Artículos SCI destacados
Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications
Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Colon, GChemical Reviews, 112 (2012) 1555-1614
Advanced nanostructured materials that demonstrate useful activity under solar excitation in fields concerned with the elimination of pollutants, partial oxidation and the valorization of chemical compounds, water splitting and CO 2 reduction processes, are discussed. Point defects present in nanoparticulated anatase present both 5-fold- and 6-fold-coordinated titanium atoms, as well as 2-fold- and 3-fold-coordinated oxygens. The requirement of using sunlight as the excitation source for the degradation reaction demands, as a principal requirement, the modification of the electronic characteristics of a UV absorber system such as anatase-TiO 2. Some reports also indicate the need for large doping concentrations for N-doping in specific cases where notable changes in the valence band onset are subsequently observed. The effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on the crystallization is reported by Yin et al. They showed that the presence of CTAB induces the appearance of BiOBr during the synthesis at 80°C using an aqueous method.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
41.30 |
DOI | Año
2012 |
Collective osmotic shock in ordered materials
Paul Zavala-Rivera, Kevin Channon, Vincent Nguyen, Easan Sivaniah, Dinesh Kabra, Richard H. Friend, S. K. Nataraj, Shaheen A. Al-Muhtaseb, Alexander Hexemer, Mauricio E. Calvo & Hernan MiguezNature Materials, 11 (2012) 53–57
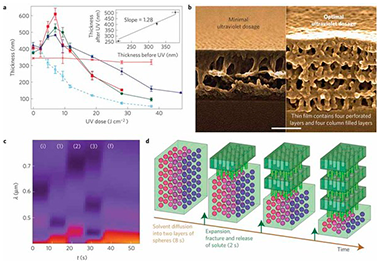
Osmotic shock in a vesicle or cell is the stress build-up and subsequent rupture of the phospholipid membrane that occurs when a relatively high concentration of salt is unable to cross the membrane and instead an inflow of water alleviates the salt concentration gradient. This is a well-known failure mechanism for cells and vesicles (for example, hypotonic shock) and metal alloys (for example, hydrogen embrittlement). We propose the concept of collective osmotic shock, whereby a coordinated explosive fracture resulting from multiplexing the singular effects of osmotic shock at discrete sites within an ordered material results in regular bicontinuous structures. The concept is demonstrated here using self-assembled block copolymer micelles, yet it is applicable to organized heterogeneous materials where a minority component can be selectively degraded and solvated whilst ensconced in a matrix capable of plastic deformation. We discuss the application of these self-supported, perforated multilayer materials in photonics, nanofiltration and optoelectronics.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
35.75 |
DOI | Año
2012 |
High voltage vacuum-deposited CH3NH3PbI3–CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cells
Avila, J; Momblona, C; Boix, P; Sessolo, M; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Vandewal, K; Miguez, H; Bolink, HJEnergy & Environmental Science, 11 (2018) 3292-3297
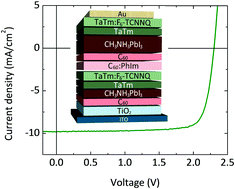
The recent success of perovskite solar cells is based on two solid pillars: the rapid progress of their power conversion efficiency and their flexibility in terms of optoelectrical properties and processing methods. That versatility makes these devices ideal candidates for multi-junction photovoltaics. We report an optically optimized double junction CH3NH3PbI3-CH3NH3PbI3 tandem solar cell where the matched short-circuit current is maximized while parasitic absorption is minimized. The use of an additive vacuum-deposition protocol allows us to reproduce calculated stack designs, which comprise several charge selective materials that ensure appropriate band alignment and charge recombination. This rationalized configuration yields an unprecedented open circuit voltage of 2.30 V. Furthermore, this tandem solar cell features efficiencies larger than 18%, higher than those of the individual sub-cells. Low photo-current values allow reducing the losses associated to the series resistance of transparent contacts, which opens the door to the realization of efficient large area modules.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
33.25 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Tandem catalytic approaches for CO2 2 enriched Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
Blay-Roger, R; Nawaz, MA; Baena-Moreno, FM; Bobadilla, LF; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAProgress in Energy and Combustion Science, 103 (2024) 101159
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis (FTS) allows the conversion of syngas to high-density liquid fuels, playing a key role in the petrochemical and global energy sectors over the last century. However, the current Global Challenges impose the need to recycle CO2 2 and foster green fuels, opening new opportunities to adapt traditional processes like FTS to become a key player in future bioenergy scenarios. This review discusses the implementation of CO2- 2- rich streams and in tandem catalysis to produce sustainable fuels via the next generation of FTS. Departing from a brief revision of the past, present, and future of FTS, we analyse a disruptive approach coupling FTS to upstream and downstream processes to illustrate the advantages of process intensification in the context of biofuel production via FTS. We showcase a smart tandem catalyst design strategy addressing the challenges to gather mechanistic insights in sequential transformations of reagents in complex reaction schemes, the precise control of structure-activity parameters, catalysts aging-deactivation, optimization of reaction parameters, as well as reaction engineering aspects such as catalytic bed arrangements and non-conventional reactor configurations to enhance the overall performance. Our review analysis includes technoeconomic elements on synthetic aviation fuels as a case of study for FTS applications in the biofuel context discussing the challenges in market penetration and potential profitability of synthetic biofuels. This comprehensive overview provides a fresh angle of FTS and its enormous potential when combined with CO2 2 upgrading and tandem catalysis to become a front-runner technology in the transition towards a low-carbon future.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
32.00 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices
Barranco, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AProgress in Materials Science, 78 (2016) 59-153
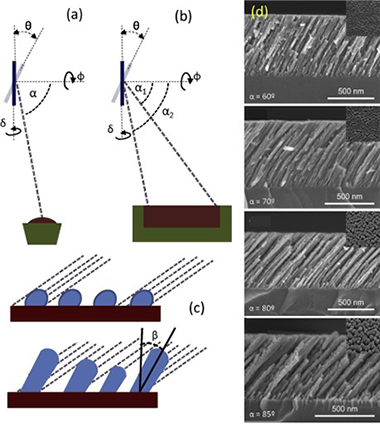
The oblique angle configuration has emerged as an invaluable tool for the deposition of nanostructured thin films. This review develops an up to date description of its principles, including the atomistic mechanisms governing film growth and nanostructuration possibilities, as well as a comprehensive description of the applications benefiting from its incorporation in actual devices. In contrast with other reviews on the subject, the electron beam assisted evaporation technique is analyzed along with other methods operating at oblique angles, including, among others, magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser or ion beam-assisted deposition techniques. To account for the existing differences between deposition in vacuum or in the presence of a plasma, mechanistic simulations are critically revised, discussing well-established paradigms such as the tangent or cosine rules, and proposing new models that explain the growth of tilted porous nanostructures. In the second part, we present an extensive description of applications wherein oblique-angle-deposited thin films are of relevance. From there, we proceed by considering the requirements of a large number of functional devices in which these films are currently being utilized (e.g., solar cells, Li batteries, electrochromic glasses, biomaterials, sensors, etc.), and subsequently describe how and why these nanostructured materials meet with these needs.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
31.14 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: from nanoparticles to technology
Balaz, P; Achimovicova, M; Balaz, M; Billik, P; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z; Criado, JM; Delogu, F; Dutkova, E; Gaffet, E; Gotor, FJ; Kumar, R; Mitov, I; Rojac, T; Senna, M; Streletskii, A; Wieczorek-Ciurowa, KChemical Society Reviews, 42 (2013) 7571-7637
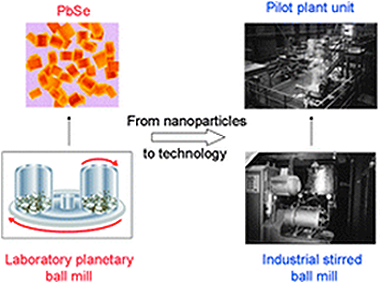
The aim of this review article on recent developments of mechanochemistry (nowadays established as a part of chemistry) is to provide a comprehensive overview of advances achieved in the field of atomistic processes, phase transformations, simple and multicomponent nanosystems and peculiarities of mechanochemical reactions. Industrial aspects with successful penetration into fields like materials engineering, heterogeneous catalysis and extractive metallurgy are also reviewed. The hallmarks of mechanochemistry include influencing reactivity of solids by the presence of solid-state defects, interphases and relaxation phenomena, enabling processes to take place under non-equilibrium conditions, creating a well-crystallized core of nanoparticles with disordered near-surface shell regions and performing simple dry time-convenient one-step syntheses. Underlying these hallmarks are technological consequences like preparing new nanomaterials with the desired properties or producing these materials in a reproducible way with high yield and under simple and easy operating conditions. The last but not least hallmark is enabling work under environmentally friendly and essentially waste-free conditions (822 references).
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
30.43 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Maximized performance of dye solar cells on plastic: a combined theoretical and experimental optimization approach
Li, Yuelong; Carretero-Palacios, Sol; Yoo, Kicheon; Kim, Jong Hak; Jimenez-Solano, Alberto; Lee, Chul-Ho; Miguez, Hernan; Ko, Min JaeEnergy & Environmental Science, 9 (2016) 2061-2071
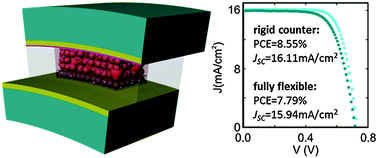
We demonstrate that a combined optimization approach based on the sequential alternation of theoretical analysis and experimental realization gives rise to plastic supported dye solar cells for which both light harvesting efficiency and electron collection are maximized. Rationalized configurations with optimized light trapping and charge extraction are realized to achieve photoanodes on plastic prepared at low temperature, showing a power conversion efficiency of 8.55% and a short circuit photocurrent of 16.11 mA cm−2, unprecedented for plastic based dye solar cell devices. Furthermore, the corresponding fully flexible designs present stable mechanical properties after several bending cycles, displaying 7.79% power conversion efficiency, an average broadband internal quantum efficiency above 90%, and a short circuit photocurrent of 15.94 mA cm−2, which is the largest reported value for bendable cells of this sort to date.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
29.52 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Analysis of Dry Reforming as direct route for gas phase CO2 conversion. The past, the present and future of catalytic DRM technologies
le Sache, E; Reina, TRProgress in Energy and Combustion Science, 89 (2022) 100970
Transition to low carbon societies requires advanced catalysis and reaction engineering to pursue green routes for fuels and chemicals production as well as CO2 conversion. This comprehensive review provides a fresh perspective on the dry reforming of methane reaction (DRM) which constitutes a straightforward approach for effective CO2 conversion to added value syngas. The bottleneck for the implementation of this process at industrial scale is the development of highly active and robust heterogeneous catalysts able to overcome the CO2 activation barrier and deliver sufficient amount of the upgrading products at the desired operation conditions. Also, its high energy demand due to the endothermic nature of the reaction imposes extra difficulties. This review critically discusses the recent progresses on catalysts design ranging from traditional metal-supported catalysts to advanced structured and nanostructured systems with promising performance. The main advantages and culprits of the different catalytic systems are introduced aiming to inspire the catalysis community to further refine these formulations towards the development of "supercatalysts" for DRM. Besides the design of increasingly complex catalyst morphologies as well as other promising alternatives aiming at reducing the energy consumption of the process or tackle deactivation through reactor design are introduced.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
29.50 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Highly Anisotropic Organometal Halide Perovskite Nanowalls Grown by Glancing-Angle Deposition
Castillo-Seoane, J; Contreras-Bernal, L; Obrero-Perez, JM; Garcia-Casas, X; Lorenzo-Lazaro, F; Aparicio, FJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Rojas, TC; Anta, JA; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JRAdvanced Materials (2022) 2107739
Polarizers are ubiquitous components in current optoelectronic devices as displays or photographic cameras. Yet, control over light polarization is an unsolved challenge, since the main drawback of the existing display technologies is the significant optical losses. In such a context, organometal halide perovskites (OMHP) can play a decisive role given their flexible synthesis with tunable optical properties such as bandgap and photoluminescence, and excellent light emission with a low non-radiative recombination rate. Therefore, along with their outstanding electrical properties have elevated hybrid perovskites as the material of choice in photovoltaics and optoelectronics. Among the different OMHP nanostructures, nanowires and nanorods have lately arisen as key players in the control of light polarization for lighting or detector applications. Herein, the fabrication of highly aligned and anisotropic methylammonium lead iodide perovskite nanowalls by glancing-angle deposition, which is compatible with most substrates, is presented. Their high alignment degree provides the samples with anisotropic optical properties such as light absorption and photoluminescence. Furthermore, their implementation in photovoltaic devices provides them with a polarization-sensitive response. This facile vacuum-based approach embodies a milestone in the development of last-generation polarization-sensitive perovskite-based optoelectronic devices such as lighting appliances or self-powered photodetectors.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
29.40 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Enhanced Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells Incorporating Dopant-Free Crystalline Spiro-OMeTAD Layers by Vacuum Sublimation
Barranco, A; Lopez-Santos, MC; Idigoras, J; Aparicio, FJ; Obrero-Perez, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Contreras-Bernal, L; Rico, V; Ferrer, J; Espinos, JP; Borras, A; Anta, JA; Sanchez-Valencia, JRAdvanced Energy Materials, (2020) 1901524
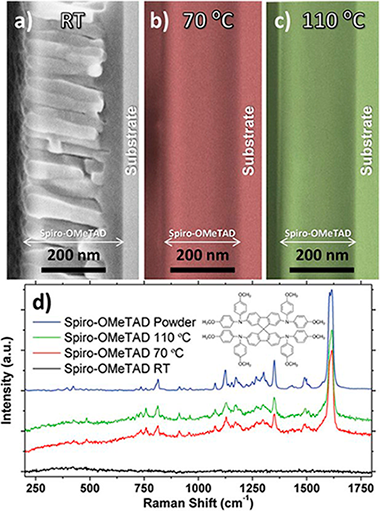
The main handicap still hindering the eventual exploitation of organometal halide perovskite-based solar cells is their poor stability under prolonged illumination, ambient conditions, and increased temperatures. This article shows for the first time the vacuum processing of the most widely used solid-state hole conductor (SSHC), i.e., the Spiro-OMeTAD [2,2 ',7,7 '-tetrakis (N,N-di-p-methoxyphenyl-amine) 9,9 '-spirobifluorene], and how its dopant-free crystalline formation unprecedently improves perovskite solar cell (PSC) stability under continuous illumination by about two orders of magnitude with respect to the solution-processed reference and after annealing in air up to 200 degrees C. It is demonstrated that the control over the temperature of the samples during the vacuum deposition enhances the crystallinity of the SSHC, obtaining a preferential orientation along the pi-pi stacking direction. These results may represent a milestone toward the full vacuum processing of hybrid organic halide PSCs as well as light-emitting diodes, with promising impacts on the development of durable devices. The microstructure, purity, and crystallinity of the vacuum sublimated Spiro-OMeTAD layers are fully elucidated by applying an unparalleled set of complementary characterization techniques, including scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering and grazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
29.37 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Ultrathin Plasma Polymer Passivation of Perovskite Solar Cells for Improved Stability and Reproducibility
Obrero-Perez, JM; Contreras-Bernal, L; Nuñez-Galvez, F; Castillo-Seoane, J; Valadez-Villalobos, K; Aparicio, FJ; Anta, JA; Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, AAdvanced Energy Materials, (2022) 2200812
Despite the youthfulness of hybrid halide perovskite solar cells, their efficiencies are currently comparable to commercial silicon and have surpassed quantum-dots solar cells. Yet, the scalability of these devices is a challenge due to their low reproducibility and stability under environmental conditions. However, the techniques reported to date to tackle such issues recurrently involve the use of solvent methods that would further complicate their transfer to industry. Herein a reliable alternative relaying in the implementation of an ultrathin plasma polymer as a passivation interface between the electron transport layer and the hybrid perovskite layer is presented. Such a nanoengineered interface provides solar devices with increased long-term stability under ambient conditions. Thus, without involving any additional encapsulation step, the cells retain more than 80% of their efficiency after being exposed to the ambient atmosphere for more than 1000 h. Moreover, this plasma polymer passivation strategy significantly improves the coverage of the mesoporous scaffold by the perovskite layer, providing the solar cells with enhanced performance, with a champion efficiency of 19.2%, a remarkable value for Li-free standard mesoporous n-i-p architectures, as well as significantly improved reproducibility.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
27.80 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Elucidating the Mechanism of Iron-Catalyzed Graphitization: The First Observation of Homogeneous Solid-State Catalysis
Hunter, RD; Takeguchi, M; Hashimoto, A; Ridings, KM; Hendy, SC; Zakharov, D; Warnken, N; Isaacs, J; Fernández-Muñoz, S; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schnepp, ZAdvanced Materials, 36 (2024) 2404170
Carbon is a critical material for existing and emerging energy applications and there is considerable global effort in generating sustainable carbons. A particularly promising area is iron-catalyzed graphitization, which is the conversion of organic matter to graphitic carbon nanostructures by an iron catalyst. In this paper, it is reported that iron-catalyzed graphitization occurs via a new type of mechanism that is called homogeneous solid-state catalysis. Dark field in situ transmission electron microscopy is used to demonstrate that crystalline iron nanoparticles “burrow” through amorphous carbon to generate multiwalled graphitic nanotubes. The process is remarkably fast, particularly given the solid phase of the catalyst, and in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction is used to demonstrate that graphitization is complete within a few minutes.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
27.40 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Direct Laser Writing: From Materials Synthesis and Conversion to Electronic Device Processing
Pinheiro, T; Morais, M; Silvestre, S; Carlos, E; Coelho, J; Almeida, HV; Barquinha, P; Fortunato, E; Martins, RAdvanced Materials, 36 (2024) 26
Direct Laser Writing (DLW) has been increasingly selected as a microfabrication route for efficient, cost-effective, high-resolution material synthesis and conversion. Concurrently, lasers participate in the patterning and assembly of functional geometries in several fields of application, of which electronics stand out. In this review, recent advances and strategies based on DLW for electronics microfabrication are surveyed and outlined, based on laser material growth strategies. First, the main DLW parameters influencing material synthesis and transformation mechanisms are summarized, aimed at selective, tailored writing of conductive and semiconducting materials. Additive and transformative DLW processing mechanisms are discussed, to open space to explore several categories of materials directly synthesized or transformed for electronics microfabrication. These include metallic conductors, metal oxides, transition metal chalcogenides and carbides, laser-induced graphene, and their mixtures. By accessing a wide range of material types, DLW-based electronic applications are explored, including processing components, energy harvesting and storage, sensing, and bioelectronics. The expanded capability of lasers to participate in multiple fabrication steps at different implementation levels, from material engineering to device processing, indicates their future applicability to next-generation electronics, where more accessible, green microfabrication approaches integrate lasers as comprehensive tools.
