Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Materiales Coloidales
Luminescence and X-ray Absorption Properties of Uniform Eu3+:(H3O)Lu3F10 Nanoprobes
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Balcerzyk, M; Ocana, MNanomaterials, 9 (2019) 1153
Show abstract ▽

Due to the high atomic number of lutetium and the low phonon energy of the fluoride matrix, Lu-based fluoride nanoparticles doped with active lanthanide ions are potential candidates as bioprobes in both X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging. This paper shows a method for the fabrication of uniform, water-dispersible Eu3+:(H3O)Lu3F10 nanoparticles doped with different Eu contents. Their luminescent properties were studied by means of excitation and emission spectra as well as decay curves. The X-ray attenuation capacity of the phosphor showing the highest emission intensity was subsequently analyzed and compared with a commercial contrast agent. The results indicated that the 10% Eu3+-doped (H3O)Lu3F10 nanoparticles fabricated with the proposed polyol-based method are good candidates to be used as dual probes for luminescent imaging and X-ray computed tomography.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/nano9081153
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Natural abundance O-17 MAS NMR and DFT simulations: New insights into the atomic structure of designed micas
Pavon, E; Osuna, FJ; Alba, MD; Delevoye, LSolid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 100 (2019) 45-51
Show abstract ▽
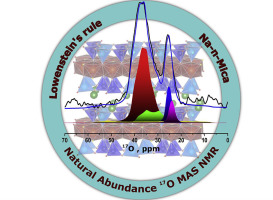
Combining O-17 Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR at natural abundance with DFT calculations is a promising methodology to shed light on the structure and disorder in tetrahedral sheets of designed micas with enhanced properties. Among brittle micas, synthetic mica is an important alternative to natural ones with a swelling sheet-like structure that results in many applications, by exploiting unique characteristics. Lowenstein's rule is one of the main chemical factor that determines the atomic structure of aluminosilicates and furthermore their properties. In the present article, O-17 MAS NMR spectroscopy is used to validate (or not) the agreement of the Lowenstein's rule with the distribution of Si and Al sites in the tetrahedral sheets of synthetic micas. O-17 MAS spectra of synthetic high-charged micas exhibit two regions of signals that revealed two distinguishable oxygen environments, namely Si-O-X (with X = Si, Al-tet , Mg) and Al-tet -O-Y (Y=Mg or Al-tet). DFT calculations were also conducted to obtain the O-17 chemical shift and other NMR features like the quadrupolar coupling constant, C-Q, for all of the oxygen environments encountered in the two model structures, one respecting the Lowenstein's rule and the other involving Al-tet -O-Al-tet and Si-O-Si environments. Our DFT calculations support the O-17 assignment, by confirming that Al-tet -O-3Mg and Al tet -O-Al tet oxygen environments show chemical shifts under 30 ppm and more important, with quadrupolar coupling constants of about 1 MHz, in line with the spectral observation. By quantifying the O-17 MAS NMR spectra at natural abundance, we demonstrate that one of the synthetic mica compositions does not meet the Lowenstein's rule.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2019.03.006
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Carbon Supported Gold Nanoparticles for the Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol
Molina, HR; Munoz, JLS; Leal, MID; Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Gallego, MNC; Odriozola, JAFrontiers in Chemistry, 7 (2019) 548
Show abstract ▽
This work is a detailed study on how to optimize gold colloids preparation and their deposition to very different in nature carbon materials. The change of the continuous phase and its dielectric constant is used to assure the good dispersion of the hydrophilic/hydrophobic carbons and the successful transfer of the preformed small size colloids to their surface. The sintering behavior of the particles during the calcination step is also studied and the optimal conditions to reduce to a minimum the particle size increase during the protecting agent removal phase are found. The as prepared catalysts have been tested in a relevant reaction in the field of environmental catalysis such as the reduction of 4-nitrophenol leading to promising results. Overall, this work proposes an important methodology to follow when a carbonaceous material are selected as catalyst supports for green chemistry reactions.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00548
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Higher hydration performance and bioactive response of the new endodontic bioactive cement MTA HP repair compared with ProRoot MTA white and NeoMTA plus
Jimenez-Sanchez, Maria Del Carmen; Segura-Egea, Juan Jose; Diaz-Cuenca, AranzazuJournal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials, 107 (2019) 2109-2120
Show abstract ▽
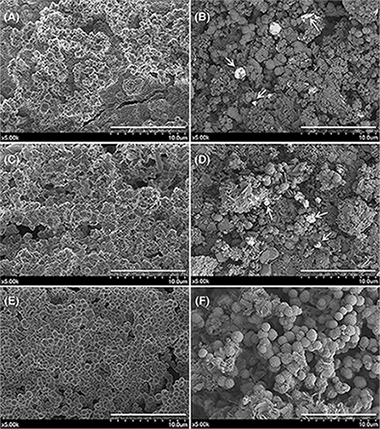
The aim of this study was to characterize the hydration performance and the bioactive response of the new bioactive endodontic cement MTA HP repair (HP), comparing its physicochemical parameters with those of ProRoot MTA White (Pro) and NeoMTA Plus (Neo). Un-hydrated precursor materials were characterized by X-ray fluorescence, laser diffraction, N2 physisorption and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM). Setting time was assessed according to ASTM specification C 266. Hydrated materials were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and (FEG-SEM). Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out, by soaking processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF) during 168 h. The cements surface was studied by FT-IR, FEG-SEM, and energy dispersive X-ray. Release to the SBF media of ionic degradation products was monitored using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. HP showed shorter initial setting time compared to Pro and Neo and produce a quick and effective bioactive response in vitro in terms of phosphate phase surface coating formation. This higher bioactive response for HP is correlated with increasing calcium aluminate content, increasing surface area of un-hydrated powder precursor and the increasing release capacity of Si ionic products of the final hydrated product. The higher bioactive response of MTA HP repair highlights this material, as very interesting to further investigate its performance to improve the outcome of vital pulp therapy procedures.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/jbm.b.34304
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Noble Metal Supported on Activated Carbon for "Hydrogen Free" HDO Reactions: Exploring Economically Advantageous Routes for Biomass Valorisation
Jin, W; Santos, JL; Pastor-Perez, L; Gu, S; Centeno, MA; Reina, TRChemcatchem (2019) 4434-4441
Show abstract ▽
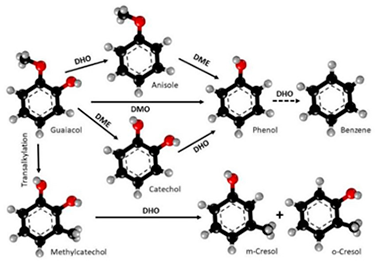
An innovative route for bio‐compounds upgrading via “hydrogen‐free” hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is proposed and evaluated using guaiacol as a model compound in a high‐pressure batch reactor. Experimental results showed that noble metal supported on activated carbon catalysts are able to conduct tandem multiple steps including water splitting and subsequent HDO. The activity of Ru/C catalyst is superior to other studied catalysts (i. e. Au/C, Pd/C and Rh/C) in our water‐only HDO reaction system. The greater dispersion and smaller metal particle size confirmed by the TEM micrographs accounts for the better performance of Ru/C. This material also presents excellent levels of stability as demonstrated in multiple recyclability runs. Overall, the proposed novel approach confirmed the viability of oxygenated bio‐compounds upgrading in a water‐only reaction system suppressing the need of external H2 supply and can be rendered as a fundamental finding for the economical biomass valorisation to produce added value bio‐fuels.
Agosto, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900841
- ‹ anterior
- 119 of 410
- siguiente ›














