Scientific Papers in SCI
2021
2021
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Photocatalytic production of hydrogen and methane from glycerol reforming over Pt/TiO2–Nb2O5
Iervolino, G; Vaiano, V; Murcia, JJ; Lara, AE; Hernández, JS; Rojas, H; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy
In this study, platinized mixed oxides (TiO2–Nb2O5) were tested on photocatalytic hydrogen production from a glycerol solution under UV light. Different samples with different Ti:Nb ratios were prepared by using a simple method that simultaneously combined a physical mixture and a platinum photochemical reduction. This method led to improved physicochemical properties such as low band gap, better Pt nanoparticle distribution on the surface, and the formation of different Pt species. Niobia content was also found to be an important factor in determining the overall efficiency of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 photocatalyst in the glycerol reforming reaction. The photocatalytic results showed that Pt on TiO2–Nb2O5 enhanced hydrogen production from the aqueous glycerol solution at a 5 wt% initial glycerol concentration. The influence of different operating conditions such as the catalyst dosage and initial glycerol concentration was also evaluated. The results indicated that the best hydrogen and methane production was equal to 6657 μmol/L and 194 μmol/L, respectively after 4 h of UV radiation using Pt/Ti:Nb (1:2) sample and with 3 g/L of catalyst dosage. Moreover, the role of water in photocatalytic hydrogen production was studied through photocatalytic activity tests in the presence of D2O. The obtained results confirmed the role of water molecules on the photocatalytic production of hydrogen in an aqueous glycerol solution.
September, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.111
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Nb-C thin films prepared by DC-MS and HiPIMS: Synthesis, structure, and tribomechanical properties
Sala, N; Abad, MD; Sánchez-López, JC; Caro, J; Colominas, CSurface & Coatings Technology, 422 (2021) 127569

Nanostructured Nb-C thin films were prepared by direct current magnetron sputtering (DC-MS) and high-power impulse magnetron sputtering (HiPIMS). The films were characterized in depth by X-ray diffraction (XRD), grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, electron probe microanalysis, and Raman spectroscopy. The mechanical properties were measured by nanoindentation, and the tribological properties were measured by pin-on-disk tests in ambient air. The wear tracks and ball scars were analyzed by Raman spectroscopy to elucidate the tribochemical reactions that occurred at the contact area and to determine the wear mechanism for each specimen type. The thermal stability of the coatings was studied up to 1000 degrees C using Raman spectroscopy and XRD. The samples prepared by DC-MS were very dense, and the phase composition changed from purely nanocrystalline (Nb2C and NbC) to a mixture of NbC crystals embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix (NbC/a-C(:H)). However, the samples prepared by HiPIMS developed a marked columnar morphology with a NbC/a-C(:H) nanocomposite structure. The hardness values ranged from 11 to 20 GPa depending on the deposition technique and the amount of the soft a-C(:H) phase present in the sample. The tribological properties of all the coatings were remarkably good when the carbon content was approximately 50 at.%. The formation of a lubricating sp(2)-rich C tribofilm between the ball and coating during the pin-on-disk tests was observed by Raman spectroscopy. The tribofilm formed preferentially on the samples prepared by HiPIMS, which had higher C contents. At 750 degrees C, the degradation of the NbC phases resulted in the formation of an additional a-C phase and niobium oxides.
September, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127569
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
One-reactor vacuum and plasma synthesis of transparent conducting oxide nanotubes and nanotrees: from single wire conductivity to ultra-broadband perfect absorbers in the NIR
Castillo-Seoane, J; Gil-Rostra, J; Lopez-Flores, V; Lozano, G; Ferrer, FJ; Espinos, JP; Ostrikov, K; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, ANanoscale, 13 (2021) 13882-13895
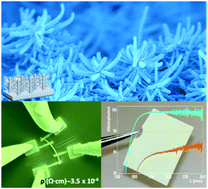
The eventual exploitation of one-dimensional nanomaterials needs the development of scalable, high yield, homogeneous and environmentally friendly methods capable of meeting the requirements for fabrication of functional nanomaterials with properties on demand. In this article, we demonstrate a vacuum and plasma one-reactor approach for the synthesis of fundamental common elements in solar energy and optoelectronics, i.e. the transparent conducting electrode but in the form of nanotube and nanotree architectures. Although the process is generic and can be used for a variety of TCOs and wide-bandgap semiconductors, we focus herein on indium doped tin oxide (ITO) as the most previously researched in previous applications. This protocol combines widely applied deposition techniques such as thermal evaporation for the formation of organic nanowires serving as 1D and 3D soft templates, deposition of polycrystalline layers by magnetron sputtering, and removal of the templates by simply annealing under mild vacuum conditions. The process variables are tuned to control the stoichiometry, morphology, and alignment of the ITO nanotubes and nanotrees. Four-probe characterization reveals the improved lateral connectivity of the ITO nanotrees and applied on individual nanotubes shows resistivities as low as 3.5 +/- 0.9 x 10(-4) omega cm, a value comparable to that of single-crystalline counterparts. The assessment of diffuse reflectance and transmittance in the UV-Vis range confirms the viability of the supported ITO nanotubes as random optical media working as strong scattering layers. Their further ability to form ITO nanotrees opens a path for practical applications as ultra-broadband absorbers in the NIR. The demonstrated low resistivity and optical properties of these ITO nanostructures open a way for their use in LEDs, IR shields, energy harvesting, nanosensors, and photoelectrochemical applications.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1039/d1nr01937f
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser-induced scanning transfer deposition of silver electrodes on glass surfaces: A green and scalable technology
Molina, R; Ertugrul, M; Larrea, A; Navarro, R; Rico, V; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR: De la Fuente, GF; Angurel, LAApplied Surface Science, 556 (2021) 149673

A pulsed laser ablation backwriting technique with high repetitive rates is implemented for the fabrication of silver coatings on glass surfaces. This method enables geometrical constraint-free deposition of metallic coatings. These exhibit sufficiently low electrical resistance to be used as electrodes in dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma elements. Ambient air deposition of metallic silver electrodes on standard glass slides is explored using a sub-ns UV laser source, combined with hybrid beam scanning methods. The green nature of the overall deposition process includes a preliminary irradiation scan to homogenise the target surface before the subsequent backwriting step. Metal transfer is achieved by combining two phenomena within a simple beam scanning process: LIRT (laserinduced reverse transfer) of silver from the target to the glass, with a partial and secondary LIFT (Laser-Induced Forward Transfer) of silver from the glass to the target. Appropriate selection of pulse energy and pulse repetition rates, beam scanning velocities and target motion enable the growth of sufficiently thick Ag deposits on glass with the required low electrical resistivity and nearly 2D constraint-free geometry. This method avoids the use of vacuum and liquids, resulting in a cheap, facile and green methodology for the deposition of silver electrodes onto transparent substrate surfaces.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149673
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
ZnO/Ag3PO4 and ZnO–Malachite as Effective Photocatalysts for the Removal of Enteropathogenic Bacteria, Dyestuffs, and Heavy Metals from Municipal and Industrial Wastewater
Murcia, JJ; Hernández Miño, JS; Rojas, H; Brijaldo, MH; Martin-Gómez, AN; Sánchez-Cid, P; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MC; Jaramillo-Pérez, CWater, 13 (2021) 2264

Different composites based on ZnO/Ag3PO4 and ZnO–malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3) were synthesized in order to determine their effectiveness in the treatment of municipal and industrial wastewaters (mainly polluted by enteropathogenic bacteria, dyes, and heavy metals). The addition of Ag3PO4 and malachite did not significantly modify the physicochemical properties of ZnO; however, the optical properties of this oxide were modified as a result of its coupling with the modifiers. The modification of ZnO led to an improvement in its effectiveness in the treatment of municipal and industrial wastewater. In general, the amount of malachite or silver phosphate and the effluent to be treated were the determining factors in the effectiveness of the wastewater treatment. The highest degree of elimination of bacteria from municipal wastewater and discoloration of textile staining wastewater were achieved by using ZnO/Ag3PO4 (5%), but an increase in the phosphate content had a detrimental effect on the treatment. Likewise, the highest Fe and Cu photoreduction from coal mining wastewater was observed by using ZnO–malachite (2.5%) and ZnO/Ag3PO4 (10%), respectively. Some of the results of this work were presented at the fourth Congreso Colombiano de Procesos Avanzados de Oxidación (4CCPAOx).