This review covers recent progress and breakthroughs in direct laser writing for multimaterial synthesis and conversion, toward processing and fabrication of electronics. Predominant laser-material processing mechanisms for the writing of conductive and semiconductive materials are discussed, alongside important considerations on laser operation and implementation for both rigid and flexible electronics, including microelectronics, energy harvesting and storage, sensors, and bioelectronics. image
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
27.40 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Synergistic Integration of Nanogenerators and Solar Cells: Advanced Hybrid Structures and Applications
Hajra, S; Ali, A; Panda, S; Song, HW; Rajaitha, PM; Dubal, D; Borras, A; In-Na, P; Vittayakorn, N; Vivekananthan, V; Kim, HJ; Divya, S; Oh, THAdvanced Energy Materials, (2024) 2400025
The rapid growth of global energy consumption and the increasing demand for sustainable and renewable energy sources have urged vast research into harnessing energy from various sources. Among them, the most promising approaches are nanogenerators (NGs) and solar cells (SCs), which independently offer innovative solutions for energy harvesting. This review paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the integration of NGs and SCs, exploring advanced hybrid structures and their diverse applications. First, an overview of the principles and working mechanisms of NGs and SCs is provided for seamless hybrid integrations. Then, various design strategies are discussed, such as piezoelectric and triboelectric NGs with different types of SCs. Finally, a wide range of applications are explored that benefit from the synergistic integration of NGs and SCs, including self-powered electronics, wearable devices, environmental monitoring, and wireless sensor networks. The potential for these hybrid systems is highlighted to address real-world energy needs and contribute to developing sustainable and self-sufficient technologies. In conclusion, this review provides valuable insights into the state-of-the-art developments in NGs and SCs integration, shedding light on advanced hybrid structures and their diverse applications.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
24.40 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Functionalized biochars as supports for Pd/C catalysts for efficient hydrogen production from formic acid
Santos, JL; Megias-Sayago, C; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 282 (2021) 119615

Biomass waste product was used to generate biochars as catalytic supports for selective hydrogen production from formic acid. The supports were obtained after pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere of non-pretreated and che-mically ZnCl2 activated raw materials (vine shoot and crystalline cellulose). The support series includes materials with different textural properties and surface chemistry. The support nature and especially textural properties firstly affects significantly Pd size and dispersion and its interaction with the support and secondly influence in a great extent the catalytic behavior of the final material. The presence of prevailing mesoporous character appeared to be the most important parameter influencing formic acid dehydrogenation and overall hydrogen production.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
24.32 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Dehydration of glucose to 5-Hydroxymethlyfurfural on bifunctional carbon catalysts
Bounoukta, CE; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 286 (2021) 119938
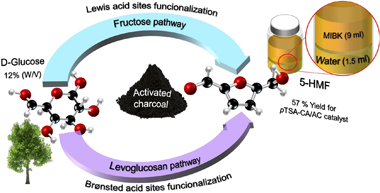
The proposed study tries to reply on one important question concerning glucose dehydration: What is the role of bare or tandem Lewis/Bronsted acid sites in the reaction and which are better? A series of mono and bifunctional catalyst are designed and screened for the glucose dehydration reaction. The results clearly reveal that catalyst activity is a function of catalyst composition. The presence of Lewis sites the reaction toward first step isomerization, while the Brunsted acid dehydrate directly glucose to HMF via levoglucosane intermediate. This study proposed also a kinetic modelling of the included reactions and their contrast with the empirical observations.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
24.32 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
IR spectroscopic insights into the coking-resistance effect of potassium on nickel-based catalyst during dry reforming of methane
Azancot, L; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 285 (2021) 119822
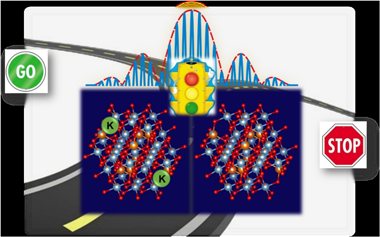
Dry reforming of methane (DRM) is an effective catalytic route for transforming CO2 and CH4 into valuable syngas and thus potentially attractive for mitigating the emission of environmental harmful gases. Therefore, it is crucial to develop rationally Ni-based catalysts highly resistant to coking and sintering. In this scenario, the addition of small amounts of potassium to nickel catalyst increases their resistance to coking during dry reforming of methane. Nonetheless, the specific role of potassium in these catalysts not have been fully understood and there are still important discrepancies between the different reported studies. This work provides a new approach on the anticoking nature of a K-promoted Ni catalyst by means of a combined IR spectroscopic study of in situ characterization by CO adsorption under static conditions and operando DRIFTS measurements under dynamic conditions of DRM reaction. The involved surface species formed during the reaction were elucidated by transient and steady-state operando DRIFTS studies. It was revealed that the existence of Ni-K interfacial sites favours the gasification of carbonaceous deposits towards reverse Boudouard reaction and reduces the sticking probability of CO2 dissociative adsorption. Moreover, the presence of strongly Mg-O-K basic sites leads to the formation of carbonate intermediates that are subsequently reduced into CO gaseous towards the associative mechanism by RWGS reaction. These results provide a fundamental understanding of the relevant anticoking effect of potassium on Ni-based catalysts.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
24.32 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Scalable synthesis of 2D Ti2CTx MXene and molybdenum disulfide composites with excellent microwave absorbing performance
Miao, BJ; Cao, YE; Zhu, QS; Nawaz, MA; Ordiozola, JA; Reina, TR; Bai, ZM; Ren, JN; Wei, FCAdvanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 6 (2023) 61
The signal crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) problems direly need to be resolved in the rapid development of modern microwave communication technology for a better working frequency and transmission power of electronic systems. Where the new absorbing materials such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)/titania (TiO2)/Ti2CTx and MoS2/Ti2CTx composites could meet the requirement of "thin, strong, light weight, and wide band" for excellent absorbing performance. In this work, a lighter Ti2CTx material was selected as the matrix, and MoS2 was in-situ grown on Ti2CTx matrix by traditional hydrothermal method and microwave solvothermal method. The fabricated composite exhibited synergic effect of two-dimensional heterostructural interface and double dielectric elements, where a small amount of TiO2 and a certain proportion of MoS2 jointly improve the impedance matching of the composite material. In here, the extreme reflection loss (RLmin) can reach - 54.70 dB (with a frequency of 7.59 GHz, 3.39 mm thickness), and the maximum effective absorption bandwidth (EAB(max)) can reach 4 GHz. Polyethylene glycol 200 was used as the solvent instead of water to make Ti2CTx less oxidized during the composite process, where the microwave heating would attain fast speed, short time, high efficiency, and uniform product. Since, the MoS2/Ti2CTx composite without oxidizing possessed a wider effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) at a thinner thickness, thus resulting in the excellent microwave absorption performance and confirming the validity and rationality of new microwave absorption materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
23.20 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Unraveling the Mo/HZSM-5 reduction pre-treatment effect on methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Caballero, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 312 (2022) 121382
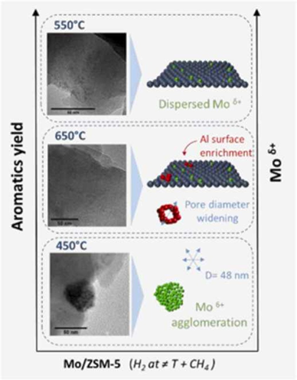
Reduction pre-treatment at different temperatures were performed over Mo/HZSM-5 system before methane dehydroaromatiztion reaction. We have shown the crucial effect of reduction temperature on the final catalytic performance. Outstanding improvement in the aromatics conversion has been attained. Thus, H-2 formation form methane cracking reaction seems to be hindered for pre-treated catalysts. As a consequence, the deposition of coke in these samples appeared also notably suppressed. The optimum performance has been achieved for reduction pre-treatment at 550 degrees C. For this temperature, we have observed that the fraction of reduced Mo species is higher.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
22.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Characterization of Re-Mo/ZSM-5 catalysts: How Re improves the performance of Mo in the methane dehydroaromatization reaction
Lopez-Martin, A; Sini, MF; Cutrufello, MG; Caballero, A; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 304 (2022) 120960
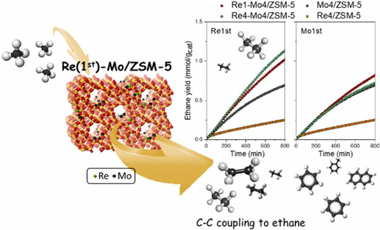
In this study, the promoting effect of rhenium addition as a co-dopant on Mo/ZSM-5 catalysts system has been analysed. Hence, bimetallic (Re-Mo/ZSM-5) catalysts have been synthesized using a sequential impregnation methodology. The catalytic performance for direct aromatization of methane reaction has been determined and correlated with their physical and chemical state combining multiple characterization techniques. An important synergy between Mo and Re, affected by the sequential impregnation, has been observed. Thus, Re1-Mo4/ZSM-5 in which Re has been incorporated first shows notably higher aromatic yields and stability against deactivation. Characterization results suggest that catalytic enhancement is due to the important effect of Re presence in close interaction with Mo. Improved evolution of ethane through C-C coupling would be correlated to this catalytic performance. As we discuss, Mo nature and location in the bimetallic systems are strongly conditioned by Re and the impregnation sequence and favours such intermediate step.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
22.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Evidence of new Ni-O-K catalytic sites with superior stability for methane dry reforming
Azancot, L; Blay, V; Blay-Roger, R; Bobadilla, LF; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 307 (2022) 121148
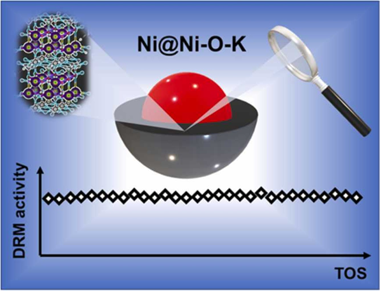
Liquid fuels produced via Fischer-Tropsch synthesis from biomass-derived syngas constitute an attractive and sustainable energy vector for the transportation sector. This study focuses on the role of potassium as a promoter in Ni-based catalysts for reducing coke deposition during catalytic dry reforming. The study provides a new structural link between catalytic performance and physicochemical properties. We identify new Ni-O-K chemical states associated with high stability in the reforming process, evidenced by different characterization techniques. The nickel particles form a core surrounded by a Ni-O-K phase layer (Ni@Ni-O-K) during the reduction of the catalyst. This phase likely presents an alkali-nickelate-type structure, in which nickel is stabilized in oxidation state + 3. The Ni-O-K formation induces essential changes in the electronic, physical, structural, and morphological properties of the catalysts, notably enhancing their long-term stability in dry reforming. This work thus provides new directions for designing more efficient catalysts for sustainable gas-to-liquids processes.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
22.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Dye sensitized solar cells as optically random photovoltaic media
Galvez, FE; Barnes, PRF; Halme, J; Miguez, HEnergy & Environmental Science, 6 (2014) 1260-1266
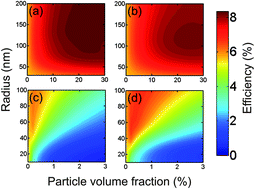
In order to enhance optical absorption, light trapping by multiple scattering is commonly achieved in dye sensitized solar cells by adding particles of a different sort. Herein we propose a theoretical method to find the structural parameters (particle number density and size) that optimize the conversion efficiency of electrodes of different thicknesses containing spherical inclusions of diverse composition. Our work provides a theoretical framework in which the response of solar cells containing diffuse scattering particles can be rationalized. Optical simulations are performed by combining a Monte Carlo approach with Mie theory, in which the angular distribution of scattered light is accounted for. Several types of scattering centers, such as anatase, gold and silver particles, as well as cavities, are considered and their effect compared. Estimates of photovoltaic performance, insight into the physical mechanisms responsible for the observed enhancements, and guidelines to improve the cell design are provided. We discuss the results in terms of light transport in weakly disordered optical media and find that the observed variations between the optimum scattering configurations attained for different electrode thicknesses can be understood as the result of the randomization of the light propagation direction at different depths within the active layer. A primary conclusion of our study is that photovoltaic performance is optimised when the scattering properties of the film are adjusted so that the distance over which incident photons are randomized is comparable to the thickness of the film. This simple relationship could also be used as a design rule to attain the optimum optical design in other photovoltaic materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
20.52 |
DOI | Año
2014 |
Alkane metathesis over immobilized pincer-ligated iridium complexes: Effect of support nature
Megías-Sayago, C; Centeno-Vega, I; Bobadilla, LF; Ivanova, S; Rendon, N; Suarez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 338 (2023) 123002
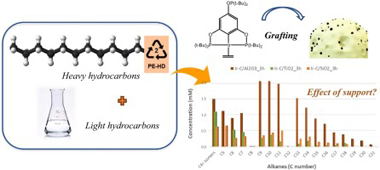
In this work, catalytic alkane metathesis has been evaluated as a suitable approach to upcycle hydrocarbons (polyolefins) at moderate temperatures. To this end, a pincer-ligated iridium complex (dehydrogenation catalyst) has been combined with a rhenium-based (metathesis) catalyst, being the effect of immobilizing the Ir complex over different supports deeply investigated. FTIR spectroscopy has been used to confirm the complex grafting and to elucidate the anchoring site to the support. Additionally, the supports have been dehydroxylated at different conditions to evaluate its possible impact in both the complex grafting and the catalytic activity. The influence of the support nature and its participation in the catalytic reaction have been clearly evidenced.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
20.20 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Unbroken Perovskite: Interplay of Morphology, Electro-optical Properties, and Ionic Movement
Correa-Baena, JP; Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Tress, W; Domanski, K; Saliba, M; Matsui, T; Jacobsson, TJ; Calvo, ME; Abate, A; Gratzel, M; Miguez, H; Hagfeldt, AAdvanced Materials, 28 (2016) 5031-5037
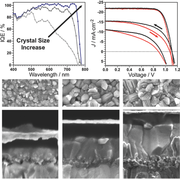
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite materials have risen up as leading components for light-harvesting applications. However, to date many questions are still open concerning the operation of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). A systematic analysis of the interplay among structural features, optoelectronic performance, and ionic movement behavior for FA(0.83)MA(0.17)Pb(I0.83Br0.17)(3) PSCs is presented, which yield high power conversion efficiencies up to 20.8%.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.79 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Metal catalysts supported on biochars: Part I synthesis and characterization
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Monzon, A; Murzin, DY; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118423
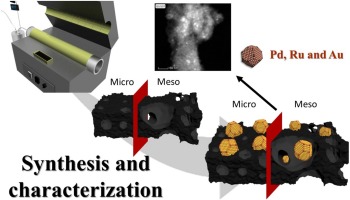
In the current study, synthesis and detailed characterization of cellulose biochars as a waste biomass model component and vine shoot biochars as a real waste biomass catalyst was performed. Although initially biochars exhibit poor textural properties, a simple activation process can make them much more suitable as a catalyst supports. A combination of physical (CO2) and chemical activation (ZnCl2) was evaluated. The characterization results indicated that the surface area and pore volume of the biochars have increased significantly by chemical activation treatment with ZnCl2. A series of metal catalysts (Pd, Au and Ru) supported on biochars was prepared and characterized. The prepared materials represent a set of noble metal catalysts supported on biochars with different textural and surface properties, which can be used to evaluate the catalytic role of the active phase and carbon support nature in catalytic reactions of interest, such as hydrodeoxygenation, described in the part II.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.50 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Hydrodeoxygenation of vanillin over noble metal catalyst supported on biochars: Part II: Catalytic behaviour
Santos, JL; Maki-Arvela, P; Warna, J; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Murzin, DYApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 268 (2020) 118425
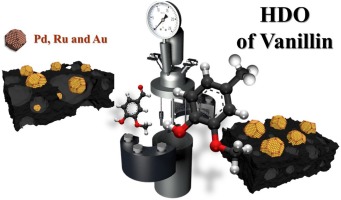
Vanillin hydrodeoxygenation was investigated using noble metal (Pd, Au, Ru) supported on active carbon prepared from waste derived biochars, which were produced via pyrolysis in CO2 atmosphere. Chemical activation with ZnCl2 and HNO3 was also used in the preparation of active carbon to enhance the specific surface area and demineralize material, respectively. Both fresh and spent catalysts were characterized with X-ray diffraction, DRIFTS, zeta potential measurement and HR-TEM. The highest selectivity to p-creosol, 92 % selectivity at complete vanillin conversion after 3 h was obtained in vanillin hydrodeoxygenation at 100 degrees C under 30 bar in hydrogen in water with Pd/C catalyst prepared via pyrolysis under CO2 from wine waste and using ZnCl2 as a chemical activation agent. Hydrodeoxygenation activity increased with increasing metal dispersion. A kinetic model including adsorption of vanillin described well the experimental data.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.50 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Experimental evidence of HCO species as intermediate in the fischer tropsch reaction using operando techniques
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 272 (2020) 119032
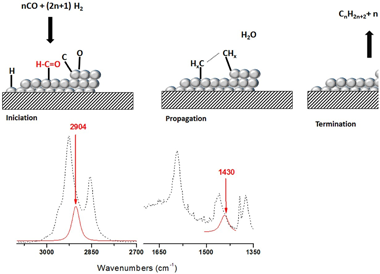
Fischer Tropsch's reaction, known from 1925, receives special attention nowadays due to its key role in the CO2 or biomass valorization to liquid fuels and chemicals. Several aspects on the exact mechanism or the role of water in this reaction are not yet completely clear. Formyl species, HCO, have been proposed as the most probable reaction intermediate, but they have never been observed under operation conditions closed to the real ones. In this work, using DRIFTS-MS operando techniques, HCO intermediates are detected under a H2/CO flow and 200 °C. IR bands at 2900 cm−1 and 1440 cm−1 attributed to ν(C–H) and δ(HCO) vibrations modes characterize these species. Evolution of these bands with the reaction time evidences its high reactivity with OH groups, which explains the positive effect of water on the CO conversion previously observed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.50 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
(NH4)4[NiMo6O24H6].5H2O / g-C3N4 materials for selective photo-oxidation of Csingle bondO and Cdouble bondC bonds
Caudillo-Flores, U; Ansari, F; Bachiller-Baeza, B; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Kubacka, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 278 (2020) 119299
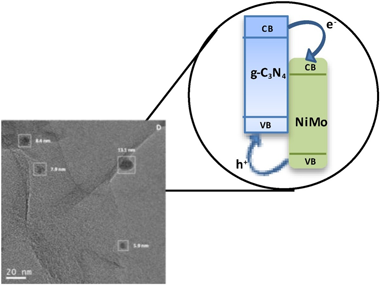
Novel composite photo-catalysts having (NH4)(4)[NiMo6O24H6]center dot 5H(2)O Polyoxometalate (POM) species deposited over g-C3N4 are synthesized. Materials were characterized through a multitechnique approach showing the stability of the carbon nitride component both through the synthesis process and under reaction. Contrarily, the POM component evolves under reaction conditions to maximize the interaction with the support. Such a behavior renders, as measured by the quantum efficiency, highly active photo-catalysts in the photo-oxidation of 2-propanol and styrene both under UV and sunlight illumination, setting up the basis for a green catalytic process. The material having a 4 wt. % POM showed improved activity with respect to both parent constituents but also higher selectivity to the partial oxidation of the alcohol and the aromatic hydrocarbon to generate added value chemical compounds. A multitechnique approach investigating charge carrier fate demonstrates the key role played by the interaction between components to promote activity and selectivity in selective oxidation reactions.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.50 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Tuning Dichroic Plasmon Resonance Modes of Gold Nanoparticles in Optical Thin Films
Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Ferrer, J; Garcia-Gutierrez, MC; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 1655-1663
A simple method is presented to tune the gold surface plasmon resonance (SPR) modes by growing anisotropic nanoparticles into transparent SiO2 thin films prepared by glancing angle deposition. In this type of composite film, the anisotropy of the gold nanoparticles, proved by gracing incidence small angle X-ray scattering, is determined by the tilted nanocolumnar structure of the SiO2 host and yields a strong film dichroism evidenced by a change from an intense colored to a nearly transparent aspect depending on light polarization and/or sample orientation. The formation in these films of lithographic non-dichroic SPR patterns by nanosecond laser writing demonstrates the potentialities of this procedure to develop novel optical encryption or anti-counterfeiting structures either at micrometer- or macroscales.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
19.44 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Highly Nonstoichiometric YAG Ceramics with Modified Luminescence Properties
Cao, WW; Becerro, AI; Castaing, V; Fang, X; Florian, P; Fayon, F; Zanghi, D; Veron, E; Zandona, A; Genevois, C; Pitcher, MJ; Allix, MAdvanced Functional Materials
Y3Al5O12 (YAG) is a widely used phosphor host. Its optical properties are controlled by chemical substitution at its YO8 or AlO6/AlO4 sublattices, with emission wavelengths defined by rare-earth and transition-metal dopants that have been explored extensively. Nonstoichiometric compositions Y3+xAl5-xO12 (x not equal 0) may offer a route to new emission wavelengths by distributing dopants over two or more sublattices simultaneously, producing new local coordination environments for the activator ions. However, YAG typically behaves as a line phase, and such compositions are therefore challenging to synthesize. Here, a series of highly nonstoichiometric Y3+xAl5-xO12 with 0 <= x <= 0.40 is reported, corresponding to <= 20% of the AlO6 sublattice substituted by Y3+, synthesized by advanced melt-quenching techniques. This impacts the up-conversion luminescence of Yb3+/Er3+-doped systems, whose yellow-green emission differs from the red-orange emission of their stoichiometric counterparts. In contrast, the YAG:Ce3+ system has a different structural response to nonstoichiometry and its down-conversion emission is only weakly affected. Analogous highly nonstoichiometric systems should be obtainable for a range of garnet materials, demonstrated here by the synthesis of Gd3.2Al4.8O12 and Gd3.2Ga4.8O12. This opens pathways to property tuning by control of host stoichiometry, and the prospect of improved performance or new applications for garnet-type materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
18.50 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
A Holistic Solution to Icing by Acoustic Waves: De-Icing, Active Anti-Icing, Sensing with Piezoelectric Crystals, and Synergy with Thin Film Passive Anti-Icing Solutions
Del Moral, J; Montes, L; Rico-Gavira, VJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Jacob, S; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Fakhfouri, A; Pandey, S; Del Val, MG; Mora, J; García-Gallego, P; Ibanez-Ibanez, PF; Rodríguez Valverde, MA; Winkler, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Functional Materials, 33 (2023) 2209421
Icing has become a hot topic both in academia and in the industry given its implications in transport, wind turbines, photovoltaics, and telecommunications. Recently proposed de-icing solutions involving the propagation of acoustic waves (AWs) at suitable substrates may open the path for a sustainable alternative to standard de-icing or anti-icing procedures. Herein, the fundamental interactions are unraveled that contribute to the de-icing and/or hinder the icing on AW-activated substrates. The response toward icing of a reliable model system consisting of a piezoelectric plate activated by extended electrodes is characterized at a laboratory scale and in an icing wind tunnel under realistic conditions. Experiments show that surface modification with anti-icing functionalities provides a synergistic response when activated with AWs. A thoughtful analysis of the resonance frequency dependence on experimental variables such as temperature, ice formation, or wind velocity demonstrates the application of AW devices for real-time monitoring of icing processes.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
18.50 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Inkjet-Printed and Nanopatterned Photonic Phosphor Motifs with Strongly Polarized and Directional Light-Emission
Cabello-Olmo, E; Romero, M; Kainz, M; Bernroitner, A; Kopp, S; Muhlberger, M; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Functional Materials, (2023) 2305907
Herein a versatile and scalable method to prepare periodically corrugated nanophosphor surface patterns displaying strongly polarized and directional visible light emission is demonstrated. A combination of inkjet printing and soft lithography techniques is employed to obtain arbitrarily shaped light emitting motifs. Such predesigned luminescent drawings, in which the polarization and angular properties of the emitted light are determined and finely tuned through the surface relief, can be used as anti-counterfeiting labels, as these two specific optical features provide additional means to identify any unauthorized or forged copy of the protected item. The potential of this approach is exemplified by processing a self-standing photoluminescent quick response code whose emission is both polarized and directionally beamed. Physical insight of the mechanism behind the directional out-coupled photoluminescence observed is provided by finite-difference time-domain calculations.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
18.50 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Plasma engineering of microstructured piezo-Triboelectric hybrid nanogenerators for wide bandwidth vibration energy harvesting
Garcia-Casas, X; Ghaffarinehad, A; Aparicio, FJ; Castillo-Seoane, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, ANano Energy, 91 (2022) 106673
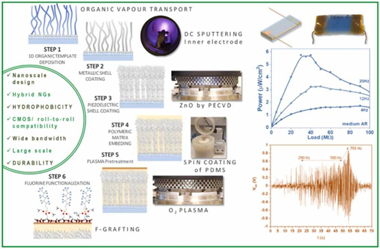
