, which sits on the fivefold-coordinated Ti that is confined between the prominent bridging oxygen rows (see figure).
Junio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1002/chem.201200627
Materiales Coloidales
Chromium incorporation into TiO2 at high pressure
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, FJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 190 (2012) 61-67
Show abstract ▽

Chromium incorporation into TiO 2 up to 3 GPa at 1300 °C and 900 °C has been studied by XRD as well as TEM. A CaCl 2 type TiO 2 polymorph has been observed in the quenched samples from high pressure. Two different mechanisms of solubility occur in the recovered samples. Chromium replaces titanium on normal octahedral sites but it also occupies interstitial octahedral sites, especially in the samples recovered from higher pressures. Interstitial chromium is responsible for an orthorhombic distortion of the TiO 2 rutile structure in the quenched samples and gives rise to a (1 1 0) twinned CaCl 2-structured polymorph. This phase is very likely the result of temperature quench at high pressure. The formation of this phase is directly related to the chromium content of the TiO 2 grains. Chromium solubility in TiO 2 increases with increasing the synthesis pressure. TiO 2 is able to accommodate up to 15.3 wt% Cr 2O 3 at 3 GPa and 1300 °C, compared to 5.7 wt% at atmospheric pressure at the same temperature.
Junio, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.01.041
- ‹ anterior
- 329 of 422
- siguiente ›