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/w13162264
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Coloidales
Persistent luminescent nanoparticles: Challenges and opportunities for a shimmering future
Castaing, V.; Arroyo, E.; Becerro, A.I.; Ocaña, M.; Lozano, G.; Míguez, H.Journal of Applied Physics, 130 (2021) 080902
Persistent phosphors are luminescent sources based on crystalline materials doped with rare-earth or transition metal cations able to produce light after the excitation source vanishes. Although known for centuries, these materials gained renewed interest after the discovery of Eu2+,RE3+ co-doped aluminates and silicates in the late 1990s due to their unprecedented afterglow properties. In contrast, persistent nanophosphors have emerged only recently as a nanoscale alternative to their bulk counterparts, offering exciting opportunities of particular relevance for in vivo imaging, optical data storage, or unconventional light generation. However, taking advantage of the avenues opened by nanoscience demands developing new synthetic strategies that allow precise control of the morphology, surface, and defect chemistry of the nanomaterials, along with a profound understanding of the physical mechanisms occurring in the nanoscale. Besides, advanced physicochemical characterization is required to assess persistent luminescence in a quantitative manner, which allows strict comparison among different persistent nanophosphors, aiming to propel their applicability. Herein, we revisit the main phenomena that determine the emission properties of persistent nanoparticles, discuss the most promising preparation and characterization protocols, highlight recent achievements, and elaborate on the challenges ahead.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1063/5.0053283
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetics and cyclability of limestone (CaCO3) in presence of steam during calcination in the CaL scheme for thermochemical energy storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Moreno, V; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 417 (2021) 129194
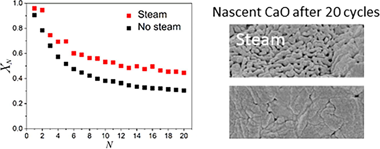
In the present work, we explore the use of steam in the CaCO3 calcination step of the Calcium Looping process devised for thermochemical energy storage (CaL-TCES). Steam produces a double benefit: firstly, it fastens calcination, allowing a reduction of the temperature needed to attain full calcination in short residence times, as those required in practice, resulting in energy savings. This behaviour is justified on the basis of a kinetics study results obtained from a non-parametric kinetic analysis, which demonstrate that the presence of steam during calcination can reduce the apparent activation energy from 175 kJ/mol to 142 kJ/mol with a steam's partial pressure of 29%. In addition, the results obtained for multicycle CaL-TCES tests show that steam alleviates the deactivation of the sorbent, which is one of the main limiting factors of this technology. This behaviour is explained in terms of the effect of steam on the microstructure of the regenerated CaO. Importantly, the values of residual conversion attained by calcining in steam are higher than those without steam.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129194
Reactividad de Sólidos
Study of the Influence of Sintering Atmosphere and Mechanical Activation on the Synthesis of Bulk Ti2AlN MAX Phase Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering
Salvo, C; Chicardi, E; García-Garrido, C; Poyato, R; Jimenez, JA; Mangalaraja, RVMaterials, 14 (2021) 4574
The influence of the mechanical activation process and sintering atmosphere on the microstructure and mechanical properties of bulk Ti2AlN has been investigated. The mixture of Ti and AlN powders was prepared in a 1:2 molar ratio, and a part of this powder mixture was subjected to a mechanical activation process under an argon atmosphere for 10 h using agate jars and balls as milling media. Then, the sintering and production of the Ti2AlN MAX phase were carried out by Spark Plasma Sintering under 30 MPa with vacuum or nitrogen atmospheres and at 1200 degrees C for 10 min. The crystal structure and microstructure of consolidated samples were characterized by X-ray Diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscopy, and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy. The X-ray diffraction patterns were fitted using the Rietveld refinement for phase quantification and determined their most critical microstructural parameters. It was determined that by using nitrogen as a sintering atmosphere, Ti4AlN3 MAX phase and TiN were increased at the expense of the Ti2AlN. In the samples prepared from the activated powders, secondary phases like Ti5Si3 and Al2O3 were formed. However, the higher densification level presented in the sample produced by using both nitrogen atmosphere and MAP powder mixture is remarkable. Moreover, the high-purity Ti2AlN zone of the MAX-1200 presented a hardness of 4.3 GPa, and the rest of the samples exhibited slightly smaller hardness values (4.1, 4.0, and 4.2 GPa, respectively) which are matched with the higher porosity observed on the SEM images.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.3390/ma14164574