We introduce herein the advanced application of low-pressure plasma procedures for the development of piezo and triboelectric mode I hybrid nanogenerators. Thus, plasma assisted deposition and functionalization methods are presented as key enabling technologies for the nanoscale design of ZnO polycrystalline shells, the formation of conducting metallic cores in core@shell nanowires, and for the solventless surface modification of polymeric coatings and matrixes. We show how the perfluorinated chains grafting of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) provides a reliable approach to increase the hydrophobicity and surface charges at the same time that keeping the PDMS mechanical properties. In this way, we produce efficient Ag/ZnO convoluted piezoelectric nanogenerators supported on flexible substrates and embedded in PDMS compatible with a contact-separation triboelectric architecture. Factors like crystalline texture, ZnO thickness, nanowires aspect ratio, and surface chemical modification of the PDMS are explored to optimize the power output of the nanogenerators aimed for harvesting from low-frequency vibrations. Just by manual triggering, the hybrid device can charge a capacitor to switch on an array of color LEDs. Outstandingly, this simple three-layer architecture allows for harvesting vibration energy in a wide bandwidth, thus, we show the performance characteristics for frequencies between 1 Hz and 50 Hz and demonstrate the successful activation of the system up to ca. 800 Hz.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
17.60 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Non-sticky interactions
Esteso, VNature Physics, 19 (2023) 161-162
Quantum mechanical fluctuations of the electromagnetic field in a vacuum between two close together objects result in an attractive force. Now, it has been experimentally shown that by exploiting a similar repulsive interaction, attraction between objects can be modulated simply by tuning temperature.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
17.60 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Effect of Connectivity on the Carrier Transport and Recombination Dynamics of Perovskite Quantum-Dot Networks
Tiede, DO; Romeo-Pérez, C; Koch, KA; Ucer, KB; Calvo, ME; Kandada, ARS; Galisteo-López, JF; Míguez, HACS Nano, 18(6) (2024) 2325-2334
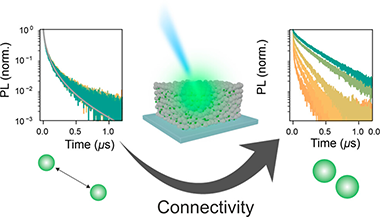
Quantum-dot (QD) solids are being widely exploited as a solution-processable technology to develop photovoltaic, light-emission, and photodetection devices. Charge transport in these materials is the result of a compromise between confinement at the individual QD level and electronic coupling among the different nanocrystals in the ensemble. While this is commonly achieved by ligand engineering in colloidal-based systems, ligand-free QD assemblies have recently emerged as an exciting alternative where nanostructures can be directly grown into porous matrices with optical quality as well as control over their connectivity and, hence, charge transport properties. In this context, we present a complete photophysical study comprising fluence- and temperature-dependent time-resolved spectroscopy to study carrier dynamics in ligand-free QD networks with gradually varying degrees of interconnectivity, which we achieve by changing the average distance between the QDs. Analysis of the photoluminescence and absorption properties of the QD assemblies, involving both static and time-resolved measurements, allows us to identify the weight of the different recombination mechanisms, both radiative and nonradiative, as a function of QD connectivity. We propose a picture where carrier diffusion, which is needed for any optoelectronic application and implies interparticle transport, gives rise to the exposure of carriers to a larger defect landscape than in the case of isolated QDs. The use of a broad range of fluences permits extracting valuable information for applications demanding either low- or high-carrier-injection levels and highlighting the relevance of a judicious design to balance recombination and diffusion.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
17.10 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Paper-based ZnO self-powered sensors and nanogenerators by plasma technology
Garcia-Casas, X; Aparicio, FJ; Budagosky, J; Ghaffarinejad, A; Orozco-Corrales, N; Ostrikov, K; Sánchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Borras, ANano Energy, 114 (2023) 108686
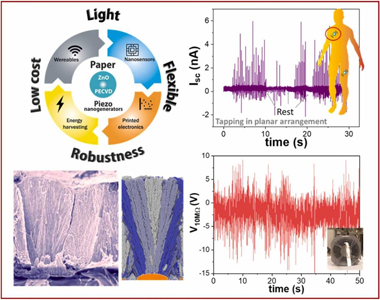
Nanogenerators and self-powered nanosensors have shown the potential to power low-consumption electronics and human-machine interfaces, but their practical implementation requires reliable, environmentally friendly and scalable processes for manufacturing and processing. Furthermore, the emerging flexible and wearable electronics technology demands direct fabrication onto innovative substrates such as paper and plastics typically incompatible with high process temperatures. This article presents a plasma synthesis approach for the fabri-cation of piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) and self-powered sensors on paper substrates. Polycrystalline ZnO nanocolumnar thin films are deposited by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition on common paper supports using a microwave electron cyclotron resonance reactor working at room temperature yielding high growth rates and low structural and interfacial stresses. Applying Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation, we elucidate the basic shadowing mechanism behind the characteristic microstructure and porosity of the ZnO thin films, relating them to an enhanced piezoelectric response to periodic and random inputs. The piezoelectric devices are assembled by embedding the ZnO films in polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and using Au thin layers as elec-trodes in two different configurations, namely laterally and vertically contacted devices. We present the response of the laterally connected devices as a force sensor for low-frequency events with different answers to the applied force depending on the impedance circuit, i.e. load values range, a behaviour that is theoretically analyzed. The characterization of the vertical devices in cantilever-like mode reaches instantaneous power densities of 80 nW/ cm2 with a mean power output of 20 nW/cm2. Besides, we analyze their actual-scenario performance by acti-vation with a fan and handwriting. Overall, this work demonstrates the advantages of implementing plasma deposition for piezoelectric films to develop robust, flexible, stretchable, and enhanced-performance nano-generators and self-powered piezoelectric sensors compatible with inexpensive and recyclable supports.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.80 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Structure-sensitivity of formic acid dehydrogenation reaction over additive-free Pd NPs supported on activated carbon
Santos, J.L.; Megías-Sayago, C.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A.Chemical Engineering Journal, 420 (2021) 127641
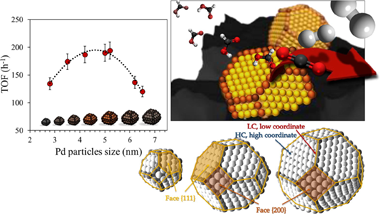
In this study the size-activity dependence of palladium based catalysts in formic acid dehydrogenation reaction was investigated and evaluated. A wide range of particle sizes was considered and the catalyst series were prepared upon variation of some synthetic parameters, precursor and solvent nature in particular. Synthesis method variations affect significantly Pd particle size and results in diverse activity toward hydrogen production. An optimal size was observed and explained by the diverse proportion of low and high coordinated Pd states available for different samples within the series. The evaluation of particles much bigger than 6 nm changes importantly the fraction of high and low coordination atoms and allows the clear confirmation of the importance of the presence of low coordination atoms on the surface of catalyst.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.74 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Kinetics and cyclability of limestone (CaCO3) in presence of steam during calcination in the CaL scheme for thermochemical energy storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Moreno, V; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 417 (2021) 129194
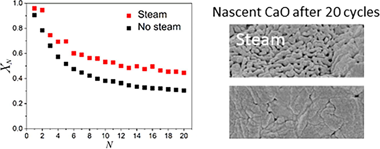
In the present work, we explore the use of steam in the CaCO3 calcination step of the Calcium Looping process devised for thermochemical energy storage (CaL-TCES). Steam produces a double benefit: firstly, it fastens calcination, allowing a reduction of the temperature needed to attain full calcination in short residence times, as those required in practice, resulting in energy savings. This behaviour is justified on the basis of a kinetics study results obtained from a non-parametric kinetic analysis, which demonstrate that the presence of steam during calcination can reduce the apparent activation energy from 175 kJ/mol to 142 kJ/mol with a steam's partial pressure of 29%. In addition, the results obtained for multicycle CaL-TCES tests show that steam alleviates the deactivation of the sorbent, which is one of the main limiting factors of this technology. This behaviour is explained in terms of the effect of steam on the microstructure of the regenerated CaO. Importantly, the values of residual conversion attained by calcining in steam are higher than those without steam.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.74 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Calcination under low CO2 pressure enhances the calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Sarrion, B; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Amghar, N; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 417 (2021) 127922
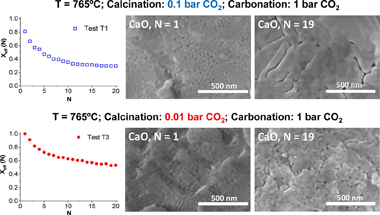
The Calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage has been investigated under novel favorable conditions, which involve calcination at moderate temperatures under CO2 at low pressure (0.01 and 0.1 bar) and carbonation at high temperature under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. Calcining at low CO2 pressures allows to substantially reduce the temperature to achieve full calcination in short residence times. Moreover, it notably enhances CaO multicycle conversion. The highest values of conversion are obtained for limestone samples calcined under 0.01 bar CO2 at 765 degrees C. Under these conditions, the residual conversion is increased by a factor of 10 as compared to conditions involving calcination under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. The enhancement of CaO conversion is correlated to the microstructure of the CaO samples obtained after calcination. As seen from SEM, BET surface and XRD analysis, calcination under low CO2 pressure leads to a remarkable decrease of pore volume and CaO crystallite size. Consequently, CaO surface area available for carbonation in the fast reaction-controlled regime and therefore reactivity in short residence times is promoted.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.74 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Phosphate-type supports for the design of WGS catalysts
Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 244 (2019) 853-862
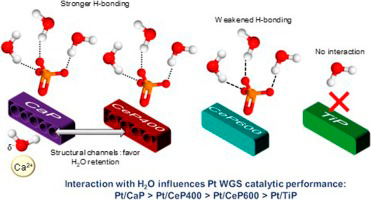
The importance of water availability during the WGS reaction has been extensively reported. Thus, the search of new supports able to interact with the water molecule is of great importance. In this work, a series of phosphate type supports containing Ce, Ca and Ti have been studied, demonstrating that water interaction with the support is closely related to the textural properties, surface composition and crystal structure of the solids. Additionally, DRIFTS results showed that different interaction mechanisms with the water molecule occur depending on the support. The system containing Ca dissociates the water molecule and interacts with it via the phosphate and Ca2+ ions. However, the Ce systems retain water in its molecular form, which interacts with the solids via hydrogen bonding with the phosphate groups. On the other hand, the Ti system experiences a loss of phosphorous, presenting a low degree of interaction with the water molecule. Additionally, the behavior of the supports with water has been successfully related to the WGS catalytic activity of the corresponding phosphate supported Pt catalysts.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.68 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Effect of support oxygen storage capacity on the catalytic performance of Rh nanoparticles for CO2 reforming of methane
Yentekakis, IV; Goula, G; Hatzisymeon, M; Betsi-Argyropoulou, I; Botzolaki, G; Kousi, K; Kondarides, DI; Taylor, MJ; Parlett, CMA; Osatiashtiani, A; Kyriakou, G; Holgado, JP; Lambert, RMApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 243 (2019) 490-501
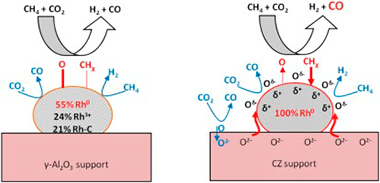
The effects of the metal oxide support on the activity, selectivity, resistance to carbon deposition and high temperature oxidative aging on the Rh-catalyzed dry reforming of methane (DRM) were investigated. Three Rh catalysts supported on oxides characterized by very different oxygen storage capacities and labilities (gamma-Al2O3, alumina-ceria-zirconia (ACZ) and ceria-zirconia (CZ)) were studied in the temperature interval 400-750 degrees C under both integral and differential reaction conditions. ACZ and CZ promoted CO2 conversion, yielding CO enriched synthesis gas. Detailed characterization of these materials, including state of the art XPS measurements obtained via sample transfer between reaction cell and spectrometer chamber, provided clear insight into the factors that determine catalytic performance. The principal Rh species detected by post reaction XPS was Rh, its relative content decreasing in the order Rh/CZ(100%) > Rh/ACZ(72%) > Fth/gamma Al2O3(55%). The catalytic activity followed the same order, demonstrating unambiguously that Rh is indeed the key active site. Moreover, the presence of CZ in the support served to maintain Rh in the metallic state and minimize carbon deposition under reaction conditions. Carbon deposition, low in all cases, increased in the order Rh/CZ < Rh/ACZ < Rh/gamma-Al2O3 consistent with a bi-functional reaction mechanism whereby backspillover of labile lattice O2- contributes to carbon oxidation, stabilization of Rh and modification of its surface chemistry; the resulting O vacancies in the support providing centers for dissociative adsorption of CO2. The lower apparent activation energy observed with CZ-containing samples suggests that CZ is a promising support component for use in low temperature DRM.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.68 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
3D core-multishell piezoelectric nanogenerators
A. Nicolas Filippin; Juan R.Sanchez-Valencia; Xabier Garcia-Casas; Victor Lopez-Flores; Manuel Macias-Montero; Fabian Frutos; Angel Barranco; Ana BorrasNano Energy, 58 (2019) 476-483
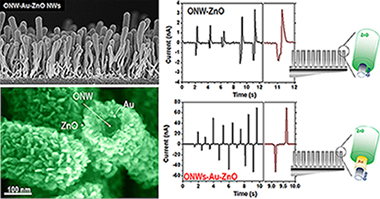
The thin film configuration presents obvious practical advantages over the 1D implementation in energy harvesting systems such as easily manufacturing and processing, and long-lasting and stable devices. However, ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators (PENGs) generally rely on the exploitation of single-crystalline nanowires because of their self-orientation in the c-axis direction and ability to accommodate long deformations resulting in high piezoelectric performance. Herein, we show an innovative approach to produce PENGs by combining polycrystalline ZnO layers fabricated at room temperature by plasma-assisted deposition with supported small-molecule organic nanowires (ONWs) acting as 1D scaffolds. Such hybrid nanostructures present convoluted core-shell morphology, formed by a single-crystalline organic nanowire conformally surrounded by a poly-crystalline ZnO shell and combine the organic core mechanical properties with the ZnO layer piezoelectric response. In a step forward towards the integration of multiple functions within a single wire, we have also developed ONW-Au-ZnO nanoarchitectures including a gold shell acting as inner electrode achieving output piezo-voltages up to 170 mV. The synergistic combination of functionalities in the ONW-Au-ZnO devices promotes an enhanced performance generating piezo-currents one order of magnitude larger than the ONW-ZnO nanowires and superior to the thin film nanogenerators for equivalent and higher thicknesses.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.60 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Negative emissions power plant based on flexible calcium-looping process integrated with renewables and methane production
Ortiz, C; García-Luna, S; Carro, A; Chacartegui, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LRenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 185 (2023) 113614
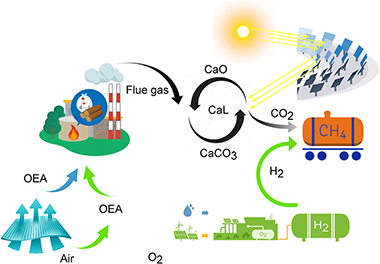
This paper provides a review of negative carbon capture technologies. Based on these technologies, here it is proposed an innovative negative emissions power plant combining the generation and storage of energy from biomass, photovoltaic, and concentrated solar power, capturing and recovering CO2 by producing H2 or CH4 as green energy carriers. The main features of the system are i) large-scale energy production system with negative CO2 emissions; ii) 100% renewable system based on biomass and solar energy with the possibility of integrating other renewables; iii) synergistic integration of processes and systems; iv) recovery of O2 generated by photovoltaic-driven electrolysis within the process of partial biomass oxycombustion and v) solar-driven limestone calcination. A detailed model of the entire plant is developed to evaluate the integration of the process. The model performance is assessed on an hourly basis throughout the whole year. The base case results show an energy consumption from 1 to 2.1 MJ/kg CO2 to capture 60–77% of CO2 emitted from the biomass plant and green methane production of more than 7500 tons/year. The negative emissions associated with the process are -612 kg CO2/MWh. It justifies the interest in the proposed negative emissions power plant.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Natural hydrogen in the energy transition: Fundamentals, promise, and enigmas
Blay-Roger, R; Bach, W; Bobadilla, LF; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JA; Amils, R; Blay, VRenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 189 (2024) 113888
Beyond its role as an energy vector, a growing number of natural hydrogen sources and reservoirs are being discovered all over the globe, which could represent a clean energy source. Although the hydrogen amounts in reservoirs are uncertain, they could be vast, and they could help decarbonize energy-intensive economic sectors and facilitate the energy transition. Natural hydrogen is mainly produced through a geochemical process known as serpentinization, which involves the reaction of water with low-silica, ferrous minerals. In favorable locations, the hydrogen produced can become trapped by impermeable rocks on its way to the atmosphere, forming a reservoir. The safe exploitation of numerous natural hydrogen reservoirs seems feasible with current technology, and several demonstration plants are being commissioned. Natural hydrogen may show variable composition and require custom separation, purification, storage, and distribution facilities, depending on the location and intended use. By investing in research, in the mid-term, more hydrogen sources could become exploitable and geochemical processes could be artificially stimulated in new locations. In the long term, it may be possible to leverage or engineer the interplay between microorganisms and geological substrates to obtain hydrogen and other chemicals in a sustainable manner.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.30 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Process design and utilisation strategy for CO2 capture in flue gases. Technical assessment and preliminary economic approach for steel mills
Navarro, JC; Baena-Moreno, FM; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Almagro, JF; Odriozola, JARenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 184 (2023) 113537
The steel industry is the most relevant sector in emerging economies due to its application in numerous fields. However, steel manufacturing involves large energy investment and produces significant greenhouse gas emissions. The current world economic and environmental scenario therefore necessitates that improvements in the footprint of the steel industry be made without affecting its viability. Considering the present challenge, we report two possible processes for Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). The first process is the competitive capture of CO2-SO2, followed by CO2 valorisation to methane. However, the CO2 capture capacity and lifetime for the adsorbent after multiple cycles could be improved through preliminary desulphurization of the gas current. The improved system demonstrates net profitability in a typical stainless steel plant. Therefore, it can be implemented in an industrial setting without profitability loss to steelmaking operations, fulfilling bot the goal of reducing CO2 emissions while protecting the mainstay of the plant.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Boosting Low-Temperature CO2 Hydrogenation over Ni-based Catalysts by Tuning Strong Metal-Support Interactions
Ye, RP; Ma, LX; Hong, XL; Reina, TR; Luo, WH; Kang, LQ; Feng, G; Zhang, RB; Fan, MH, Zhang, RGAngewandte Chemie-International Edition, 63 (2024) e202317669
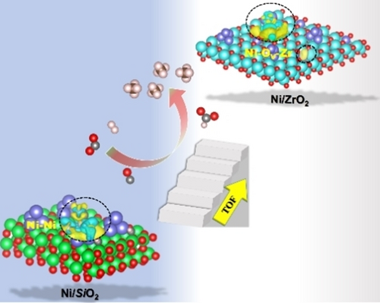
Rational design of low-cost and efficient transition-metal catalysts for low-temperature CO2 activation is significant and poses great challenges. Herein, a strategy via regulating the local electron density of active sites is developed to boost CO2 methanation that normally requires >350 °C for commercial Ni catalysts. An optimal Ni/ZrO2 catalyst affords an excellent low-temperature performance hitherto, with a CO2 conversion of 84.0 %, CH4 selectivity of 98.6 % even at 230 °C and GHSV of 12,000 mL g−1 h−1 for 106 h, reflecting one of the best CO2 methanation performance to date on Ni-based catalysts. Combined a series of in situ spectroscopic characterization studies reveal that re-constructing monoclinic-ZrO2 supported Ni species with abundant oxygen vacancies can facilitate CO2 activation, owing to the enhanced local electron density of Ni induced by the strong metal-support interactions. These findings might be of great aid for construction of robust catalysts with an enhanced performance for CO2 emission abatement and beyond.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
16.10 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Electrocatalytic CO2 conversion to C-2 products: Catalysts design, market perspectives and techno-economic aspects
Ruiz-López, E; Gandara-Loe, J; Baena-Moreno, F; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JARenewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 161 (2022) 112329
The energy crisis caused by the incessant growth in global energy demand joint to its associated greenhouse emissions motivates the urgent need to control and mitigate atmospheric CO2 levels. Leveraging CO2 as carbon pool to produce value-added products represents a cornerstone of the circular economy. Among the CO2 utilization strategies, electrochemical reduction of CO2 conversion to produce fuels and chemicals is booming due to its versatility and end-product flexibility. Herein most of the studies focused on C-1 products although C-2 and C2+ compounds are chemically and economically more appealing targets requiring advanced catalytic materials. Still, despite the complex pathways for C2+ products formation, their multiple and assorted applications have motivated the search of suitable electrocatalysts. In this review, we gather and analyse in a comprehensive manner the progress made regarding C2+ products considering not only the catalyst design and the electrochemistry features but also techno-economic aspects in order to envisage the most profitable scenarios. This state-of-the-art analysis showcases that electrochemical reduction of CO2 to C-2 products will play a key role in the decarbonisation of the chemical industry paving the way towards a low-carbon future.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.90 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Strong Light-Matter Coupling in Lead Halide Perovskite Quantum Dot Solids
Bujalance, C; Caliò, Dirin, DN; Tiede, DO; Gaisteo-López, JF; Feist, J; García-Vidal, FJ; Kovalenko, MV; Míguez, HACS Nano, 18(6) (2024) 4922-4931
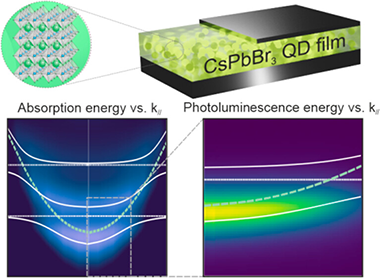
Strong coupling between lead halide perovskite materials and optical resonators enables both polaritonic control of the photophysical properties of these emerging semiconductors and the observation of fundamental physical phenomena. However, the difficulty in achieving optical-quality perovskite quantum dot (PQD) films showing well-defined excitonic transitions has prevented the study of strong light-matter coupling in these materials, central to the field of optoelectronics. Herein we demonstrate the formation at room temperature of multiple cavity exciton-polaritons in metallic resonators embedding highly transparent Cesium Lead Bromide quantum dot (CsPbBr3-QD) solids, revealed by a significant reconfiguration of the absorption and emission properties of the system. Our results indicate that the effects of biexciton interaction or large polaron formation, frequently invoked to explain the properties of PQDs, are seemingly absent or compensated by other more conspicuous effects in the CsPbBr3-QD optical cavity. We observe that strong coupling enables a significant reduction of the photoemission line width, as well as the ultrafast modulation of the optical absorption, controllable by means of the excitation fluence. We find that the interplay of the polariton states with the large dark state reservoir plays a decisive role in determining the dynamics of the emission and transient absorption properties of the hybridized light-quantum dot solid system. Our results should serve as the basis for future investigations of PQD solids as polaritonic materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.80 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Multifold Enhanced Photon Upconversion in a Composite Annihilator System Sensitized by Perovskite Nanocrystals
Chua, XW; Dai, LJ; Anaya, M; Salway, H; Ruggeri, E; Bi, PQ; Yang, ZH; Stranks, SD; Yang, LACS Nano, 18 (2024) 15229-15238
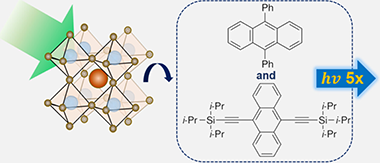
Photon upconversion via triplet-triplet annihilation (TTA-UC) provides a pathway to overcoming the thermodynamic efficiency limits in single-junction solar cells by allowing the harvesting of sub-bandgap photons. Here, we use mixed halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3, X = Br/I) as triplet sensitizers, with excitation transfer to 9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA) and/or 9,10-bis[(triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl]anthracene (TIPS-An) which act as the triplet annihilators. We observe that the upconversion efficiency is five times higher with the combination of both annihilators in a composite system compared to the sum of the individual single-acceptor systems. Our work illustrates the importance of using a composite system of annihilators to enhance TTA upconversion, demonstrated in a perovskite-sensitized system, with promise for a range of potential applications in light-harvesting, biomedical imaging, biosensing, therapeutics, and photocatalysis.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.80 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Patterning and control of the nanostructure in plasma thin films with acoustic waves: mechanical vs. electrical polarization effects
García-Valenzuela, A.; Fakhouri, A.; Oliva-Ramírez, M.; Rico-Gavira, V.; Rojas, T.C.; Alvarez, R.; Menzel, S.B.; Palmero, A.; Winkler, A.; González-Elipe, A.R.Materials Horizons, 8 (2021) 515-524
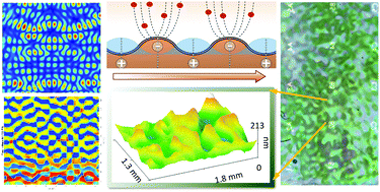
