Scientific Papers in SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Large-scale high-temperature solar energy storage using natural minerals
Benitez-Guerrero, Monica; Sarrion, Beatriz; Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.; Manuel Valverde, JoseSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 168 (2017) 14-21 DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.04.013
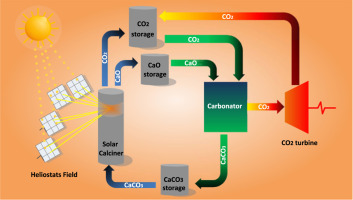
Abstract
The present work is focused on thermochemical energy storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants by means of the Calcium-Looping (CaL) process using cheap, abundant and non-toxic natural carbonate minerals. CaL conditions for CSP storage involve calcination of CaCO3 in the solar receiver at relatively low temperature whereas carbonation of CaO is carried out at high temperature and high CO2 concentration to use the heat of reaction for power production by means of a CO2 closed power cycle. Under these conditions, large CaO particles derived from limestone to be used in industrial processes are rapidly deactivated due to pore plugging, which limits the extent of the reaction. This is favored by the relatively small pores of the CaO skeleton generated by low temperature calcination, the large thickness of the CaCO3 layer built upon the CaO surface and the very fast carbonation kinetics. On the other hand, at CaL conditions for CSP storage does not limit carbonation of CaO derived from dolomite (dolime). Dolime is shown to exhibit a high multicycle conversion regardless of particle size, which is explained by the presence of inert MgO grains that allow the reacting gas to percolate inside the porous particles.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.04.013
The epigraphic stela of Montoro (Cordoba): the earliest monumental script in Iberia?
Sanjuan, LG; Diaz-Guardamino, M; Wheatley, DW; Barra, JPV; Rodriguez, JAL; Rogerio-Candelera, MA; Erbez, AJ; Barker, D; Strutt, K; Ariza, MCAntiquity, 91 (2017) 916-932 DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2017.86
Abstract
A remarkable stela from Montoro, southern Spain, is unique in its morphology, epigraphic traits and landscape context. A programme of chemical characterisation, digital imaging, and geo-lithological and epigraphic analyses were conducted to determine its age and significance, and the results were integrated with data from archaeological investigations of the surrounding area. This multi-faceted approach allowed the stela to be interpreted within the context of early interactions between literate Mediterranean societies of the Late Bronze Age and Iron Age and non-literate Iberian societies. A key outcome of this research is a wider understanding of the complex patterns in the use and perception of early scripts.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2017.86
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
One-reactor plasma assisted fabrication of ZnO@TiO2 multishell nanotubes: assessing the impact of a full coverage on the photovoltaic performance
Filippin, Alejandro Nicolas; Macias-Montero, Manuel; Saghi, Zineb; Idigoras, Jesus; Burdet, Pierre; Sanchez-Valencia, Juan R.; Barranco, Angel; Migdley, Paul A.; Anta, Juan A.; Borras, AnaScientific Reports, 7 (2017) art 9621 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09601-7
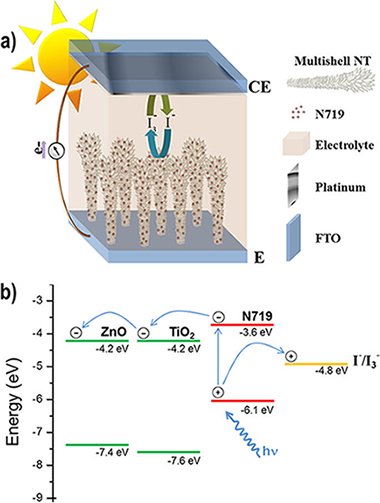
Abstract
This paper addresses the fabrication of vertically aligned ZnO@TiO2multishell nanotubes by a combined full vacuum-plasma approach at mild temperatures. The growth is carried out within the premises of a one-reactor approach, i.e. minimizing the number of vacuum chambers and sample transferences. In this way, the interface between ZnO and TiO2 is fully preserved from humidity thus increasing ZnO durability and stability. These nanostructures are studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy in STEM (EDX-STEM). High density one-dimensional arrays of these nanotubes formed on FTO substrates are applied as photoanode in a dye-sensitized solar cell (DSC). The evolution of the dye adsorption capacity and solar cells parameters are explored as a function of the crystallinity and thickness of the TiO2 shell. The results show the critical effect of a full coverage by TiO2 of ZnO core to explain the mixed results found in the literature.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09601-7
Reactividad de Sólidos
Flash sintering of highly insulating nanostructured phase-pure BiFeO3
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Lebrun, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Raj, RJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 100 (2017) 3365-3369 DOI: 10.1111/jace.14990
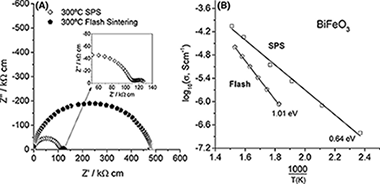
Abstract
We show that BiFeO3, that is electrically homogeneous, is a good insulator, and has a low dielectric constant (the properties desired in its applications), can be produced by flash sintering, which is nominally difficult to achieve by conventional and spark plasma sintering processes. The flash-sintered specimens had a uniform microstructure with a nanometric grain size of similar to 20 nm.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.14990
Materiales Avanzados
Thermal study of residues from greenhouse crops plant biomass
Morales, Laura; Garzon, Eduardo; Maria Martinez-Blanes, Jose; Jose Sanchez-Soto, PedroJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 129 (2017) 1111-1120 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6243-2

Abstract
The principal aim of this work is to examine the effect of thermal treatments using a muffle furnace (static heating) and by simultaneous TG/DTA (dynamic heating) on selected greenhouse crops plant biomass investigated here as the first time. The effect of fractionation by sieving (<25 and <2.5 mm), preheating at 150 °C for 48 h and leaching with water on the thermal behavior has been studied. The observation of similar profiles of mass variation corresponding to several samples heated in air up to 1150 °C allows to conclude that particle size did not influence the thermal evolution, but the effect of heating cycle is evidenced. Thermal analysis in air of a representative sample showed the several mass variation steps and DTA exothermic effects produced by the complex thermal decomposition and pyrolysis of the organic matter. Elemental analysis (CHNS and O) of the starting samples and thermally treated revealed the effect of the temperature, with formation of ashes with lower C content from 44.37 to 0.70 mass% as a minimum after elimination of organic matter by heating. Leaching increased the thermal mass variation as an effect of elimination of water-soluble components. According to the present results, the size fractionation of the greenhouse crops biomass did not influence the results of elemental composition. The present study has provided results of interest concerning this biomass source of renewable energy originated by the remains of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), being estimated the highest of all the biomass produced by the greenhouse crops agricultural industry in Almería (SE Spain).
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-017-6243-2
Reactividad de Sólidos
Simultaneous adsorption and photocatalytic behavior of hybrid mesoporous ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite
Emrooz, HBM; Gotor, FJMaterials Research Express, 4 (2017) art. 085037 DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aa85cf
Abstract
Mesoporous ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite was synthesized with a facile process. At first a large pore volume (1.86 cm(3).g(-1)), moderate pore size (about 12.8 nm) and moderate surface area (586 m(2).g(-1)) mesoporous SiO2 was synthesized in an acidic PH using cationic surfactant. ZnS nanoparticles were infiltrated in the porosities of the synthesized SiO2, with a room temperature post grafting method. The synthesized particles have been characterized with transmission electron microscopy (TEM), x-ray diffraction (XRD), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), furrier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). Results confirm the mesoporous characteristics of ZnS-SiO2 nanocomposite with specific surface area as high as 248 m(2).g(-1), pore volume of 0.89 cm(3).g(-1) and average pore diameter of about 14.4 nm. Simultaneous adsorption-photocatalytic behavior of this hybrid mesoporous nanocomposite for degradation of methylene blue (MB) was investigated. The efficiency of this material was compared with that of mesoporous SiO2 and also lone ZnS nanoparticles. Results showed that by using ultraviolet irradiation, ZnS-SiO2 can degrade greater than 85% of MB only after 3 min. The case for lone ZnS is less than 5% after 30 min. Degradation mechanism of MB using ZnS-SiO2 and ultraviolet radiation was explained with simultaneous adsorption and photocatalytic phenomena. Ultraviolet irradiation can degrade adsorbed MB of mesoporous SiO2 which can prevent it from saturation.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/aa85cf
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties and electronic transitions of zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Tougaard, SApplied Optics, 56 (2017) 6611-6621 DOI: 10.1364/AO.56.006611
Abstract
Optical properties and electronic transitions of four oxides, namely zinc oxide, ferric oxide, cerium oxide, and samarium oxide, are determined in the ultraviolet and extreme ultraviolet by reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy using primary electron energies in the range 0.3 - 2.0 keV. This technique allows the evaluation of the optical response in these ultraviolet spectral regions of a thin layer of material, and the analysis is straightforward. It is performed within the dielectric response theory by means of the QUEELS-epsilon(k,omega)-REELS software developed by Tougaard and Yubero [Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 824 ( 2004)]. The method consists basically in the fitting of experimentally determined single-scattering electron energy loss cross sections with a parametric energy loss function of the corresponding material, to the one calculated within a dielectric response formalism. The obtained refractive index and extinction coefficients, as well as the identified electronic transitions are compared, when available, with previously published results.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1364/AO.56.006611
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cutin from agro-waste as a raw material for the production of bioplastics
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Heredia, A; Dominguez, E; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Athanassiou, A; Benitez, JJJournal of Experimental Botany, 68 (2017) 5401-5410 DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx272
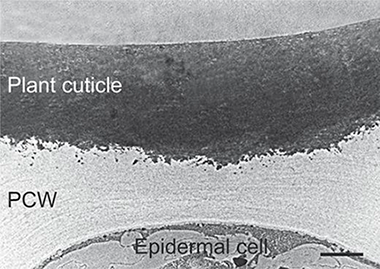
Abstract
Cutin is the main component of plant cuticles constituting the framework that supports the rest of the cuticle components. This biopolymer is composed of esterified bi- and trifunctional fatty acids. Despite its ubiquity in terrestrial plants, it has been underutilized as raw material due to its insolubility and lack of melting point. However, in recent years, a few technologies have been developed to obtain cutin monomers from several agro-wastes at an industrial scale. This review is focused on the description of cutin properties, biodegradability, chemical composition, processability, abundance, and the state of art of the fabrication of cutin-based materials in order to evaluate whether this biopolymer can be considered a source for the production of renewable materials.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx272
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
The role of cobalt hydroxide in deactivation of thin film Co-based catalysts for sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; Hufschmidt, D; de Haro, MCJ; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 210 (2017) 342-351 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.005
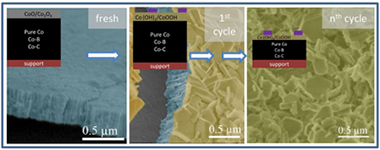
Abstract
