Scientific Papers in SCI
2023
2023
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Origin of anomalously stabilizing ice layers on methane gas hydrates near rock surface
Li, Y; Corkery, RW; Carretero-Palacios, S; Berland, K; Esteso, V; Fiedler, J; Milton, KA; Brevik, I; Bostrom, MPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 25 (2023) 6636-6652 DOI: 10.1039/d2cp04883c
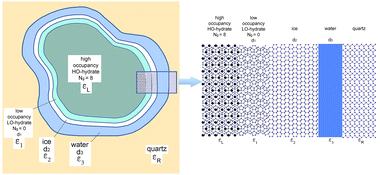
Abstract
Gas hydrates (GHs) in water close to freezing temperatures can be stabilised via the formation of ice layers. In a recent work [Bostrom et al., Astron. Astrophys., A54, 650, 2021], it was found that a surface region with partial gas dilution could be essential for obtaining nano- to micron-sized anomalously stabilizing ice layers. In this paper, it is demonstrated that the Casimir-Lifshitz free energy in multi-layer systems could induce thinner, but more stable, ice layers in cavities than those found for gas hydrates in a large reservoir of cold water. The thickness and stability of such ice layers in a pore filled with cold water could influence the leakage of gas molecules. Additional contributions, e.g. from salt-induced stresses, can also be of importance, and are briefly discussed.
March, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d2cp04883c
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Engineering exsolved catalysts for CO2 conversion
Ali, SA; Safi, M; Merkouri, LP; Soodi, S; Iakovidis, A; Duyar, MS; Neagu, D; Reina, TR; Kousi, KFrontiers in Energy Research, 11 (2023) 1150000 DOI: 10.3389/fenrg.2023.1150000
Abstract
Introduction: Innovating technologies to efficiently reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emission or covert it into useful products has never been more crucial in light of the urgent need to transition to a net-zero economy by 2050. The design of efficient catalysts that can make the above a viable solution is of essence. Many noble metal catalysts already display high activity, but are usually expensive. Thus, alternative methods for their production are necessary to ensure more efficient use of noble metals.Methods: Exsolution has been shown to be an approach to produce strained nanoparticles, stable against agglomeration while displaying enhanced activity. Here we explore the effect of a low level of substitution of Ni into a Rh based A-site deficienttitanate aiming to investigate the formation of more efficient, low loading noblemetal catalysts.Results: We find that with the addition of Ni in a Rh based titanate exsolution is increased by up to similar to 4 times in terms of particle population which in turn results in up to 50% increase in its catalytic activity for CO2 conversion.Discussion: We show that this design principle not only fulfills a major research need in the conversion of CO2 but also provides a step-change advancement in the design and synthesis of tandem catalysts by the formation of distinct catalytically active sites.
March, 2023 · DOI: 10.3389/fenrg.2023.1150000
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Boosting the photocatalytic properties of NaTaO3 by coupling with AgBr
Puga, F; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MCPhotochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 22 (2023) 549-566 DOI: 10.1007/s43630-022-00334-9
Abstract
AgBr/NaTaO3 composites, with different molar % of NaTaO3 (Br/NTO(X%)), have been synthesized by simple precipitation methods; bare NaTaO3 was synthesized by hydrothermal procedure, while AgBr was synthesized by a precipitation procedure using cetyl-tri-methyl-ammonium bromide (CTAB) and AgNO3. Samples have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption, UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Photocatalytic activity of the as-prepared photo-catalysts was evaluated through photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B (RhB), methyl orange (MO) and caffeic acid (CAFA) under UV and visible illumination. Single AgBr material and Br/NTO(X%) composites displayed the ability to absorb light in the visible region, while NaTaO3 is only photoactive under UV irradiation. Based on the position of conduction and valence bands of AgBr and NaTaO3, the heterojunction between these two photo-catalysts corresponds to a type II junction. In the case of photocatalytic degradation of RhB and CAFA, Br/NTO(x%) composites have highest photocatalytic activity than that obtained by both parental materials under the same operational conditions. AgBr and Br/NTO(x%) composites achieve a fast degradation of MO, together with a considerable adsorption capacity, attributed to the presence of a remaining amount of residual CTAB on the AgBr surface. In summary, coupling AgBr with NaTaO3 improves the photocatalytic activity under both UV and visible illumination with respect to the parental components, but the performance of the composites is highly dependent on the type of substrate to be degraded and the illumination conditions.
March, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s43630-022-00334-9
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-based lacquers from industrially processed tomato pomace for sustainable metal food packaging
Benitez, JJ; Ramirez-Pozo, MC; Duran-Barrantes, MM; Heredia, A; Tedeschi, G; Ceseracciu, L; Guzman-Puyol, S; Marrero-López, D; Becci, A; Amato, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JAJournal of Cleaner Production, 386 (2023) 1356836 DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135836

Abstract
Bio-based lacquers prepared from an underutilized tomato processing residue such as pomace have been investigated as sustainable alternatives to bisphenol A (BPA)-based coatings for metal food packaging. The fabrication methodology consisted of a two-step process: spray-coating of a paste of the lipid fraction of tomato pomace with a mixture ethanol:H2O (3:1, v:v) on common metal substrates, used for food canning, such as aluminum (Al), chromium-coated tin-free steel (TFS), and electrochemically tin-plated steel (ETP), followed by the self melt-polycondensation of such lipid fraction. The polymerization reaction was conducted at 200 degrees C for different times (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min) and was monitored by specular infrared spectroscopy, resulting in maximum degrees of esterification of-92% for Al and-85% for TFS and ETP substrates. The anticorrosion performance of the coatings was studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy at different immersion times (time intervals of 2-5 h during an overall stability test up to 170 h) in an aqueous solution of 1 wt% NaCl. The degree of polymerization and the physical properties of the coatings showed a strong dependence on the metal substrate used. In general, the best results were found for tomato pomace-based lacquers applied on aluminum, achieving higher mechanical strength (critical load of 1739 +/- 198 mN for Al, 1078 +/- 31 mN for ETP, and 852 +/- 206 mN for TFS), hydrophobicity (water contact angle-95 degrees for Al,-91 degrees for ETP, and-88 degrees for TFS), and improved anticorrosion performance (coating resistance of 0.7 M omega cm2 after 170 h of immersion for Al, 0.7 M omega cm2 after 70 h of immersion for TFS, and negligible coating resistance for ETP). In view of the technical innovation proposed in the present paper, the estimation of the environmental sustainability of the process has been considered relevant to fit the circular economy target. For this purpose, a life cycle analysis (LCA) was applied to the overall process, revealing multiple advantages for both the environment and human health.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135836
Reactividad de Sólidos
Structural, Vibrational, and Magnetic Characterization of Orthoferrite LaFeO3 Ceramic Prepared by Reaction Flash Sintering
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAMaterials, 16 (2023) 1019 DOI: 10.3390/ma16031019
Abstract
LaFeO3 perovskite ceramics have been prepared via reaction flash technique using Fe2O3 and La2O3 as precursors. The obtained pellets have been investigated using several techniques. The formation of LaFeO3 has been clearly confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The scanning electron microscopy micrographs have shown the microporous character of the obtained pellets due to the low temperature and dwell time used in the synthesis process (10 min at 1173 K). The orthorhombic-rhombohedral phase transition has been observed at approximately 1273 K in differential thermal analysis measurements, which also allows us to determine the Neel temperature at 742 K. The fitted Mossbauer spectra exposed the presence of a single sextet ascribed to the Fe+3 ions in the tetrahedral site. Finally, magnetic measurements at room temperature indicate the antiferromagnetic character of the sample.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16031019
Materiales Semiconductores para la Sostenibilidad
Non-sticky interactions
Esteso, VNature Physics, 19 (2023) 161-162 DOI: 10.1038/s41567-022-01935-y
Abstract
Quantum mechanical fluctuations of the electromagnetic field in a vacuum between two close together objects result in an attractive force. Now, it has been experimentally shown that by exploiting a similar repulsive interaction, attraction between objects can be modulated simply by tuning temperature.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1038/s41567-022-01935-y