Nanostructuration and 2D patterning of thin films are common strategies to fabricate biomimetic surfaces and components for microfluidic, microelectronic or photonic applications. This work presents the fundamentals of a surface nanotechnology procedure for laterally tailoring the nanostructure and crystalline structure of thin films that are plasma deposited onto acoustically excited piezoelectric substrates. Using magnetron sputtering as plasma technique and TiO2 as case example, it is demonstrated that the deposited films depict a sub-millimetre 2D pattern that, characterized by large lateral differences in nanostructure, density (up to 50%), thickness, and physical properties between porous and dense zones, reproduces the wave features distribution of the generated acoustic waves (AW). Simulation modelling of the AW propagation and deposition experiments carried out without plasma and under alternative experimental conditions reveal that patterning is not driven by the collision of ad-species with mechanically excited lattice atoms of the substrate, but emerges from their interaction with plasma sheath ions locally accelerated by the AW-induced electrical polarization field developed at the substrate surface and growing film. The possibilities of the AW activation as a general approach for the tailored control of nanostructure, pattern size, and properties of thin films are demonstrated through the systematic variation of deposition conditions and the adjustment of AW operating parameters.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.72 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Plasma Enabled Conformal and Damage Free Encapsulation of Fragile Molecular Matter: from Surface-Supported to On-Device Nanostructures
Alcaire, M; Aparicio, FJ; Obrero, J; Lopez-Santos, C; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Frutos, F; Ostrikov, K; Borras, A; Barranco, AAdvanced Functional Materials, (2019) art. 1903535
Damage-free encapsulation of molecular structures with functional nanolayers is crucial to protect nanodevices from environmental exposure. With nanoscale electronic, optoelectronic, photonic, sensing, and other nanodevices based on atomically thin and fragile organic matter shrinking in size, it becomes increasingly challenging to develop nanoencapsulation that is simultaneously conformal at atomic scale and does not damage fragile molecular networks, while delivering added device functionality. This work presents an effective, plasma-enabled, potentially universal approach to produce highly conformal multifunctional organic films to encapsulate atomically thin graphene layers and metalorganic nanowires, without affecting their molecular structure and atomic bonding. Deposition of adamantane precursor and gentle remote plasma chemical vapor deposition are synergized to assemble molecular fragments and cage-like building blocks and completely encapsulate not only the molecular structures, but also the growth substrates and device elements upon nanowire integration. The films are insulating, transparent, and conformal at sub-nanometer scale even on near-tip high-curvature areas of high-aspect-ratio nanowires. The encapsulated structures are multifunctional and provide effective electric isolation, chemical and environmental protection, and transparency in the near-UV-visible-near-infrared range. This single-step, solvent-free remote-plasma approach preserves and guides molecular building blocks thus opening new avenues for precise, atomically conformal nanofabrication of fragile nanoscale matter with multiple functionalities.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.62 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Angular response of photonic crystal based dye sensitized solar cells
López López, C.; Colodrero, S.; Calvo, M.E. and Míguez, H.Energy & Environmental Science, 6 (2013) 1260-1266
Herein we report an experimental analysis of the performance of photonic crystal based dye solar cells (PC-DSCs) as the incident light angle moves away from the normal with respect to the cell surface. Nanoparticle multilayers operating at different wavelength ranges were coupled to the working electrode of a dye solar cell for this study. The interplay between optical and photovoltaic properties with the incident light angle is discussed. We demonstrate that an efficiency enhancement is attained for PC-DSCs at all angles measured, and that rational design of the photonic crystal back mirror leads to a reduction of the photocurrent losses related to the tilt angle of the cell, usually labeled as cosine losses. Angular variations of the cell transparency are also reported and discussed. These angular properties are relevant to the application of these solar devices in building integrated photovoltaics as potential window modules.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.49 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Tuning of Cell–Biomaterial Anchorage for Tissue Regeneration
Leal-Egana, Aldo; Diaz-Cuenca, Aranzazu; Boccaccini, Aldo RAdvanced Materials, 25 (2013) 4049-4057
Which mechanisms mediate cell attachment to biomaterials? What role does the surface charge or wettability play on cell–material anchorage? What are the currently investigated strategies to modify cell–matrix adherence spatiotemporally? Considering the development of scaffolds made of biocompatible materials to temporarily replace the structure and/or function of the extracellular matrix, focus is given to the analysis of the specific (i.e., cell adhesive peptide sequences) and unspecific (i.e., surface charge, wettability) mechanisms mediating cell-matrix interactions. Furthermore, because natural tissue regeneration is characterized by the dynamic attachment/detachment of different cell populations, the design of advanced scaffolds for tissue engineering, based in the spatiotemporal tuning of cell–matrix anchorage is discussed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.41 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Plasma assisted CO2 dissociation in pure and gas mixture streams with a ferroelectric packed-bed reactor in ambient conditions
Navascues, P; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AChemical Engineering Journal, 430 (2022) 133066
Carbon dioxide decomposition is a challenging target to combat climate change. Nonthermal plasmas are advantageous for this purpose because they operate at ambient conditions and can be easily scaled-up. In this study, we attempt the CO2 splitting into CO and O-2 in a parallel plate packed-bed plasma reactor moderated with Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) as fermelectric component, achieving conversion rates and energy efficiencies higher than those obtained with BaTiO3 in our experimental device. The analysis of the reaction mechanisms with optical emission spectroscopy under various operating conditions has shown a direct correlation between energy efficiency and intensity of CO* emission bands. These results and those obtained with a LiNbO3 plate placed onto the active electrode suggest that high temperature electrons contribute to the splitting of CO2 through an enhancement in the formation of CO2+ intermediate species. Results obtained for CO2 + O-2 mixtures confirm this view and suggest that back recombination processes involving CO and O-2 may reduce the overall splitting efficiency. The study of mixtures of CO2 and dry air has proved the capacity of fermelectric packed-bed reactors to efficiently decompose CO2 with no formation of harmful NxOy subproducts in conditions close to those in real facilities. The found enhancement in energy efficiency with respect to that found for the pure gas decomposition supports that new reaction pathways involving nitrogen molecules are contributing to the dissociation reaction. We conclude that PZT moderated packed-bed plasma reactors is an optimum alternative for the decompositon of CO2 in real gas flows and ambient conditions.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Albero: An alternative natural material for solar energy storage by the calcium-looping process
Moreno, V; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, P; Perejon, A; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 440 (2022) 135707
Large-scale thermochemical energy storage (TCES) is gaining relevance as an alternative to current thermal energy storage systems in Concentrated Solar Power plants. Among the different systems, the reversible reaction between CaO and CO2 stands out due to the wide availability and low cost of the raw material: limestone. Direct solar absorption of the storage media would improve the efficiency of solar-to-thermal energy storage due to reduced thermal transfer barriers, but the solar optical absorption of CaCO3 is poor. In this work, we propose the use of a Ca-rich calcarenite sedimentary rock so-called albem as an alternative to limestone. We demonstrate that this reddish material exhibits an average solar absorptance that is approximately ten times larger than limestone. Moreover, the multicycle carbonation/calcination performance under different experimental conditions has been studied by thermogravimetry, and similar values to those exhibited for limestone have been obtained. Besides, the material is cheap (6 Elton), and simulations showed that the use of this material would significantly improve the overall CaL-CSP efficiency at the industrial level.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Ionomer-Free Nickel-Iron bimetallic electrodes for efficient anion exchange membrane water electrolysis
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gomez-Sacedon, C; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; De Lucas-Consuegra, AChemical Engineering Journal, 433 (2022) 133774
A bottleneck for the deployment of the Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (AEMWE) is the manufacturing of efficient and long lasting anodes and cathodes for the cells. Highly performant bimetallic Ni/Fe catalyst films with various atomic ratios have been prepared by magnetron sputtering in an oblique angle configuration (MS-OAD) and used as anodes for AEMWE. Electrocatalytic experiments in a small three-electrode cell and a thorough analysis of the electrode properties with various physico-chemical characterization tech-niques have been used to select the nanostructured anode catalyst which, depicting an optimized Ni/Fe ratio, presents the maximum activity for the oxygen evolution reaction. These anode layers are then scale-up for their integration in an AEMWE cell where the influence of assembly conditions and the effect of adding an ionomer to the anodes have been studied. The obtained results have demonstrated the outstanding properties of the fabri-cated bimetallic films in terms of activity, stability, and operation under ionomer-free conditions. Current density values around 400 and 600 mA cm(-2) at 40??& nbsp;and 60 C (2.0 V), respectively, much higher than those obtained with pure Ni, were obtained with an optimized membrane electrode assembly. The high yield obtained with these electrodes gains further relevance when considering that the current yield per unit mass of the anodic active phase catalyst (i.e., 1086 mA mg(-1) at 2.0 V and 40??) is the highest among equivalent values reported in literature. The possibilities and prospects of the use of bimetallic catalyst films prepared by MS-OAD for AEMWE are discussed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Shepherding reaction intermediates to optimize H-2 yield using composite-doped TiO2-based photocatalysts
Barba-Nieto, I.; Colon, G; Fernández-García, M; Kubacka, AChemical Engineering Journal, 442 (2022) 136333
Optimization of Pt-promoted TiO2-based is key to promote the photocatalytic production of hydrogen using sacrificial alcohol molecules. Combination of doping and surface decoration of the mentioned base photoactive material is here exploited to maximize hydrogen yield. Using the quantum efficiency parameter, it is shown that the resulting composite system can boost activity up to 7.3 times within the whole methanol:water mixture ratio, yielding quantum efficiencies in the ca. 13-16 % range. The key role of the different components in generating charge carrier species and their use to trigger the sacrificial molecule evolution and control reaction kinetics are examined through an in-situ spectroscopic study. The study unveils the complex reaction mechanism, with generation of C1 to C3 molecules from different carbon-containing radicals, and interprets the physical origin of the huge H2 production enhancement occurring in doped-composite titania-based catalysts.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Au and Pt Remain Unoxidized on a CeO2-Based Catalyst during the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Reina, TR; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Lopez-Flores, V; Martinez, LMT; Zitolo, A; Ivanova, S; Xu, WQ; Centeno, MA; Rodriguez, JA; Odriozola, JAJournal of the American Chemical Society, 144 (2022) 446-453
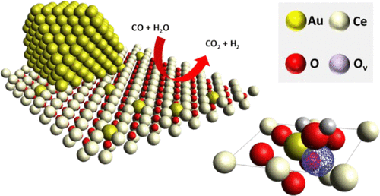
The active forms of Au and Pt in CeO2-based catalysts for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction are an issue that remains unclear, although it has been widely studied. On one hand, ionic species might be responsible for weakening the Ce-O bonds, thus increasing the oxygen mobility and WGS activity. On the other hand, the close contact of Au or Pt atoms with CeO2 oxygen vacancies at the metal-CeO2 interface might provide the active sites for an efficient reaction. In this work, using in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy, we demonstrate that both Au and Pt remain unoxidized during the reaction. Remarkable differences involving the dynamics established by both species under WGS atmospheres were recognized. For the prereduced Pt catalyst, the increase of the conversion coincided with a restructuration of the Pt atoms into cuboctahedrical metallic particles without significant variations on the overall particle size. Contrary to the relatively static behavior of Pt-0, Au-0 nanoparticles exhibited a sequence of particle splitting and agglomeration while maintaining a zero oxidation state despite not being located in a metallic environment during the process. High WGS activity was obtained when Au atoms were surrounded by oxygen. The fact that Au preserves its unoxidized state indicates that the chemical interaction between Au and oxygen must be necessarily electrostatic and that such an electrostatic interaction is fundamental for a top performance in the WGS process.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.00 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Hydrogen production by catalytic aqueous-phase reforming of waste biomass: a review
González-Arias, J; Zhang, Z; Reina, TR; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Chemistry Letters, 21 (2023) 3089-3104
The rising adverse effects of climate change call for a rapid shift to low-carbon energy and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. For that, biorefineries appear as promising alternatives to produce energy, chemicals, and fuels using biomass and waste as raw materials. Here, we review catalytic aqueous-phase reforming to convert biomass and organic waste carbohydrates into renewable hydrogen, with focus on reforming basics; catalyst design; reforming of model compounds, wastewater and biomass; economics and life cycle assessment. We found that platinum and palladium are technically highly effective, yet their high price may limit upscaling. Alternatively, addition of tin to nickel gives acceptable results and improves hydrogen selectivity from 35 to 90%. We observed that hydrogen production decreases from 14% for crude glycerol to 2% for pure glycerol, thus highlighting the need to do experiments with real wastewater. The rare experiments on real wastewater from brewery, juice, tuna, and cheese industries have given hydrogen production rates of up to 149.7 mg/L. Aqueous-phase reforming could be shortly competitive with prices around 3-6 USD per kg of hydrogen, which are nearing the current market prices of 2-3 USD per kg.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
15.00 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Strong angular and spectral narrowing ofelectroluminescence in an integrated Tamm-plasmon-driven halide perovskite LED
Ying, Z; Jiménez-Solano, A; Gatkowski, K; Sun, Y; Ferrer Orri, J; Frohna, K; Salway, H; Kahmann, S; Nie, S; Vega, G; Kar, S; Novak, MP; Máckowski, S; Nyga, P; Ducati, C; Greenham, NC; Lotsch, BV; Anaya, M; Stranks, SDNature Commications, 15 (2024) 5802
Next-generation light-emitting applications such as displays and opticalcommunications require judicious control over emitted light, includingintensity and angular dispersion. To date, this remains a challenge as con-ventional methods require cumbersome optics. Here, we report highly direc-tional and enhanced electroluminescence from a solution-processed quasi-2-dimensional halide perovskite light-emitting diode by building a devicearchitecture to exploit hybrid plasmonic-photonic Tamm plasmon modes. Byexploiting the processing and bandgap tunability of the halide perovskitedevice layers, we construct the device stack to optimise both optical andcharge-injection properties, leading to narrow forward electroluminescencewith an angular full-width half-maximum of 36.6° compared with the con-ventional isotropic control device of 143.9°, and narrow electroluminescencespectral full-width half-maximum of 12.1 nm. The device design is versatile andtunable to work with emission lines covering the visible spectrum with desireddirectionality, thus providing a promising route to modular, inexpensive, anddirectional operating light-emitting devices.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.70 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Photonic structuring improves the colour purity of rare-earth nanophosphors
Geng, DL; Cabello-Olmo, E; Lozano, G; Miguez, HMaterials Horizons, 5 (2018) 661-667
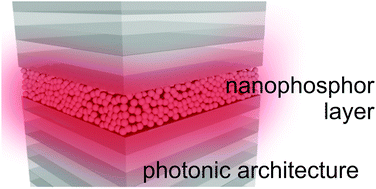
Nanophosphor integration in an optical cavity allows unprecedented control over both the chromaticity and the directionality of the emitted light, without modifying the chemical composition of the emitters or compromising their efficiency. Our approach opens a route towards the development of nanoscale photonics based solid state lighting.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.36 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Chemical CO2 recycling via dry and bi reforming of methane using Ni-Sn/Al2O3 and Ni-Sn/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts
Stroud, T; Smith, TJ; Le Sache, E; Santos, JL; Centeno, MA; Arellano-Garcia, H; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 224 (2018) 125-135
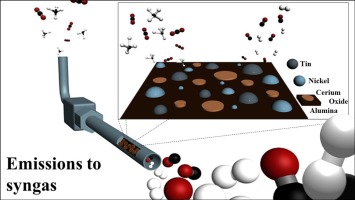
Carbon formation and sintering remain the main culprits regarding catalyst deactivation in the dry and bi-reforming of methane reactions (DRM and BRM, respectively). Nickel based catalysts (10 wt.%) supported on alumina (Al2O3) have shown no exception in this study, but can be improved by the addition of tin and ceria. The effect of two different Sn loadings on this base have been examined for the DRM reaction over 20 h, before selecting the most appropriate Sn/Ni ratio and promoting the alumina base with 20 wt.% of CeO2. This catalyst then underwent activity measurements over a range of temperatures and space velocities, before undergoing experimentation in BRM. It not only showed good levels of conversions for DRM, but exhibited stable conversions towards BRM, reaching an equilibrium H-2/CO product ratio in the process. In fact, this work reveals how multicomponent Ni catalysts can be effectively utilised to produce flexible syngas streams from CO2/CH4 mixtures as an efficient route for CO2 utilisation.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Solar pilot plant scale hydrogen generation by irradiation of Cu/TiO2 composites in presence of sacrificial electron donors
Maldonado, MI; Lopez-Martin, A; Colon, G; Peral, J; Martinez-Costa, JI; Malato, SApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 229 (2018) 15-23
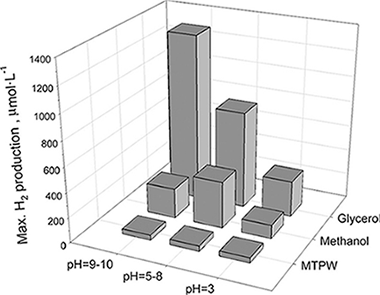
A Cu/TiO2 photocatalyst has been synthesised by reducing a Cu precursor with NaBH4 onto the surface of a sulphate pretreated TiO2 obtained by a sol-gel procedure. The catalyst, that shows a clearly defined anatase phase with high crystallinity and relatively high surface area, and contains Cu2O and CuO deposits on its surface, has been used to produce hydrogen in a solar driven pilot plant scale photocatalytic reactor. Different electron donor aqueous solutions (methanol, glycerol, and a real municipal wastewater treatment plant influent) have been tested showing similar or even higher energy efficiency than those obtained using more expensive noble metal based photocatalytic systems. The glycerol solutions have provided the best reactive environments for hydrogen generation.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
A direct in situ observation of water-enhanced proton conductivity of Eu-doped ZrO2: Effect on WGS reaction
Garcia-Moncada, N; Bobadilla, LF; Poyato, R; Lopez-Cartes, C; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 231 (2018) 343-356
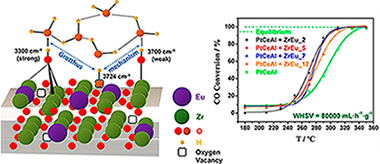
Eu-doped ZrO2 solid solutions have been synthesized in order to prepare proton conductors as water-enhancer additives for the WGS reaction. Elemental characterization has been carried out revealing homogeneous dopant distribution resulting in fluorite-type solid solutions for Eu2O3 contents up to similar to 9 mol.%. Representative samples of the Eu-doped ZrO2 series have been analysed by Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) in inert, oxygen and wet conditions. The solid solution with 5 mol.% of Eu2O3 has presented the highest conductivity values for all tested conditions indicating an optimal amount of dopant. Moreover, the presence of vapour pressure results in an increment of the conductivity at temperatures lower than 300 degrees C, meanwhile at higher temperatures the conductivity is the same than that in inert conditions. To elucidate these results, in situ DRIFTS studies were carried out. These experiments evidenced the existence of water dissociation at oxygen vacancies (band at 3724 cm(-1)) as well as the presence of physisorbed water at temperatures up to similar to 300 degrees C where the band at 5248 cm(-1) characteristic of these species disappeared. These results points to a layer model where the physisorbed water interacts with surface hydroxyls generated by dissociated water that improves the proton conductivity through Grotthuss' mechanism in the RT-300 degrees C temperature range. These samples were successfully tested in WGS reaction as additive to a typical Pt-based catalyst. The presence of the mixed oxide reveals an increase of the catalyst' activity assisted by the proton conductor, since improves the water activation step.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Selective CO methanation with structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts
Munoz-Murillo, A; Martinez, LM; Dominguez, MI; Odriozola, JA; Centeno, MAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 236 (2018) 420-427
Active and selective structured RuO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO methanation using a flow simulating CO2-rich reformate gases from WGS and PROX units (H-2 excess, CO2 presence and 300 ppm CO concentration) were prepared. Both, the RuO2/Al2O3 powder and the slurry prepared from it for its structuration by washcoating of the metallic micromonolithic structure, were also active and selective. Both the slurry (S-RuAl) and micro monoliths (M-RuAl) were able to completely and selectively methanate CO at much lower temperatures than the parent RuAI powder. The optimal working temperature in which the CO conversion is maximum and the CO2 conversion is minimized was determined to be from 149 degrees C to 239 degrees C for S-RuAl and from 165 degrees C to 232 degrees C for M-RuAl, whilst it was from 217 degrees C to 226 degrees C for RuAI powder. TPR, XRD and TEM measurements confirmed that the changes in the activity and selectivity for CO methanation among the considered catalysts can be related with modifications in the surface particle size of ruthenium and its reducibility. These were ascribed to the metallic substrate, the presence of PVA and colloidal alumina in the slurry preparation, the aqueous and acidic media and the thermal treatment used, resulting in a more active and selective catalysts than the parent powder.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
New concept for old reaction: Novel WGS catalyst design
Garcia-Moncada, N; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 238 (2018) 1-5
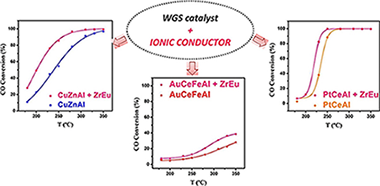
The viability of water gas shift catalytic system for mobile application passes through obligatory reactor volume reduction, achieved normally by using less charge of more efficient catalyst. Completely new concept for catalyst design is proposed: a catalytic system including classically reported WGS catalysts of different nature or active phase (Cu, Pt or Au) mechanically mixed with an ionic conductor. The influence of the later on catalyst activity is studied and discussed, more precisely its effect on the rate of the reaction-limiting step and catalysts' efficiency. It is demonstrated with this study, that the presence of an ionic conductor in contact with a WGS catalyst is essential for the water supply (dissociation and transport), thereby potentiating the water activation step, whatever the mechanism and catalyst overall performance.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
CO/H-2 adsorption on a Ru/Al2O3 model catalyst for Fischer Trospch: Effect of water concentration on the surface species
Jimenez-Barrera, E; Bazin, P; Lopez-Cartes, C; Romero-Sarria, F; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 237 (2018) 986-995
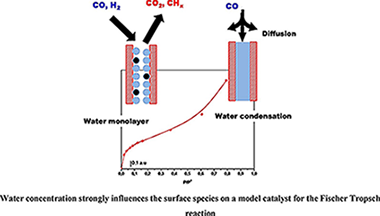
Water presence and concentration strongly influence CO conversion and CS+ selectivity in the Fischer Tropsch reaction. In this work, the influence of the water concentration was investigated using a model Ru/Al2O3 (5 wt. %) catalyst. The surface species formed after CO and H-2 adsorption in dry and wet (different water concentrations) conditions were analyzed by FTIR. Firstly, water adsorption was carried out up to complete filling of the pores and then CO was put in contact with the catalyst. The absence of adsorbed CO species in these conditions evidences that CO diffusion in water controls the access of the gas to the active sites and explains the negative effect of high water concentrations reported by some authors. Moreover, the adsorption of a mixture of CO + H-2 + H2O, being the water concentration close to that needed to have a monolayer, and a dry mixture of CO + H-2 were carried out and compared. Results evidence that water in this low concentration, is able to gasify the surface carbon species formed by CO dissociation on the metallic sites. This cleaning effect is related to the positive effect of water on CO conversion detected by some authors.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Nanoporous Pt-based catalysts prepared by chemical dealloying of magnetron-sputtered Pt-Cu thin films for the catalytic combustion of hydrogen
Giarratano, F; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Montes, O; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 235 (2018) 168-176
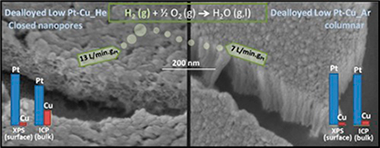
In this work, we prepared SiC-supported Pt-Cu thin films by magnetron sputtering for use as catalysts for the combustion of hydrogen under oxidizing conditions. We tested the catalysts as prepared and after chemical dealloying. A methodology is presented to fabricate catalytic thin films of a desired composition with tailored magnetron targets with lower Pt consumption. The deposition gas was changed to prepare columnar (Ar-deposited) and closed-porous (He-deposited) films to study the effect of the microstructure on the activity. The effect of composition was also studied for the columnar samples. The as-prepared Pt-Cu thin films showed significant activity only at temperatures higher than 100 °C. Dealloying permitted an increase in the activity to achieve near room-temperature activity. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was the most active, being able to convert as much as 13.15 LH2·min−1 gPt−1 at 70 °C (Ea = 1 kJ mol−1). This sample was preferentially dealloyed on the surface, yielding an almost pure Pt shell (96% at. Pt) and a Cu-depleted interior (71% at. Pt). This compositional inhomogeneity enabled the sample to achieve enhanced activity compared to the Ar-deposited columnar sample (with similar initial composition, but uniformly dealloyed), probably due to the compressive surface lattice strain. The dealloyed closed-porous He-deposited sample was shown to be durable over five cycles.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Tailoring structured WGS catalysts: Impact of multilayered concept on the water surface interactions
