Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma deposition of perylene-adamantane nanocomposite thin films for NO 2 room-temperature optical sensing
Aparicio, FJ; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Alcaire, M; Gonzalez, JC; Serra, C; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 8731-8740
Show abstract ▽
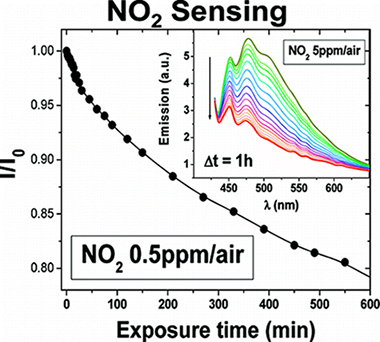
This work reports the preparation, by a new remote assisted plasma deposition process, of luminescent nanocomposite thin films consisting of an insoluble organic matrix where photonically active perylene molecules are embedded. The films are obtained by the remote plasma deposition of adamantane and perylene precursor molecules. The results show that the adamantane precursor is very effective to improve the perylene–adamantane nanocomposite transparency in comparison with plasma deposited perylene films. The plasma deposited adamantane films have been characterized by secondary-ion mass spectrometry and FT-IR spectroscopy. These techniques and atomic force microscopy (AFM) have been also used for the characterization of the nanocomposite films. Their optical properties (UV–vis absorption, fluorescence, and refractive index) have been also determined and their sensing properties toward NO2 studied. It is found that samples with the perylene molecules embedded within the transparent plasma deposited matrix are highly sensitive toward this gas and that the sensitivity of the films can be adjusted by modifying the aggregation state of the perylene molecules, as determined by the analysis of their fluorescence spectra. By monitoring the fluorescence emission of these films, it has been possible to detect a NO2 concentration as low as 0.5 ppm in air at room temperature. Because of their chemical stability and transparency in the UV region, the remote plasma deposited adamantane thin films have revealed as an optimum host matrix for the development of photonically active composites for sensing applications.
Abril, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp209272s
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Electrostatic Induced Molecular Tilting in Self-Assembled Monolayers of n-Octadecylamine on Mica
Oviedo, J; San-Miguel, MA; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 7099-7105
Show abstract ▽
Self-assembled monolayers of n-octadecylamine on mica (ODA/mica SAMs) have been investigated by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and by attenuated total reflectance infrared (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron (XPS) spectroscopies. Topographic data characterizes a stable configuration with the alkyl skeleton tilted approximate to 46 degrees from the surface normal that is rationalized according to a well established structural alkyl chain packing model. Extended contact with air increases molecular tilting up to approximate to 58 degrees. ATR-FTIR and XPS reveal the presence of protonated amino groups within the monolayer and its increment upon exposure to air. The transition between both tilted states is explained assuming the protonation reaction as the driving force and introducing a model to evaluate an electrostatic repulsions term in the overall cohesive energy balance of the system. ODA molecules in the self-assembled monolayer respond to their spontaneous protonation by atmospheric water by tilting as a mechanism to relax the repulsions between -NH3+ heads.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp300829g
Sonication induced reduction of the Ojen (Andalucia, Spain) vermiculite under air and under nitrogen
Poyato, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Lerf, A; Wagner, FEUltrasonics Sonochemistry, 19 (2012) 373-375
Show abstract ▽
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications
Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Colon, GChemical Reviews, 112 (2012) 1555-1614
Show abstract ▽
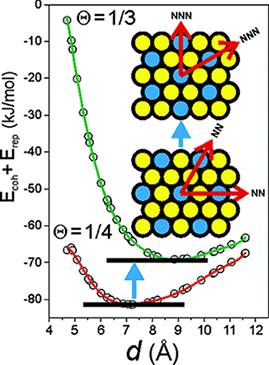
Advanced nanostructured materials that demonstrate useful activity under solar excitation in fields concerned with the elimination of pollutants, partial oxidation and the valorization of chemical compounds, water splitting and CO 2 reduction processes, are discussed. Point defects present in nanoparticulated anatase present both 5-fold- and 6-fold-coordinated titanium atoms, as well as 2-fold- and 3-fold-coordinated oxygens. The requirement of using sunlight as the excitation source for the degradation reaction demands, as a principal requirement, the modification of the electronic characteristics of a UV absorber system such as anatase-TiO 2. Some reports also indicate the need for large doping concentrations for N-doping in specific cases where notable changes in the valence band onset are subsequently observed. The effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on the crystallization is reported by Yin et al. They showed that the presence of CTAB induces the appearance of BiOBr during the synthesis at 80°C using an aqueous method.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/cr100454n
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and Structure Resolution of RbLaF4
Rollet, AL; Allix, M; Veron, E; Deschamps, M; Montouillout, V; Suchomel, MR; Suard, E; Barre, M; Ocana, M; Sadoc, A; Boucher, F; Bessada, C; Massiot, D; Fayon, FInorganic Chemistry, 51 (2012) 2272-2282
Show abstract ▽
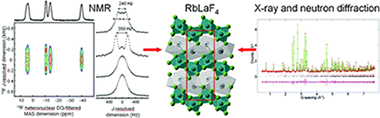
The synthesis and structure resolution of RbLaF4 are described. RbLaF4 is synthesized by solid-state reaction between RbF and LaF3 at 425 degrees C under a nonoxidizing atmosphere. Its crystal structure has been resolved by combining neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction data refinements (Pnma, a = 6.46281(2) angstrom, b = 3.86498(1) angstrom, c = 16.176:29(4) angstrom, Z = 4). One-dimensional Rb-87, La-139, and F-19 MAS NMR spectra have been recorded and are in agreement with the proposed structural model. Assignment of the F-19 resonances is performed on the basis of both F-19-La-139 J-coupling multiplet patterns observed in a heteronudear DQ-filtered J-resolved spectrum and F-19-Rb-87 HMQC MAS experiments. DFT calculations of both the F-19 isotropic chemical shieldings and the Rb-87, La-139 electric field gradient tensors using the GIPAW and PAW methods implemented in the CASTEP code are in good agreement with the experimental values and support the proposed structural model. Finally, the conductivity of RbLaF4 and luminescence properties of Eu-doped LaRbF4 are investigated.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/ic202301e
- ‹ anterior
- 335 of 422
- siguiente ›