Deactivation of a Co catalyst prepared as thin film by magnetron sputtering was studied for the sodium borohydride (SB) hydrolysis reaction under different conditions. Under high SB concentration in single run experiments, the formation of a B-O passivating layer was observed after 1.5 and 24 h use. This layer was not responsible for the catalyst deactivation. Instead, a peeling-off mechanism produced the loss of cobalt. This peeling-off mechanism was further studied in cycling experiments (14 cycles) under low SB concentrations. Ex-situ study of catalyst surface after use and solid reaction products (precipitates) was performed by X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). The presence of cobalt hydroxide and oxyhydroxide was detected as major components on the catalyst surface after use and as precipitates in the supernatant solutions after washing. Cobalt borate, cobalt carbonate and oxycarbonate were also formed but in lesser amounts. These oxidized cobalt species were formed and further detached from the catalyst at the end of the reaction and/or during catalyst washing by decomposition of the unstable in-situ formed cobalt boride. Leaching of cobalt soluble species was negligible. Thin film mechanical detachment was also found but in a smaller extent. To study the influence of catalyst composition on deactivation processes, cycling experiments were performed with Co-B and Co-C catalysts, also prepared as thin films. We found that the deactivation mechanism proposed by us for the pure Co catalyst also occurred for a different pure Co (prepared at higher pressure) and the Co-B and Co-C samples in our experimental conditions.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.04.005
Materiales Coloidales
Crystal structure, NIR luminescence and X-ray computed tomography of Nd3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Cantelar, E; Cusso, F; Briat, A; Boyer, D; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 46 (2017) 6580-6587 DOI: 10.1039/c7dt00453b
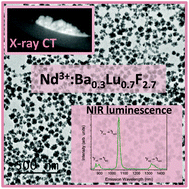
Abstract
Uniform, hydrophilic 50 nm diameter Nd3+-doped Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres are synthesized at 120 degrees C using a singular one-pot method based on the use of ethylene glycol as solvent, in the absence of any additive. The composition and crystal structure of the undoped material are analyzed in detail using ICP and XRD, which reveals a BaF2 cubic crystal structure that is able to incorporate 70 mol% of Lu ions. This finding contrasts with the reported phase diagram of the system, where the maximum solubility is around 30 mol% Lu. XRD proves as well that the Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 structure is able to incorporate Nd3+ ions up to, at least 10 mol%, without altering the uniform particles morphology. The Nd-doped particles exhibit near-infrared luminescence when excited at 810 nm. The maximum emission intensity with the minimum concentration quenching effect is obtained at 1.5% Nd doping level. X-ray computed tomography experiments are carried out on powder samples of the latter composition. The sample significantly absorbs X-ray photons, thus demonstrating that the Nd3+-doped Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 nanospheres are good candidates as contrast agents in computed tomography.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c7dt00453b
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New insights into surface-functionalized swelling high charged micas: Their adsorption performance for non-ionic organic pollutants
Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 52 (2017) 179-186 DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.042

Abstract
The major components of the wastewater from the petroleum refineries are benzene, toluene and phenol and one of the techniques applied to the treatment of effluents is sorption using organo-functionalized clay. The materials exploited in the present study are a family of surface-functionalized synthetic micas and their sorption capacities for non-ionic organic pollutants are analyzed. The organo-functionalization of their surface provides them the capacity to sorb effectively non-ionic pollutants in the interface. Their adsorption performance is a function of the alkylamonium properties such as the chain length, the mass fraction and the organization of the organic cation in the interlayer space of the micas.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.042
Reactividad de Sólidos
Lead-Free Polycrystalline Ferroelectric Nanowires with Enhanced Curie Temperature
Datta, Anuja; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Al Orabi, Rabih Al Rahal; Calahorra, Yonatan; Ou, Canlin; Sahonta, Suman-Lata; Fornari, Marco; Kar-Narayan, SohiniAdvanced Functional Materials, 27 (2017) 1701169 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201701169
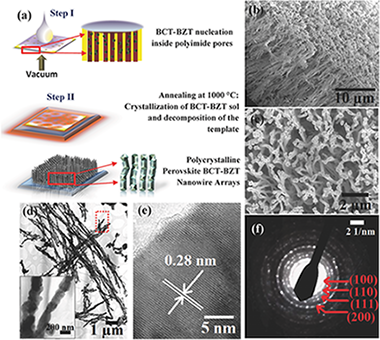
Abstract
Ferroelectrics are important technological materials with wide-ranging applications in electronics, communication, health, and energy. While lead-based ferroelectrics have remained the predominant mainstay of industry for decades, environmentally friendly lead-free alternatives are limited due to relatively low Curie temperatures (T-C) and/or high cost in many cases. Efforts have been made to enhance T-C through strain engineering, often involving energy-intensive and expensive fabrication of thin epitaxial films on lattice-mismatched substrates. Here, a relatively simple and scalable sol-gel synthesis route to fabricate polycrystalline (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Zr0.1Ti0.9)O-3 nanowires within porous templates is presented, with an observed enhancement of T-C up to similar to 300 degrees C as compared to similar to 90 degrees C in the bulk. By combining experiments and theoretical calculations, this effect is attributed to the volume reduction in the template-grown nanowires that modifies the balance between different structural instabilities. The results offer a cost-effective solution-based approach for strain-tuning in a promising lead-free ferroelectric system, thus widening their current applicability.
August, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201701169
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Plasma assisted deposition of single and multistacked TiO2 hierarchical nanotube photoanodes
Filippin, AN; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Idigoras, J; Rojas, TC; Barranco, A; Anta, JA; Borras, ANanoscale, 9 (2017) 8133-8141 DOI: 10.1039/c7nr00923b
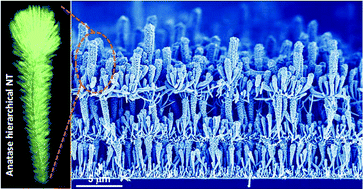
Abstract
We present herein an evolved methodology for the growth of nanocrystalline hierarchical nanotubes combining physical vapor deposition of organic nanowires (ONWs) and plasma enhanced chemical vacuum deposition of anatase TiO2 layers. The ONWs act as vacuum removable 1D and 3D templates, with the whole process occurring at temperatures ranging from RT to 250 degrees C. As a result, a high density of hierarchical nanotubes with tunable diameter, length and tailored wall microstructures are formed on a variety of processable substrates as metal and metal oxide films or nanoparticles including transparent conductive oxides. The reiteration of the process leads to the development of an unprecedented 3D nanoarchitecture formed by stacking the layers of hierarchical TiO2 nanotubes. As a proof of concept, we present the superior performance of the 3D nanoarchitecture as a photoanode within an excitonic solar cell with efficiencies as high as 4.69% for a nominal thickness of the anatase layer below 2.75 mu m. Mechanical stability and straightforward implementation in devices are demonstrated at the same time. The process is extendable to other functional oxides fabricated by plasma-assisted methods with readily available applications in energy harvesting and storage, catalysis and nanosensing.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c7nr00923b
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Surface chemistry and germination improvement of Quinoa seeds subjected to plasma activation
Gomez-Ramierez, A.; Lopez-Santos, C.; Cantos, M.; Garcia, J. L.; Molina, R.; Cotrino, J.; Espinos, J. P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A. R.Scientific Reports, 7 (2017) art. 5924 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06164-5

Abstract
Plasma treatment is recognized as a suitable technology to improve germination efficiency of numerous seeds. In this work Quinoa seeds have been subjected to air plasma treatments both at atmospheric and low pressure and improvements found in germination rate and percentage of success. Seed water uptake by exposure to water vapor, although slightly greater for plasma treated seeds, did not justify the observed germination improvement. To identify other possible factors contributing to germination, the chemical changes experienced by outer parts of the seed upon plasma exposure have been investigated by X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDX). XPS revealed that the outer layers of the Quinoa plasma treated seeds were highly oxidized and appeared enriched in potassium ions and adsorbed nitrate species. Simultaneously, SEM-EDX showed that the enrichment in potassium and other mineral elements extended to the seed pericarp and closer zones. The disappearance from the surface of both potassium ions and nitrate species upon exposure of the plasma treated seeds to water vapor is proposed as a factor favoring germination. The use of XPS to study chemical changes at seed surfaces induced by plasma treatments is deemed very important to unravel the mechanisms contributing to germination improvement.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06164-5
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Coloidales
Photonic Tuning of the Emission Color of Nanophosphor Films Processed at High Temperature
Geng, Dongling; Lozano, Gabriel; Calvo, Mauricio E.; Nunez, Nuria O.; Becerro, Ana I.; Ocana, Manuel; Miguez, HernanAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) art. 1700099 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700099
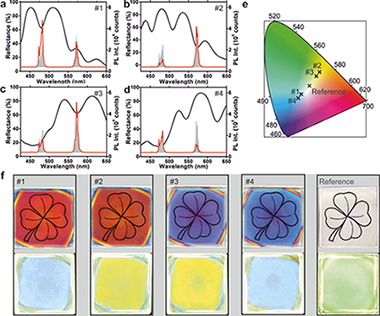
Abstract
Photonics offers new possibilities to tailor the photoluminescence process in phosphor-converted light emitting diodes. Herein, it is demonstrated that the emission color of thin layers of rare-earth doped nanocrystals can be strongly modulated in tunable spectral ranges using optical resonators specifically designed to this end. GdVO4:Dy3+ nanoparticles of controlled size and shape are synthesized using a solvothermal method with which highly transparent nanophosphor thin films are prepared. This paper designs and fabricates optical multilayers, which are transparent in the UV and resonant at the frequencies where the Dy3+ ions emit, to prove that the color coordinates of this emitter can be tuned from green to blue or yellow with unprecedented precision. Key to the achievement herein reported is the careful analysis of the structural and optical properties of thin nanophosphor layers with the processing temperature in order to achieve efficient photoluminescence while preserving the transparency of the film. The results open a new path for fundamental and applied research in solid-state lighting in which photonic nanostructures allow controlling the emission properties of state-of-the-art materials without altering their structure or chemical composition.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700099
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Low-Temperature Plasma Processing of Platinum Porphyrins for the Development of Metal Nanostructured Layers
Filippin, AN; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Idigoras, J; Macias-Montero, M; Alcaire, M; Aparicio, FJ; Espinos, JP; Lopez-Santos, C; Frutos, F; Barranco, A; Anta, JA; Borras, AAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 4 (2017) 1601233 DOI: 10.1002/admi.201601233
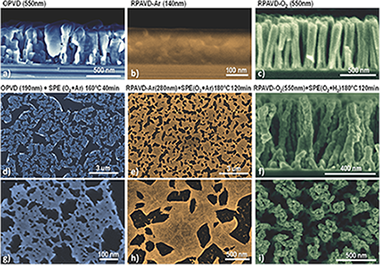
Abstract
This article establishes the bases for a vacuum and plasma supported methodology for the fabrication at mild temperatures of nanostructured platinum in the form of porous layers and nanocolumns using platinum octaethylporphyrin as precursor. In addition, the application of these materials as tunable optical filters and nano-counterelectrodes is proved. On one hand, the transparency in the ultraviolet-visible-near infrared range can be adjusted precisely between 70% and 1% by tuning the deposition and processing conditions, obtaining a high spectral planarity. Deviations of the spectra from an ideal flat filter are below 4%, paving the way to the fabrication of neutral density filters. The transparency limit values yield a sheet resistivity of approximate to 1350 and 120 Omega square(-1), respectively. On the other hand, the catalytic properties of the nanostructures are further demonstrated by their implementation as counterelectrodes of excitonic solar cells surpassing the performance of commercial platinum as counterelectrode in a 20% of the overall cell efficiency due to simultaneous enhancement of short-circuit photocurrent and open-circuit photovoltage. One of the most interesting features of the developed methodology is its straightforward application to other metal porphyrins and phthalocyanines readily sublimable under mild vacuum and temperature conditions.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.201601233