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Le Sache, E; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 222 (2018) 124-132
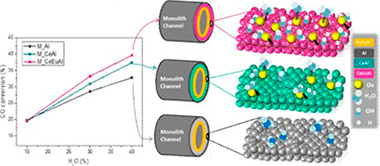
A novel multilayer approach for designing structured WGS catalyst is employed in this study as a response to the lack of new strategies in the literature. The approach proposes the use of two successive layers with different functionalities on metallic micromonolith substrate. The WGS catalyst behavior is modulated by the nature of the inner layer which determines the active species surface population by acting on the water activation step. The catalytic promotion attained by introducing inner ceria containing solids with increasing number of oxygen defects is intensely analyzed through FT-IR and H2O-TPD. Several evidences about the participation of the oxygen vacancies, as key sites, for water absorption processes are established. Besides, remarkable relationships between the water absorption strengths and the water splitting processes within their influence on the catalyst performance are also discussed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Enhanced photocatalytic removal of phenol from aqueous solutions using ZnO modified with Ag
Vaiano, V.; Matarangolo, M.; Murcia, J.J.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 225 (2018) 197-206
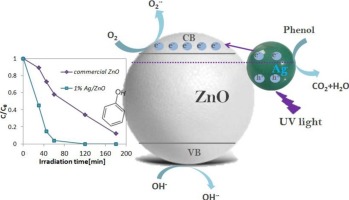
Different photocatalysts based on commercial ZnO modified by silver photodeposition were prepared in this work. The samples were characterized by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), specific surface area (SSA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and UV–vis diffuse reflectance (UV–vis DRS). XRD and XPS showed that Ag/ZnO samples are composed of metallic Ag (Ag0) and ZnO structure was identified. Furthermore, TEM analysis evidenced that the number of silver particles increased with the Ag content. At last, UV–vis DRS results revealed a reflectance band for Ag/ZnO samples, ascribed to the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption of metal silver particles. Commercial ZnO and Ag/ZnO samples were evaluated in the phenol removal under UV light irradiation. It was observed an enhancement of photocatalytic phenol removal from aqueous solutions by silver addition in comparison to commercial ZnO. In particular, the phenol removal increased with the silver content from 0.14 to 0.88 wt%, after this content (i.e 1.28 wt%) the phenol degradation significantly decreased indicating that the optimal Ag content was equal to 0.88 wt%. The influence of the best photocatalyst dosage and the change of the initial phenol concentration in solution were also investigated in this work and the best photocatalytic performance was obtained by using 50 mg L−1 of phenol initial concentration and 0.15 g L−1 of photocatalyst dosage. Finally, the optimized Ag/ZnO photocatalyst was employed for the treatment of a real drinking wastewater containing phenol in which the almost total phenol removal was achieved after 180 min of UV irradiation time.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.23 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Metallic nanostructures for efficient LED lighting
Lozano, G; Rodriguez, SRK; Verschuuren, MA; Rivas, JGLight: Science and Applications, 5 (2016) e16080
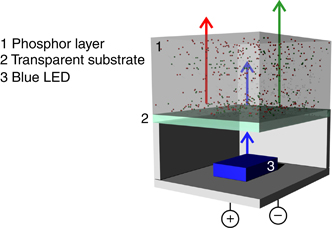
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are driving a shift toward energy-efficient illumination. Nonetheless, modifying the emission intensities, colors and directionalities of LEDs in specific ways remains a challenge often tackled by incorporating secondary optical components. Metallic nanostructures supporting plasmonic resonances are an interesting alternative to this approach due to their strong light-matter interaction, which facilitates control over light emission without requiring external secondary optical components. This review discusses new methods that enhance the efficiencies of LEDs using nanostructured metals. This is an emerging field that incorporates physics, materials science, device technology and industry. First, we provide a general overview of state-of-the-art LED lighting, discussing the main characteristics required of both quantum wells and color converters to efficiently generate white light. Then, we discuss the main challenges in this field as well as the potential of metallic nanostructures to circumvent them. We review several of the most relevant demonstrations of LEDs in combination with metallic nanostructures, which have resulted in light-emitting devices with improved performance. We also highlight a few recent studies in applied plasmonics that, although exploratory and eminently fundamental, may lead to new solutions in illumination.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
14.10 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Optofluidic Modulation of Self-Associated Nanostructural Units Forming Planar Bragg Microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Barranco, A; Loffler, M; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Nano, 10 (2016) 1256-1264
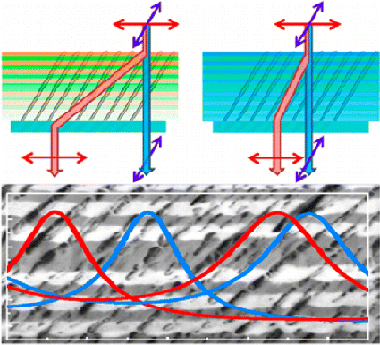
Bragg microcavities (BMs) formed by the successive stacking of nanocolumnar porous SiO2 and TiO2 layers with slanted, zigzag, chiral, and vertical configurations are prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles while azimuthally varying the substrate orientation during the multilayer growth. The slanted and zigzag BMs act as wavelength-selective optical retarders when they are illuminated with linearly polarized light, while no polarization dependence is observed for the chiral and vertical cavities. This distinct optical behavior is attributed to a self-nanostructuration mechanism involving a fence-bundling association of nanocolumns as observed by focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy in the slanted and zigzag microcavities. The outstanding retarder response of the optically active BMs can be effectively modulated by dynamic infiltration of nano- and mesopores with liquids of different refraction indices acting as a switch of the polarization behavior. The unprecedented polarization and tunable optofluidic properties of these nanostructured photonic systems have been successfully simulated with a simple model that assumes a certain birefringence for the individual stacked layers and accounts for the light interference phenomena developed in the BMs. The possibilities of this type of self-arranged nanostructured and optically active BMs for liquid sensing and monitoring applications are discussed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.94 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Interplay of Resonant Cavity Modes with Localized Surface Plasmons: Optical Absorption Properties of Bragg Stacks Integrating Gold Nanoparticles
Olalla Sánchez-Sobrado, Gabriel Lozano, Mauricio E. Calvo, Ana Sánchez-Iglesias, Luis M. Liz-Marzán, Hernán MíguezAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 2108-2112
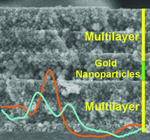
A procedure to prepare porous photonic crystal resonators containing gold nanoparticles is reported. The optical absorption of the ensemble, resulting from the excitation of the localized surface plasmon of the metallic beads, is finely tuned by a gradual shift of the cavity mode. This is achieved by infiltration of the void network with different guest compounds.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.88 |
DOI | Año
2011 |
Selective Dichroic Patterning by Nanosecond Laser Treatment of Ag Nanostripes
Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Toudert, J; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Lahoz, R; de la Fuente, GF; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 848-853
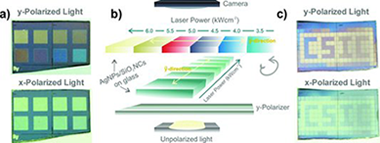
A simple route for the fabrication of dichroic optical structures based on Ag nanoparticles deposited onto SiO2 nanocolumns is presented. The strict control of the optical response is achieved after infrared laser treatment of the supported nanoparticles with a commercial nanosecond pulsed laser. Preliminary examples of the utilization of the laser-treated AgNPs/SiO2 nanocolumn system for optical recoding and encryption are shown.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.88 |
DOI | Año
2011 |
Transparent Nanometric Organic Luminescent Films as UV-Active Components in Photonic Structures
Aparicio, FJ; Holgado, M; Borras, A; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Griol, A; Barrios, CA; Casquel, R; Sanza, FJ; Sohlstrom, H; Antelius, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, AAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 761-765
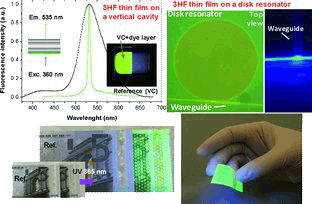
A new kind of visible-blind organic thin-film material, consisting of a polymeric matrix with a high concentration of embedded 3-hydroxyflavone (3HF) dye molecules, that absorbs UV light and emits green light is presented. The thin films can be grown on sensitive substrates, including flexible polymers and paper. Their suitability as photonic active components photonic devices is demonstrated.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.88 |
DOI | Año
2011 |
Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells with Tunable Structural Color
W. Zhang, M. Anaya, G. Lozano, M.E. Calvo, M.B. Johnston, H. Míguez, H.J. SnaithNano Letters, 15 (2015) 1698-1702
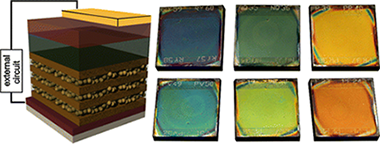
The performance of perovskite solar cells has been progressing over the past few years and efficiency is likely to continue to increase. However, a negative aspect for the integration of perovskite solar cells in the built environment is that the color gamut available in these materials is very limited and does not cover the green-to-blue region of the visible spectrum, which has been a big selling point for organic photovoltaics. Here, we integrate a porous photonic crystal (PC) scaffold within the photoactive layer of an opaque perovskite solar cell following a bottom-up approach employing inexpensive and scalable liquid processing techniques. The photovoltaic devices presented herein show high efficiency with tunable color across the visible spectrum. This now imbues the perovskite solar cells with highly desirable properties for cladding in the built environment and encourages design of sustainable colorful buildings and iridescent electric vehicles as future power generation sources.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.78 |
DOI | Año
2015 |
Diverse Applications of Nanomedicine
Pelaz, Beatriz; Alexiou, Christoph; Alvarez -Puebla, Ramon A.; Alves, Frauke; Andrews, Anne M.; Ashraf, Sumaira; Balogh, Lajos P.; Ballerini, Laura; Bestetti, Alessandra; Brendel, Cornelia; Bosi, Susanna; Carril, Monica; Chan, Warren C. W.; Chen, ChunyingACS Nano, 11 (2017) 2312-2381
The design and use of materials in the nanoscale size range for addressing medical and health-related issues continues to receive increasing interest. Research in nanomedicine spans a multitude of areas, including drug delivery, vaccine development, antibacterial, diagnosis and imaging tools, wearable devices, implants, high-throughput screening platforms, etc. using biological, nonbiological, biomimetic, or hybrid materials. Many of these developments are starting to be translated into viable clinical products. Here, we provide an overview of recent developments in nanomedicine and highlight the current challenges and upcoming opportunities for the field and translation to the clinic.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.71 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Lead-Free Polycrystalline Ferroelectric Nanowires with Enhanced Curie Temperature
Datta, Anuja; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Al Orabi, Rabih Al Rahal; Calahorra, Yonatan; Ou, Canlin; Sahonta, Suman-Lata; Fornari, Marco; Kar-Narayan, SohiniAdvanced Functional Materials, 27 (2017) 1701169
Ferroelectrics are important technological materials with wide-ranging applications in electronics, communication, health, and energy. While lead-based ferroelectrics have remained the predominant mainstay of industry for decades, environmentally friendly lead-free alternatives are limited due to relatively low Curie temperatures (T-C) and/or high cost in many cases. Efforts have been made to enhance T-C through strain engineering, often involving energy-intensive and expensive fabrication of thin epitaxial films on lattice-mismatched substrates. Here, a relatively simple and scalable sol-gel synthesis route to fabricate polycrystalline (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O-3 nanowires within porous templates is presented, with an observed enhancement of T-C up to similar to 300 degrees C as compared to similar to 90 degrees C in the bulk. By combining experiments and theoretical calculations, this effect is attributed to the volume reduction in the template-grown nanowires that modifies the balance between different structural instabilities. The results offer a cost-effective solution-based approach for strain-tuning in a promising lead-free ferroelectric system, thus widening their current applicability.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.33 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Low CO2 hydrogen streams production from formic acid through control of the reaction pH
Santos, JL; Lopez, ER; Ivanova, S; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 455 (2023) 140645
There are multiple factors that influence the catalyst performance in the reaction of formic acid dehydrogena-tion: the nature of catalyst and/or support, the used solvent and reaction variables such as temperature, time, formic acid concentration, presence/absence of formates and pH of the solution. This work evaluates a series of important parameters like the influence of the pH by itself, the influence of the nature of used alkali agents and the effect of direct formate addition as reactive on hydrogen production via formic acid dehydrogenation over a commercially available catalyst. The catalytic performance appears to depend on the ionic radius of the cations of the used base which reflects consequently on the hydrogen selectivity. The best base to be used must have lower hydrated cationic radii and a starting pH around 4 to achieve important hydrogen selectivity for medium term formic acid conversion.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Catalytic conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons via simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 over the regulated acidity of SAPO-34
Meng, FH; Wang, LA; Nawaz, MA; Wang, Q; Gong, ZY; Li, ZChemical Engineering Journal,

Direct conversion of syngas to light hydrocarbons has been intensively studied in recent years; however, the high selectivity of light hydrocarbons is still a challenging task to achieve a high CO conversion. Here, a bifunctional catalyst consisting of a methanol synthesis catalyst (CZA) and a methanol to dimethyl ether (DME) catalyst (Al2O3) was employed with a hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst (SAPO-34), for syngas conversion to light hydrocarbons in a dual fixed-bed reactor. The conversion of simulated intermediates CO/CO2/DME/N2/H2 with a molar ratio of 9/6/4/5/76, obtained from syngas conversion to DME over CZA and Al2O3, was studied over SAPO-34 zeolites. It was found that SP34-0.1 with Si/Al ratio of 0.1, exhibited low amount of strong acid (0.60 mmol/g) and high selectivity to light olefins (74.1%), while SP34-0.4 with Si/Al ratio of 0.4 exhibited high amount of strong acid (1.00 mmol/g) leading to high selectivity of light paraffins (88.4%). The in-situ DRIFTS analysis illustrated that DME can be rapidly adsorbed on the hydroxyl site of SAPO-34 and decomposed into the surface methyl species, where SP34-0.4 could produce more dimethylcyclopentenyl cationic species than SP340.1. It was suggested that the overall reaction route led to a high selectivity to light olefins (84.2%) with a CO conversion of 61.2% on (CZA + Al2O3) catalyst combined with SP34-0.1, while a high selectivity to light paraffins (76.3%) could be achieved by combining with SP34-0.4 at 70.3% CO conversion. Since, the current study interprets that the selectivity of hydrocarbons can be adjusted by regulating the acidity of SAPO-34 to achieve a high CO conversion in the dual fixed-bed reactor scheme.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Fabrication of ordered crystalline zirconium nanoporous membranes by an one-step procedure
Marquez, F; Morant, C; Pirota, KR; Borras, A; Sanz, JM; Elizalde, ENano Today, 4 (2009) 21-26
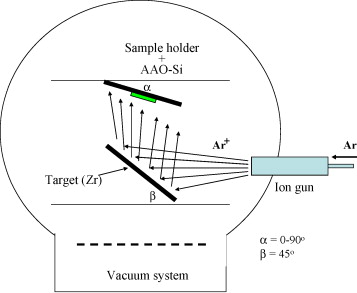
Crystalline porous zirconium membranes were obtained by physical vapor deposition on AAO templates at room temperature. These membranes were found to have similar hexagonal nanohole arrays as the template and high crystallinity. The pore size of the synthesized metallic membranes could be controlled during the synthesis through appropriate parameters in the experimental procedure.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.24 |
DOI | Año
2009 |
1-dimensional TiO2 nano-forests as photoanodes for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells fabrication
Salado, M; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Kazim, S; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SNano Energy, 35 (2017) 215-222
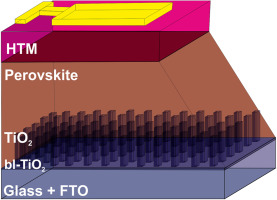
During the last years, perovskite solar cells have gained increasing interest among the photovoltaic community, in particularly after reaching performances at par with mature thin film based PV. This rapid evolution has been fostered by the compositional engineering of perovskite and new device architectures. In the present work, we report the fabrication of perovskite solar cells based on highly ordered 1-dimensional vertically oriented TiO2 nano-forests. These vertically oriented porous TiO2 photoanodes were deposited by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration, a method which is scalable to fabricate large area devices. Mixed (MA0.15FA0.85)Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3 or triple cation Cs0.05(MA0.15FA0.85)0.95Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3 based perovskites were then infiltrated into these 1-dimensional nanostructures and power conversion efficiencies of 16.8% along with improved stability was obtained. The devices fabricated using 1D-TiO2 were found to be more stable compare to the classical 3-dimensional TiO2 photoanodes prepared by wet chemistry. These 1-D photoanodes will be of interest for scaling up the technology and in other opto-electrical devices as they can be easily fabricated utilizing industrially adapted methodologies.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.12 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Chemistry and Electrocatalytic Activity of Nanostructured Nickel Electrodes for Water Electrolysis
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Consuegra, AD; Yubero, FACS Catalysis, 10 (2020) 6159-6170
Herein we have developed nanostructured nickel-based electrode films for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE). The electrodes were prepared by magnetron sputtering (MS) in an oblique angle configuration and under various conditions aimed at preparing metallic, oxide, or oxyhydroxide films. Their electrochemical analysis has been complemented with a thorough physicochemical characterization to determine the effect of microstructure, chemical state, bilayer structure, and film thickness on the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The maximum electrocatalytic activity was found for the metallic electrode, where analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) demonstrated that the active catalytic phase at the surface after its electrochemical conditioning is a kind of oxidized nickel oxide/hydroxide layer with the thickness of a few nanometers. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis of these steady-state working electrodes supports that the enhanced performance of the metallic nickel anode vs other chemical states resides in the easier electron transfer through the electrode films and the various interlayers built up during their fabrication and activation. The long-term steady-state operation of the anodes and their efficiency for water splitting was proved in a full-cell AEMWE setup incorporating magnetron-sputtered metallic nickel as the cathode. This work proves that MS is a suitable technique to prepare active, stable, and low-cost electrodes for AEMWE and the capacity of this technique to control the chemical state of the electrocatalytically active layers involved in the OER.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.08 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Sonogashira Cross-Coupling and Homocoupling on a Silver Surface: Chlorobenzene and Phenylacetylene on Ag(100)
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Orozco, N; Holgado, JP; Beaumont, SK; Kyriakou, G; Watson, DJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Feria, L; Sanz, JF; Lambert, RMJournal of the American Chemical Society, 137 (2015) 940-947
Scanning tunneling microscopy, temperature-programmed reaction, near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations were used to study the adsorption and reactions of phenylacetylene and chlorobenzene on Ag(100). In the absence of solvent molecules and additives, these molecules underwent homocoupling and Sonogashira cross-coupling in an unambiguously heterogeneous mode. Of particular interest is the use of silver, previously unexplored, and chlorobenzene—normally regarded as relatively inert in such reactions. Both molecules adopt an essentially flat-lying conformation for which the observed and calculated adsorption energies are in reasonable agreement. Their magnitudes indicate that in both cases adsorption is predominantly due to dispersion forces for which interaction nevertheless leads to chemical activation and reaction. Both adsorbates exhibited pronounced island formation, thought to limit chemical activity under the conditions used and posited to occur at island boundaries, as was indeed observed in the case of phenylacetylene. The implications of these findings for the development of practical catalytic systems are considered.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
13.04 |
DOI | Año
2015 |
Recent progress on the enhancement of photocatalytic properties of BiPO4 using π–conjugated materials
Naciri, Y., Hsini, A., Ajmal, Z., Navio, J.A., Bakiz, B., Albourine, A., Ezahri, M., Benlhachemi, A.Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 280 (2020) 102160
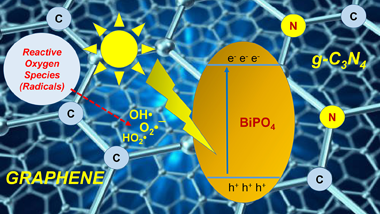
Semiconductor photocatalysis is regarded as most privileged solution for energy conversion and environmental application. Recently, photocatalysis methods using bismuth-based photocatalysts, such as BiPO4, have been extensively investigated owing to their superior efficacy regarding organic pollutant degradation and their further mineralization into CO2 and H2O. It is well known that BiPO4 monoclinic phase exhibited better photocatalytic performance compared to Degussa (Evonik) P25 TiO2 in term of ultraviolet light driven organic pollutants degradation. However, its wide band gap, poor adsorptive performance and large size make BiPO4 less active under visible light irradiation. However, extensive research works have been conducted in the past with the aim of improving visible light driven BiPO4 activity by constructing a series of heterostructures, mainly coupled with π-conjugated architecture (e.g., conductive polymer, dye sensitization and carbonaceous materials). However, a critical review of modified BiPO4 systems using π-conjugated materials has not been published to date. Therefore, this current review article was designed with the aim of presenting a brief current state-of-the-art towards synthesis methods of BiPO4 in the first section, with an especial focuses onto its crystal-microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties. Moreover, the most relevant strategies that have been employed to improve its photocatalytic activities are then addressed as the main part of this review. Finally, the last section presents ongoing challenges and perspectives for modified BiPO4 systems using π–conjugated materials
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.98 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
High-Throughput Fabrication of Resonant Metamaterials with Ultrasmall Coaxial Apertures via Atomic Layer Lithography
Yoo, D; Nguyen, NC; Martin-Moreno, L; Mohr, DA; Carretero-Palacios, S; Shaver, J; Peraire, J; Ebbesen, TW; Oh, SHNano Letters, 16 (2016) 2040-2046
We combine atomic layer lithography and glancing angle ion polishing to create wafer-scale metamaterials composed of dense arrays of ultrasmall coaxial nanocavities in gold films. This new fabrication scheme makes it possible to shrink the diameter and increase the packing density of 2 nm-gap coaxial resonators, an extreme subwavelength structure first manufactured via atomic layer lithography, both by a factor of 100 with respect to previous studies. We demonstrate that the nonpropagating zeroth-order Fabry-Perot mode, which possesses slow light-like properties at the cutoff resonance, traps infrared light inside 2 nm gaps (gap volume similar to lambda(3)/10(6)). Notably, the annular gaps cover only 3% or less of the metal surface, while open-area normalized transmission is as high as 1700% at the epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) condition. The resulting energy accumulation alongside extraordinary optical transmission can benefit applications in nonlinear optics, optical trapping, and surface-enhanced spectroscopies. Furthermore, because the resonance wavelength is independent of the cavity length and dramatically red shifts as the gap size is reduced, large-area arrays can be constructed with lambda(resonance) >> period, making this fabrication method ideal for manufacturing resonant metamaterials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.71 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Biomorphic ceramics from wood-derived precursors
Ramirez-Rico, J.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; Singh, M.International Materials Reviews, 62 (2017) Issue 8

Materials development is driven by microstructural complexity and, in many cases, inspired by biological systems such as bones, shells and wood. In one approach, one selects the main microstructural features responsible for improved properties and design processes to obtain materials with such microstructures (continuous-fibre-reinforced ceramics, porous ceramics, fibrous ceramic monoliths, etc.). In a different approach, it is possible to use natural materials directly as microstructural templates. Biomorphic ceramics are produced from natural and renewable resources (wood or wood-derived products). A wide variety of SiC-based ceramics can be fabricated by infiltration of silicon or silicon alloys into cellulose-derived carbonaceous templates, providing a low-cost route to advanced ceramic materials with near-net shape potential and amenable to rapid prototyping. These materials have tailorable microstructure and properties, and behave like ceramic materials manufactured by advanced ceramic processing approaches. This review aims to be a comprehensive description of the development of bioSiC ceramics: from wood templates and their microstructure to potential applications of bioSiC materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Photocatalytic oxidation of pollutants in gas-phase via Ag3PO4-based semiconductor photocatalysts: Recent progress, new trends, and future perspectives
Y. Naciri; A. Hsini; A. Bouziani; R. Djellabi; Z. Ajmal; M. Laabd; J.A. Navío; A. Mills; C.L. Bianchi; H.Li; B. Bakiz; A. AlbourineCritical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 52 (2022) 2339-2382