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting with ITO/WO3/BiVO4/CoPi Multishell Nanotubes Enabled by a Vacuum and Plasma Soft- Template Synthesis
Gil-Rostra, J; Castillo-Seoane, J; Guo, Q; Sobrido, ABJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 15 (2023) 9250-9262 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c19868
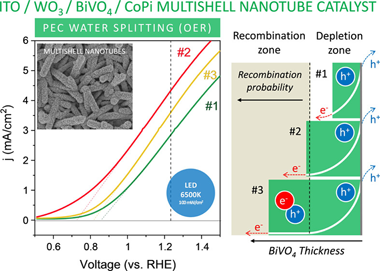
Abstract
A common approach for the photoelectrochemical (PEC) splitting of water relies on the application of WO3 porous electrodes sensitized with BiVO4 acting as a visible photoanode semiconductor. In this work, we propose a new architecture of photoelectrodes consisting of supported multishell nanotubes (NTs) fabricated by a soft-template approach. These NTs are formed by a concentric layered structure of indium tin oxide (ITO), WO3, and BiVO4, together with a final thin layer of cobalt phosphate (CoPi) co-catalyst. The photoelectrode manufacturing procedure is easily implementable at a large scale and successively combines the thermal evaporation of single crystalline organic nanowires (ONWs), the magnetron sputtering deposition of ITO and WO3, and the solution dripping and electrochemical deposition of, respectively, BiVO4 and CoPi, plus the annealing in air under mild conditions. The obtained NT electrodes depict a large electrochemically active surface and outperform the efficiency of equivalent planar-layered electrodes by more than one order of magnitude. A thorough electrochemical analysis of the electrodes illuminated with blue and solar lights demonstrates that the characteristics of the WO3/BiVO4 Schottky barrier heterojunction control the NT electrode efficiency, which depended on the BiVO4 outer layer thickness and the incorporation of the CoPi electrocatalyst. These results support the high potential of the proposed soft-template methodology for the large-area fabrication of highly efficient multishell ITO/WO3/BiVO4/CoPi NT electrodes for the PEC splitting of water.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c19868
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Determination of the optical constants of ligand-free organic lead halide perovskite quantum dots
Rubino, A; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HNanoscale, 15 (2023) 2553-2560 DOI: 10.1039/d2nr05109e
Abstract
Precise knowledge of the optical constants of perovskite lead halide quantum dots (QDs) is required to both understand their interaction with light and to rationally design and optimize the devices based on them. However, their determination from colloidal nanocrystal suspensions, or films made out of them, remains elusive, as a result of the difficulty in disentangling the optical constants of the organic capping ligands and those of the semiconductor itself. In this work, we extract the refractive index and extinction coefficient of ligand-free methylammonium lead iodide (MAPbI(3)) and bromide (MAPbBr(3)) nanocrystals. In order to prevent the use of organic ligands in the preparation, we follow a scaffold assisted synthetic procedure, which yields a composite film of high optical quality that can be independently and precisely characterized and modelled. In this way, the contribution of the guest nanocrystals can be successfully discriminated from that of the host matrix. Using a Kramers-Kronig consistent dispersion model along with an effective medium approximation, it is possible to derive the optical constants of the QDs by fitting the spectral dependence of light transmitted and reflected at different angles and polarizations. Our results indicate a strong dependence of the optical constants on the QD size. Small nanocrystals show remarkably large values of the extinction coefficient compared to their bulk counterparts. This analysis opens the door to the rigorous modelling of solar cells and light-emitting diodes with active layers based on perovskite QDs.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d2nr05109e
Materiales Avanzados
Effect of L-Glutamic Acid on the Composition and Morphology of Nanostructured Calcium Phosphate as Biomaterial
Takabait, F; Martinez-Martinez, S; Mahtout, L; Graba, Z; Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Perez-Villarejo, LMaterials, 16 (2023) 1262 DOI: 10.3390/ma16031262
Abstract
