Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanophotonics for current and future white light-emitting devices
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Lozano, GJournal of Applied Physics, 130 (2021) 200901
Photonic nanostructures have proven useful to enhance the performance of a wide variety of materials and devices for sensing, catalysis, light harvesting, or light conversion. Herein, we discuss the role of nanophotonics in current and next-generation designs of white light-emitting diodes (LEDs). We discuss recent developments on luminescent materials designed as alternatives to rare earth-doped inorganic microcrystals, i.e., phosphors, for color conversion in LEDs, which has opened the door to the integration of resonant photonic architectures. Nanophotonics enables the devised light-matter interaction with luminescent materials in the nanoscale, which allows providing emitting devices with both enhanced performance and novel functionalities to tackle technological challenges
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0065825
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Zinc Polyaleuritate Ionomer Coatings as a Sustainable, Alternative Technology for Bisphenol A-Free Metal Packaging
Morselli, D; Cataldi, P; Paul, UC; Ceseracciu, L; Benitez, JJ; Scarpellini, A; Guzman-Puyol, S; Heredia, A; Valentini, P; Pompa, PP; Marrero-López, D; Athanassiou, A; Heredia-Guerrero, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9 (2021) 15484-15495
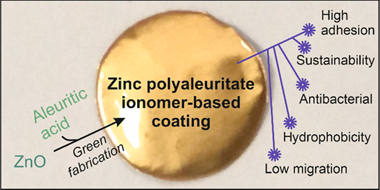
Sustainable coatings for metal food packaging were prepared from ZnO nanoparticles (obtained by the thermal decomposition of zinc acetate) and a naturally occurring polyhydroxylated fatty acid named aleuritic (or 9,10,16-trihydroxy-hexadecanoic) acid. Both components reacted, originating under specific conditions zinc polyaleuritate ionomers. The polymerization of aleuritic acid into polyaleuritate by a solvent-free, melt polycondensation reaction was investigated at different times (15, 30, 45, and 60 min), temperatures (140, 160, 180, and 200 degrees C), and proportions of zinc oxide and aleuritic acid (0:100, 5:95, 10:90, and 50:50, w/w). Kinetic rate constants calculated by infrared spectroscopy decreased with the amount of Zn due to the consumption of reactive carboxyl groups, while the activation energy of the polymerization decreased as a consequence of the catalyst effect of the metal. The adhesion and hardness of coatings were determined from scratch tests, obtaining values similar to robust polymers with high adherence. Water contact angles were typical of hydrophobic materials with values >= 94 degrees. Both mechanical properties and wettability were better than those of bisphenol A (BPA)-based resins and most likely are related to the low migration values determined using a hydrophilic food simulant. The presence of zinc provided a certain degree of antibacterial properties. The performance of the coatings against corrosion was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at different immersion times in an aqueous solution of NaCl. Considering the features of these biobased lacquers, they can be potential materials for bisphenol A-free metal packaging.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c04815
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Recent Advances in Alkaline Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis and Electrode Manufacturing
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Sacedon, CG; Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; De Lucas-Consuegra, AMolecules, 26 (2021) 6326
Water electrolysis to obtain hydrogen in combination with intermittent renewable energy resources is an emerging sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Among the available electrolyzer technologies, anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) has been paid much attention because of its advantageous behavior compared to other more traditional approaches such as solid oxide electrolyzer cells, and alkaline or proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Recently, very promising results have been obtained in the AEMWE technology. This review paper is focused on recent advances in membrane electrode assembly components, paying particular attention to the preparation methods for catalyst coated on gas diffusion layers, which has not been previously reported in the literature for this type of electrolyzers. The most successful methodologies utilized for the preparation of catalysts, including co-precipitation, electrodeposition, sol-gel, hydrothermal, chemical vapor deposition, atomic layer deposition, ion beam sputtering, and magnetron sputtering deposition techniques, have been detailed. Besides a description of these procedures, in this review, we also present a critical appraisal of the efficiency of the water electrolysis carried out with cells fitted with electrodes prepared with these procedures. Based on this analysis, a critical comparison of cell performance is carried out, and future prospects and expected developments of the AEMWE are discussed.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216326
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Recent Advances in the Bronsted/Lewis Acid Catalyzed Conversion of Glucose to HMF and Lactic Acid: Pathways toward Bio-Based Plastics
