Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Avanzados
Phyllite clays as raw materials replacing cement in mortars: Properties of new impermeabilizing mortars
Arce, Carolina; Garzon, Eduardo; Sanchez-Soto, Pedro J.Construction and Building Materials, 224 (2019) 348-358
Show abstract ▽

The aim of this investigation was to determine the suitability of phyllite clays as a raw construction material. For that purpose, the cement in mortars was replaced by a phyllite clay (0–90 wt%) making this study the first of its kind to be performed. These materials were prepared with different water proportions according to the water content and water/cement and water/binder (cement plus phyllite clay) relationships. A comparative study of the most important properties of the resulting experimental mortars was carried out, such as apparent density, water retentivity, consistency and mechanical strength (flexural and compressive strength), along with an evaluation of the pozzolanic activity and permeability. The results showed that the increase of phyllite decreases the apparent density, the consistency and mechanical properties of the mortar, while water retentivity fluctuates. Good correlations (R2 > 0.84) were obtained between flexural and compressive strength for the mortars after 28 days of curing. Pozzolanic activity was observed at cement replacement of 80 wt% of phyllite. Moreover, new impermeabilizing mortars constituted by phyllite clay and cement have been obtained according to the low coefficients of permeability. Taking into account the findings of this research, phyllite clays can be applied as raw construction materials with savings derived from replacing cement in mortars and the low energy consumption involved in their production. However, the present study concluded that the use of phyllite clays did not improve the mechanical strength of these new mortars but, in contrast, they can be applied for impermeabilization purposes in Construction and Civil Engineering.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.081
Materiales Coloidales
Encapsulation of Upconversion Nanoparticles in Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas
Rahmani, S; Jimenez, CM; Aggad, D; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Ocana, M; Ali, LMA; Nguyen, C; Nieto, AIB; Francolon, N; Oliveiro, E; Boyer, D; Mahiou, R; Raehm, L; Gary-Bobo, M; Durand, JO; Charnay, CMolecules, 24 (2019) 22
Show abstract ▽
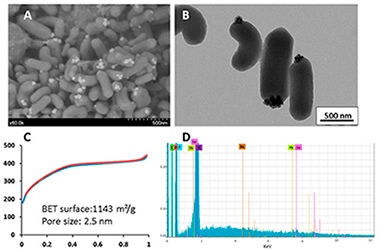
(1) Background: Nanomedicine has recently emerged as a promising field, particularly for cancer theranostics. In this context, nanoparticles designed for imaging and therapeutic applications are of interest. We, therefore, studied the encapsulation of upconverting nanoparticles in mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. Indeed, mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles have been shown to be very efficient for drug delivery, and upconverting nanoparticles are interesting for near-infrared and X-ray computed tomography imaging, depending on the matrix used. (2) Methods: Two different upconverting-based nanoparticles were synthesized with Yb3+-Er3+ as the upconverting system and NaYF4 or BaLuF5 as the matrix. The encapsulation of these nanoparticles was studied through the sol-gel procedure with bis(triethoxysilyl)ethylene and bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane in the presence of CTAB. (3) Results: with bis(triethoxysilyl)ethylene, BaLuF5: Yb3+-Er3+, nanoparticles were not encapsulated, but anchored on the surface of the obtained mesoporous nanorods BaLuF5: Yb3+-Er3+@Ethylene. With bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane, BaLuF5: Yb3+-Er3+ and NaYF4: Yb3+-Er(3+)nanoparticles were encapsulated in the mesoporous cubic structure leading to BaLuF5: Yb3+-Er3+@Ethane and NaYF4: Yb3+-Er3+@Ethane, respectively. (4) Conclusions: upconversion nanoparticles were located on the surface of mesoporous nanorods obtained by hydrolysis polycondensation of bis(triethoxysilyl)ethylene, whereas encapsulation occurred with bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane. The later nanoparticles NaYF4: Yb3+-Er3+@Ethane or BaLuF5: Yb3+-Er3+@Ethane were promising for applications with cancer cell imaging or X-ray-computed tomography respectively.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/molecules24224054
Reactividad de Sólidos
Graphene nanoplatelets for electrically conductive 3YTZP composites densified by pressureless sintering