Calcium phosphate (CaP) with several chemical compositions and morphologies was prepared by precipitation using aqueous solutions of L-Glutamic acid (H(2)G) and calcium hydroxide, both mixed together with an aqueous solution (0.15 M) of phosphoric acid. Plate-shaped dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (brushite) particles were obtained and identified at a lower concentration of the solution of the reactants. The Ca/P ratio deduced by EDS was similar to 1, as expected. The nanoscale dimension of carbonate apatite and amorphous calcium phosphate, with variable Ca/P ratios, were revealed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis (SEM-EDS). They were characterized in medium and high concentrations of calcium hydroxide (0.15 M and 0.20 M). The equilibria involved in all the reactions in aqueous solution were determined. The thermodynamic calculations showed a decrease in the amount of chelate complexes with an increase in pH, being the opposite of [CaPO4-] and [CaHG(+)]. This fluctuation showed an evident influence on the morphology and polymorphism of CaP particles obtained under the present experimental conditions, with potential use as a biomaterial.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16031262
Materiales Coloidales
Europium doped-double sodium bismuth molybdate nanoparticles as contrast agents for luminescence bioimaging and X-ray computed tomography
Calderon-Olvera, RM; Nunez, NO; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Monje-Moreno, JM; Munoz-Rui, MJ; Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Arroyo, E; Torres-Herrero, B; De la Fuente, JM; Ocaña, MInorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 10(11) (2023) 3202 DOI: 10.1039/D2QI02664C
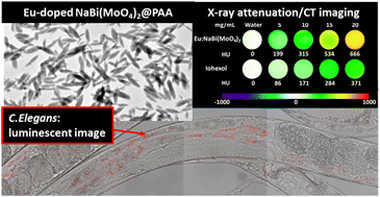
Abstract
A one-pot method for the synthesis of uniform Eu3+-doped NaBi(MoO4)2 nanoparticles with an ellipsoidal shape and tetragonal crystal structure functionalized with polyacrylic acid is reported for the first time in the literature. The method is based on a homogeneous precipitation reaction from solutions in an ethylene glycol/water medium containing appropriate bismuth, sodium, and molybdate precursors and polyacrylic acid. The luminescence properties (excitation and emission spectra and luminescence lifetime) of such nanoparticles are evaluated for different Eu3+ doping levels, finding an intense red emission for all synthesized samples. The X-ray attenuation properties of the nanoparticles have been also analyzed, which were found to be better than those of a commercially computed tomography contrast agent (iohexol). The dispersibility of the nanoparticles in a physiological medium was also analyzed, finding that they could be well dispersed in a 2-N-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid monohydrate medium (pH = 6.5). Finally, the cell viability of such a phosphor has been analyzed using MIA-PaCa-2 cells and its in vivo toxicity has been evaluated using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans model finding no significant toxicity in both cases up to a nanoparticle concentration of 100 μg mL−1, which is within the range required for most in vivo applications. The developed Eu3+-doped NaBi(MoO4)2 nanoparticles are, therefore, excellent candidates for their use as bimodal probes for luminescence imaging and X-ray computed tomography.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/D2QI02664C
Reactividad de Sólidos
Determination of the activation energy under isothermal conditions: revisited
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 148 (2023) 1679-1686 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11728-3
Abstract
The kinetic analysis of solid-state processes aims at obtaining fundamental information that can be used for predicting the time evolution of a process within a wide range of conditions. It is an extended belief that the determination of the kinetic parameters from the analysis of curves recorded under isothermal conditions is strongly conditioned by the kinetic model used to fit the experimental data. Thus, much effort is devoted to finding the model that truly describes a process in order to calculate the kinetic parameters with accuracy. In this work, we demonstrate that the value of activation energy determined from kinetic analysis of isothermal curves is independent of the kinetic model used to fit the experimental data and, taking advantage of the underlying reason for this, a method for determining the activation energy with two isothermal curves is proposed.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11728-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Incorporation of a Metal Catalyst for the Ammonia Synthesis in a Ferroelectric Packed-Bed Plasma Reactor: Does It Really Matter?