Megias-Sayago, C; Navarro-Jaen, S; Drault, F; Ivanova, SCatalysts, 11 (2021) 1395

One of the most trending topics in catalysis recently is the use of renewable sources and/or non-waste technologies to generate products with high added value. That is why, the present review resumes the advances in catalyst design for biomass chemical valorization. The variety of involved reactions and functionality of obtained molecules requires the use of multifunctional catalyst able to increase the efficiency and selectivity of the selected process. The use of glucose as platform molecule is proposed here and its use as starting point for biobased plastics production is revised with special attention paid to the proposed tandem Bronsted/Lewis acid catalysts.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/catal11111395
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Polyaniline coated tungsten trioxide as an effective adsorbent for the removal of orange G dye from aqueous media
Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Bouziani, A.; Aarab, N.; Essekri, A; Imgharn, A.; Laabd. M.; Navío, J.A.;Puga, F.; Lakhmirid, R.; Albourine, A.RSC Advances, 11 (2021) 31272-31283

In this work, the core–shell PANI@WO3 composite was obtained from the reaction of aniline monomer polymerization with WO3 particles; sodium persulfate was used as an oxidant. Various analytical techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to characterize the as-prepared PANI@WO3 adsorbent, which well confirmed that the WO3 particles were coated by polyaniline polymer. The PANI@WO3 composite was tested as an adsorbent to remove reactive orange G (OG) for the first time. pH, adsorbent dose, contact time, initial dye concentration, and temperature were systematically investigated in order to study their effect on the adsorption process. The experimental findings showed that the PANI@WO3 composite has considerable potential to remove an aqueous OG dye. Langmuir and Freundlich's models were used to analyze the equilibrium isotherms of OG dye adsorption on the PANI@WO3 composite. As a result, the best correlation of the experimental data was provided by the Langmuir model, and the maximum capacity of adsorption was 226.50 mg g−1. From a thermodynamic point of view, the OG dye adsorption process occurred spontaneously and endothermically. Importantly, PANI@WO3 still exhibited an excellent adsorption capability after four regeneration cycles, indicating the potential reusability of the PANI@WO3 composite. These results indicate that the as prepared PANI@WO3 composite could be employed as an efficient adsorbent and was much better than the parent material adsorption of OG dye.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/D1RA04135E
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Ultrastrong Exciton-Photon Coupling in Broadband Solar Absorbers
Bujalance, C; Esteso, V; Calio, L; Lavarda, G; Torres, T; Feist, J; Garcia-Vidal, FJ; Bottari, G; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 12 (2021) 10706-10712
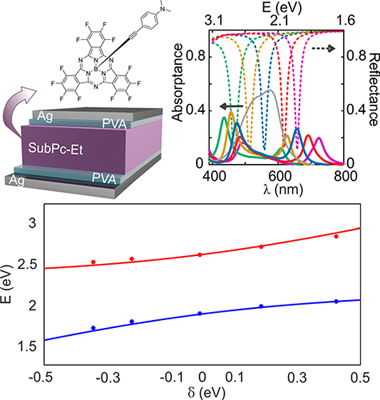
The recent development of organic polaritonic solar cells, in which sunlight absorbers and photon modes of a resonator are hybridized as a result of their strong coupling, has revealed the potential this interaction offers to control and enhance the performance of these devices. In this approach, the photovoltaic cell is built in such a way that it also behaves as an optical cavity supporting spectrally well-defined resonances, which match the broad absorption bands of the dyes employed. Herein we focus on the experimental and theoretical analysis of the specific spectral and angular optical absorption characteristics of a broadband light harvester, namely a subphthalocyanine, when operating in the ultrastrong coupling regime. We discuss the implications of having a broad distribution of oscillator strengths and demonstrate that rational design of the layered structure is needed to optimize both the spectral and the angular response of the sunlight harvester dye.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02898
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
K-Promoted Ni-Based Catalysts for Gas-Phase CO2 Conversion: Catalysts Design and Process Modelling Validation
Gandara-Loe, J; Portillo, E; Odriozola, JA; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LFrontiers in Chemistry, 9 (2021) 785571
The exponential growth of greenhouse gas emissions and their associated climate change problems have motivated the development of strategies to reduce CO2 levels via CO2 capture and conversion. Reverse water gas shift (RWGS) reaction has been targeted as a promising pathway to convert CO2 into syngas which is the primary reactive in several reactions to obtain high-value chemicals. Among the different catalysts reported for RWGS, the nickel-based catalyst has been proposed as an alternative to the expensive noble metal catalyst. However, Ni-based catalysts tend to be less active in RWGS reaction conditions due to preference to CO2 methanation reaction and to the sintering and coke formation. Due to this, the aim of this work is to study the effect of the potassium (K) in Ni/CeO2 catalyst seeking the optimal catalyst for low-temperature RWGS