Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials - Part II: Leaching tests to evaluate the efficiency of materials in the remediation of contaminated soils
Gonzalez-Nunez, R; Alba, MD; Orta, MM; Vidal, M; Rigol, AChemosphere, 87 (2012) 829-837
Show abstract ▽
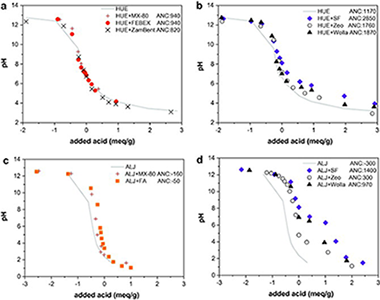
The effect of the addition of materials on the leaching pattern of As and metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb, and Cd) in two contaminated soils was investigated. The examined materials included bentonites, silicates and industrial wastes, such as sugar foam, fly ashes and a material originated from the zeolitization of fly ash. Soil + material mixtures were prepared at 10% doses. Changes in the acid neutralization capacity, crystalline phases and contaminant leaching over a wide range of pHs were examined by using pHstat leaching tests. Sugar foam, the zeolitic material and MX-80 bentonite produced the greatest decrease in the leaching of pollutants due to an increase in the pH and/or the sorption capacity in the resulting mixture. This finding suggests that soil remediation may be a feasible option for the reuse of non-hazardous wastes.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.015
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanoclay Nucleation Effect in the Thermal Stabilization of a Polymer Nanocomposite: A Kinetic Mechanism Change
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 11797-11807
Show abstract ▽
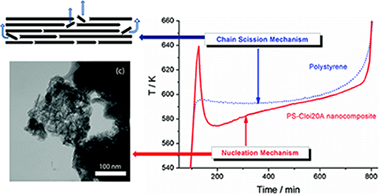
The enhanced thermal stability of polymer-clay nanocomposites over the original polymers is one of their most interesting features, and it has been profusely studied within the last decades. Here, a thorough kinetic analysis of polystyrene and a montmorillonite-polystyrene nanocomposite has been performed making use of state-of-the-art kinetic procedures. It has been found that the degradation mechanism changes from a chain scission process for the polymer to a complex two-step nucleation-driven reaction for the nanocomposite. This mechanism change can explain the delayed onset of degradation found in the nanocomposite. Moreover, observation by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has shown that the clay platelets within the composite could act as nucleation centers for the decomposition.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp302466p
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Correlation lengths, porosity and water adsorption in TiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Garcia-Gutierrez, MC; Hernandez, JJ; Rueda, DR; Ezquerra, TANanotechnology, 23 (2012) 205701
Show abstract ▽
This paper reports a thorough microstructural characterization of glancing angle deposited (GLAD) TiO 2 thin films. Atomic force microscopy (afm), grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering (GISAXS) and water adsorption isotherms have been used to determine the evolution of porosity and the existence of some correlation distances between the nanocolumns constituting the basic elements of the films nanostructure. It is found that the deposition angle and, to a lesser extent, the film thickness are the most important parameters controlling properties of the thin film. The importance of porosity and some critical dimensions encountered in the investigated GLAD thin films is highlighted in relation to the analysis of their optical properties when utilized as antireflective coatings or as hosts and templates for the development of new composite materials.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/20/205701
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide OMS-2 nanomaterials deposited on AISI 304 stainless steels monoliths for CO oxidation
Martinez, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General, 423 (2012) 137-145
Show abstract ▽

Gold supported on cryptomelane-type OMS-2 catalysts deposited on AISI 304 stainless steels monoliths have been prepared for the first time, characterised and tested in the CO oxidation reaction. An easy and non-conventional method of incorporation of gold to the cryptomelane solid is used. This method allows the preparation of the monolithic catalysts without altering the structural and textural characteristics of the parent OMS-2 material. Although these catalysts do not show an optimal performance for the oxidation of CO, the presence of small gold particles enhances the catalytic performances of the cryptomelane producing promissory CO oxidation catalysts. The non-conventional gold deposition favours a partial loss of K + into the channels, resulting in an increment of the average oxidation state of manganese which favours the catalytic behaviour of these kinds of materials. This study can be taken as a starting point to obtain very active gold catalysts supported on OMS-2 materials through the optimisation of the gold-support interaction and the decrease in the gold particle size.
Mayo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.026
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Self-assembly at room temperature of thermally stable discrete and extended oligomers of polycyclic aromatics on Ag(100): induced dipoles and cooperative effects
Papageorgiou, AC; Alavi, A; Lambert, RMChemical Communications, 48 (2012) 3394-3396
Show abstract ▽
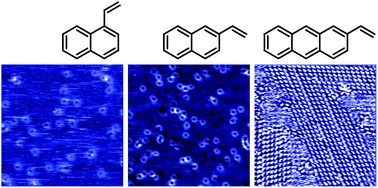
Thermally stable nanoarchitectures are realized on the Ag(100) surface by self-assembly of asymmetrically substituted arenes. The process is instigated by adsorption-induced molecule → surface charge transfer that gives rise to in-plane dipole moments. Observation and calculation indicate that cooperative interactions further enhance the stability of these polarizable systems.
Abril, 2012 | DOI: 10.1039/c2cc17728e
- ‹ anterior
- 333 of 422
- siguiente ›