Navascues, P; Garrido-Garcia, J; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Gomez-Ramirez, AACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 11 (2023) 3621-3632 DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05877
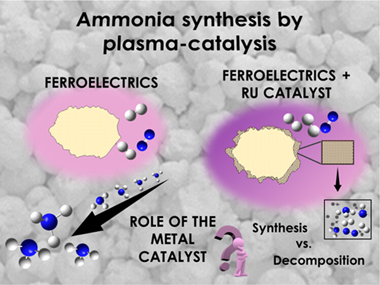
Abstract
Plasma-catalysis has been proposed as a potential alternative for the synthesis of ammonia. Studies in this area focus on the reaction mechanisms and the apparent synergy existing between processes occurring in the plasma phase and on the surface of the catalytic material. In the present study, we approach this problem using a parallel-plate packed-bed reactor with the gap between the electrodes filled with pellets of lead zirconate titanate (PZT), with this ferroelectric material modified with a coating layer of alumina (i.e., Al2O3/PZT) and the same alumina layer incorporating ruthenium nanoparticles (i.e., Ru-Al2O3/PZT). At ambient temperature, the electrical behavior of the ferroelectric packed-bed reactor differed for these three types of barriers, with the plasma current reaching a maximum when using Ru-Al2O3/PZT pellets. A systematic analysis of the reaction yield and energy efficiency for the ammonia synthesis reaction, at ambient temperature and at 190 °C and various electrical operating conditions, has demonstrated that the yield and the energy efficiency for the ammonia synthesis do not significantly improve when including ruthenium particles, even at temperatures at which an incipient catalytic activity could be inferred. Besides disregarding a net plasma-catalysis effect, reaction results highlight the positive role of the ferroelectric PZT as moderator of the discharge, that of Ru particles as plasma hot points, and that of the Al2O3 coating as a plasma cooling dielectric layer.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05877
Reactividad de Sólidos
Flexible Kinetic Model Determination of Reactions in Materials under Isothermal Conditions
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Perejón, A; Sánchez-Jiménez, PE; Pérez-Maqueda, LAMaterials, 16 (2023) 1851 DOI: 10.3390/ma16051851
Abstract
Kinetic analysis remains a powerful tool for studying a large variety of reactions, which lies at the core of material science and industry. It aims at obtaining the kinetic parameters and model that best describe a given process and using that information to make reliable predictions in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, kinetic analysis often relies on mathematical models derived assuming ideal conditions that are not necessarily met in real processes. The existence of nonideal conditions causes large modifications to the functional form of kinetic models. Therefore, in many cases, experimental data hardly obey any of these ideal models. In this work, we present a novel method for the analysis of integral data obtained under isothermal conditions without any type of assumption about the kinetic model. The method is valid both for processes that follow and for those that do not follow ideal kinetic models. It consists of using a general kinetic equation to find the functional form of the kinetic model via numerical integration and optimization. The procedure has been tested both with simulated data affected by nonuniform particle size and experimental data corresponding to the pyrolysis of ethylene-propylene-diene.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16051851
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Flexible NiRu Systems for CO2 Methanation: From Efficient Catalysts to Advanced Dual-Function Materials
Merkouri, LP; Martin-Espejo, JL; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Duyar, MS; Reina, TRNanomaterials, 13 (2023) 506 DOI: 10.3390/nano13030506
Abstract