Lopez-Pernia, C; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, RJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (2015) 4435-4439
Show abstract ▽
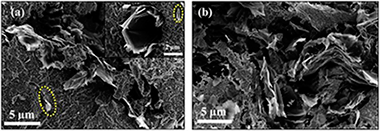
3 mol% yttria tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline (3YTZP) ceramic composites with 2.5, 5 and 10 vol% graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) were pressureless sintered in argon atmosphere between 1350 and 1450 degrees C. The effects of the GNP content and the sintering temperature on the densification, microstructure and electrical properties of the composites were investigated. An isotropic distribution of GNP surrounding ceramic regions was exhibited regardless the GNP content and sintering temperature used. Electrical conductivity values comparable to the ones of fully dense composites prepared by more complex techniques were obtained, even though full densification was not achieved. While the composite with 5 vol% GNP exhibited electrical anisotropy with a semiconductor-type behaviour, the composite with 10 vol% GNP showed an electrically isotropic metallic-type behaviour.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.05.067
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Kinetic energy-induced growth regimes of nanocolumnar Ti thin films deposited by evaporation and magnetron sputtering
Alvarez, R.; Garcia-Valenzuela, A.; Rico, V; Garcia-Martin, J. M.; Cotrino, J.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A. R.; Palmero, A.Nanotechnology, 30 (2019) 475603
Show abstract ▽
We experimentally analyze different growth regimes of Ti thin films associated to the existence of kinetic energy-induced relaxation mechanisms in the material's network when operating at oblique geometries. For this purpose, we have deposited different films by evaporation and magnetron sputtering under similar geometrical arrangements and at low temperatures. With the help of a well-established growth model we have found three different growth regimes: (i) low energy deposition, exemplified by the evaporation technique, carried out by species with typical energies in the thermal range, where the morphology and density of the film can be explained by solely considering surface shadowing processes, (ii) magnetron sputtering under weak plasma conditions, where the film growth is mediated by surface shadowing mechanisms and kinetic-energy-induced relaxation processes, and (iii) magnetron sputtering under intense plasma conditions, where the film growth is highly influenced by the plasma, and whose morphology is defined by nanocolumns with similar tilt than evaporated films, but with much higher density. The existence of these three regimes explains the variety of morphologies of nanocolumnar Ti thin films grown at oblique angles under similar conditions in the literature.
Noviembre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab3cb2
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Comparison of the effects generated by the dry-soft grinding and the photodeposition of Au and Pt processes on the visible light absorption and photoactivity of TiO2
Galeano, L; Valencia, S; Marin, JM; Restrepo, G; Navio, JA; Hidalgo, MCMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) 1050d9
Show abstract ▽
The influence of dry-soft grinding and photodeposition of gold (Au) or platinum (Pt) in the improvement of the photoactivity of TiO2 synthesized by an integrated sol-gel and solvothermal method was studied. TiO2 was modified by a dry-soft grinding process in a planetary ball mill (TiO2(G)). Subsequently, Au or Pt particles were photodeposited in both unmodified TiO2 and TiO2(G) obtaining Au-TiO2, Pt-TiO2, Au-TiO2(G), and Pt-TiO2(G) materials. The photoactivity of the materials was evaluated in the phenol photodegradation under simulated solar radiation. Pt-TiO2 showed the greatest degree of photoactivity improvement in comparison with TiO2 and TiO2-P25. The dry-soft grinding process led to a high photocatalytic activity of TiO2(G) that was similar to Pt-TiO2 activity as consequence of a slight increase in the crystallinity in TiO2(G) due to an additional anatase formation in comparison with TiO2. However, further photocatalytic improvement in TiO2(G) were not achieved with the addition of Au or Pt. Therefore, the dry-soft grinding treatment and noble metal deposition led to similar improvements in the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 for phenol oxidation.
Octubre, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab4316
- ‹ anterior
- 113 of 410
- siguiente ›














