Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monolithic stirrer reactor: The selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase over Au/Al2O3 nanostructured catalysts
Regenhardt, SA; Meyer, CI; Sanz, O; Sebastian, V; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Marchi, AJ; Garetto, TFMolecular Catalysis, 481 (2020) 110219
Show abstract ▽
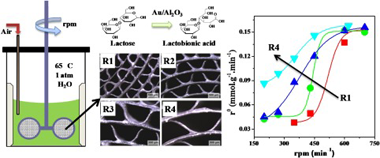
The performance of rotating metallic monolith stirrer reactor was studied for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase at 65 degrees C, atmospheric pressure and with air as oxidant agent. The Au/Al(2)O(3)deposition on metallic substrates was performed by wash-coating, producing catalyst coating thicknesses between 5 and 20 mu m. Monoliths with different configuration (channel size between 0.36 and 1.06 mm) were used as stirrer blades in a batch reactor. Internal and external mass transfer limitations were observed during liquid phase lactose oxidation. For stirring rates equal or higher than 600 rpm there were no important external diffusional restrictions and this was also independent of the monolith configuration. Coating with thickness higher than 15 mu m presents loss of catalyst effectiveness due to internal diffusional restrictions. Excellent stability in the catalytic tests was obtained after three regeneration-reaction cycles. Regeneration was carried out at 400 degrees C in air flow. Gold particle size distribution in the monolith washcoat, determined by TEM before and after reaction, was homogeneous with a medium size of around 5 nm. This is in agreement with the very good reproducibility and stability obtained in the catalytic tests. After calcination at 500 degrees C, some sintering and a heterogeneous distribution of metal particle size was observed, accompanied by a slight loss in catalyst activity. It is concluded that metallic monolith stirrer reactors are a promising application for selective lactose oxidation in liquid phase.
Febrero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2018.10.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of Mn2+-doped ZnS by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJJournal of Materials Science, 55 (2020) 1603-1613
Show abstract ▽
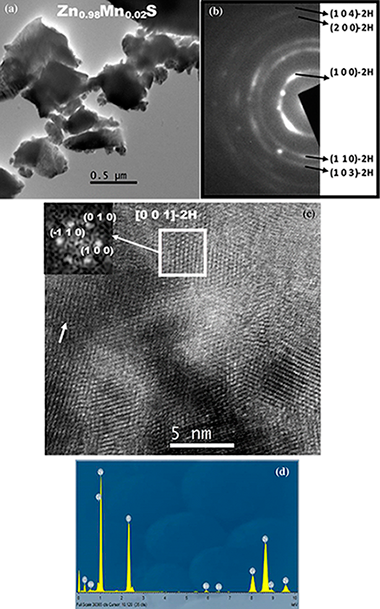
The mechanochemical process denoted as a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction was successfully applied in obtaining Mn-doped ZnS samples with Mn content between 0 and 5 mol%. The process consists in milling Zn/Mn/S powder elemental mixtures with the appropriate stoichiometry, which promotes after approximately 80 min the induction of a combustion reaction. The doping level was properly adjusted by controlling the atomic ratio of the starting mixture. A complete characterization of samples was carried out, including X-ray diffraction, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectroscopy and emission and excitation photoluminescence measurements. A wurtzite structure, in which Mn2+ replaces Zn2+, was obtained with a nanometric character. The photoluminescence of samples showed the characteristic (Mn2+T1)-T-4-(6)A(1) emission that was highly dependent on the doping level. The maximum luminescence efficiency through the ZnS excitation was found for a doping value of 1 mol%. The photoluminescence showed virtually no contribution from the host emission, which confirmed that samples were properly doped.