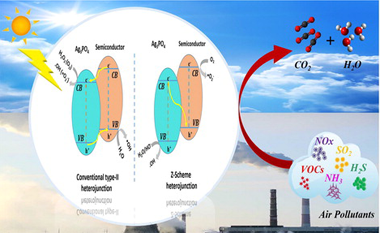
Air pollution has become a significant challenge for both developing and developed nations. due to its close association with numerous fatal diseases such as cancer, respiratory, heart attack, and brain stroke. Over recent years, heterogeneous semiconductor photocatalysis has emerged as an effective approach to air remediation due to the ease of scale-up, ready application in the field, use of solar light and ready availability of a number of different effective photocatalysts. To date, most work in this area has been conducted using UV-absorbing photocatalysts, such as TiO2 and ZnO; However, recent studies have revealed Ag3PO4 as an attractive, visible-light-absorbing alternative, with a bandgap of 2.43 eV. In particular, this material has been shown to be an excellent photocatalyst for the removal of many types of pollutants in the gas phase. However, the widespread application of Ag3PO4 is restricted due to its tendency to undergo photoanodic corrosion and the poor reducing power of its photogenerated conductance band electrons, which are unable to reduce O2 to superoxide •O2 −. These limitations are critically evaluated in this review. In addition, recent studies on the modification of Ag3PO4 via combination with the conventional heterojunctions or Z-scheme junctions, as well as the photocatalytic mechanistic pathways for enhanced gas-pollutants removal, are summarized and discussed. Finally, an overview is given on the future developments that are required in order to overcome these challenges and so stimulate further research into this promising field.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.60 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Comprehensive Experimental and Theoretical Study of the CO plus NO Reaction Catalyzed by Au/Ni Nanoparticles
Kyriakou, G; Marquez, AM; Holgado, JP; Taylor, MJ; Wheatley, AEH; Mehta, JP; Sanz, JF; Beaumont, SK; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 9 (2019) 4919-4929
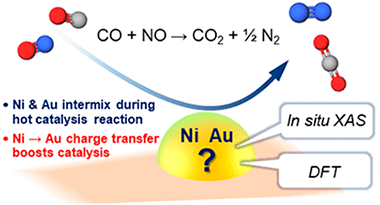
The catalytic and structural properties of five different nanoparticle catalysts with varying Au/Ni composition were studied by six different methods, including in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The as-prepared materials contained substantial amounts of residual capping agent arising from the commonly used synthetic procedure. Thorough removal of this material by oxidation was essential for the acquisition of valid catalytic data. All catalysts were highly selective toward N-2 formation, with 50-50 Au:Ni material being best of all. In situ X-ray absorption near edge structure spectroscopy showed that although Au acted to moderate the oxidation state of Ni, there was no clear correlation between catalytic activity and nickel oxidation state. However, in situ extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy showed a good correlation between Au Ni coordination number (highest for Ni50Au50) and catalytic activity. Importantly, these measurements also demonstrated substantial and reversible Au/Ni intermixing as a function of temperature between 550 degrees C (reaction temperature) and 150 degrees C, underlining the importance of in situ methods to the correct interpretation of reaction data. DFT calculations on smooth, stepped, monometallic and bimetallic surfaces showed that N + N recombination rather than NO dissociation was always rate-determining and that the activation barrier to recombination reaction decreased with increased Au content, thus accounting for the experimental observations. Across the entire composition range, the oxidation state of Ni did not correlate with activity, in disagreement with earlier work, and theory showed that NiO itself should be catalytically inert. Au-Ni interactions were of paramount importance in promoting N + N recombination, the rate-limiting step.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.35 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Graphene Formation Mechanism by the Electrochemical Promotion of a Ni Catalyst
Espinos, JP; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; de Lucas-Consuegra, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Catalysis, 9 (2019) 11447-11454
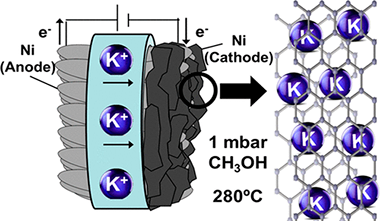
In this work, we show that multilayer graphene forms by methanol decomposition at 280 degrees C on an electrochemically promoted nickel catalyst film supported on a K-beta Al2O3 solid electrolyte. In operando near ambient pressure photoemission spectroscopy and electrochemical measurements have shown that polarizing negatively the Ni electrode induces the electrochemical reduction and migration of potassium to the nickel surface. This elemental potassium promotes the catalytic decomposition of methanol into graphene and also stabilizes the graphene formed via diffusion and direct K-C interaction. Experiments reveal that adsorbed methoxy radicals are intermediate species in this process and that, once formed, multilayer graphene remains stable after electrochemical oxidation and back migration of potassium to the solid electrolyte upon positive polarization. The reversible diffusion of ca. 100 equivalent monolayers of potassium through the carbon layers and the unprecedented low-temperature formation of graphene and other carbon forms are mechanistic pathways of high potential impact for applications where mild synthesis and operation conditions are required.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.35 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Phase-Contact Engineering in Mono- and Bimetallic Cu-Ni Co-catalysts for Hydrogen Photocatalytic Materials
Munoz-Batista, MJ; Meira, DM; Colon, G; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, MAngewandte Chemie-International Edition, 57 (2018) 1199-1203
Understanding how a photocatalyst modulates its oxidation state, size, and structure during a photocatalytic reaction under operando conditions is strongly limited by the mismatch between (catalyst) volume sampled by light and, to date, the physicochemical techniques and probes employed to study them. A synchrotron micro-beam X-ray absorption spectroscopy study together with the computational simulation and analysis (at the X-ray cell) of the light-matter interaction occurring in powdered TiO2-based monometallic Cu, Ni and bimetallic CuNi catalysts for hydrogen production from renewables was carried out. The combined information unveils an unexpected key catalytic role involving the phase contact between the reduced and oxidized non-noble metal phases in all catalysts and, additionally, reveals the source of the synergistic Cu-Ni interaction in the bimetallic material. The experimental method is applicable to operando studies of a wide variety of photocatalytic materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.26 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Unravelling the Role of Oxygen Vacancies in the Mechanism of the Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction by Operando DRIFTS and Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy
Bobadilla, LF; Santos, JL; Ivanova, S; Odriozola, JA; Urakawa, AACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 7455-7467
The reaction mechanism of the reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction was investigated using two commercial gold-based catalysts supported on Al2O3 and TiO2. The surface species formed during the reaction and reaction mechanisms were elucidated by transient and steady-state operando DRIFTS studies. It was revealed that RWGS reaction over Au/Al2O3 proceeds through the formation of formate intermediates that are reduced to CO. In the case of the Au/TiO2 catalyst, the reaction goes through a redox mechanism with the suggested formation of hydroxycarbonyl intermediates, which further decompose to CO and water. The Ti-3+ species, the surface hydroxyls, and oxygen vacancies jointly participate. The absence of carbonyl species adsorbed on gold particles during the reaction for both catalysts indicates that the reaction pathway involving dissociative adsorption of CO2 on Au particles can be discarded. To complete the study, operando ultraviolet visible spectroscopy was successfully applied to confirm the presence of Ti3+ and to understand the role of the oxygen vacancies of TiO2 support in activating CO2 and thus the subsequent RWGS reaction.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.22 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Understanding the Role of the Acid Sites in 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation to 2,5-Furandicarboxylic Acid Reaction over Gold Catalysts: Surface Investigation on CexZr1-xO2 Compounds
Megias-Sayago, C; Chakarova, K; Penkova, A; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis, 8 (2018) 11154-11164
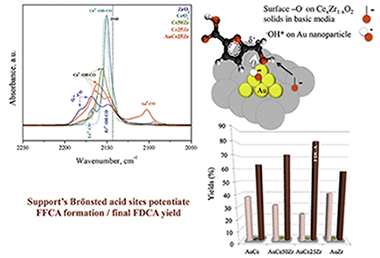
A series of CexZr1-xO2 supports with different Ce/Zr molar ratios were utilized for the preparation of gold catalyst used in the selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. The used method of gold deposition allows the preparation of gold particles with homogeneous size and shape distribution, a formulation very useful for studies dedicated to revealing the support participation in the reaction. The supports are characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy using CO as probe molecule, and the sample catalytic activity is thereafter correlated to the support acid site distribution. The possible participation of its Lewis/Bronsted acidity in the reaction mechanism is also proposed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.22 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Transparent porous films with real refractive index close to unity for photonic applications
Miranda-Muñoz, JM; Viaña, JM; Calvo, ME; Lozano, G; Míguez, HMaterials Horizons (2024).
Herein, we demonstrate mechanically stable large-area thin films with a purely real refractive index (n) close to 1 in the optical range. At specific wavelengths, it can reach values as small as n = 1.02, the lowest reported for thin solid slabs. These are made of a random network of interwoven spherical silica shells, created by chemical vapour deposition of a thin layer of silica on the surface of randomly packed monodisperse polymer nanoparticles that form a film. Thermal processing of the composites results in highly porous silica-based transparent thin films. We demonstrate the potential of this approach by making novel photonic materials such as strong optical diffusers, built by integrating scattering centers within the ultralow n transparent films, or highly efficient light-emitting slabs, in which losses by total internal reflection are practically absent as a result of the almost null optical impedance at the film-air interface.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.20 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
The Calcium-Looping (CaCO3/CaO) process for thermochemical energy storage in Concentrating Solar Power plants
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gimenez, PRenewable & Sustanaible Energy Reviews, 113 (2019) 109252
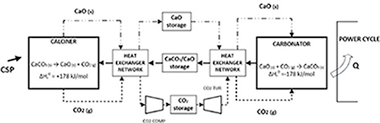
Energy storage based on thermochemical systems is gaining momentum as a potential alternative to molten salts in Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) plants. This work is a detailed review about the promising integration of a CaCO3/CaO based system, the so-called Calcium-Looping (CaL) process, in CSP plants with tower technology. The CaL process relies on low cost, widely available and non-toxic natural materials (such as limestone or dolomite), which are necessary conditions for the commercial expansion of any energy storage technology at large scale. A comprehensive analysis of the advantages and challenges to be faced for the process to reach a commercial scale is carried out. The review includes a deep overview of reaction mechanisms and process integration schemes proposed in the recent literature. Enhancing the multicycle CaO conversion is a major challenge of the CaL process. Many lab-scale analyses carried out show that residual effective CaO conversion is highly dependent on the process conditions and the CaO precursors used, reaching values in a wide range (0.07–0.82). The selection of the optimal operating conditions must be based on materials performance, process integration, technology and economics aspects. Global plant efficiencies over 45% (without considering solar-side losses) show the interest of the technology. Furthermore, the technological maturity and potential of the process is assessed. The direction towards which future works should be headed is discussed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
12.11 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Iron-catalyzed graphitization for the synthesis of nanostructured graphitic carbons
Hunter, RD; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schnepp, ZJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 10 (2022) 4489-4516
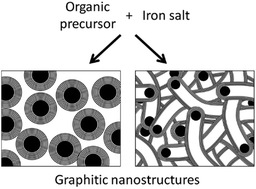
Carbons are versatile and diverse materials that have numerous applications across energy and environmental sciences. Carbons with a graphitic structure are particularly appealing due to their high chemical stability, large surface areas and high thermal and electronic conductivity. Numerous methods exist to produce nanostructured graphitic carbons but some of these can be energy-intensive and/or have problems with scalability. One option that is being increasingly explored is the process of iron-catalyzed graphitization. This simply involves the pyrolysis of carbon-rich precursors in the presence of an iron catalyst and has been used to produce carbons with a wide range of structures and properties. This review will examine the current field of iron-catalyzed graphitization, with a focus on molecular organic or biomass precursors. Bio-derived precursors are particularly attractive as a potential option for sustainable production of graphitic carbons. We start with a brief introduction to some key carbon structures, the current applications in which they are employed and some of the key methods that have been developed to produce nanostructured graphitic carbons. We will then review the history of catalytic graphitization before evaluating the wide range of conditions and precursors that have been employed in catalytic graphitization. Finally, this review will investigate the current challenges facing iron-catalyzed graphitization, looking particularly at the limitations of the current understanding of the mechanistic aspects of graphitization, with a view to outlining where research in this field might progress.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.90 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Theory and Practice: Bulk Synthesis of C3B and its H2- and Li-Storage Capacity
King, TC; Matthews, PD; Glass, H; Cormack, JA; Holgado, JP; Leskes, M; Griffin, JM; Scherman, OA; Barker, PD; Grey, CP; Dutton, SE; Lambert, RM; Tustin, G; Alavi, A; Wright, DSAngewandte Chemie International Edition, 54 (2015) 5919-5923
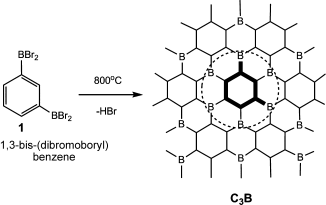
Previous theoretical studies of C3B have suggested that boron-doped graphite is a promising H2- and Li-storage material, with large maximum capacities. These characteristics could lead to exciting applications as a lightweight H2-storage material for automotive engines and as an anode in a new generation of batteries. However, for these applications to be realized a synthetic route to bulk C3B must be developed. Here we show the thermolysis of a single-source precursor (1,3-(BBr2)2C6H4) to produce graphitic C3B, thus allowing the characteristics of this elusive material to be tested for the first time. C3B was found to be compositionally uniform but turbostratically disordered. Contrary to theoretical expectations, the H2- and Li-storage capacities are lower than anticipated, results that can partially be explained by the disordered nature of the material. This work suggests that to model the properties of graphitic materials more realistically, the possibility of disorder must be considered.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.71 |
DOI | Año
2015 |
Gold promoted Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared from hydrotalcite precursors: Advanced materials for the WGS reaction
Santos, JL; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 201 (2017) 310-317
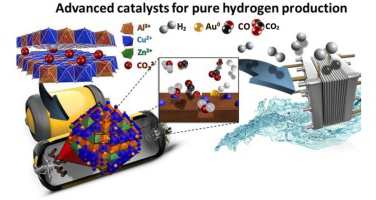
Outstanding catalysts for the water was shift reaction are reported in this work. The combination of gold nanoparticles with Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 prepared from hydrotalcite-like precursors leads to very promising systems for pure hydrogen production. Full CO conversion is reached at temperatures as low as 180 degrees C. The key point seems to be the cooperation of Au and Cu and the optimal metal-oxide contact derived from the synthesis method. The high activity of gold for low temperature CO oxidation and the suitability of copper for the WGS results in a perfect synergy. Moreover the materials developed in this work present good stability and tolerance towards start/stop cycles an indispensable requisite for a realistic application in an integrated hydrogen fuel processor.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Pt-impregnated catalysts on powdery SiC and other commercial supports for the combustion of hydrogen under oxidant conditions
Arzac, G. M.; Montes, O.; Fernandez, A.Applied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 201 (2017) 391-399
We report the study of the catalytic hydrogen combustion over Pt-impregnated powdery silicon carbide (SiC) using H2PtCl6 as precursor. The reaction was conducted in excess of oxygen. beta-SiC was selected for the study because of its thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, chemical inertness and surface area. The obtained Pt particles over SiC were medium size (average particle diameter of 5 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt). The activity of the Pt-impregnated catalyst over SiC was compared to those obtained in oxidized form over TiO2 and Al2O3 commercial supports (Pt particles very small in size, average particle diameter of 1 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt in both cases). The case of a SiO2 support was also discussed. Those Pt/SiC particles were the most active because of their higher contribution of surface Pt, indicating that partially oxidized surfaces have better activity than those totally oxidized in these conditions. SiC was modified with an acid treatment and thus bigger (average particle diameter of 7 nm for 0.5 wt% Pt) and more active Pt particles were obtained. Durability of the SiC and TiO2 supported catalysts was tested upon 5 cycles and both have shown to be durable and even more active than initially. Exposure to the oxidative reaction mixture activates the catalysts and the effect is more pronounced for the completely oxidized particles. This is due to the surface oxygen chemisorption which activates catalystsi surface.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Structuring Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 WGS catalyst: Introduction of buffer layer
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Laguna, OH; Martinez, LM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 200 (2017) 420-427
This work is devoted to the development of novel structured catalytic system for WGS reaction. The new concept is related to the presence of a pre-catalytic "buffer" layer formed by WGS-inert oxide, i.e. not involved in CO conversion, but able to increase the number of participating sites in water dissociation step during the reaction. The performance of the proposed systems appears to depend strongly on the stream composition, being its effect beneficial in highly reducing atmospheres making it ideal for cleanup application. An increment of the partial kinetic order for water species is observed and reveals the key role of the water activation for superior catalytic behavior.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Study of the E. coli elimination from urban wastewater over photocatalysts based on metallized TiO2
Murcia, JJ; Avila-Martinez, EG; Rojas, H; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCApplied Catalysis B-Envionmental, 200 (2017) 469-476
In this study, a series of photocatalysts based on TiO2 was tested in the elimination of Escherichia coli (E. coli) from urban wastewater. Firstly, TiO2 obtained by sol-gel method was modified by sulfation, and then gold or platinum nanoparticles were photodeposited on sulfated titania surface. Platinized samples were also prepared with different Pt content of 0.5 and 2 wt.%. The samples thus obtained were extensively characterized and it was found that sulfation considerably increases the S-BET value of TiO2 and promotes the anatase phase formation; it was also found that 0.5 wt.% Pt-TiO2 sample presents the lowest noble metal particle size and the best particle dispersion. All the photocatalysts synthesized have shown bactericidal effect and the results obtained by using bare and metalized TiO2 were considerably better than the results obtained with the commercial TiO2 P25 Evonic. Different light intensities were also evaluated in the photocatalytic tests and it was found that 120 W/m(2) leads to obtain the highest E. coli elimination from wastewater samples; however no total elimination of E. coli or other species of bacteria was achieved even after 5 h of photocatalytic treatment without catalyst. Total elimination of the E. coli was achieved after 3 h of photocatalytic reaction by using 120 Wim(2) of light intensity and 2 wt.% Pt-TiO2 as photocatalyst; no bacterial regrowth was observed even after 72 h.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
The role of cobalt hydroxide in deactivation of thin film Co-based catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 210 (2017) 342-351
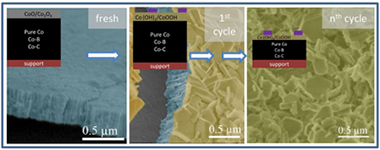
Deactivation of a Co catalyst prepared as thin film by magnetron sputtering was studied for the sodium borohydride (SB) hydrolysis reaction under different conditions. Under high SB concentration in single run experiments, the formation of a B-O passivating layer was observed after 1.5 and 24 h use. This layer was not responsible for the catalyst deactivation. Instead, a peeling-off mechanism produced the loss of cobalt. This peeling-off mechanism was further studied in cycling experiments (14 cycles) under low SB concentrations. Ex-situ study of catalyst surface after use and solid reaction products (precipitates) was performed by X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). The presence of cobalt hydroxide and oxyhydroxide was detected as major components on the catalyst surface after use and as precipitates in the supernatant solutions after washing. Cobalt borate, cobalt carbonate and oxycarbonate were also formed but in lesser amounts. These oxidized cobalt species were formed and further detached from the catalyst at the end of the reaction and/or during catalyst washing by decomposition of the unstable in-situ formed cobalt boride. Leaching of cobalt soluble species was negligible. Thin film mechanical detachment was also found but in a smaller extent. To study the influence of catalyst composition on deactivation processes, cycling experiments were performed with Co-B and Co-C catalysts, also prepared as thin films. We found that the deactivation mechanism proposed by us for the pure Co catalyst also occurred for a different pure Co (prepared at higher pressure) and the Co-B and Co-C samples in our experimental conditions.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.70 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Introducing structural colour in DSCs by using photonic crystals: interplay between conversion efficiency and optical properties
Colonna, D; Colodrero, S; Lindstrom, H; Di Carlo, A; Miguez, HEnergy & Environmental Science, 5 (2012) 8238-8243
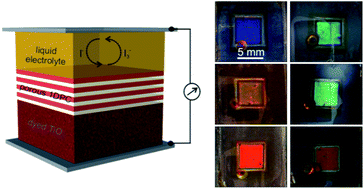
Herein we analyze experimentally the effect that introducing highly reflecting photonic crystals, operating at different spectral ranges, has on the conversion efficiency of dye sensitized solar cells. The interplay between structural colour and cell performance is discussed on the basis of the modified spectral response of the photogenerated current observed and the optical characterization of the cells. We demonstrate that, with the approach herein discussed, it is possible to achieve relatively high efficiencies using thin electrodes while preserving transparency. At the same time, the appearance of the device can be controllably modified, which is of relevance for their potential application in building integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) as window modules.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.65 |
DOI | Año
2012 |
Integrating catalytic tandem reactions for the next of biofuels: A
Blay-Roger, R; Carrasco-Ruiz, S; Reina, TR; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Nawaz, MAChem Catalysis, 4 (2024) 100987
In this piece, we explore the transformative potential of sustainable biofuel production as a solution to the energy crisis and a pivotal element in realizing the environmental and societal ambitions of Society 5.0. Through a critical examination of "bottom-up"and "topdown"strategies for converting bio-feedstocks sourced from anthropogenic activities into renewable fuels, the work underscores the need for innovation in catalysts and process intensification. By highlighting the advances and challenges in harnessing unconventional feedstocks and integrating renewable energy, this work points to a future where biofuels stand as a cornerstone of a sustainable energy landscape. The significance of this discussion extends beyond the technical realm, offering a vision for a circular economy that reduces dependence on fossil fuels, addresses climate change, and promotes global energy security. It calls for a united front among researchers, industry leaders, and policymakers to drive the biofuel sector toward efficiency, scalability, and widespread adoption.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.50 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Resonant Photocurrent Generation in Dye-Sensitized Periodically Nanostructured Photoconductors by Optical Field Confinement Effects
Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Luque-Raigon, JM; Miguez, HJournal of the American Chemical Society, 135 (2013) 7803-7806
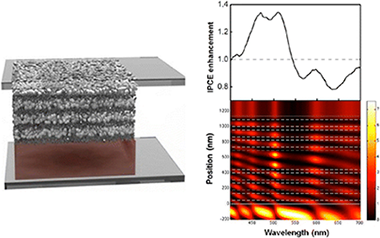
Herein we show experimental evidence of resonant photocurrent generation in dye-sensitized periodically nanostructured photoconductors, which is achieved by spectral matching of the sensitizer absorption band to different types of localized photon modes present in either periodic or broken symmetry structures. Results are explained in terms of the calculated spatial distribution of the electric field intensity within the configurations under analysis.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.44 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Cobalt Carbide Identified as Catalytic Site for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde
A. Rodríguez-Gómez; J.P. Holgado; A. CaballeroACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 5243-5247
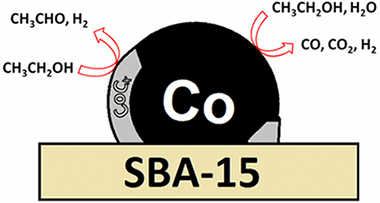
Two cobalt catalysts, Co/SBA-15 and Co/SiO2, have been studied in steam reforming of ethanol (SRE). Besides the steam reforming products, ethoxide dehydrogenation to acetaldehyde is observed as one of the main reactions. Although by hydrogen treatment cobalt is reduced to the metallic state, under SRE conditions, a phase appears that has been identified as cobalt carbide and correlates with acetaldehyde production. These findings provide insights about the catalytic sites, for SRE, in cobalt catalysts. Comparison with previous results shows that these conclusions are not translatable to other cobalt catalysts, stressing the importance of the support on the catalytic behavior of cobalt.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.38 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Reactive Surface Explored by NAP-XPS: Why Ionic Conductors Are Promoters for Water Gas Shift Reaction
García-Moncada, N; Penkova, A; González-Castaño, M; Odriozola, JAACS Catalysis (2024).