Reactividad de Sólidos
Characterization of of mechanosynthesized Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples unencumbered by secondary phases or compositional inhomogeneity
Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Hayward, MA; Criado, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 711 (2017) 541-551 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.289
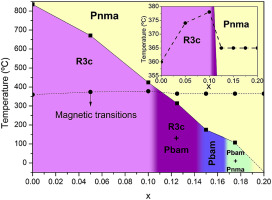
Abstract
High-quality samples, in terms of phase purity and dielectric properties, of composition Bi1-xSmxFeO3 (0.05 <= x <= 0.20) have for the first time been prepared by mechanosynthesis. Close inspection of the powder diffraction data, analysis via Rietveld refinement and TEM microscopy demonstrates that the Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples contain only perovskite phases. Additionally, by a combination of Rietveld analysis, TEM, DSC, temperature-dependent XRD and permittivity data a tentative phase diagram has been proposed where the high temperature paraelectric phase Pnma has been confirmed for samarium substituted BiFeO3. Regarding the physical properties, the samples resulted to be electrically homogenous and highly insulating at room temperature, suggesting that other sources of conductivity, such as mixed valence of Fe associated with possible oxygen non-stoichiometry, have been avoided during the samples synthesis. In spite of the high quality of the samples, the dielectric and magnetic behaviour of the Bi1-xSmxFeO3 samples change only modestly on Sm substitution, with neither a great change in the resistivity or remnant magnetisation of Sm substituted samples in comparison with BiFeO3.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.289
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Formation of Subsurface W5+ Species in Gasochromic Pt/WO3 Thin Films Exposed to Hydrogen
Castillero, Pedro; Rico-Gavira, Victor; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Barranco, Angel; Perez-Dieste, Virginia; Escudero, Carlos; Espinos, Juan P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121 (2017) 15719-15727 DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03385
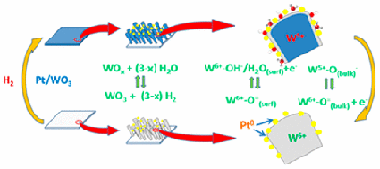
Abstract
M/WO3 (M = Pt, Pd) systems formed by a porous WO3 thin film decorated by metal nanoparticles are known for their reversible coloring upon exposure to H2 at room temperature. In this work, this gasochromic behavior is investigated in situ by means of near-ambient photoemission (NAPP). Pt/WO3 systems formed by very small Pt nanoparticles (10 ± 1 nm average size) incorporated in the pores of nanocolumnar WO3 thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at an oblique angle have been exposed to a small pressure of hydrogen at ambient temperature. The recorded UV–vis transmission spectra showed the reversible appearance of a very intense absorption band responsible for the blue coloration of these gasochromic films. In an equivalent experiment carried out in the NAPP spectrometer, W 4f, O 1s, Pt 4f, and valence band photoemission spectra have been recorded at various photon energies to follow the evolution of the reduced tungsten species and hydroxyl groups formed upon film exposure to hydrogen. The obtained results are compared with those of a conventional X-ray photoemission study after hydrogen exposure between 298 and 573 K. As investigated by NAPP, the gasochromic behavior at 298 K is accounted for by a reaction scheme in which hydrogen atoms resulting from the dissociation of H2 onto the Pt nanoparticles are spilt over to the WO3 substrate where they form surface OH–/H2O species and subsurface W5+ cations preferentially located in buried layers of the oxide network.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b03385
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Cobalt Carbide Identified as Catalytic Site for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde
A. Rodríguez-Gómez; J.P. Holgado; A. CaballeroACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 5243-5247 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01348
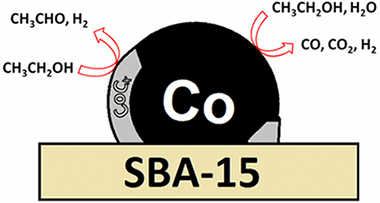
Abstract
Two cobalt catalysts, Co/SBA-15 and Co/SiO2, have been studied in steam reforming of ethanol (SRE). Besides the steam reforming products, ethoxide dehydrogenation to acetaldehyde is observed as one of the main reactions. Although by hydrogen treatment cobalt is reduced to the metallic state, under SRE conditions, a phase appears that has been identified as cobalt carbide and correlates with acetaldehyde production. These findings provide insights about the catalytic sites, for SRE, in cobalt catalysts. Comparison with previous results shows that these conclusions are not translatable to other cobalt catalysts, stressing the importance of the support on the catalytic behavior of cobalt.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01348
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cs+ immobilization by designed micaceous adsorbent under subcritical conditions
Osuna, FJ; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 143 (2017) 293-299 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.03.041
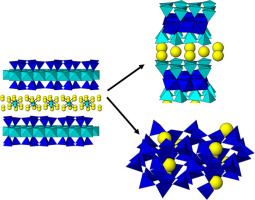
Abstract
The adsorption of Cs+ by clay minerals is a complicate process, being cation exchange and frayed-edge sites the major mechanisms that govern it. However, environmental variables have a significant impact on the process. In this work, the influence of the temperature and time in the cesium adsorption capacity of Na-Mica-n (n = 2 and 4) have been explored under subcritical conditions. Those synthetic micas were able to immobilize cations Cs+ combining adsorption at nonspecific sites, at specific sites and chemical reaction. The distribution constant of Cs+ was larger in the Na-Mica-2 denoting a higher concentration of specific adsorption sites when layer charge decreased.
July, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.03.041
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
High surface area biopolymeric-ceramic scaffolds for hard tissue engineering
Romero-Sanchez, LB; Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Diaz-Cuenca, ABiomedical Physics & Engineering Express, 3 (2017) art UNSP 035012 DOI: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa7001
Abstract
The development of scaffolds mimicking native bone tissue composition and structure is a challenge in bone tissue engineering. 3D scaffolds with both an interconnected macropore structure and nanotextured surfaces are required. However, 3D scaffolds processed by microfabrication usually lack of nanotextured surface, while nanotextured materials generated by bottom-up nanofabrication are difficult to process conforming scaffolds having well interconnected microsized cavities. In this work, the processing of reticulated (macropore interconnected) structures using nanostructured precursors has been performed to improve the mechanical properties of the scaffolds. The application of a fibrillar collagen coating, using less than 1 wt% collagen per scaffold, has allow a significant increase of the compressive strength while preserving a high surface area and nanopore accessibility. Besides, the fibrillar nanostructured collagen coating promotes hydroxyapatite mineralization. Two different collagen-coating procedures are applied showing interesting differences in terms of mechanical performance.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa7001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
About the enhancement of chemical yield during the atmospheric plasma synthesis of ammonia in a ferroelectric packed bed reactor
Gomez-Ramirez, Ana; Montoro-Damas, Antonio M.; Cotrino, Jose; Lambert, Richard M.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Plasma Processes and Polymers, 14 (2017) e1600081 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201600081

Abstract
Plasma reactions offer an attractive alternative route for the synthesis of a variety of valuable chemical compounds. Here we investigate the parameters that determine the efficiency of ammonia synthesis in a ferroelectric packed bed dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor. The effects of varying the operating frequency, the size of the ferroelectric pellets and the inter-electrode distance have been systematically studied. Under optimised conditions nitrogen conversions in excess of 7% were achieved, higher than those previously obtained using DBD reactors. These findings are discussed with respect to variations in the electrical characteristics of the reactor under operating conditions and in the light of emission spectra obtained as a function of reactant flow rates. These encouraging results signpost future developments that could very substantially improve the efficiency of ammonia synthesis by means of DBD technology.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201600081
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of the impact energy on the chemical homogeneity of a (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N) solid solution obtained via a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
de La Obra, AG; Gotor, FJ; Chicardi, EJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 708 (2017) 1008-1017 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.109
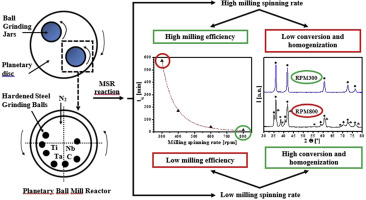
Abstract
A titanium-tantalum-niobium carbonitride solid solution, (Ti,Ta,Nb)(C,N), was synthesised in a planetary mill via a mechanochemical process that involves a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from stoichiometric Ti/Ta/Nb/C mixtures that are milled under a nitrogen atmosphere. The influence of the spinning rate of the planetary mill, which determines the impact energy of the milling process, on the ignition time (t(ig)) of the MSR process as well as the chemical homogeneity of the final product was analysed. The results indicated that the dependence of tig on the spinning rate followed a potential function with a potential factor of 4.85, implying a remarkable reduction in the milling time required to induce the self-sustaining reaction at increasing spinning rates (i.e., from 4200 min at 200 rpm to 15 min at 800 rpm). However, the chemical and structural characterisation of the obtained products at ignition without any extra milling treatment indicated that a single solid solution phase was only obtained at the lowest spinning rates (i.e., less than 300 rpm). At increasing rates, the relative amount of the intended solid solution phase continuously decreased, and new undesirable secondary phases were formed. Despite the long milling times required for the milling experiments that were performed at the slowest spinning rates, iron contamination from the milling media was negligible due to the low intensity milling regime.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.109
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High-temperature creep of carbon nanofiber-reinforced and graphene oxide-reinforced alumina composites sintered by spark plasma sintering
Cano-Crespo, Rafael; Malmal Moshtaghioun, Bibi; Gomez-Garcia, Diego; Dominguez-Rodriguez, Arturo; Moreno, RodrigoCeramics International, 43 (2017) 7136-7141 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.146
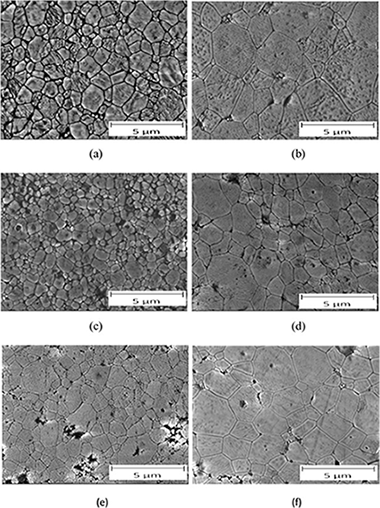
Abstract
Alumina (Al2O3) ceramic composites reinforced with either graphene oxide (GO) or carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were prepared using Spark Plasma Sintering. The effects of GO and CNFs on the microstructure and in consequence on their mechanical properties were investigated. The microstructure of the sintered materials have been characterized quantitatively prior to and after the creep experiments in order to discover the deformation mechanism. Graphene-oxide reinforced alumina composites were found to be more creep resistant than carbon nanofibers-reinforced alumina ones or monolithic alumina with the same grain size distribution. In all the cases, grain boundary sliding was identified as the deformation mechanism
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.02.146
Reactividad de Sólidos