reaction. We synthesised Ni-based catalyst with different amounts of K:Ni ratio (0.5:10, 1:10, and 2:10) and fully characterised using different physicochemical techniques where was observed the modification on the surface characteristics as a function of the amount of K. Furthermore, it was observed an improvement in the CO selectivity at a lower temperature as a result of the K-Ni-support interactions but also a decrease on the CO2 conversion. The 1K catalyst presented the best compromise between CO2 conversion, suppression of CO2 methanation and enhancing CO selectivity. Finally, the experimental results were contrasted with the trends obtained from the thermodynamics process modelling observing that the result follows in good agreement with the modelling trends giving evidence of the promising behaviour of the designed catalysts in CO2 high-scale units.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.785571
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of helium incorporation on growth process and properties of aluminum thin films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering
Ibrahim, S; Lahboub, FZ; Brault, P; Petit, A; Caillard, A; Millon, E; Sauvage, T; Fernandez, A; Thomann, AlSurface & Coatings Technology, 426 (2021) 127808
The effect of helium content on the morphology, crystallinity, and composition of aluminum films was investigated by depositing He-loaded Al films onto Si substrates via direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering in different Ar/He plasma mixtures. Three different plasma regimes were identified depending on the percentage of He in the gas phase. For a low He to total gas ratio (ΓHe ≤ 70%), the plasma is dominated by argon, where Ar+ ions contribute to sputter out the target atoms. The films deposited in this regime exhibited the classical dense columnar structure and contain very low amount of He (below 2%). Then, as ΓHe increases, helium ions begin to be formed and more fast He neutrals reach the substrate, affecting the film growth. As He amount increased in the gas phase up to 95%, the proportion of He inserted in the films rised up to ⁓15 at. %. Moreover, bubbles/porosity were formed inside the films; those obtained in pure He plasma presented a highly porous fiberform nanostructure. All results confirmed that the modification of the film characteristics was related to the change of the deposition conditions when Ar was replaced by He and to the insertion/release mechanisms of He during the growth.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127808
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
By-products revaluation in the production of design micaceous materials
Mouchet, A; Raffin, F; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAplied Clay Science, 214 (2021) 106292
One of the main objectives of a sustainable development and circular economy is the recycling of by-products generated in industrial and agricultural production processes. One of the possible solution is the use of such by-product materials in the synthesis of environmental adsorbents. In the current research, we present the synthesis of a high charge swelling mica with enhance adsorbent properties from blast furnace slag and rice husk ash. Moreover, to ensure the sustainable synthesis a natural bentoniteis used as Si and Al source. Thus, the current study investigated the fabrication of swelling high charged micas, Na-Mn (n (layer charge) = 2 or 4), from FEBEX bentonite, blast furnace slag and rice husk ash thorough the NaCl melt method. The reaction yield, cation framework distribution and structural characteristic of micas have been studied thorough X-ray Diffraction and Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. The yields of Na-Mn synthesis and degree of purity of the mica depends on the nature of these precursors. Thus, a sustainable, non-expensive and environmental friendly process has been evaluated.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106292
Materiales Coloidales
NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanoparticles: synthesis, luminescence and photocatalytic properties
Nunez, NO; Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Calderon-Olvera, RM; Becerro, AI; Colon, G; Ocana, MDalton Transactions, 50 (2021) 16539-16547
Abstract
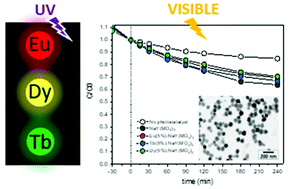
We report on a novel synthesis method, which produces NaY(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles having an almost spherical shape and hydrophilic character. The procedure is also suitable for the preparation of NaY(MoO4)(2)-based nanophosphors by doping this host with lanthanide cations (Eu3+, Tb3+ and Dy3+), which, under UV illumination, exhibit intense luminescence whose color is determined by the selected doping cation (red for Eu3+, green for Tb3+ and yellow for Dy3+). The effects of the cations doping level on the luminescent properties are analyzed in terms of emission intensities and luminescent lifetime, to find the optimum phosphors. Finally, the performance of these nanophosphors and that of the undoped system for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B, used as a model compound, is also analyzed.
November, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1dt02365a
- ‹ previous
- 41 of 214
- next ›