Near-ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAP-XPS) experiments have been carried out in N-2 and N-2-H2O atmospheres on a Pt-based catalyst physically mixed with an Eu-doped ZrO2 ionic conductor as a function of temperature under realistic conditions of the water gas shift (WGS) reaction. This work aims to demonstrate the significant effect of having active H2O on the ionic conductor surface at reaction temperatures to provide it to Pt metal sites. The ionic conductor, Eu-doped zirconia matrix, presents defects (oxygen vacancies, O-v) that allows upon H2O dissociation the formation of a hydrogen-bonded molecular water layer favoring diffusion through a Grotthuss mechanism below 300 degrees C. In the presence of H2O, the O-v are occupied by hydroxyl species as observed in the Eu 4d spectra, which differentiate two types of Eu oxidation states. The Eu3+-to-Eu2+ atomic ratio increases with the occupancy of the O-v by hydroxyls. Moreover, while the Pt-based catalyst alone is unable to create Pt-OH bonds, the physical mixture of the Pt-based catalyst and the ionic conductor allows the formation of Pt-OH bonds from room temperature up to 300 degrees C. These data demonstrate that the increase in molecular water concentration on the ionic conductor surface up to 300 degrees C acts as a reservoir to provide water to the Pt surface, enhancing the catalyst performance in the WGS reaction, supporting the importance of the surface H2O concentration in the reaction kinetics.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.30 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Enroute to the Carbon-Neutrality Goals via the Targeted Development of Ammonia as a Potential Nitrogen-Based Energy Carrier
Nawaz, MA; Blay-Roger, R; Saif, M; Meng, FH; González-Arias, J; Miao, BJ; Bobadilla, LF; Ramírez-Reina, T; Odriozola, J.A.ACS Catalysis, 13 (2023) 14415-14453

The reliance of a future carbon-free horizon is strongly aligned with the long-term energy storage avenues which are completely derived from renewable energy resources. Ammonia with its high energy content and density can perform as a decent candidate for buffering the short-term storage options. However, the current NH3 production majorly feeding the current huge desire for ammonia is dominated by the conventional nonrenewable Haber–Bosch (H–B) process route, thus continuously damaging the target of carbon neutrality goals. High-purity hydrogen (H2) gas is an essential precursor for the H–B process; however, it is a significant energy consumer (about 2% of the global energy supply) and contributes over 420 million tons of CO2/annum. Therefore, the research on the renewable synthesis of nitrogen-based energy carriers (such as ammonia) from the direct electrochemical, photocatalytic, or plasma catalytic processes; its conversion; and utilization to the potential derivatives has been a hot topic in the past few decades. A prospective analysis of the highly appealing processes has been summarized in this study, which could facilitate the adaption of renewable alternatives as an effective approach for zero carbon emission, paving the excellent pathways along the road to the development of nitrogen-based energy technologies, especially the targeted development of ammonia. Further, this Review covers the current and future impacts of the H–B process, the development of aspiring ammonia synthesis routes (via electro, photo, bio, chemical loop, or plasma catalysis), and its conversion and utilization to the renewable derivatives in terms of fabrication of model catalysts, advanced characterization technology, and efficient device design.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
The Need for Flexible Chemical Synthesis and How Dual-Function Materials Can Pave the Way
Merkouri, LP; Paksoy, AI; Reina, TR; Duyar, MSACS Catalysis, 13 (2023) 7230-7242
Since climate change keeps escalating, it is imperativethat theincreasing CO2 emissions be combated. Over recent years,research efforts have been aiming for the design and optimizationof materials for CO2 capture and conversion to enable acircular economy. The uncertainties in the energy sector and the variationsin supply and demand place an additional burden on the commercializationand implementation of these carbon capture and utilization technologies.Therefore, the scientific community needs to think out of the boxif it is to find solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change.Flexible chemical synthesis can pave the way for tackling market uncertainties.The materials for flexible chemical synthesis function under a dynamicoperation, and thus, they need to be studied as such. Dual-functionmaterials are an emerging group of dynamic catalytic materials thatintegrate the CO2 capture and conversion steps. Hence,they can be used to allow some flexibility in the production of chemicalsas a response to the changing energy sector. This Perspective highlightsthe necessity of flexible chemical synthesis by focusing on understandingthe catalytic characteristics under a dynamic operation and by discussingthe requirements for the optimization of materials at the nanoscale.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.30 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Low-pressure calcination to enhance the calcium looping process for thermochemical energy storage
Ortiz, C; Carro, A; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Cleaner Production, 363 (2022) 132295
The Calcium-Looping (CaL) process, based on the multicyclic calcination-carbonation of CaCO3/CaO, is considered a promising Thermochemical Energy Storage (TCES) technology to be integrated into Concentrating Solar Power (CSP) plants. This work proposes a novel CaL integration that operates at low-pressure calcination under pure CO2 and a moderated temperature. Low-pressure calcination (0.01 bar) provides a suitable solution to mitigate CaO sintering and its consequent loss of reactivity in the carbonation stage. Since the temperature for quick calcination in a pure CO2 atmosphere is decreased (from around 950 °C at 1 bar to 765 °C at 0.01 bar), the energy losses at the receiver are minimised. In addition, a reduced calcination temperature allows for the use of metallic receivers already tested at the MW-scale, which significantly increases the CSP-CaL integration reliability. Moreover, multicycle CaO reactivity is promoted in short residence times, allowing the use of a simpler reactor design. Furthermore, there is an increase of 85% in the energy storage density of the system. The proposed plant proposes a smooth integration of the CaL process in CSP plants, with a moderate storage level and supported by a natural gas backup system (solar share higher than 50%). The results show that the solar thermal-to electric efficiency is above 30%.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.10 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Plasticized, greaseproof chitin bioplastics with high transparency and biodegradability
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Benitez, JJ; Porras-Vazquez, JM; Tedeschi, G; Morales, Y; Fernandez-Ortuno, D; Athanassiou, A; Guzman-Puyol, SFood Hydrocolloids, 145 (2023) 109072
A mixture of trifluoroacetic acid:trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFA:TFAA) was used to dissolve chitin from shrimp shells. Free-standing films were prepared by blending the chitin solution and glycerol at different percentages, followed by drop-casting, and the complete evaporation of the solvents. After this process, the chitin matrix showed an amorphous molecular structure, as determined by X-ray diffraction. Optical, mechanical, thermal, and antioxidant properties were also thoroughly investigated. The incorporation of glycerol induced a plasticizing effect on the mechanical response of films and improved their transparency. In addition, hydrodynamic and barrier properties were determined by contact angle and water vapor/oxygen transmission rates, respectively, and revealed typical values of other polysaccharides. These bioplastics also presented an excellent greaseproof behavior with the highest degree of oil repellency as determined by the Kit test. Moreover, the overall migration was evaluated by using Tenax & REG; as a dry food simulant and levels were compliant with European regulations. Their antifungal properties were tested using Botrytis cinerea as a model. Biodegradability was also determined by measuring the biological oxygen demand in seawater. Degradation rates were high and similar to those of other fully-degradable materials.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
11.00 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Synergizing carbon capture and utilization in a biogas upgrading plant based on calcium chloride: Scaling-up and profitability analysis
Baena-Moreno, FM; Reina, TR; Rodriguez-Galan, M; Navarrete, B; Vilches, LFScience of The Total Environment, 758 (2021) 143645
Herein we analyze the profitability of a novel regenerative process to synergize biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization. Our proposal is a promising alternative which allows to obtain calcium carbonate as added value product while going beyond traditional biogas upgrading methods with high thermal energy consumption. Recently we have demonstrated the experimental viability of this route. In this work, both the scale-up and the profitability of the process are presented. Furthermore, we analyze three representative scenarios to undertake a techno-economic study of the proposed circular economy process. The scale-up results demonstrate the technical viability of our proposal. The precipitation efficiency and the product quality are still remarkable with the increase of the reactor size. The techno-economic analysis reveals that the implementation of this circular economy strategy is unprofitable without subsidies. Nonetheless, the results are somehow encouraging as the subsides needed to reach profitability are lower than in other biogas upgrading and carbon dioxide utilization proposals. Indeed, for the best-case scenario, a feed-in tariff incentive of 4.3 (sic)/MWh makes the approach profitable. A sensitivity study through tornado analysis is also presented, revealing the importance of reducing bipolar membrane electrodialysis energy consumption. Overall our study envisages the big challenge that the EU faces during the forthcoming years. The evolution towards bio-based and circular economies requires the availability of economic resources and progress on engineering technologies.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.75 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ removal by designed functionalized swelling high-charged micas
Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDScience of The Total Environment, 764 (2021) 142811
The increasing accumulation of toxic heavy metals in the environment has generated the need of efficient removal systems, being the adsorption method the most popular one applied in aqueous solutions. Of particular concern is the case of Pb2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ due to their high potential hazard. In this paper, we describe the feasibility of a new family of nanomaterials, swelling high charge micas, in the removal of these cations from aqueous solutions. Batch adsorption experiments were carried out in the as-made micas, NaMn, and after functionalization with ethylammonium, EA-Mn, and mercaptoethylammonium, MEA-Mn. The results have demonstrated that all of them are efficient heavy metal adsorbents, being Na-M2 the best adsorbent for Pb2+ and Cd2+, and, MEA-M2 for Hg2+.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.75 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Phase-pure BiFeO3 produced by reaction flash-sintering of Bi2O3 and Fe2O3
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Sayagues, MJ; Raj, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 6 (2018) 5356-5366
Mixed powders of Bi2O3 and Fe2O3 are shown to yield single-phase, dense nanostructured polycrystals of BiFeO3 in reaction flash sintering experiments, carried out by applying a field of 50 V cm(-1) and with the current limit set to 35 mA mm(-2). The furnace was heated at a constant rate with the reaction sintering taking place abruptly upon reaching 625 degrees C. Remarkably, an intermediate bismuth-rich phase of the oxide that forms just before reaching the flash temperature transforms, and at the same time sinters, into singlephase BiFeO3 within a few seconds after the onset of the flash. The BiFeO3 so produced is electrically insulating, a property that is critical to its applications. This one-step synthesis of single-phase polycrystals of complex oxides from their basic constituents, by reaction flash sintering, is a significant development in the processing of complex oxides, which are normally difficult to sinter by conventional methods.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.73 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Pt/CePO4 catalysts for the WGS reaction: influence of the water-supplier role of the support on the catalytic performance
Navarro-Jaen, S; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 6 (2018) 17001-17010
For Pt catalysts which have demonstrated great activity for the WGS reaction, the activation of water is described as the rate-limiting step. Such limitation could be overcome through the design of supports able to supply water. In this study, the hexagonal and monoclinic phases of CePO4 have been evaluated as supports for Pt WGS catalysts. The hexagonal structure presents channels containing water, absent in the monoclinic structure. The presence of these channels in the hexagonal phase increases the interaction with the water molecules, leading to an enhancement of the WGS catalytic performance. DRIFTS results showed that dissociation of water does not occur on these supports, while calculated apparent activation energies present values similar to those reported in the literature for the dissociation of water in Pt (111). These results suggest that cerium phosphates act as water suppliers, increasing the number of available species to be dissociated on the Pt surface.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.73 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Waterproof-breathable films from multi-branched fluorinated cellulose esters
Tedeschi, G; Guzman-Puyol, S; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Goldoni, L; Koschella, A; Heinze, T; Cavallo, G; Dichiarante, V; Terraneo, G; Athanassiou, A; Metrangolo, P; Heredia-Guerrero, JACarbohydrate Polymers, 271 (2021) 118031
Cellulose ester films were prepared by esterification of cellulose with a multibranched fluorinated carboxylic acid, "BRFA" (BRanched Fluorinated Acid), at different anhydroglucose unit:BRFA molar ratios (i.e., 1:0, 10:1, 5:1, and 1:1). Morphological and optical analyses showed that cellulose-BRFA materials at molar ratios 10:1 and 5:1 formed flat and transparent films, while the one at 1:1 M ratio formed rough and translucent films. Degrees of substitution (DS) of 0.06, 0.09, and 0.23 were calculated by NMR for the samples at molar ratios 10:1, 5:1, and 1:1, respectively. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy confirmed the esterification. DSC thermograms showed a single glass transition, typical of amorphous polymers, at -11 degrees C. The presence of BRFA groups shifted the mechanical behavior from rigid to ductile and soft with increasing DS. Wettability was similar to standard fluoropolymers such as PTFE and PVDF. Finally, breathability and water uptake were characterized and found comparable to materials typically used in textiles.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.72 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Subnanometric Pt clusters dispersed over Cs-doped TiO2 for CO2 upgrading via low-temperature RWGS: operando mechanistic insights to guide an optimal catalyst design
Torres-Sempere, G; Blay-Roger, R; Luque-Alvarez, LA; Santos, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Pastor-Pérez, L; Centeno, MA; Hernández, WY; Yousef, I; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TRJournal of Matertials Chemistry A, 12 (2024) 1779-1792

The RWGS reaction is gathering momentum as an effective route for CO2 valorisation and given its endothermic nature the challenge lies in the design of active low-temperature catalysts. Herein we have designed two catalysts based on subnanometric Pt clusters providing effective CO2 conversion and, more importantly, high CO selectivity in the low-temperature range. The impact of Cs as a dopant in the catalyst's formulation is crucial leading to full selectivity at 300 °C. The reaction mechanisms for the studied systems namely Pt/TiO2 and PtCs/TiO2 are significantly different due to the presence of the alkali promoter. The presence of Cs neutralises the hydroxide groups of the TiO2 surface, changing the reaction pathway. The Pt/TiO2 catalyst follows a redox mechanism where CO2 dissociates to CO in the oxygen vacancies, and then these vacancies are recovered by the migration of H2 by spill over phenomena. On the other hand, the Cs doped catalyst has two possible mechanism pathways: the (ii) formyl/acyl pathway, where –CHO species are formed and, depending on the reaction conditions, evolve to CO gas or oxygenated compounds, and (ii) frustrated Lewis pair (FLP) assisted CO2 reduction route, in which the FLP induces the heterolytic dissociation of H2 and the subsequent hydrogenation of CO2 to CO. The latter route enabled by Cs-doping combined with the subnanometric Pt domains seems to be responsible for the excellent catalytic behaviour leading to fully selective low-temperature RWGS systems and thus unlocking new possibilities for less energy demanding CO2 valorisation units based on RWGS.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.70 |
DOI | Año
2024 |
Are Ni/ and Ni5Fe1/biochar catalysts suitable for synthetic natural gas production? A comparison with g-Al2O3 supported catalysts
González-Castaño, M; Morales, C; de Miguel, JCN; Boelte, JH; Klepel, O; Flege, JI; Arellano-Garcia, HGreen Energy & Environment, 8 (2023) 744-756
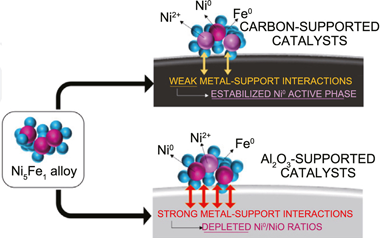
Among challenges implicit in the transition to the post-fossil fuel energetic model, the finite amount of resources available for the technological implementation of CO2 revalorizing processes arises as a central issue. The development of fully renewable catalytic systems with easier metal recovery strategies would promote the viability and sustainability of synthetic natural gas production circular routes. Taking Ni and NiFe catalysts supported over g-Al2O3 oxide as reference materials, this work evaluates the potentiality of Ni and NiFe supported biochar catalysts for CO2 methanation. The development of competitive biochar catalysts was found dependent on the creation of basic sites on the catalyst surface. Displaying lower Turn Over Frequencies than Ni/Al catalyst, the absence of basic sites achieved over Ni/C catalyst was related to the depleted catalyst performances. For NiFe catalysts, analogous Ni5Fe1 alloys were constituted over both alumina and biochar supports. The highest specific activity of the catalyst series, exhibited by the NiFe/C catalyst, was related to the development of surface basic sites along with weaker NiFe-C interactions, which resulted in increased Ni0:NiO surface populations under reaction conditions. In summary, the present work establishes biochar supports as a competitive material to consider within the future low-carbon energetic panorama.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.70 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Greaseproof, hydrophobic, and biodegradable food packaging bioplastics from C6-fluorinated cellulose esters
Guzman-Puyol, S; Tedeschi, G; Goldoni, L; Benitez, JJ; Ceseracciu, L; Koschella, A; Heinze, T; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrera, JAFood Hydrocolloids, 128 (2022) 107562
Tridecafluorononanoic acid (TFNA), a C6-fluorinated carboxylic acid, was esterified with cellulose at different molar ratios (0:1, 1:1, 2:1, and 3:1) in a trifluoroacetic acid (TFA):trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA):CHCl3 (2:1:1, v:v:v) solvent mixture. Free-standing films were obtained for all formulations and are presented as alternatives to composites and blends of paper with fluorinated molecules. Mechanical properties were investigated by tensile tests, and a plasticizer effect of fluorinated chains was observed. Interestingly, the wettability of these new cellulose derivatives was similar or even better than other common cellulose derivatives and fluorinated poly-mers employed in food packaging. Hydrodynamic properties were also improved by addition of TFNA, resulting in materials with water vapor permeability values comparable to other cellulose-based food packaging materials. In addition, films with the higher amounts of TFNA showed the required oil resistance for papers used in food packaging applications, as determined by the Kit Test. Finally, the biodegradation of these C6-fluorinated cel-lulose esters, assessed by biological oxygen demand (BOD) in seawater, was higher than typical bio-based polymers used in food packaging. The bioplastic synthesized at a molar ratio 1:1 (TFNA:cellulose) showed excellent performances in terms of greaseproof, hydrophobicity, ductility, and biodegradability, representing a sustainable alternative to typical plastics used in food packaging.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.70 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Unravelling the CO2 capture and conversion mechanism of a NiRu-Na2O switchable dual-function material in various CO2 utilisation reactions
Merkouri, LP; Martin-Espejo, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Penkova, A; Reina, T; Duyar, MSJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 11 (2023) 13209-13216
Time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS was performed to elucidate the CO2 capture and conversion mechanisms of a NiRuNa/CeAl DFM in CO2 methanation, reverse water-gas shift, and dry reforming of methane. CO2 was captured mainly in the form of carbonyls and bidentate carbonates, and a spillover mechanism occurred to obtain the desired products.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.70 |
DOI | Año
2023 |
Does shaping catalysts modify active phase sites? A comprehensive in situ FTIR spectroscopic study on the performance of a model Ru/Al2O3 catalyst for the CO methanation
Bobadilla, LF; Munoz-Murillo, A; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 357 (2019) 248-257

Routinely, it seems assumed that the catalytic layer coated on monoliths and microchannel reactors preserve the properties of the initial powder catalyst. However, this assumption should be reasonably demonstrated since the set of chemical and physical manipulations involved in the preparation of these catalytic devices hardly does not alter the surface of the starting catalyst powders. This work aims to evaluate the transformations that takes place in a model Ru/Al2O3 catalyst during a typical slurry preparation procedure and their impact on the catalytic performance for the CO methanation reaction and the selective methanation of CO in CO2-rich reformate gases. For this purpose, we have conducted an in situ comprehensive study by means of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) in which the nature of the species present on the surface of the catalyst during CO hydrogenation was analyzed. This study reveals that during the preparation of the slurry the starting Ru/Al2O3 catalyst suffers a redispersion of metallic Ru particles and more surface hydroxyls are created by the incorporation of additional alumina. These modifications have a noticeable influence in the catalytic performance and despite their importance, these aspects have been poorly considered in other studies.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.65 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Multicycle CO2 capture activity and fluidizability of Al-based synthesized CaO sorbents
Azimi, B; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JMChemical Engineering Journal, 358 (2019) 679-690
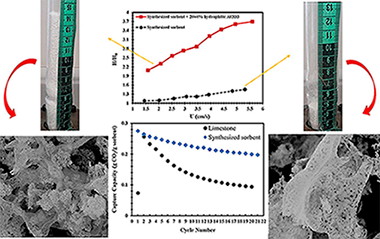
CaO-based materials have been identified as promising sorbents for highly efficient pre-combustion and post-combustion CO2 capture in fluidized beds operated at high temperatures by means of the Calcium Looping (CaL) process. However, Ca-based sorbents suffer from a decline of the capture capacity over multiple sorption/desorption cycles, mainly due to sintering, and from a markedly heterogeneous fluidization behavior due to the strength of interparticle attractive forces as compared to particle weight. The present study is focused on the development of novel synthetic CaO/Al2O3 sorbents for CO2capture with enhanced CaL performance and fluidizability by dry mixing with flow conditioner nanopowders. The influence of initial precursors on the sorbents multicycle activity at realistic CaL conditions has been investigated. The formation of a stable Ca9Al6O18 mixed-phase during the preparation of the sorbents promotes the multicycle capture capacity. The type of Ca and Al precursors, either soluble or insoluble, can significantly affect the dispersion of this stabilizer (Ca9Al6O18) in the sorbent matrix and, consequently, may affect the carbonation activity of the materials. The sorbent prepared from soluble aluminum nitrate and calcium nitrate precursors by sol-gel method exhibits a very stable multicycle capture capacity with a capture capacity around 0.2 g of CO2/g of sorbent after 21 cycles keeping a 72% of its initial capture capacity. The fluidizability of this promising sorbent was also investigated as affected by the addition of three different flow conditioners. Fluidization experiments confirmed the positive effect of using hydrophilic alumina and hydrophobic silica nanoparticles on improving the fluidizability of the synthesized sorbents.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.65 |
DOI | Año
2019 |
Critical Role of Oxygen in Silver-Catalyzed Glaser-Hay Coupling on Ag(100) under Vacuum and in Solution on Ag Particles
Orozco, N; Kyriakou, G; Beaumont, SK; Sanz, JF; Holgado, JP; Taylor, MJ; Espinos, JP; Marquez, AM; Watson, DJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 3113-3120
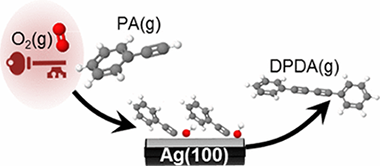