Febrero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-019-04138-8
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic Performance of Bulk and Al2O3-Supported Molybdenum Oxide for the Production of Biodiesel from Oil with High Free Fatty Acids Content
Navajas, A; Reyero, I; Jimenez-Barrera, E; Romero-Sarria, F; Llorca, J; Gandia, LMCatalysts, 10 (2020) 158
Show abstract ▽
Non-edible vegetable oils are characterized by high contents of free fatty acids (FFAs) that prevent from using the conventional basic catalysts for the production of biodiesel. In this work, solid acid catalysts are used for the simultaneous esterification and transesterification with methanol of the FFAs and triglycerides contained in sunflower oil acidified with oleic acid. Molybdenum oxide (MoO3), which has been seldom considered as a catalyst for the production of biodiesel, was used in bulk and alumina-supported forms. Results showed that bulk MoO3 is very active for both transesterification and esterification reactions, but it suffered from severe molybdenum leaching in the reaction medium. When supported on Al2O3, the MoO3 performance improved in terms of active phase utilization and stability though molybdenum leaching remained significant. The improvement of catalytic performance was ascribed to the establishment of MoO3-Al2O3 interactions that favored the anchorage of molybdenum to the support and the formation of new strong acidic centers, although this effect was offset by a decrease of specific surface area. It is concluded that the development of stable catalysts based on MoO3 offers an attractive route for the valorization of oils with high FFAs content.
Febrero, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/catal10020158
Reactividad de Sólidos
Processing and properties of Bi0.98R0.02FeO3 (R = La, Sm, Y) ceramics flash sintered at similar to 650 degrees C in <5 s
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Raj, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 103 (2020) 136-144
Show abstract ▽
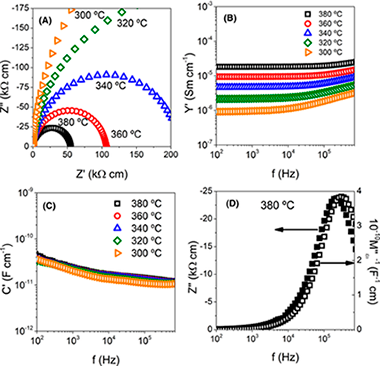
We show that flash sintering produces single‐phase, nanograin‐sized polycrystals of isovalent‐substituted multiferroic ceramics of complex compositions. Single‐phase polycrystals of Bi0.98R0.02FeO3 (R = La, Sm, Y) were produced at a furnace temperature of ~650°C in a few seconds by the application of an electric field of 50 V cm−1, with the current limit set to 40 mA mm−2. The dielectric and insulating properties compared favorably with expected values. Impedance spectroscopy suggests electrically homogenous microstructure, except for the sample Bi0.98La0.02FeO3 that shows a small grain boundary contribution to the impedance. These results reinforce the enabling nature of flash sintering for ceramics which pose difficulties in conventional sintering because they contain low melting constituents or develop secondary phases during the sintering protocol.
Enero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.16718
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Finite Size Effects on Light Propagation throughout Random Media: Relation between Optical Properties and Scattering Event Statistics
Miranda-Munoz, JM; Esteso, V; Jimenez-Solano, A; Lozano, G; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 8 (2020) 1901196
Show abstract ▽
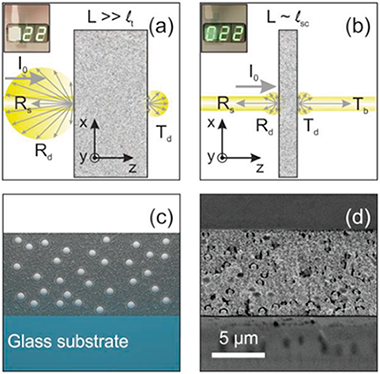
This work introduces a thorough analysis of light transport in thin optically disordered media. The diffusive properties of a turbid material are generally dictated by the transport mean free path, lt. For depths larger than this characteristic length, light propagation can be considered fully randomized. There is however a range of thicknesses for which light becomes only partly randomized, as it only undergoes a single or very few scattering events. The effects of such finitude are experimentally and theoretically studied on the optical properties of the material, such as the angular distribution of scattered light. Simulations provide insight into the phenomena that occur within the optically disordered slab, like the number of scattering events that photons undergo during propagation throughout the material, as a function of the built‐in wavelength dependent scattering mean free path, lsc. This approach provides fundamental information about photon transport in finite optically random media, which can be put into practice to design diffusers with specific requirements in terms of the spectral and angular properties of the scattered light.
Enero, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201901196
- ‹ anterior
- 107 of 410
- siguiente ›