CO2 emissions in the atmosphere have been increasing rapidly in recent years, causing global warming. CO2 methanation reaction is deemed to be a way to combat these emissions by converting CO2 into synthetic natural gas, i.e., CH4. NiRu/CeAl and NiRu/CeZr both demonstrated favourable activity for CO2 methanation, with NiRu/CeAl approaching equilibrium conversion at 350 degrees C with 100% CH4 selectivity. Its stability under high space velocity (400 L center dot g(-1)center dot h(-1)) was also commendable. By adding an adsorbent, potassium, the CO2 adsorption capability of NiRu/CeAl was boosted, allowing it to function as a dual-function material (DFM) for integrated CO2 capture and utilisation, producing 0.264 mol of CH4/kg of sample from captured CO2. Furthermore, time-resolved operando DRIFTS-MS measurements were performed to gain insights into the process mechanism. The obtained results demonstrate that CO2 was captured on basic sites and was also dissociated on metallic sites in such a way that during the reduction step, methane was produced by two different pathways. This study reveals that by adding an adsorbent to the formulation of an effective NiRu methanation catalyst, advanced dual-function materials can be designed.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/nano13030506
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
CO2 Methanation over Nickel Catalysts: Support Effects Investigated through Specific Activity and Operando IR Spectroscopy Measurements
Gonzalez-Rangulan, VV; Reyero, I; Bimbela, F; Romero-Sarria, F; Daturi, M; Gandia, LMCatalysts, 13 (2023) 448 DOI: 10.3390/catal13020448
Abstract
Renewed interest in CO2 methanation is due to its role within the framework of the Power-to-Methane processes. While the use of nickel-based catalysts for CO2 methanation is well stablished, the support is being subjected to thorough research due to its complex effects. The objective of this work was the study of the influence of the support with a series of catalysts supported on alumina, ceria, ceria-zirconia, and titania. Catalysts' performance has been kinetically and spectroscopically evaluated over a wide range of temperatures (150-500 degrees C). The main results have shown remarkable differences among the catalysts as concerns Ni dispersion, metallic precursor reducibility, basic properties, and catalytic activity. Operando infrared spectroscopy measurements have evidenced the presence of almost the same type of adsorbed species during the course of the reaction, but with different relative intensities. The results indicate that using as support of Ni a reducible metal oxide that is capable of developing the basicity associated with medium-strength basic sites and a suitable balance between metallic sites and centers linked to the support leads to high CO2 methanation activity. In addition, the results obtained by operando FTIR spectroscopy suggest that CO2 methanation follows the formate pathway over the catalysts under consideration.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/catal13020448
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Improved stability of design clay minerals at high temperature: A comparison study with natural ones
Osuna, FJ; Chaparro, JR; Pavon, E; Alba, MDCeramics International, 49 (2023) 5279-5291 DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.046
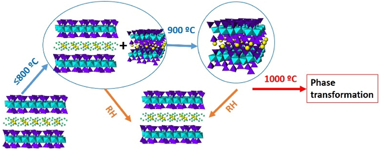
Abstract
Clay minerals are ceramics materials that are involved in a wide range of economic uses. But, their structure and composition are modified by heating and, consequently, compromise their final applications. The actual tem-peratures at which changes occur vary greatly from one group to another group and even for different specimens within a given group. The aim of this research has been to evaluate the thermal behaviour of a set of design swelling micas, Na-Mica -n (Mn) and compare them with a set of natural smectites. All samples were heated in the range 200 degrees C to 1000 degrees C; afterwards, they were rehydrated thorough water suspension (0.4% wt). The results have shown that swelling micas have better property of hydration/dehydration than natural clay minerals and those with higher layer charge exhibited higher rehydration ability and dehydration temperature.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.10.046
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Low CO2 hydrogen streams production from formic acid through control of the reaction pH
Santos, JL; Lopez, ER; Ivanova, S; Monzon, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 455 (2023) 140645 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140645
Abstract