The essential role of oxygen in enabling heterogeneously catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling of phenylacetylene on Ag(100) was elucidated by STM, laboratory and synchrotron photoemission, and DFT calculations. In the absence of coadsorbed oxygen, phenylacetylene formed well-ordered dense overlayers which, with increasing temperature, desorbed without reaction. In striking contrast, even at 120 K, the presence of oxygen led to immediate and complete disruption of the organic layer due to abstraction of acetylenic hydrogen with formation of a disordered mixed layer containing immobile adsorbed phenylacetylide. At higher temperatures phenylacetylide underwent Glaser–Hay coupling to form highly ordered domains of diphenyldiacetylene that eventually desorbed without decomposition, leaving the bare metal surface. DFT calculations showed that, while acetylenic H abstraction was otherwise an endothermic process, oxygen adatoms triggered a reaction-initiating exothermic pathway leading to OH(a) + phenylacetylide, consistent with the experimental observations. Moreover, it was found that, with a solution of phenylacetylene in nonane and in the presence of O2, Ag particles catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling with high selectivity. Rigorous exclusion of oxygen from the reactor strongly suppressed the catalytic reaction. Interestingly, too much oxygen lowers the selectivity toward diphenyldiacetylene. Thus, vacuum studies and theoretical calculations revealed the key role of oxygen in the reaction mechanism, subsequently borne out by catalytic studies with Ag particles that confirmed the presence of oxygen as a necessary and sufficient condition for the coupling reaction to occur. The direct relevance of model studies to a mechanistic understanding of coupling reactions under conditions of practical catalysis was reaffirmed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.61 |
DOI | Año
2017 |
Electrocatalytic System for the Simultaneous Hydrogen Production and Storage from Methanol
Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Valverde, JL; de Lucas-Consuegra, AACS Catalysis, 6 (2016) 1942-1951
This paper reports a groundbreaking approach for simultaneous hydrogen production and storage that entails catalysis, electrochemistry, surface science, and materials synthesis. A novel electrocatalytic system is developed based on nickel nanocolumnar films of controlled microstructure prepared on K-βAl2O3 solid electrolyte supports by oblique angle physical vapor deposition. The outstanding characteristics of this system are a hydrogen storage capacity of up to 19 g of H2 (100 g of Ni)−1, which is unparalleled in the literature and the possibility of controlling its release electrochemically, under fixed mild conditions (280 °C and normal pressure). H2 is produced in situ by methanol steam re-forming on the Ni catalyst, and it spills over onto graphene oxide aggregates formed during the catalytic process, as confirmed by SEM, FTIR, and Raman spectroscopy. The proposed storage mechanism considers a synergetic contribution of both Ni and graphene oxide, promoted by K+ ions, in enhancing the hydrogen storage capacity of the system.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.61 |
DOI | Año
2016 |
Structural Evolution in Iron-Catalyzed Graphitization of Hard Carbons
Gomez-Martin, A; Schnepp, Z; Ramirez-Rico, JChemistry of Materials, 33 (2021) 3087-3097
Despite the recent interest in catalytic graphitization to obtain graphite-like materials from hard-carbon sources, many aspects of its mechanism are still poorly unknown. We performed a series of in situ experiments to study phase transformations during graphitization of a hard-carbon precursor using an iron catalyst at temperatures up to 1100 degrees C and ex situ total scattering experiments up to 2000 degrees C to study the structural evolution of the resulting graphitized carbon. Our results show that upon heating and cooling, iron undergoes a series of reductions to form hematite, magnetite, and wustite before forming a carbide that later decomposes into metallic iron and additional graphite and that the graphitization fraction increases with increasing peak temperature. Structural development with temperature results in decreasing sheet curvature and increased stacking, along with a decrease in turbostratic disorder up to 1600 degrees C. Higher graphitization temperatures result in larger graphitic domains without further ordering of the graphene sheets. Our results have implications for the synthesis of novel biomass-derived carbon materials with enhanced crystallinity.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.51 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Role of particle size on the multicycle calcium looping activity of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Duran-Martin, JD; Jimenez, PES; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Arcenegui-Troya, J; Trinanes, PG; Maqueda, LAPJournal of Advanced Research, 22 (2020) 67-76
The calcium looping process, based on the reversible reaction between CaCO3 and CaO, is recently attracting a great deal of interest as a promising thermochemical energy storage system to be integrated in Concentrated Solar Power plants (CaL-CSP). The main drawbacks of the system are the incomplete conversion of CaO and its sintering-induced deactivation. In this work, the influence of particle size in these deactivation mechanisms has been assessed by performing experimental multicycle tests using standard limestone particles of well-defined and narrow particle size distributions. The results indicate that CaO multicycle conversion benefits from the use of small particles mainly when the calcination is carried out in helium at low temperature. Yet, the enhancement is only significant for particles below 15 μm. On the other hand, the strong sintering induced by calcining in CO2 at high temperatures makes particle size much less relevant for the multicycle performance. Finally, SEM imaging reveals that the mechanism responsible for the loss of activity is mainly pore-plugging when calcination is performed in helium, whereas extensive loss of surface area due to sintering is responsible for the deactivation when calcination is carried out in CO2 at high temperature.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.48 |
DOI | Año
2020 |
Selective UV Reflecting Mirrors Based on Nanoparticle Multilayers
Smirnov, JRC; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 2805-2811
A new type of nanostructured selective ultraviolet (UV) reflecting mirror is presented. Periodic porous multilayers with photonic crystal properties are built by spin-coating-assisted layer-by-layer deposition of colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles of ZrO2 and SiO2 (electronic band gap at λ < 220 nm). These optical filters are designed to block well-defined wavelength ranges of the UVA, UVB, and UVC regions of the electromagnetic spectrum while preserving transparency in the visible. The shielding against those spectral regions arises exclusively from optical interference phenomena and depends only on the number of stacked layers and the refractive index contrast between them. In addition, it is shown that the accessible pore network of the as-deposited multilayer allows preparing thin, flexible, self-standing, transferable, and adaptable selective UV filters by polymer infiltration, without significantly losing reflectance intensity, i.e., preserving the dielectric contrast. These films offer a degree of protection comparable to that of traditional ones, without any foreseeable unwanted secondary effects, such as photodegradation, increase of local temperature or, as is the case for organic absorbers, generation of free radicals, all of which are caused by light absorption.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.44 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Vertically Aligned Hybrid Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanowires for Photonics Applications
Macias-Montero, M; Filippin, AN; Saghi, Z; Aparicio, FJ; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AAdvanced Functional Materiales, 23 (2013) 5981-5989
A family of 1D organic/inorganic core/shell materials formed by an inner organic nanowire (ONW) conformally covered with an inorganic wide band gap semiconductor (ZnO or TiO2) layer is presented. The developed procedure is a two-steps vacuum methodology involving the formation of supported single crystal small-molecule nanowires by physical vapor deposition and plasma enhance chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) of the inorganic shell. Critical characteristics of the last technique are the possibilities of low temperature and remote configuration deposition. Additionally, an initial step has to be included in order to create nucleation centers for the growth of the ONWs. The procedure and its general character in terms of the variability in organic core and inorganic shells composition and the applicability of the technique to different substrates are presented. The formation of the inorganic shell with no damage of the organic core single-crystalline structure is demonstrated by high resolution transmission electron microscopy. The vertical alignment of the hybrid nanostructure is achieved thanks to the interaction of the 1D organic nanostructured surfaces and the glow discharge during the deposition of the inorganic shell by PECVD. The optical properties of these core/shell NWs are studied by fluorescence spectroscopy and microscopy, and their application as nanoscale waveguides in the 550–750 nm range addressed.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.44 |
DOI | Año
2013 |
Flame confinement in biomass combustion systems for particles abatement
Ciria, D; Orihuela, MP; Moreno-Naranjo, P; Chacartegui, R; Ramirez-Rico, J; Becerra, JAEnergy Conversion and Management, 264 (2022) 115706
This work explores the use of open-pore, inert ceramic foams with different pore sizes as particle abatement systems in small biomass combustion systems. Porous foams made of silicon carbide with pore sizes 10 to 60 pores-per-inch were installed in an in-house designed combustion unit operated with wood pellets. Their effects on the temperature distribution inside the chamber, particulate and gases emissions were studied using different airflow rates in the reaction-limited regime (low equivalence ratio) to minimise stoichiometric factors. The influence of pore size, foam position with respect to the flame and space velocity were assessed. The confinement of the flame with inert foams was found to substantially modify the temperature distribution in the combustion chamber, improve the air-fuel mixture, and favour the thermal decomposition of the pellet, leading to a reduction in particulate emissions when compared to free-flame combustion at the same experimental conditions. In general, the amount of particulate matter was found to decrease by up to one order of magnitude as the pore size of the foam was reduced, while the temperature gradient in the combustion chamber was increased. Nitrogen oxides and carbon dioxide emissions were essentially unchanged, irrespectively of the pore size of the foam. It is expected that these values will be improved with longer residence times, as happens in operations with reduced excess air ratios. These results suggest that it is possible to control pollutants derived from domestic heating within the most restrictive current regulations on particulate emissions by integrating flame confinement designs with better operating practices and efficient abatement systems.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.40 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
3D-printed structured catalysts for CO2 methanation reaction: Advancing of gyroid-based geometries
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Baena-Moreno, F; De Miguel, JCN; Miah, KUM; Arroyo-Torralvo, F; Ossenbrink, R; Odriozola, JA; Benzinger, W; Hensel, A; Wenka, A; Arellano-García, HEnergy Conversion and Management, 258 (2022) 115464
This work investigates the CO2 methanation rate of structured catalysts by tuning the geometr y of 3D-printed metal Fluid Guiding Elements (FGEs) structures based on periodically variable pseudo-gyroid geometries. The enhanced performance showed by the structured catalytic systems is mostly associated with the capability of the FGEs substrate geometries for efficient heat usages. Thus, variations on the channels diameter resulted in ca. 25% greater CO2 conversions values at intermediate temperature ranges. The highest void fraction evidenced in the best performing catalyst (3D-1) favored the radial heat transfer and resulted in significantly enhanced catalytic activity, achieving close to equilibrium (75%) conversions at 400 ? and 120 mL/min. For the 3D-1 catalyst, a mathematical model based on an experimental design was developed thus enabling the estimation of its behavior as a function of temperature, spatial velocity, hydrogen to carbon dioxide (H-2/CO2) ratio, and inlet CO2 concentration. Its optimal operating conditions were established under 3 different scenarios: 1) no restrictions, 2) minimum H-2:CO2 ratios, and 3) minimum temperatures and H-2/CO2 ratio. For instance, for the lattest scenario, the best CO2 methanation conditions require operating at 431 ?, 200 mL/min, H-2/CO2 = 3 M ratio, and inlet CO2 concentration = 10 %.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.40 |
DOI | Año
2022 |
Highly Versatile Upconverting Oxyfluoride-Based Nanophosphor Films
Ngo, TT; Cabello-Olmo, E; Arroyo, E; Becerro, AI; Ocana, M; Lozano, G; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 30051-30060
Fluoride-based compounds doped with rare-earth cations are the preferred choice of materials to achieve efficient upconversion, of interest for a plethora of applications ranging from bioimaging to energy harvesting. Herein, we demonstrate a simple route to fabricate bright upconverting films that are transparent, self-standing, flexible, and emit different colors. Starting from the solvothermal synthesis of uniform and colloidally stable yttrium fluoride nanoparticles doped with Yb3+ and Er3+, Ho3+, or Tm3+, we find the experimental conditions to process the nanophosphors as optical quality films of controlled thickness between few hundreds of nanometers and several micrometers. A thorough analysis of both structural and photophysical properties of films annealed at different temperatures reveals a tradeoff between the oxidation of the matrix, which transitions through an oxyfluoride crystal phase, and the efficiency of the upconversion photoluminescence process. It represents a significant step forward in the understanding of the fundamental properties of upconverting materials and can be leveraged for the optimization of upconversion systems in general. We prove bright multicolor upconversion photoluminescence in oxyfluoride-based phosphor transparent films upon excitation with a 980 nm laser for both rigid and flexible versions of the layers, being possible to use the latter to coat surfaces of arbitrary shape. Our results pave the way toward the development of upconverting coatings that can be conveniently integrated in applications that demand a large degree of versatility.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.38 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Solid-State Dewetting of Gold on Stochastically Periodic SiO2 Nanocolumns Prepared by Oblique Angle Deposition
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Wang, D; Flock, D; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Schaaf, PACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 11385-11395
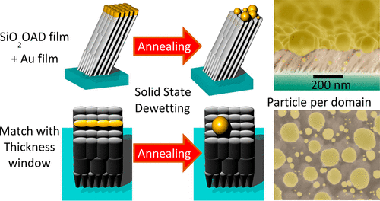
Solid-state dewetting (SSD) on patterned substrates is a straightforward method for fabricating ordered arrays of metallic nanoparticles on surfaces. However, a drawback of this procedure is that the patterning of substrates usually requires time-consuming and expensive two-dimensional (2D) fabrication methods. Nanostructured thin films deposited by oblique angle deposition (OAD) present at the surface a form of stochastically arranged periodic bundles of nanocolumns that might act as a patterned template for fabricating arrays of nanoparticles by SSD. In this work, we explore this concept and investigate the effect of three different types of OAD SiO2 thin films on the SSD of Au deposited on their surface. We demonstrate that the size and spatial distribution of the particles can be tailored through the surface morphology of these OAD film substrates. It has been found that the SSD of the evaporated Au layer gives rise to a bimodal size distribution of particles. A majority of them appeared as mesoparticles with sizes.100 nm and the rest as nanoparticles with similar to 10 nm, respectively, located either on top of the nanocolumns following their lateral distribution (i.e., resulting from a patterning effect) or incorporated inside the open mesopores existing among them. Moreover, on the SiO2-OAD thin films where interconnected nanocolumnar bundles arrange in the form of discrete motifs, the patterning effect gave rise to the formation of approximately one Au mesoparticle per motif, which is one of the assets of patterned SSD. The morphological, optical (i.e., plasmon resonance), and crystalline structural characteristics of Au mesoparticles suggest that the interplay between a discontinuous nanocolumnar surface acting as a template and the poor adhesion of Au onto SiO2 are key factors for the observed template effect controlling the SSD on the surface of OAD thin films.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.38 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Form Birefringence in Resonant Transducers for the Selective Monitoring of VOCs under Ambient Conditions
Oliva-Ramirez, Manuel; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Berthon, Hermine; Goven, Mathilde; Portoles, Jose; Gil-Rostra, Jorge; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Yubero, FranciscoACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13 (2021) 19148-19158
In this work, we have developed a new kind of nanocolumnar birefringent Bragg microcavity (BBM) that, tailored by oblique angle deposition, behaves as a selective transducer of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Unlike the atomic lattice origin of birefringence in anisotropic single crystals, in the BBM, it stems from an anisotropic self-organization at the nanoscale of the voids and structural elements of the layers. The optical adsorption isotherms recorded upon exposure of these nanostructured systems to water vapor and VOCs have revealed a rich yet unexplored phenomenology linked to their optical activity that provides both capacity for vapor identification and partial pressure determination. This photonic response has been reproduced with a theoretical model accounting for the evolution of the form birefringence of the individual layers upon vapor condensation in nanopores and internanocolumnar voids. BBMs that repel water vapor but are accessible to VOCs have been also developed through grafting of their internal surfaces with perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane molecules. These nanostructured photonic systems are proposed for the development of transducers that, operating under environmental conditions, may respond specifically to VOCs without any influence by the degree of humidity of the medium.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.38 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Self-Assembly of the Nonplanar Fe(III) Phthalocyanine Small-Molecule: Unraveling the Impact on the Magnetic Properties of Organic Nanowires
Filippin, AN; Lopez-Flores, V; Rojas, TC; Saghi, Z; Rico, VJ; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Espinos, JP; Zitolo, A; Viret, M; Midgley, PA; Barranco, A; Borras, AChemistry of Materials, 30 (2018) 879-887
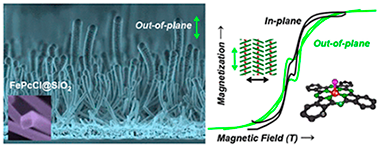
In this article we show for the first time the formation of magnetic supported organic nanowires (ONWs) driven by self-assembly of a nonplanar Fe(III) phthalocyanine chloride (FePcCl) molecule. The ONWs grow by a crystallization mechanism on roughness-tailored substrates. The growth methodology consists of a vapor deposition under low vacuum and mild temperature conditions. The structure, microstructure, and chemical composition of the FePcCl NWs are thoroughly elucidated and compared with those of Fe(II) phthalocyanine NWs by a consistent and complementary combination of advanced electron microscopies and X-ray spectroscopies. In a further step, we vertically align the NWs by conformal deposition of a SiO2 shell. Such orientation is critical to analyze the magnetic properties of the FePcCl and FePc supported NWs. A ferromagnetic behavior below 30 K with an easy axis perpendicular to the phthalocyanine plane was observed in the two cases with the FePcCl nanowires presenting a wider hysteresis. These results open the path to the fabrication of nanostructured one-dimensional small-molecule spintronic devices.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.16 |
DOI | Año
2018 |
Enhanced Directional Light Extraction from Patterned Rare-Earth Phosphor Films
Cabello-Olmo, E; Molet, P; Mihi, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001611
The combination of light‐emitting diodes (LEDs) and rare earth (RE) phosphors as color‐converting layers comprises the basis of solid‐state lighting. Indeed, most LED lamps include a photoluminescent coating made of phosphor material, i.e., crystalline matrix suitably doped with RE elements, to produce white light from a blue or ultraviolet LED chip. Transparent phosphor‐based films constitute starting materials for new refined emitters that allow different photonic designs to be implemented. Among the different photonic strategies typically employed to tune or enhance emission, surface texturing has proved its versatility and feasibility in a wide range of materials and devices. However, most of the nanofabrication techniques cannot be applied to RE phosphors directly because of their chemical stability or because of their cost. The first monolithic patterned structure of down‐shifting nanophosphors with square arrays of nanoholes with different lattice parameters is reported in this study. It is shown that a low‐cost soft‐nanolithography procedure can be applied to red‐emitting nanophosphors (GdVO4:Eu3+ nanocrystals) to tune their emission properties, attaining a twofold directional enhancement of the emitted light at predesigned emission wavelengths in specific directions.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.05 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
Anisotropic Resistivity Surfaces Produced in ITO Films by Laser-Induced Nanoscale Self-organization
Lopez-Santos, C; Puerto, D; Siegel, J; Macias-Montero, M; Florian, C; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Solis, JAdvanced Optical Materials, 9 (2021) 2001086
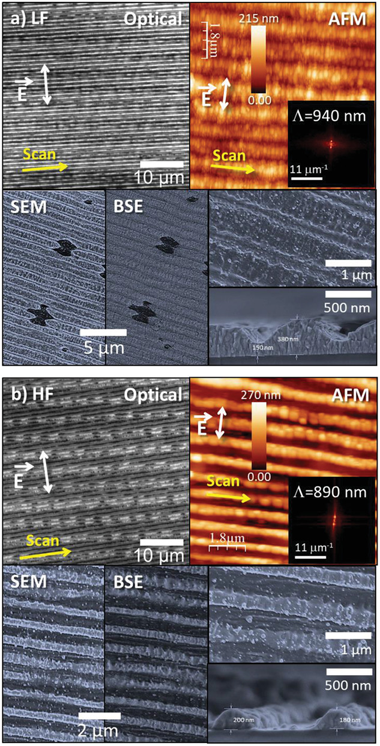
Highly anisotropic resistivity surfaces are produced in indium tin oxide (ITO) films by nanoscale self-organization upon irradiation with a fs-laser beam operating at 1030 nm. Anisotropy is caused by the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) extended over cm-sized regions. Two types of optimized structures are observed. At high fluence, nearly complete ablation at the valleys of the LIPSS and strong ablation at their ridges lead to an insulating structure in the direction transverse to the LIPSS and conductive in the longitudinal one. A strong diminution of In content in the remaining material is then observed, leading to a longitudinal resistivity rho(L) approximate to 1.0 omega center dot cm. At a lower fluence, the material at the LIPSS ridges remains essentially unmodified while partial ablation is observed at the valleys. The structures show a longitudinal conductivity two times higher than the transverse one, and a resistivity similar to that of the pristine ITO film (rho approximate to 5 x 10(-4) omega center dot cm). A thorough characterization of these transparent structures is presented and discussed. The compositional changes induced as laser pulses accumulate, condition the LIPSS evolution and thus the result of the structuring process. Strategies to further improve the achieved anisotropic resistivity results are also provided.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.05 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
The Complex Interplay of Lead Halide Perovskites with Their Surroundings
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2021) 2100133
Photoexcitation of lead halide perovskites induces a restructuration of the material that simultaneously enhances its emission properties and triggers its degradation. These concomitant processes are strongly dependent on the surroundings of the perovskite, both while and after being processed, underlining the relevance the environment and the interfacial design have in the stability and performance of these materials and the devices based on them. This shocking observation reveals that when subjected to external illumination, lead halide perovskites undergo a number of photophysical processes that strongly modify their structure and thus their optoelectronic properties. Such photoinduced instability stems from a defective structure directly linked to the low-temperature and solution-processed fabrication routes generally employed to build perovskite solar cells with efficiencies comparable to state-of-the-art values. On the other hand, these same inexpensive and unsophisticated procedures make this material a promising component in energy conversion devices. Here, an analysis is provided regarding the different impact on the perovskite structure, hence on its optoelectronic performance, that the interaction with its surroundings has, providing specific examples that highlight this interplay, describing the kind of modification it induces, and listing the related effects on the optoelectronic properties that should be accounted for when characterizing them.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.05 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
The Role of the Atmosphere on the Photophysics of Ligand-Free Lead-Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
Moran-Pedroso, M; Rubino, A; Calvo, ME; Espinos, JP; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, (2021) 2100605
Lead halide perovskite (LHP) nanocrystals (NCs) have gained attention over the past decade due to their outstanding optoelectronic properties, making them a suitable material for efficient photovoltaic and light emitting devices. Due to its soft nature, these nanostructures undergo strong structural changes upon irradiation, where these light-induced processes are strongly influenced by the environment. Since most processing routes for LHP NCs are based on colloidal approaches, the role of factors such as stabilizing ligands or solvents is usually hard to disentangle from the interaction of external radiation with the perovskite material. Employing a recently proposed synthetic approach, where ligand-free NCs can be grown within metal-oxide-based insulating nanoporous matrices, it has been feasible to perform a clean study of the effect of the surrounding atmosphere on the photophysical properties of perovskite NCs, avoiding the interference of protective capping layers or solvents. Simultaneous light-induced photo-activation and darkening processes are monitored and disentangled, and their relation with bulk and surface processes, respectively, demonstrated.
| Factor de Impacto Web of Science
10.05 |
DOI | Año
2021 |
icms