Non-isothermal Characterization of the Precipitation Hardening of a Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn Alloy
Donoso, E; Dianez, MJ; Criado, JM; Espinoza, R; Mosquera, EMetallurgical and Materials Transactions A-Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 48A (2017) 3090-3095 DOI: 10.1007/s11661-017-4063-4
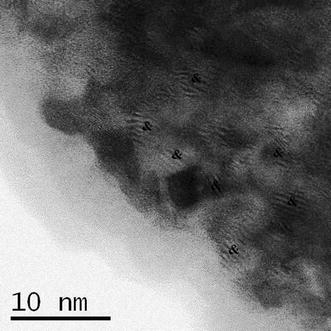
Abstract
The precipitation hardening of a Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn alloy has been studied by means of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM), and hardness measurements. The calorimetric curves, in the range of temperatures analyzed, show the presence of one exothermic reaction followed by an endothermic one. The exothermic DSC peak is due to the segregation of Cu2NiZn precipitates and it is associated to a noticeable improvement of the mechanical properties of the alloy. The endothermic effect is associated to the dissolution of the Cu2NiZn precipitates into the copper matrix for restoring the starting Cu-11Ni-19Zn-1Sn homogeneous solid solution. The reaction mechanisms of these processes have been proposed from the kinetic analysis of the exothermic and endothermic DSC signals. The results obtained point out that tin plays a decisive role on the precipitation hardening of the alloy, because age hardening is not observed in the case of a Cu-Ni-Zn ternary alloy of similar composition.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s11661-017-4063-4
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
In Situ Determination of the Water Condensation Mechanisms on Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes
Macias-Montero, Manuel; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Nicolas Filippin, A.; Rico, Victor J.; Espinos, Juan P.; Fraxedas, Jordi; Perez-Dieste, Virginia; Escudero, Carlos; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Borras, AnaLangmuir, 33 (2017) 6449-6456 DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00156
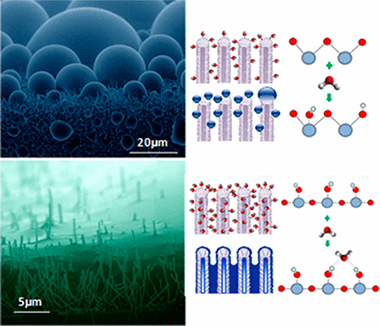
Abstract
One-dimensional (1D) nanostructured surfaces based on high-density arrays of nanowires and nanotubes of photoactive titanium dioxide (TiO2) present a tunable wetting behavior from superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic states. These situations are depicted in a reversible way by simply irradiating with ultraviolet light (superhydrophobic to superhydrophilic) and storage in dark. In this article, we combine in situ environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) and near ambient pressure photoemission analysis (NAPP) to understand this transition. These experiments reveal complementary information at microscopic and atomic level reflecting the surface wettability and chemical state modifications experienced by these 1D surfaces upon irradiation. We pay special attention to the role of the water condensation mechanisms and try to elucidate the relationship between apparent water contact angles of sessile drops under ambient conditions at the macroscale with the formation of droplets by water condensation at low temperature and increasing humidity on the nanotubes surfaces. Thus, for the as-grown nanotubes, we reveal a metastable and superhydrophobic Cassie state for sessile drops that tunes toward water dropwise condensation at the microscale compatible with a partial hydrophobic Wenzel state. For the UV-irradiated surfaces, a filmwise wetting behavior is observed for both condensed water and sessile droplets. NAPP analyses show a hydroxyl accumulation on the as-grown nanotubes surfaces during the exposure to water condensation conditions, whereas the water filmwise condensation on a previously hydroxyl enriched surface is proved for the superhydrophilic counterpart.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00156
Reactividad de Sólidos
The Oxy-CaL process: A novel CO2 capture system by integrating partial oxy-combustion with the Calcium-Looping process
Ortiz, C; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Benitez-Guerrero, M; Perejon, A; Romeo, LMApplied Energy, 196 (2017) 1-17 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.120
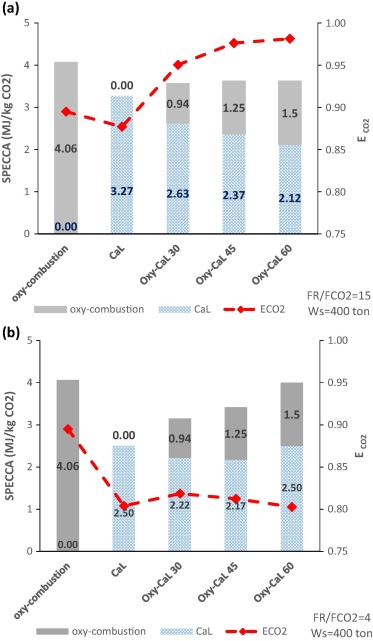
Abstract
This paper proposes a novel CO2 capture technology from the integration of partial oxy-combustion and the Calcium -Looping capture process based on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of limestone derived CaO. The concentration of CO2 in the carbonator reactor is increased by means of partial oxycombustion, which enhances the multicycle CaO conversion according to thermogravimetric analysis results carried out in our work, thus improving the CO2 capture efficiency. On the other hand, energy consumption for partial oxy-combustion is substantially reduced as compared to total oxy-combustion. All in all, process simulations indicate that the integration of both processes has potential advantages mainly regarding power plant flexibility whereas the overall energy penalty is not increased. Thus, the resulting energy consumption per kilogram of CO2 avoided is kept smaller than 4 MI/kg CO2, which remains below the typical values reported for total oxy-combustion and amine based CO2 capture systems whereas CO2 capture efficiency is enhanced in comparison with the Calcium -Looping process.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.120
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Failure mode and effect analysis of a large scale thin-film CIGS photovoltaic module
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Sanchez-Cortezon, E; Lopez-Lopez, C; Aninat, R; Alba, MDEngireering failure analysis, 76 (2017) 55-60 DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.02.004
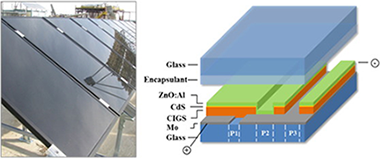
Abstract
The efficiency of thin-film CIGS based cells at the laboratory scale is now getting closer to conventional Silicon technologies. As a consequence, the long-term stability of CIGS is now one of the main challenges left to address in order to assess its potential as an alternative for photovoltaic plants. This paper reports an overview of the critical risks for the commercial viability of the CIGS thin-film technology. The key causes of the potential failures of this technology are determined through the Failure Mode Analysis and Effects (FMEA) methodology. To validate the results obtained from the FMEA, aging tests and outdoor monitoring were also carried out. Based on the results obtained, we argue that the encapsulation material is the main cause of degradation in CIGS modules.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.02.004
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel, simple and rapid route to the synthesis of boron cabonitride nanosheets: combustive gaseous unfolding
Jalaly, Maisam; Jose Gotor, Francisco; Semnan, Masih; Jesus Sayagues, MariaScientific Reports, 7 (2017) art. 3453 DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03794-7
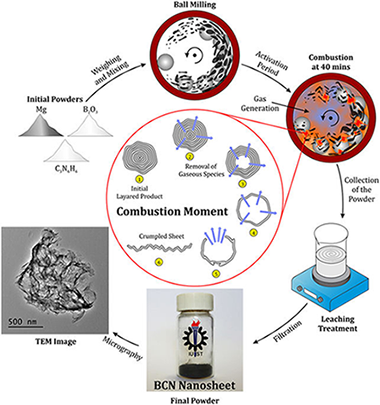
Abstract
The ternary compound boron carbonitride (BCN) was synthesized in the form of few-layer nanosheets through a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). Magnesium was used to reduce boron trioxide in the presence of melamine in a combustive manner. The process to form the nanostructured material was very rapid (less than 40 min). The prepared powder was investigated by various techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR), Micro-Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). The thermal stability and the optical behavior of the BCN nanosheets were also studied by thermal analysis and UV-vis spectroscopy, respectively. The formation mechanism of the nanosheet morphology was described in detail.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03794-7
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A compact and portable optofluidic device for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing
Lahoz, F; Martin, IR; Walo, D; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 50 (2017) 21 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa6cdd
Abstract
Optofluidic lasers have been widely investigated over the last few years mainly because they can be easily integrated in sensor devices. However, high power pulse lasers arc required as excitation sources, which, in practice, limit the portability of the system. Trying to overcome some of these limitations, in this paper we propose the combined use of a small CW laser with a Fabry-Perot optofluidic planar microcavity showing high sensitivity and versatility for detection of liquid properties and label-free sensing. Firstly, a fluorescein solution in ethanol is used to demonstrate the high performances of the FP microcavity as a temperature sensor both in the laser (high pump power above laser threshold) and in the fluorescence (low pump power) regimes. A shift in the wavelength of the resonant cavity modes is used to detect changes in the temperature and our results show that high sensitivities could be already obtained using cheap and portable CW diode lasers. In the second part of the paper, the demonstration of this portable device for label-free sensing is illustrated under low CW pumping. The wavelength positions of the optolluidic resonant modes are used to detect glucose concentrations in water solutions using a protein labelled with a fluorescent dye as the active medium.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa6cdd
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Analysis of Ni species formed on zeolites, mesoporous silica and alumina supports and their catalytic behavior in the dry reforming of methane
Drobna, Helena; Kout, Martin; Soltysek, Agnieszka; Gonzalez-Delacruz, Victor M.; Caballero, Alfonso; Capek, LiborReaction Kinetics Mechanisms and Catalysis, 121 (2017) 255-274 DOI: 10.1007/s11144-017-1149-3
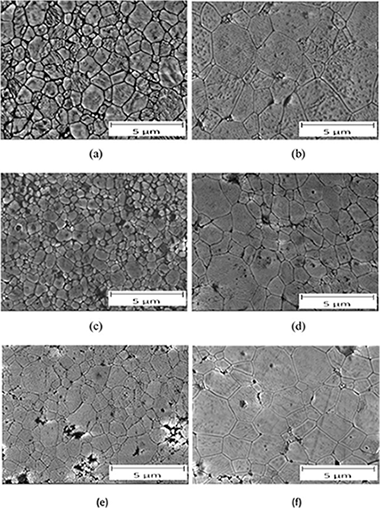
Abstract
The presented investigation is focused on the analysis of Ni species formed on microporous (zeolites MFI and FAU) and mesoporous materials (Al-MCM- 41 and SBA-15) and alumina supports and their catalytic behavior in the dry reforming of methane. The paper lays emphasis on the relationship between the catalytic behavior of Ni-based catalysts and their textural/structural properties. Ni-based catalysts were prepared by wet impregnation (11 wt% of Ni) followed by calcination in air and reduction in hydrogen. The properties of Ni-based catalysts were also compared prior and after the catalytic tests. The critical role was played by the high value of the specific surface area and the high strength of the interaction between the Ni species and the support, which both determined the high dispersion and stability of metal Ni-0 particles. Ni-Al-MCM-41 and Ni-SBA-15 showed the values of the conversion of CO2 and CH4 above 90% (stable during 12 h). Slightly lower values of the conversion of CO2 and CH4 were observed over Ni-Al2O3 (also stable during 12 h). In contrast to these materials, Ni-MFI and Ni-FAU exhibited the worse metallic Ni-0 particles dispersion and very bad catalytic behavior.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s11144-017-1149-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Impact of moisture on efficiency-determining electronic processes in perovskite solar cells
Salado, Manuel; Contreras-Bernal, Lidia; Calio, Laura; Todinova, Anna; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Ahmad, Shahzada; Borras, Ana; Idigoras, Jesus; Anta, Juan A.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 5 (2017) 10917-10927 DOI: 10.1039/c7ta02264f
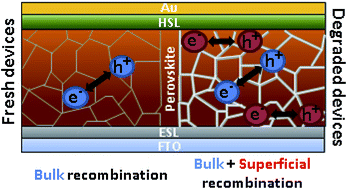
Abstract
Moisture-induced degradation in perovskite solar cells was thoroughly investigated by structural (SEM, EDS, XRD and XPS) and device characterization (impedance and intensity modulated photocurrent spectroscopy) techniques. Both the influence of the perovskite composition and the nature of the hole selective material were analyzed. The degradation rate was found to be significantly slower for mixed perovskites and P3HT-based devices. However, for a fixed degradation degree (defined as a 50% drop from the initial photocurrent), all configurations show similar features in small-perturbation analysis. Thus, a new mid-frequency signal appears in the impedance response, which seems to be related to charge accumulation at the interfaces. In addition, faster recombination, with a more important surface contribution, and slower transport were clearly inferred from our results. Both features can be associated with the deterioration of the contacts and the formation of a higher number of grain boundaries.
June, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c7ta02264f
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Critical Role of Oxygen in Silver-Catalyzed Glaser-Hay Coupling on Ag(100) under Vacuum and in Solution on Ag Particles
Orozco, N; Kyriakou, G; Beaumont, SK; Sanz, JF; Holgado, JP; Taylor, MJ; Espinos, JP; Marquez, AM; Watson, DJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 7 (2017) 3113-3120 DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00431
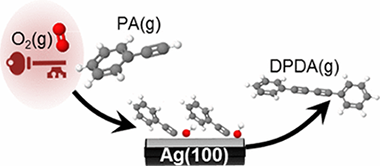
Abstract
The essential role of oxygen in enabling heterogeneously catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling of phenylacetylene on Ag(100) was elucidated by STM, laboratory and synchrotron photoemission, and DFT calculations. In the absence of coadsorbed oxygen, phenylacetylene formed well-ordered dense overlayers which, with increasing temperature, desorbed without reaction. In striking contrast, even at 120 K, the presence of oxygen led to immediate and complete disruption of the organic layer due to abstraction of acetylenic hydrogen with formation of a disordered mixed layer containing immobile adsorbed phenylacetylide. At higher temperatures phenylacetylide underwent Glaser–Hay coupling to form highly ordered domains of diphenyldiacetylene that eventually desorbed without decomposition, leaving the bare metal surface. DFT calculations showed that, while acetylenic H abstraction was otherwise an endothermic process, oxygen adatoms triggered a reaction-initiating exothermic pathway leading to OH(a) + phenylacetylide, consistent with the experimental observations. Moreover, it was found that, with a solution of phenylacetylene in nonane and in the presence of O2, Ag particles catalyzed Glaser–Hay coupling with high selectivity. Rigorous exclusion of oxygen from the reactor strongly suppressed the catalytic reaction. Interestingly, too much oxygen lowers the selectivity toward diphenyldiacetylene. Thus, vacuum studies and theoretical calculations revealed the key role of oxygen in the reaction mechanism, subsequently borne out by catalytic studies with Ag particles that confirmed the presence of oxygen as a necessary and sufficient condition for the coupling reaction to occur. The direct relevance of model studies to a mechanistic understanding of coupling reactions under conditions of practical catalysis was reaffirmed.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.7b00431
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis, Characterisation, and Photocatalytic Behaviour of Mesoporous ZnS Nanoparticles Prepared Using By-Product Templating
Emrooz, HBM; Rahmani, AR; Gotor, FJAustralian Journal of Chemistry, 70 (2017) 1099-1105 DOI: 10.1071/CH17192
Abstract
High surface area mesoporous ZnS nanoparticles (MZN) were obtained with the aid of the by-product of the synthesising reaction. This by-product, namely NaNO3, can be considered as a soft template responsible for the formation of pores. Ethanol and water were chosen as the synthesis media. Ultrasonic waves were used as an accelerator for the synthesis of MZNs. Photocatalytic activities of the synthesised samples for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) were investigated under ultraviolet irradiation. Synthesised specimens were characterised using field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, N-2-physisorption, and FT-IR spectroscopy. Results indicated that the synthesis media has a pronounced effect on the surface properties of the final porous particles by several mechanisms. The specific surface area of the MZN samples synthesised in water and ethanol were determined to be 53 and 201m(2)g(-1), respectively. The difference in the specific surface area was attributed to the weak solvation of S2- ions (Na(2)S5H(2)O in ethanol) and also to the by-product of the synthesis reaction. The photocatalytic behaviour of the mesoporous ZnS nanoparticles synthesised in these two media were investigated and the results have been interpreted with the aid of effective surface area, pore volume, and bandgap energy of the specimens.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1071/CH17192
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Design and Realization of a Novel Optically Disordered Material: A Demonstration of a Mie Glass
Miranda-Munoz, Jose M.; Lozano, Gabriel; Miguez, HernanAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) art. 1700025 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700025
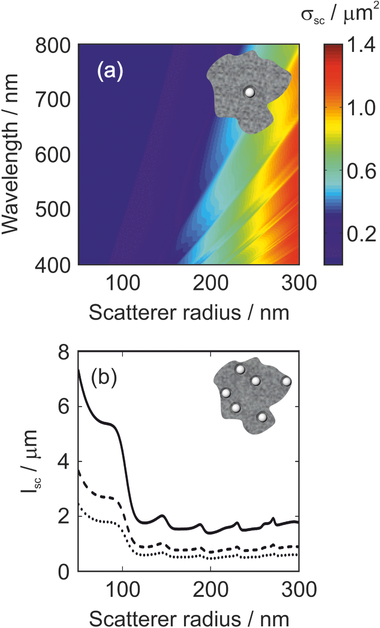
Abstract
Herein, a diffusive material presenting optical disorder is introduced, which represents an example of a Mie glass. Comprising spherical crystalline TiO2 nanoparticles randomly dispersed in a mesoporous TiO2 matrix, it is proved that the scattering of light in this inhomogeneous solid can be predicted in an unprecedented manner from single-particle considerations employing Mie theory. To that aim, a study of the dependence of the key parameters employed is performed to describe light propagation in random media, i.e., the scattering mean free path and the transport mean free path, as a function of the size and concentration of the spherical inclusions based on a comparison between experimental results and analytical calculations. It is also demonstrated that Mie glasses enable enhanced fluorescence intensity due to a combined absorptance enhancement of the excitation light combined with an improved outcoupling of the emitted light. The method offers the possibility to perform a deterministic design for the realization of a light diffuser with tailor-made scattering properties.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700025
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Energy-Sensitive Ion- and Cathode-Luminescent Radiation-Beam Monitors Based on Multilayer Thin-Film Designs
Gil-Rostra, Jorge; Ferrer, Francisco J.; Pedro Espinos, Juan; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Yubero, FranciscoACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 16313-16320 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01175
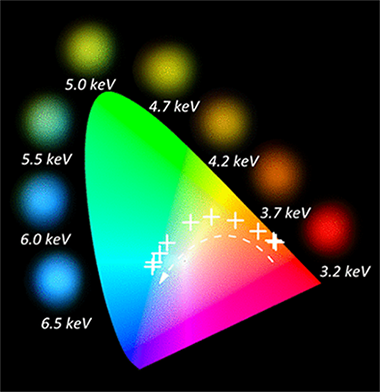
Abstract
A multilayer luminescent design concept is presented to develop energy sensitive radiation-beam monitors on the basis of colorimetric analysis. Each luminescent layer within the stack consists of rare-earth-doped transparent oxides of optical quality and a characteristic luminescent emission under excitation with electron or ion beams. For a given type of particle beam (electron, protons, alpha particles, etc.), its penetration depth and therefore its energy loss at a particular buried layer within the multilayer stack depend on the energy of the initial beam. The intensity of the luminescent response of each layer is proportional to the energy deposited by the radiation beam within the layer, so characteristic color emission will be achieved if different phosphors are considered in the layers of the luminescent stack. Phosphor doping, emission efficiency, layer thickness, and multilayer structure design are key parameters relevant to achieving a broad colorimetric response. Two case examples are designed and fabricated to illustrate the capabilities of these new types of detector to evaluate the kinetic energy of either electron beams of a few kilo-electron volts or a particles of alpha few mega-electron volts.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01175
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
NO photooxidation with TiO2 photocatalysts modified with gold and platinum
Rodriguez, MJH; Melian, EP; Santiago, DG; Diaz, OG; Navio, JA; Rodriguez, JMDApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 205 (2017) 148-157 DOI: 10.10161/j.apcatb.2016.12.006
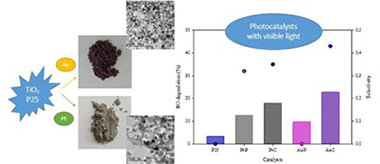
Abstract
In this study, a comparative analysis is made of TiO2 modified with Pt or Au in NO photoxidation under different radiation and humidity conditions. The metals were deposited on the TiO2 surface using two methods, photodeposition and chemical reduction. All catalysts were supported on borosilicate 3.3 plates using a dip-coating technique. These modified photocatalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller measurements (BET), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectrum analysis (XPS). It was found from the XPS results that Pt and oxidized Pt species coexist on the samples obtained by photodeposition and chemical reduction. In the case of Au, though other oxidation states were also detected the dominant oxidation state for both catalysts is Au. TEM results showed most Au-C particles are below 5 nm, whereas for Au-P the nanoparticles are slightly bigger. With UV irradiation, the Pt modified catalysts do not show any significant improvement in NO photocatalytic oxidation in comparison with the unmodified P25. For Au, both modified photocatalysts (Au-P and Au-C) exceed the photocatalytic efficiency of the unmodified P25, with Au-C giving slightly better results. The incorporation of metals on the TiO2 increases its activity in the visible region.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.10161/j.apcatb.2016.12.006
Reactividad de Sólidos
New findings on thermal degradation properties of fluoropolymers
Liu, SE; Zhou, WL; Yan, QL; Qi, XF; An, T; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Zhao, FQJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 128 (2017) 675-685 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-016-5963-z
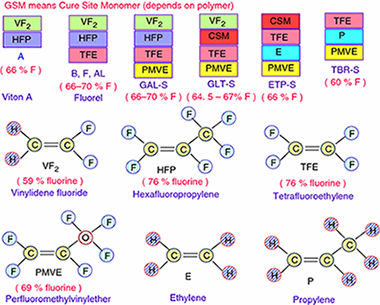
Abstract
In this paper, the thermal degradation properties of Viton A and Fluorel are investigated by both isoconversional and combined kinetic analysis methods using non-isothermal thermogravimetry technique. It has been found that the heating rate has little affect on the degradation residue of Fluorel and Viton A, where around 1.3% char was formed for Fluorel and 3.5% for Viton A. Different from the literature, the decomposition of Viton A should be considered as an overlapped dehydrofluorination and carbon chain scission process, with activation energy of 214 +/- 11 and 268 +/- 13 kJ mol(-1), respectively. The effect of dehydrofluorination on degradation of Fluorel is not so significant due to low content of H, and hence, it could be considered as a single-step mechanism with average activation energy of 264 +/- 14 kJ mol(-1). The thermal stability of Fluorel is much better than that of Viton A, and the predicted half-life is around 218 min for Fluorel and 49 min for Viton A at 420 A degrees C, which are consistent with experimental values. If using a single-step model as in the literature for Viton A, its half-life at 420 A degrees C would be underestimated for > 20%.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-016-5963-z
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
1-dimensional TiO2 nano-forests as photoanodes for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells fabrication
Salado, M; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Kazim, S; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SNano Energy, 35 (2017) 215-222 DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.03.034
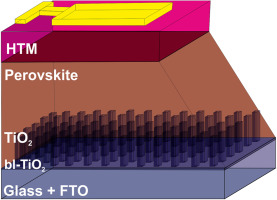
Abstract