Materiales Avanzados
Geopolymers made from metakaolin sources, partially replaced by Spanish clays and biomass bottom ash
Eliche-Quesada, D; Calero-Rodriguez, A; Bonet-Martinez, E;Perez-Villarejo, L; Sanchez-Soto, PJJournal of Building Engineering, 40 (2021) 102761
The main objective of this investigation is to study the effect of the substitution of metakaolin (MK) (from calcined industrial kaolin) by four different calcined natural Southern Spain clays traditionally used in the brick and tile sector, as well as by the biomass bottom ash residue (BBA) from the combustion of a mix of olive and pine pruning on the synthesis of geopolymer with physical, mechanical and thermal properties comparable to those of classic construction materials. As alkaline activator, a 8 M solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate have been used. Raw materials, metakaolin; Spanish clays: black clay (BC), yellow clay (YC), white clay (WC), red clay (RC) and BBA were characterized by chemical analysis (XRF), mineralogical analysis (XRD), and particle size analysis. Control geopolymers containing only metakaolin, and batch of geopolymers were formulated containing equal proportions of metakaolin, BBA and each of the four types of clay. After the curing period, at 60 degrees C for 1 day geopolymers were demolded and stored 27 days at room temperature. Geopolymers were characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy coupled with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), XRD and Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spec troscopy (ATR-FTIR). Their physical, mechanical and thermal properties have also been studied. The addition of BBA and different types of calcined clays to metakaolin gives rise to geopolymers with higher mechanical properties increasing the compressive strength of the control geopolymer containing only MK (24.9 MPa) by more than 50% for the GMK-BBA-WC geopolymers (38.5 MP a). The clays act as fillers and/or promote the precipitation of calcium-rich phases (Ca)-A-S-H-G gel that coexists with the (Na)-A-S-H gel type. The relevant results of physical, mechanical and thermal properties obtained in this research demonstrate the potential of Spanish clays and BBA as binders and substitutes for metakaolin.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102761
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcination under low CO2 pressure enhances the calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage
Sarrion, B; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Amghar, N; Chacartegui, R; Valverde, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAChemical Engineering Journal, 417 (2021) 127922
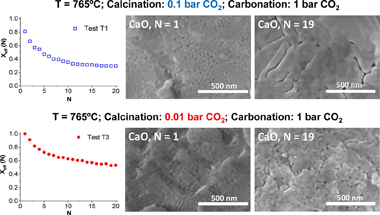
The Calcium Looping performance of limestone for thermochemical energy storage has been investigated under novel favorable conditions, which involve calcination at moderate temperatures under CO2 at low pressure (0.01 and 0.1 bar) and carbonation at high temperature under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. Calcining at low CO2 pressures allows to substantially reduce the temperature to achieve full calcination in short residence times. Moreover, it notably enhances CaO multicycle conversion. The highest values of conversion are obtained for limestone samples calcined under 0.01 bar CO2 at 765 degrees C. Under these conditions, the residual conversion is increased by a factor of 10 as compared to conditions involving calcination under CO2 at atmospheric pressure. The enhancement of CaO conversion is correlated to the microstructure of the CaO samples obtained after calcination. As seen from SEM, BET surface and XRD analysis, calcination under low CO2 pressure leads to a remarkable decrease of pore volume and CaO crystallite size. Consequently, CaO surface area available for carbonation in the fast reaction-controlled regime and therefore reactivity in short residence times is promoted.
August, 2021 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127922
- ‹ previous
- 44 of 214
- next ›














