Artículos SCI
2023
2023
Reactividad de Sólidos
Touch-free reactive flash sintering of dense strontium hexaferrite permanent magnet
Jalali, SIA; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Chacartegui, R; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Raj, R; Pérez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society (2023)
Show abstract ▽
This work presents an extension of the touch-free flash sintering technique. In the proposed technique, chemical reaction and sintering occur in a single step, without the use of electrodes, in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. We show that a dense, single-phase strontium hexaferrite magnet can be produced from a mixture of commercial carbonate and oxide powders in a single step in a little more than a minute. This new technique implies significant reduction in energy and time consumption (primarily because of ultrafast processing) relative to conventional sintering.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.19389
Ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized by 1,2,3-triazolylidene ligands in the hydrogen isotope exchange of E-H bonds (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) using deuterium gas
Molinillo, P; Puyo, M; Vattier, F; Lacroix, B; Rendon, N; Lara, P; Suarez, ANanoscale
Show abstract ▽
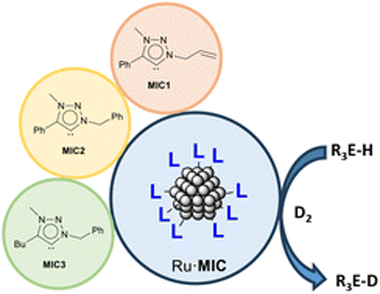
A series of ruthenium nanoparticles (Ru & BULL;MIC) stabilized with different mesoionic 1,2,3-triazolylidene (MIC) ligands were prepared by decomposition of the Ru(COD)(COT) (COD = 1,5-cyclooctadiene; COT = 1,3,5-cyclooctatriene) precursor with H-2 (3 bar) in the presence of substoichiometric amounts of the stabilizer (0.1-0.2 equiv.). Small and monodisperse nanoparticles exhibiting mean sizes between 1.1 and 1.2 nm were obtained, whose characterization was carried out by means of transmission electron microscopy (TEM), including high resolution TEM (HRTEM), inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). In particular, XPS measurements confirmed the presence of MIC ligands on the surfaces of the nanoparticles. The Ru & BULL;MIC nanoparticles were used in the isotopic H/D exchange of different hydrosilanes, hydroboranes, hydrogermananes and hydrostannanes using deuterium gas under mild conditions (1.0 mol% Ru, 1 bar D-2, 55 & DEG;C). Selective labelling of the E-H (E = B, Si, Ge, Sn) bond in these derivatives, with high levels of deuterium incorporation, was observed.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/d3nr02637j
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Plasmas and acoustic waves to pattern the nanostructure and chemistry of thin films
Rico, V; Regodon, GF; Garcia-Valenzuela, A; Alcaide, AM; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Rojas, TC; Alvarez, R; Palomares, FJ; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARActa Materialia, 255 (2023) 119058
Show abstract ▽
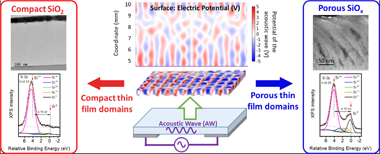
In this work, piezoelectric AWs and plasmas have been brought together during the growth of a thin film as a novel methodology of plasma-assisted thin film structuration. The ensuing effects have been investigated on a model system where SiO2 and SiOx (x<2) thin films have been deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles (MS-OAD) on an electro-acoustically excited LiNbO3 piezoelectric substrate under resonant conditions. The microstructure of the resulting films was 2D patterned and depicted submillimeter size intermingled zones with different optical characteristics, compositions (SiO2 and SiOx) and porosity, from highly porous to dense and compact regions. The 2D nanostructural pattern mimics the AW distribution and has been accounted for by means of a specific simulation model. It is concluded that the morphological and chemical film pattern replicates the distribution of polarization potential on the surface of the AW activated substrate immersed in the plasma. Moreover, we show that the main mechanism responsible for the appearance of domains with different morphology and chemical composition is the focused impingement of Ar+plasma ions on certain regions of the substrate. The general character of this patterning process, the underlying physics and its possibilities to tailor the composition and microstructure of dielectric thin film materials are discussed.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.119058
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Charting a path to catalytic upcycling of plastic micro/nano fiber pollution from textiles to produce carbon nanomaterials and turquoise hydrogen
Silvia Parrilla-Lahoz; Marielis C. Zambrano; Vlad Stolojan; Rachida Bance-Soualhi; Joel J. Pawlak; Richard A. Venditti; Tomas Ramirez Reina; Melis S. DuyarRSC Sustainability, 1 (2023) 1177-1183
Show abstract ▽
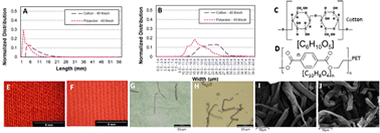
Washing synthetic textile fibers releases micro/nano plastics, endangering the environment. As new filters and associated regulations are developed to prevent fiber release from washing machines, there emerges a need to manage the collected waste, for which the only current options are combustion or landfill. Herein we show for the first time the application of a catalytic pyrolysis approach to upcycle textile derived fibrous micro/nano plastics waste, with the aim of keeping carbon in the solid phase and preventing its release as a greenhouse gas. Herein, we demonstrate the co-production of hydrogen and carbon nanomaterials from the two most prevalent global textile microfiber wastes: cotton and polyester. Our results pave a way forward to a realistic process design for upcycling mixed micro/nano fiber waste collected from laundering, drying, vacuuming, and environmental cleanup.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1039/D3SU00095H
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Ti6Al4V coatings on titanium samples by sputtering techniques: Microstructural and mechanical characterization
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Rodriguez-Albelo, M; Sanchez-Perez, M; Godinho, V; Lopez-Santos, C; Torres, YJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 952 (2023) 170018
Show abstract ▽

Although titanium is widely used as biomaterial, the control of the interface properties between its surface and the surrounding physiological environment (like bone, other tissues or biofluids) results crucial to achieve a successful osseointegration and good biomechanical and functional performance. In this work, commercially pure titanium (Grade IV) discs obtained by conventional powder metallurgy were coated with 1-3 mu m of Ti6Al4V (Grade V) alloy using DC-pulsed or high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS) technique with the aim of improving their biomedical performance. SEM, confocal microscopy, X-ray dif-fraction, nanoindentation and wetting measurements are used to evaluate the bio-interface role of the titanium-coated implants. Conformal Ti6Al4V coatings with controlled nano-roughness can be deposited with enhanced mechanical (H = 5-8 GPa; E = 140-160 GPa) and hydrophobic properties thanks to a dense columnar structure. The increased Ti-O bonding at the interface helps to prevent the corrosion due to the formation of a surface passivation layer. Particularly in the case of the HiPIMS process, the surface mod-ification of titanium implants (chemistry, morphology and structure) appears as an effective strategy for satisfying the biomedical requirements and functionality, with enhanced mechanical properties and na-nostructuration for prevention of bacteria colonization.
Agosto, 2023 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170018
- ‹ anterior
- 17 of 412
- siguiente ›