During the last years, perovskite solar cells have gained increasing interest among the photovoltaic community, in particularly after reaching performances at par with mature thin film based PV. This rapid evolution has been fostered by the compositional engineering of perovskite and new device architectures. In the present work, we report the fabrication of perovskite solar cells based on highly ordered 1-dimensional vertically oriented TiO2 nano-forests. These vertically oriented porous TiO2 photoanodes were deposited by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration, a method which is scalable to fabricate large area devices. Mixed (MA0.15FA0.85)Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3 or triple cation Cs0.05(MA0.15FA0.85)0.95Pb(I0.85Br0.15)3 based perovskites were then infiltrated into these 1-dimensional nanostructures and power conversion efficiencies of 16.8% along with improved stability was obtained. The devices fabricated using 1D-TiO2 were found to be more stable compare to the classical 3-dimensional TiO2 photoanodes prepared by wet chemistry. These 1-D photoanodes will be of interest for scaling up the technology and in other opto-electrical devices as they can be easily fabricated utilizing industrially adapted methodologies.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.03.034
Reactividad de Sólidos
Structure evolution in the LaMn1 − xFexO3 + δ system by Rietveld analysis
Cordoba, J. M.; Ponce, M.; Sayagues, M. J.Solis State Ionics, 303 (2017) 132-137 DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2017.02.020
Abstract
The synthesis of LaMn1 − xFexO3 + δ (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) solid solutions perovskite powder was carried out using high-energy milling from the constituent oxides, and further crystallization by high temperature treatment. The compositions of the crystalline phases as a function of x were determined by X-ray powder diffraction using a Rietveld refinement. The relationship between composition and structure was covered. This showed that LaMn1 − xFexO3 + δ exists with the rhombohedral structure (R-3c, 167) only below x = 0.3 and with the orthorhombic structure (Pnma, 62) over x = 0.7. The rhombohedral phase coexists with the orthorhombic phase between 0.4 < x < 0.6.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2017.02.020
Reactividad de Sólidos
CO2 capture performance of Ca-Mg acetates at realistic Calcium Looping conditions
Miranda-Pizarro, J; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PEFuel, 196 (2017) 497-507 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.119

Abstract
The Calcium Looping (CaL) process, based on the cyclic carbonation/calcination of CaO, has emerged in the last years as a potentially low cost technique for CO2 capture at reduced energy penalty. In the present work, natural limestone and dolomite have been pretreated with diluted acetic acid to obtain Ca and Ca-Mg mixed acetates, whose CO2 capture performance has been tested at CaL conditions that necessarily imply sorbent regeneration under high CO2 partial pressure. The CaL multicycle capture performance of these sorbents has been compared with that of CaO directly derived from limestone and dolomite calcination. Results show that acetic acid pretreatment of limestone does not lead to an improvement of its capture capacity, although it allows for a higher calcination efficiency to regenerate CaO at reduced temperatures (similar to 900 degrees C) as compared to natural limestone (>similar to 930 degrees C). On the other hand, if a recarbonation stage is introduced before calcination to reactivate the sorbent, a significantly higher residual capture capacity is obtained for the Ca -Mg mixed acetate derived from dolomite as compared to either natural dolomite or limestone. The main reason for this behavior is the enhancement of carbonation in the solid-state diffusion controlled phase. It is argued that the presence of inert MgO grains in the mixed acetate with reduced segregation notably promotes solid state diffusion of ions across the porous structure created after recarbonation.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.119
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide detection at NiO nanoporous thin film-electrodes prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles
Salazar, Pedro; Rico, Victor; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Electrochimica Acta, 235 (2017) 534-542 DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.087
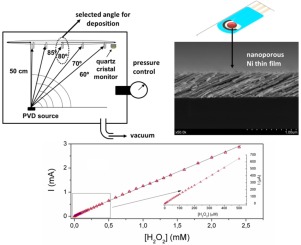
Abstract
In this work we report a non-enzymatic sensor for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) detection based on nanostructured nickel thin films prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles. Porous thin films deposited on ITO substrates were characterized by X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microcopy (SEMs), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and electrochemical techniques such as Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) and Constant Potential Amperometry (CPA). The microstructure of the thin films consisted of inclined and separated Ni nanocolumns forming a porous thin layer of about 500 nm thickness. Prior to their use, the films surface was electrochemically modified and the chemical state studied by CV and XPS analysis. These techniques also showed that Ni2+/Ni3+ species were involved in the electrochemical oxidation and detection of H2O2 in alkaline medium. Main analytical parameters such as sensitivity (807 mA M(-1)cm(-2)), limit of detection (3.22 mu M) and linear range (0.011-2.4 mM) were obtained under optimal operation conditions. Sensors depicted an outstanding selectivity and a high stability and they were successfully used to determine H2O2 concentration in commercial antiseptic solutions.
May, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.087
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structural and catalytic properties of Au/MgO-type catalysts prepared in aqueous or methanol phase: application in the CO oxidation reaction
Hernandez, Willinton Y.; Alic, Funda; Navarro-Jaen, Sara; Centeno, Miguel A.; Vermeir, Pieter; Van der Voort, Pascal; Verberckmoes, AnJournal of Materials Science, 52 (2017) 4727-4741 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-016-0715-9

Abstract
Au/MgO and Au/Mg(OH)(2)-type catalysts for CO oxidation reaction were prepared by using two different synthesis methods in presence of either an aqueous or methanol phase. The influence of the porous and morphological properties of the starting magnesium oxide supports was analyzed and correlated with the catalytic performances of the final gold-supported catalysts. It was found that the deposition of gold in the presence of methanol as a solvent avoids the total rehydration of the MgO support and maintains the textural and morphological properties of the starting oxides. The support synthesized by a surfactant-assisted hydrothermal route, having a combined meso-macroporous structure (i.e., MgO-P) showed a positive influence on the CO oxidation reaction as it favored the dispersion of gold and the surface-to-gas phase interaction during the catalytic process.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-016-0715-9
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Deep insight into Zr/Fe combination for successful Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 WGS catalyst doping
Gonzalez-Castano, M; Ivanova, S; Ioannides, T; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Science & Technology, 7 (2017) 1556-1564 DOI: 10.1039/c6cy02551j
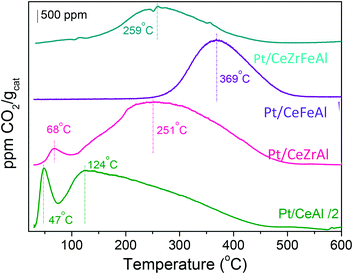
Abstract
Efficient promotion of the Pt/CeO2/Al2O3 catalytic system was achieved by the addition of two different ceria promoters, Zr and Fe. From the exhaustive data analysis, the key features for enhanced catalytic performance and the roles of each doping metal are established. The combination of both doping agents manifests a synergistic effect reflected in noteworthy improvements in H2 reducibility. In addition, the catalyst's doping influences its chemisorptive properties, which is reflected in an increase of the easiness of carbonaceous species desorption, thus leading to superior catalyst resistance toward deactivation.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c6cy02551j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Solvent-Free Synthesis of Quaternary Semiconductor Cu-Fe-Sn-S Nanocrystals
Balaz, Peter; Balaz, Matej; Sayagues, Maria J.; Skorvanek, Ivan; Zorkovska, Anna; Dutkova, Erika; Briancin, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav; Kovac, Jaroslav, Jr.; Shpotyuk, YaroslavNanoscale Research Letters, 12 (2017) art. 256 DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2029-5
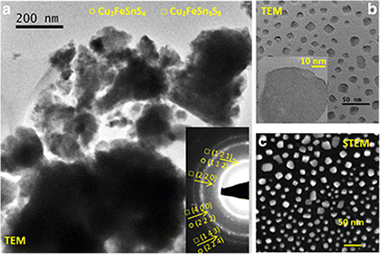
Abstract
In this study, we demonstrate a one-pot mechanochemical synthesis of the nanocomposite composed of stannite Cu2FeSnS4 and rhodostannite Cu2FeSn3S8 nanocrystals using a planetary ball mill and elemental precursors (Cu, Fe, Sn, S). By this approach, unique nanostructures with interesting properties can be obtained. Methods of XRD, Raman spectroscopy, UV-Vis, nitrogen adsorption, SEM, EDX, HRTEM, STEM, and SQUID magnetometry were applied. Quaternary tetragonal phases of stannite and rhodostannite with crystallite sizes 18-19 nm were obtained. The dominant Raman peaks corresponding to the tetragonal stannite structure corresponding to A-symmetry optical modes were identified in the spectra. The bandgap 1.25 eV calculated from UV-Vis absorption spectrum is very well-acceptable value for the application of the synthesized material. The SEM micrographs illustrate the clusters of particles in micron and submicron range. The formation of agglomerates is also illustrated on the TEM micrographs. Weak ferromagnetic properties of the synthesized nanocrystals were documented.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1186/s11671-017-2029-5
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically Synthesized CuFeSe2 Nanoparticles and Their Properties
Dutkova, E; Skorvanek, I; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Kovac, J; Balaz, PActa Physica Polonica A, 131 (2017) 1156-1158 DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.131.1156
Abstract
The mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline CuFeSe2 particles prepared by high-energy milling in a planetary mill in an argon atmosphere from copper, iron, and selenium for 60 min is reported for the first time. The CuFeSe2 nanoparticles crystallize in tetragonal structure with mean crystallite size of about 32 +/- 1 nm. High resolution transmission electron microscopy measurements confirmed the presence of agglomerates which are formed by small nanocrystalline domains (5-40 nm). The magnetic data revealed that paramagnetic CuFeSe2 nanoparticles coexist with a small amount of ferromagnetic impurities at room temperature. The magnetic transition towards a weak ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic behavior occurs in CuFeSe2 at approximately 79 K. The band gap of the CuFeSe2 particles is 0.95 eV which is wider than the band gap in bulk materials (0.16 eV), which could be in many aspects of application more beneficial.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.131.1156
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
High UV-photocatalytic activity of ZnO and Ag/ZnO synthesized by a facile method
C. Jaramillo-Páez; J.A. Navío; M.C. Hidalgo; M. MacíasCatalysis Today, 284 (2017) 121-128 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
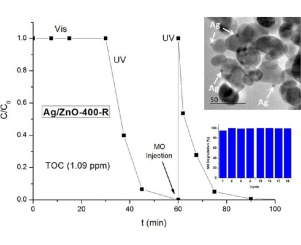
Abstract
ZnO nanoparticles have been successfully synthesized by a facile precipitation procedure by mixing aqueous solutions of Zn(II) acetate and dissolved Na2CO3 at pH ca. 7.0 without template addition. We have investigated the effect of annealing temperature in the final surface and structural properties. Photocatalytic studies were performed using two selected substrates, Methyl Orange and Phenol, both as single model substrates and in mixtures of them.
