Artículos SCI
2022
2022
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Strength and thermal shock resistance of fiber-bonded Si-Al-C-O and Si-Ti-C-O ceramics
Vera, MC; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, M; Ramirez-Rico, JInternational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 19 (2022) 1126-1135
Show abstract ▽
Silicon carbide-based fiber-bonded ceramics, obtained from hot pressing of woven silicon carbide fibers, are a cost-effective alternative to ceramic-matrix composites due to their ease of fabrication, involving few processing steps, and competitive thermomechanical properties. In this work, we studied the high-temperature strength and thermal shock resistance of Si-Al-C-O and Si-Ti-C-O fiber-bonded SiC ceramics obtained from hot pressing of two types of ceramic fibers, by mechanical testing in four-point bending. The bending strength of Si-Al-C-O-based fiber-bonded ceramics at room temperature is similar to 250-260 MPa and remains constant with temperature, while the bending strength of Si-Ti-C-O increases slightly from the initial 220 to similar to 250 MPa for the highest temperature. Both materials retain up to 90% of their room temperature strength after thermal shocks of 1400 degrees C and show no reduction in elastic moduli. After thermal shock, failure mode is the same as in the case of as-received materials.
Marzo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1111/ijac.13928
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multiscale ultrafast laser texturing of marble for reduced surface wetting
Ariza, R; Alvarez-Alegria, M; Costas, G; Tribaldo, L; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Siegel, J; Solis, JApplied Surface Science, 577 (2022) 152850
Show abstract ▽
The modification of the wetting properties of marble surfaces upon multi-scale texturing induced by ultrafast laser processing (340 fs pulse duration, 1030 nm wavelength) has been investigated with the aim of evaluating its potential for surface protection. The contact angle (CA) of a water drop placed on the surface was used to assess the wettability of the processed areas. Although the surfaces are initially hydrophilic upon laser treatment, after a few days they develop a strong hydrophobic behavior. Marble surfaces have been irradiated with different scan line separations to elucidate the relative roles of multi-scale roughness (nano-and micro-texture) and chemical changes at the surface. The time evolution of the contact angle has been then monitored up to 11 months after treatment. A short and a long-term evolution, associated to the combined effect of multi-scale roughness and the attachment of chemical species at the surface over the time, have been observed. XPS and ATR measurements are consistent with the progressive hydroxylation of the laser treated surfaces although the additional contribution of hydrocarbon adsorbates to the wettability evolution cannot be ruled-out. The robustness of the results has been tested by CA measurements after cleaning in different conditions with very positive results.
Marzo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151850
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Rhodamine 6G and 800 intermolecular heteroaggregates embedded in PMMA for near-infrared wavelength shifting
Castillo-Seoane, J; Gonzalez-García, L; Obrero-Pérez, JM; Aparicio, FJ; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JRJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 10 (2022) 7119-7131
Show abstract ▽
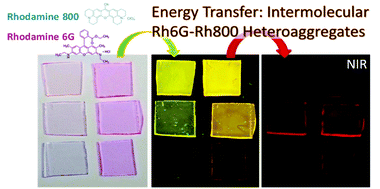
The opto-electronic properties of small-molecules and functional dyes usually differ when incorporated into solid matrices with respect to their isolated form due to an aggregation phenomenon that alters their optical and fluorescent properties. These spectroscopic modifications are studied in the framework of the exciton theory of aggregates, which has been extensively applied in the literature for the study of molecular aggregates of the same type of molecules (homoaggregation). Despite the demonstrated potential of the control of the heteroaggregation process (aggregation of different types of molecules), most of the reported works are devoted to intramolecular aggregates, complex molecules formed by several chromophores attached by organic linkers. The intramolecular aggregates are specifically designed to hold a certain molecular structure that, on the basis of the exciton theory, modifies their optical and fluorescent properties with respect to the isolated chromophores that form the molecule. The present article describes in detail the incorporation of Rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) and 800 (Rh800) into polymeric matrices of poly-(methyl methacrylate), PMMA. The simultaneous incorporation of both dyes results in an enhanced fluorescent emission in the near-infrared (NIR), originating from the formation of ground-state Rh6G-Rh800 intermolecular heteroaggregates. The systematic control of the concentration of both rhodamines provides a model system for the elucidation of the heteroaggregate formation. The efficient energy transfer between Rh6G and Rh800 molecules can be used as wavelength shifters to convert effectively the light from visible to NIR, a very convenient wavelength range for many practical applications which make use of inexpensive commercial detectors and systems.
Marzo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1039/d1tc06167d
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel Multi-Phase Flash Sintering (MPFS) technique for 3D complex-shaped ceramics
Molina-Molina, S; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Duran-Olivencia, FJ; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Pérez-Maqueda, LAApplied Materials Today, 26 (2022) 101274
Show abstract ▽
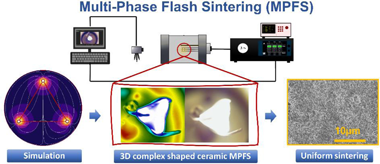
This work demonstrates the first proof-of-concept of Multi-Phase Flash Sintering (MPFS). This novel technique essentially consists of applying a rotating electric field to the sample by means of a multi-phase voltage source as furnace temperature increases. Several ceramic materials with different types of electrical conductivities are sintered within seconds at furnace temperatures much lower than those used for traditional DC flash sintering due to the higher power densities administered by a multi-phase power supply. Thus, ceramic materials are flashed at relatively lower applied voltages which minimizes undesired phenomena such as localization and preferential current pathways. Furthermore, MPFS allows diverse electrode configurations to promote a more uniform electric field distribution, enhancing the sintering of 3D complex-shaped specimens. MPFS could be a true breakthrough in materials processing, as 3D complex-shaped specimens are homogeneously sintered at reduced temperatures, while keeping all the advantages of conventional flash sintering.
Marzo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101274
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Analysis of Dry Reforming as direct route for gas phase CO2 conversion. The past, the present and future of catalytic DRM technologies
le Sache, E; Reina, TRProgress in Energy and Combustion Science, 89 (2022) 100970
Show abstract ▽
Transition to low carbon societies requires advanced catalysis and reaction engineering to pursue green routes for fuels and chemicals production as well as CO2 conversion. This comprehensive review provides a fresh perspective on the dry reforming of methane reaction (DRM) which constitutes a straightforward approach for effective CO2 conversion to added value syngas. The bottleneck for the implementation of this process at industrial scale is the development of highly active and robust heterogeneous catalysts able to overcome the CO2 activation barrier and deliver sufficient amount of the upgrading products at the desired operation conditions. Also, its high energy demand due to the endothermic nature of the reaction imposes extra difficulties. This review critically discusses the recent progresses on catalysts design ranging from traditional metal-supported catalysts to advanced structured and nanostructured systems with promising performance. The main advantages and culprits of the different catalytic systems are introduced aiming to inspire the catalysis community to further refine these formulations towards the development of "supercatalysts" for DRM. Besides the design of increasingly complex catalyst morphologies as well as other promising alternatives aiming at reducing the energy consumption of the process or tackle deactivation through reactor design are introduced.
Marzo, 2022 | DOI: 10.1016/j.pecs.2021.100970
- ‹ anterior
- 56 of 410
- siguiente ›














