Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials - Part II: Leaching tests to evaluate the efficiency of materials in the remediation of contaminated soils
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Orta, MM; Vidal, M; Rigol, AChemosphere, 87 (2012) 829-837
Show abstract ▽
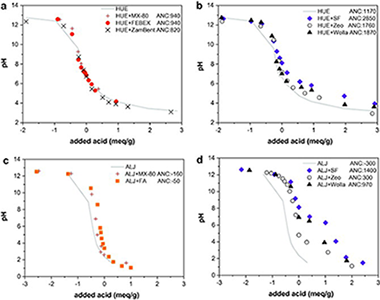
The effect of the addition of materials on the leaching pattern of As and metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb, and Cd) in two contaminated soils was investigated. The examined materials included bentonites, silicates and industrial wastes, such as sugar foam, fly ashes and a material originated from the zeolitization of fly ash. Soil + material mixtures were prepared at 10% doses. Changes in the acid neutralization capacity, crystalline phases and contaminant leaching over a wide range of pHs were examined by using pHstat leaching tests. Sugar foam, the zeolitic material and MX-80 bentonite produced the greatest decrease in the leaching of pollutants due to an increase in the pH and/or the sorption capacity in the resulting mixture. This finding suggests that soil remediation may be a feasible option for the reuse of non-hazardous wastes.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.015
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Hydrothermal synthesis of BiVO4: Structural and morphological influence on the photocatalytic activity
Obregon, S; Caballero, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 117 (2012) 59-66
Show abstract ▽
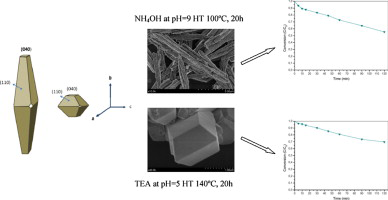
BiVO 4 hierarchical heterostructures are synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the degradation of methylene blue under UV-vis irradiation. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that BiVO 4 present the monoclinic crystalline phase with different morphologies depending on the pH value, type of precipitating agent and hydrothermal temperature and treatment time. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with needle-like morphology.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.12.037
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of diffuse light scattering designs on the efficiency of dye solar cells: An integral optical and electrical description
Galvez, FE; Kemppainen, E; Miguez, H; Halme, JJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 11426-11433
Show abstract ▽
Herein, we present an integral optical and electrical theoretical analysis of the effect of different diffuse light scattering designs on the performance of dye solar cells. Light harvesting efficiencies and electron generation functions extracted from optical numerical calculations based on a Monte Carlo approach are introduced in a standard electron diffusion model to obtain the steady-state characteristics of the different configurations considered. We demonstrate that there is a strong dependence of the incident photon to current conversion efficiency, and thus of the overall conversion efficiency, on the interplay between the value of the electron diffusion length considered and the type of light scattering design employed, which determines the spatial dependence of the electron generation function. Other effects, like the influence of increased photoelectron generation on the photovoltage, are also discussed. Optimized scattering designs for different combinations of electrode thickness and electron diffusion length are proposed.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp2092708
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic activity of single and mixed nanosheet-like Bi2WO6 and TiO2 for Rhodamine B degradation under sunlike and visible illumination
Murcia-Lopez, S; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 423-424 (2012) 34-41
Show abstract ▽
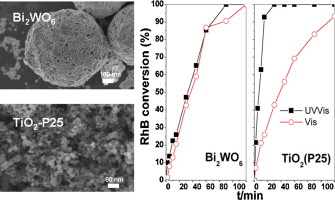
The photocatalytic activity, under sunlike illumination, for Rhodamine B (RhB) degradation using Bi2WO6-TiO2 samples, is reported. Two different kinds of Bi2WO6-TiO2 samples were studied, obtained by distinct methods: first, a mechanical mixing, by adding to synthesized nanosheet-like Bi2WO6 powder the corresponding amount of TiO2 nanoparticles (P25) in order to obtain physical mixtures of both catalysts with different percentages of TiO2 (5, 10 and 50 wt%); second, a single Bi2WO6-TiO2 heterostructure was prepared by adding commercial TiO2-P25 to the Bi2WO6 precursors (50 wt%) prior to the hydrothermal treatment, thus obtaining a sample with "in situ" TiO2 incorporation. Comparisons between the photocatalytic behaviour of these samples and those exhibited by the single materials Bi2WO6 and TiO2 (P25) were carried out, in order to establish the effect not only of the TiO2 addition but also of the way in which TiO2 (P25) is incorporated. The role of each single photocatalyst in the mixtures in the RhB degradation and mineralization under sunlike and just visible illumination was also studied.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark plasma sintering of Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x monolithic ceramics obtained by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Borrell, A; Salvador, MD; Garcia-Rocha, V; Fernandez, A; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJMaterials Science and Engineering A, 543 (2012) 173-179
Show abstract ▽
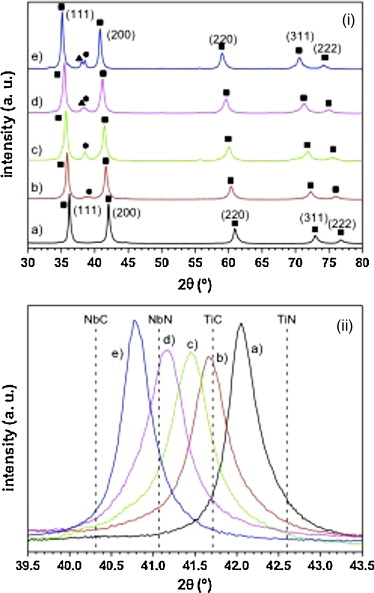
Nanometer-sized titanium-niobium carbonitride powders (Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x) with different Ti/Nb atomic ratios were obtained by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction, and sintered by spark plasma sintering technique at 1500°C for 1min in a vacuum atmosphere. Mechanical properties such as hardness and Young's modulus were determined by nanoindentation technique and friction and wear coefficients assessed by ball-on-disk testing using alumina ball in dry sliding conditions. The fracture surface and wear tracks of samples were examined by scanning electron microscopy. Results showed that it is possible to obtain dense monolithic ceramics from the solid solution (Ti yNb 1-yC xN 1-x) with good mechanical properties and excellent wear resistance. The optimum values of nanomechanical properties were found for the Ti 0.3Nb 0.7C 0.5N 0.5 ceramic composition, which exhibited a high hardness over 26.0GPa and Young's modulus around 400GPa.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.071
- ‹ anterior
- 332 of 422
- siguiente ›