It has been stated that calcination treatments lead to a significant improvement in the photocatalytic properties of the studied samples, even better than TiO2(P25). As expected, the addition of Ag+ during the photocatalytic degradation of MO increases the reaction rate of the degradation of MO, giving a resultant Ag/ZnO photocatalyst which, after recovery, can be reused at least 18 times for the MO degradation tests, being even more photoactive than ZnO.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.11.021
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of Thermal Pretreatment and Nanosilica Addition on Limestone Performance at Calcium-Looping Conditions for Thermochemical Energy Storage of Concentrated Solar Power
Valverde, Jose Manuel; Barea-Lopez, Manuel; Perejon, Antonio; Sanchez-Jimenez, Pedro E.; Perez-Maqueda, Luis A.Enery & Fuels, 31 (2017) 4226-4236 DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
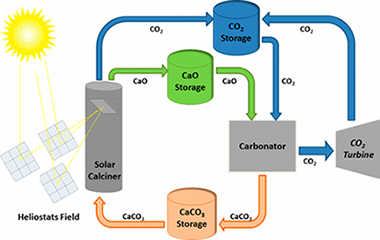
Abstract
The share of renewable energies is growing rapidly, partly in response to the urgent need for mitigating CO2 emissions from fossil fuel power plants. However, cheap and efficient large-scale energy storage technologies are not yet available to allow for a significant penetration of renewable energies into the grid. Recently, a potentially low-cost and efficient thermochemical energy storage (TCES) system has been proposed, based on the integration of the calcium-looping (CaL) process into concentrated solar power plants (CSPs). The CaL process relies on the multicycle carbonation/calcination of CaO, which can be derived from calcination of widely available, cheap, and nontoxic natural limestone (CaCO3). This work explores the effect on the multicycle activity of limestone-derived CaO of thermal pretreatment under diverse atmospheres and the addition of nanosilica, which would be expected to hinder CaO grain sintering. Importantly, optimum CaL conditions for CSP energy storage differ radically from those used in the application of the CaL process for CO2 capture. Thus, calcination should be ideally carried out under low CO2 partial pressure at moderate temperature (below 750 degrees C), whereas CO2 concentration and temperature should be high for carbonation in order to maximize thermoelectric efficiency. When limestone is subjected to carbonation/calcination cycles at these conditions, its performance is critically dependent on the type of pretreatment. Our results indicate that the multicycle CaO activity is correlated with the size of the particles and the CaO pore size distribution. Thus, CaO activity is impaired as particle size is increased and/or CaO pore size is decreased. These observations suggest that pore plugging poses a main limitation to the multicycle performance of limestone-derived CaO at the optimum CaL conditions for TCES in CSPs, which is supported by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Strategies to enhance the performance of natural limestone at these conditions should be therefore oriented toward minimizing pore plugging rather than CaO grain sintering, which stands as the main limitation at CaL conditions for CO2 capture.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03364
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Features of electrical properties of BE-C(Fe) biocarbons carbonized in the presence of an Fe-containing catalyst
Popov, VV; Orlova, TS; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 59 (2017) 703-709 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783417040205
Abstract
The effect of partial graphitization on electrical and galvanomagnetic properties of BE-C(Fe) biomorphic carbons produced by beech wood carbonization at temperatures of 850-1600A degrees C in the presence of an iron-containing catalyst is studied. The use of an Fe catalyst at D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C leads to the formation of nanoscale graphite-phase inclusions; its total volume and nanocrystallite sizes increase with D cent (carb). The data on the carrier concentration and mobility are obtained. It was shown that partially graphitized BE-C(Fe) carbons with D cent (carb) ae<yen> 1000A degrees C in the conductivity type and magnetoresistance features relate to highly disordered metal systems whose conductivity can be described taking into account the contribution of quantum corrections, mainly the correction caused by the electron-electron interaction. It is shown that nonmonotonic dependences of the Hall constant R on the magnetic field are characteristic of BE-C(Fe) samples with 1000 ae<currency> D cent (carb) < 1600A degrees C, which is most probably caused by the contribution of various carrier groups, i.e., electrons and holes. In BE-C(Fe) samples with D cent (carb) = 1600A degrees C, the Hall coefficient corresponds to the metal state, which is associated with conducting medium homogenization resulting from the formation of a significant graphite phase volume.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783417040205
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Formation of nitrile species on Ag nanostructures supported on a-Al2O3: a new corrosion route for silver exposed to the atmosphere
Pelaez, RJ; Espinos, JP; Afonso, CNNanotechnology, 28 (2017) 175709 DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa65c0
Abstract
The aging of supported Ag nanostructures upon storage in ambient conditions (air and room temperature) for 20 months has been studied. The samples are produced on glass substrates by pulsed laser deposition (PLD); first a 15 nm thick buffer layer of amorphous aluminum oxide (a-Al2O3) is deposited, followed by PLD of Ag. The amount of deposited Ag ranges from that leading to a discontinuous layer up to an almost-percolated layer with a thickness of <6 nm. Some regions of the as-grown silver layers are converted, by laser induced dewetting, into round isolated nanoparticles (NPs) with diameters of up to ~25 nm. The plasmonic, structural and chemical properties of both as-grown and laser exposed regions upon aging have been followed using extinction spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, respectively. The results show that the discontinuous as-grown regions are optically and chemically unstable and that the metal becomes oxidized faster, the smaller the amount of Ag. The corrosion leads to the formation of nitrile species due to the reaction between NO x species from the atmosphere adsorbed at the surface of Ag, and hydrocarbons adsorbed in defects at the surface of the a-Al2O3 layer during the deposition of the Ag nanostructures by PLD that migrate to the surface of the metal with time. The nitrile formation thus results in the main oxidation mechanism and inhibits almost completely the formation of sulphate/sulphide. Finally, the optical changes upon aging offer an easy-to-use tool for following the aging process. They are dominated by an enhanced absorption in the UV side of the spectrum and a blue-shift of the surface plasmon resonance that are, respectively, related to the formation of a dielectric overlayer on the Ag nanostructure and changes in the dimensions/features of the nanostructures, both due to the oxidation process.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa65c0
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Improving the pollutant removal efficiency of packed-bed plasma reactors incorporating ferroelectric components
Gomez-Ramirez, Ana; Montoro-Damas, Antonio M.; Rodriguez, Miguel A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Cotrino, JoseChemical Engineering Journal, 314 (2017) 311-319 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.065

Abstract
In this work we have studied the plasma removal of air contaminants such as methane, chloroform, toluene and acetone in two parallel plate packed-bed dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactors of different sizes. Removal and energy efficiencies have been determined as a function of the residence time of the contaminated air within the reactor, the kind of packed-bed material (ferroelectrics or classical dielectric materials), the frequency and the incorporation of a ferroelectric plate onto the active electrode together with the inter-electrode ferroelectric pellets filling the gap. Results at low frequency with the small reactor and the ferroelectric plate showed an enhancement in energy efficiency (e.g., it was multiplied by a factor of six and three for toluene and chloroform, respectively) and in removal yield (e.g., it increased from 22% to 52% for chloroform and from 15% to 21% for methane). Such enhancements have been attributed to the higher energy of plasma electrons and a lower reactor capacitance found for this plate-modified configuration. A careful analysis of reaction efficiencies and electron energy distributions for the different investigated conditions and the simulation of the electric field at the necks between ferroelectric/dielectric pellets complete the present study. Overall, the obtained results prove the critical role of the barrier architecture and operating conditions for an enhanced performance of pollution removal processes using DBD systems.
April, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.065
Materiales Coloidales
Morphology control of uniform CaMoO4 microarchitectures and development of white light emitting phosphors by Ln doping (Ln = Dy3+, Eu3+)
Laguna, Mariano; Nuñez, Nuria O.; Becerro, Ana I.; Ocaña, ManuelCrystengcomm, 19 (2017) 1590-1600 DOI: 10.1039/c6ce02611g
Abstract
A very simple synthesis procedure based on precipitation reactions at moderate temperature (120 degrees C) from solutions containing calcium nitrate and sodium molybdate, using mixed solvents (polyols and water) has been developed, which produces uniform tetragonal CaMoO4 microarchitectures with different morphologies (peanuts, cocoons, spindles and spheres) composed of self-assembled entities. The morphology and crystal size of such assemblies could be tuned by a simple change of the nature of the components of the solvent mixture or their volumetric ratio in such a mixture. All particles presented similar excitation and emission spectra arising from a charge transfer process within the MoO4 2-groups. The emitted light presented a bluish-green color and its intensity was higher for the spindle-type particles. This synthesis procedure was also suitable for doping peanut-like CaMoO4 architectures with Eu3+ or Dy3+ cations up to a 1% molar ratio (Ln/Ln + Ca), without altering their morphology or crystalline structure. The so prepared phosphors emitted an intense red (Eu-doped) or greenish (Dy-doped) light when excited through the MoO42- group excitation band, indicating the presence of an energy transfer process from such groups to the Ln(3+) cations. Finally, a white light emitting phosphor with chromaticity coordinates x = 0.335 and y = 0.365 and a correlated color temperature of 5407 K was developed by codoping peanut-type CaMoO4 particles with suitable amounts of Dy3+ (0.35%) and Eu3+ (0.15%) cations, which could find applications in white light emitting diodes.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1039/c6ce02611g
Reactividad de Sólidos
A Promising approach to the kinetics of crystallization processes: The sample controlled thermal analysis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 100 (2017) 1125-1133 DOI: 10.1111/jace.14604
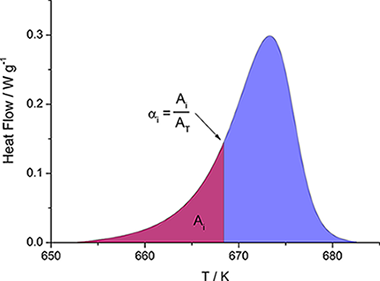
Abstract
Constant Rate Thermal Analysis (CRTA) method implies controlling the temperature in such a way that the reaction rate is maintained constant all over the process. This method allows determining simultaneously both the kinetic parameters and the kinetic model from a single experiment as the shape of the CRTA -T curves strongly depends on the kinetic model. CRTA method has been developed in the market only for thermogravimetric and thermodilatometric systems and, therefore, its use has been limited until now to the kinetic study of processes involving changes in mass or size of the samples, respectively. To overcome this obstacle, a method has been developed in this work for using the DSC signal for controlling the process rate in such a way that CRTA would be applied to the kinetic analysis of either phase transformations or crystallizations. The advantages of CRTA for performing the kinetics of crystallization processes have been here successfully demonstrated for the first time after selecting the crystallization of zirconia gel as test reaction.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.14604
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Antibacterial response of titanium oxide coatings doped by nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation
Esparza, J; Fuentes, GF; Bueno, R; Rodriguez, R; Garcia, JA; Vitas, AI; Rico, V; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 314 (2017) 67-71 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.11.002
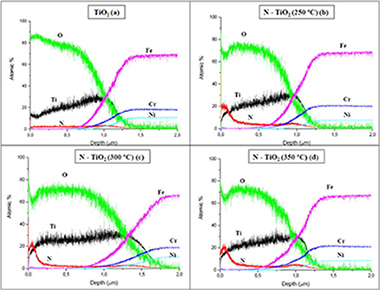
Abstract
Plasma immersion ion implantation technology has been utilized to enhance the photocatalytic activity of the anatase phase of TiO2 thin films deposited by cathodic arc evaporation PVD. The main objective of this study is to shift the light absorbance of the titania in order to obtain antibacterial activity under visible light irradiation. TiO2 thin films, deposited on polished stainless steel AISI 304 and silicon wafers, were implanted with nitrogen ions (N+/N2+) at 20 kV energy and different temperatures between 250 and 350 °C. The antibacterial activity of nitrogen implanted titania coatings has been monitored for Escherichia coli under visible light irradiation. Additionally ultra violet/visible spectrophotometry tests have been carried out to measure the changes in the light absorbance of the doped films. Further characterization has been performed, including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and glow discharge optical emission spectrometry. As a result of Nitrogen implantation, the light absorption peak shifted from ultra violet region (UV-A) to visible wavelength range, which led to an increase of the antibacterial efficacy under visible light irradiation.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.11.002
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Preferential oxidation of CO on a La-Co-Ru perovskite-type oxide catalyst
Pereniguez, R; Caballero, A; Ferri, DCatalysis Communication, 92 (2017) 75-79 DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.12.020
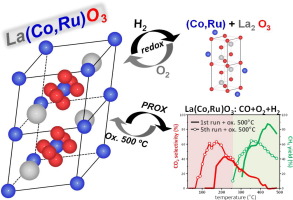
Abstract
A Ru-containing perovskite-type oxide La(Co,Ru)O3 of nominal composition LaCo0.8Ru0.2O3 was prepared by ultrasonic spray combustion and tested for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX). EXAFS indicated that Ru adopted the coordination environment of Co in LaCoO3 while Co was present as LaCoO3 and Co3O4. PROX activity was replaced by CO hydrogenation activity above 250 °C. Short oxidation at 500 °C between temperature programmed reaction ramps did not restore the initial La(Co,Ru)O3 structure but generated a catalyst with improved PROX activity compared to the initial La(Co,Ru)O3. Under reductive PROX conditions the material experienced structural changes that improved its overall catalytic activity only if the catalyst was oxidized after each temperature programmed ramp.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2016.12.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Monitoring the Reaction Mechanism in Model Biogas Reforming by InSitu Transient and Steady-State DRIFTS Measurements
Bobadilla, LF; Garcilaso, V; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemsuschem, 10 (2017) 1193-1201 DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201601379
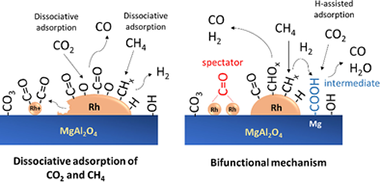
Abstract
In this work, the reforming of model biogas was investigated on a Rh/MgAl2O4 catalyst. In situ transient and steady-state diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) measurements were used to gain insight into the reaction mechanism involved in the activation of CH4 and CO2. It was found that the reaction proceeds through of an initial pathway in which methane and CO2 are both dissociated on Rh metallic sites and additionally a bifunctional mechanism in which methane is activated on Rh sites and CO2 is activated on the basic sites of the support surface via a formate intermediate by H-assisted CO2 decomposition. Moreover, this plausible mechanism is able to explain why the observed apparent activation energy of CO2 is much lower than that of CH4. Our results suggest that CO2 dissociation facilitates CH4activation, because the oxygen-adsorbed species formed in the decomposition of CO2 are capable of reacting with the CHx species derived from methane decomposition.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201601379
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Reliability of new poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma plus silicon dioxide layers for pre-prosthetic guided bone regeneration processes
Castillo-Dali, G; Castillo-Oyague, R; Batista-Cruzado, A; Lopez-Santos, C; Rodriguez-Gonzalez-Elipe, A; Saffar, JL; Lynch, CD; Gutierrez-Perez, JL; Torres-Lagares, DMedicina Oral Patología Oral y Cirugia Oral, 22 (2017) E242-E250 DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21512
Abstract
Background: The use of cold plasmas may improve the surface roughness of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) membranes, which may stimulate the adhesion of osteogenic mediators and cells, thus accelerating the biodegradation of the barriers. Moreover, the incorporation of metallic-oxide particles to the surface of these membranes may enhance their osteoinductive capacity. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to evaluate the reliability of a new PLGA membrane after being treated with oxygen plasma (PO2) plus silicon dioxide (SiO2) layers for guided bone regeneration (GBR) processes.
Material and Methods: Circumferential bone defects (diameter: 11 mm; depth: 3 mm) were created on the top of eight experimentation rabbits' skulls and were randomly covered with: (1) PLGA membranes (control), or (2) PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 barriers. The animals were euthanized two months afterwards. A micromorphologic study was then performed using ROI (region of interest) colour analysis. Percentage of new bone formation, length of mineralised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and intensity of ostheosynthetic activity were assessed and compared with those of the original bone tissue. The Kruskal-Wallis test was applied for between-group com asignificance level of a=0.05 was considered.
Results: The PLGA/ PO2/SiO2 membranes achieved the significantly highest new bone formation, length of miner-alised bone, concentration of osteoclasts, and ostheosynthetic activity. The percentage of regenerated bone supplied by the new membranes was similar to that of the original bone tissue. Unlike what happened in the control group, PLGA/PO2/SiO2 membranes predominantly showed bone layers in advanced stages of formation. Conclusions: The addition of SiO2 layers to PLGA membranes pre-treated with PO2 improves their bone-regeneration potential. Although further research is necessary to corroborate these conclusions in humans, this could be a promising strategy to rebuild the bone architecture prior to rehabilitate edentulous areas.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21512
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Multicolored Emission and Lasing in DCM-Adamantane Plasma Nanocomposite Optical Films
Alcaire, M; Cerdan, L; Zamarro, FL; Aparicio, FJ; Gonzalez, JC; Ferrer, FJ; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Barranco, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9 (2017) 8948-8959 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
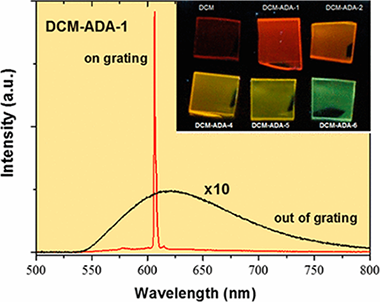
Abstract
We present a low-temperature versatile protocol for the fabrication of plasma nanocomposite thin films to act as tunable emitters and optical gain media. The films are obtained by the remote plasma-assisted deposition of a 4-(dicyano-methylene)-2-methy1-6-(4-dimethylamino-styry1)-4Hpyran (DCM) laser dye alongside adamantane. The experimental parameters that determine the concentration of the dye in the films and their optical properties, including light absorption, the refractive index, and luminescence, are evaluated. Amplified spontaneous emission experiments in the DCM/adamantane nano composite waveguides show the improvement of the copolymerized nano composites' properties compared to films that were deposited with DCM as the sole precursor. Moreover, one-dimensional distributed feed-back laser emission is demonstrated and characterized in some of the nanocomposite films that are studied. These results open new paths for the optimization of the optical and lasing properties of plasma nanocomposite polymers, which can be straightforwardly integrated as active components in optoelectronic devices.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b01534
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Aperiodic Metal-Dielectric Multilayers as Highly Efficient Sunlight Reflectors
Alberto Jiménez-Solano; Miguel Anaya; Mauricio E. Calvo; Mercedes Alcon-Camas; Carlos Alcañiz; Elena Guillén; Noelia Martínez; Manuel Gallas; Thomas Preussner; Ramón Escobar-Galindo; Hernán MíguezAdvanced Optical Materials, 5 (2017) 1600833 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
Abstract
The optimum reflection of the solar spectrum at well-defined incident directions as well as its durability in time are, both, fundamental requirements of the optics of thermosolar and photovoltaic energy conversion systems. The stringent high performance needed for these applications implies that, almost exclusively, second face mirrors based on silver are employed for this purpose. Herein, the possibility to develop solar mirrors using other metals, such as copper and aluminum, is theoretically and experimentally analyzed. It is found that reflectors based on these inexpensive metals are capable of reflecting the full solar spectrum with efficiencies comparable to that of silver-based reflectors. The designs herein proposed are based on aperiodic metal-dielectric multilayers whose optimized configuration is chosen employing a code based on a genetic algorithm that allows selecting the best one among 108 tested reflectors. The use of metals with wider spectral absorption bands is compensated by the use of multilayered designs in which metal absorption is almost suppressed, as the analysis of the electric field intensity distribution demonstrates. The feasibility of the proposed mirrors is demonstrated by their actual fabrication by large area deposition techniques amenable for mass production.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600833
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Ceramics of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2 densified by spark plasma sintering and the effect of post-annealing in air
Sponchia, G; Moshtaghioun, BM; Benedetti, A; Riello, P; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Ortiz, ALScripta Materialia, 130 (2017) 128-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.021
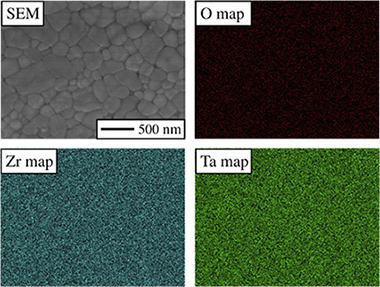
Abstract
16 mol% Ta-doped ZrO2 powders were synthesized and densified by spark-plasma sintering (SPS) in vacuum, followed by post-SPS annealing in air, thus obtaining two ultrafine-grained ceramics consisting of Ta-doping stabilized orthorhombic ZrO2. The as-SPSed ceramic is black because it is actually a suboxide essentially with reduced cations and abundant oxygen vacancies, whereas the post-annealed ceramic is white because it is an oxide without vacancies and with only partially reduced cations. Both ceramics are relatively hard and brittle, but the as-SPSed ceramic was slightly more so, attributable to crystallographic and microstructural differences. Implications of interest for the ceramics community are discussed.
March, 2017 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.021
- ‹ previous
- 18 of 37
- next ›