There are multiple factors that influence the catalyst performance in the reaction of formic acid dehydrogena-tion: the nature of catalyst and/or support, the used solvent and reaction variables such as temperature, time, formic acid concentration, presence/absence of formates and pH of the solution. This work evaluates a series of important parameters like the influence of the pH by itself, the influence of the nature of used alkali agents and the effect of direct formate addition as reactive on hydrogen production via formic acid dehydrogenation over a commercially available catalyst. The catalytic performance appears to depend on the ionic radius of the cations of the used base which reflects consequently on the hydrogen selectivity. The best base to be used must have lower hydrated cationic radii and a starting pH around 4 to achieve important hydrogen selectivity for medium term formic acid conversion.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140645
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Spinel ferrite catalysts for CO2 reduction via reverse water gas shift reaction
Navarro, JC; Hurtado, C; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Bobadilla, LF; Ivanova, S; Cumbrera, FL; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of CO2 Utilization, 68 (2023) 102356 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102356
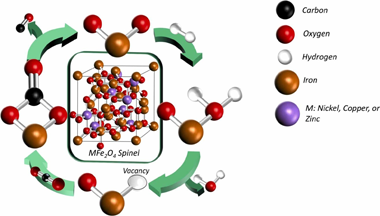
Abstract
The production of CO via Reverse Water Gas Shift (RWGS) reaction is a suitable route for CO2 valorization. In this study a series of modified spinels AB2O4 (A site symbolscript Ni, Zn and Cu and B symbolscript are investigated as RWGS catalysts and their structure-to-function relationships derived from the changes on the A-site cation are ratio-nalized. For all ferrite systems, the RWGS reaction the process main activity and selectivity is governed by the B -site cation, but the variations on the A-site metals determines catalysts' structural features and stability in the reaction. Among the catalyst series, superior RWGS performance displayed the ferrites modified with Cu and Ni associated to the greater oxygen vacancy population for those spinels enabled by the partial allocation on symbolscript cations into the tetrahedral sites.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102356
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effect of phenol concentration on the photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoparticles
Gonzalez, RL; De la Fuente, O; Garcia, RL; Lopez, MDU; Owen, PQ; Lopez, MCH; Lemus, MAAJournal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 98(8) (2023) 1826-1836 DOI: 10.1002/jctb.7334
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Phenol and its derivatives are considered toxic compounds, even at low concentrations. Their accumulation in water effluents has become a serious problem that could be resolved by using zinc oxide (ZnO)-based photocatalysts.RESULTS: ZnO nanoparticles were synthesized through the precipitation method, using zinc nitrate and sodium carbonate as reagents. The as-synthesized powder was calcined for 4 h at 500 degrees C (2 degrees C min(-1)). X-Ray diffraction analysis confirmed a hexag-onal crystalline phase (wurtzite) with an average crystallite size of 38 nm. The Kubelka-Munk method was used to determine a band gap of 3.27 eV through UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectrum and a Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) specific area of 12 m(2) g(-1) was obtained from N2 adsorption analysis. The photocatalytic activity of ZnO was evaluated under visible light (300 W) lamp, with 1 mg mL(-1) of photocatalyst and using phenol solutions at different concentrations of 5,10, 25, and 50 ppm; the obtained degradation percentages were 98%, 97%, 94%, and 71%, respectively. Three cycles were performed with the ZnO used in the reactions with phenol at 5 and 50 ppm, decreasing the degraded percentages to 87% and 65%, respectively. The generation of hydroxyl radicals was estimated for the ZnO and ZnO samples after three cycles by means of fluorescence spectroscopy analy-sis. It was observed that the first-used ZnO material generated a significant amount of hydroxyl radicals.CONCLUSION: When compared to ZnO after three cycles of reaction, the amount of generated hydroxyl radicals decreased. It was observed that the higher the amount of phenol, the lower the generation of hydroxyl radicals after reuse; this was probably due to the presence of some adsorbed by-products of the photocatalytic reaction on the surface of ZnO, as the FTIR spectrum of the post-reaction sample showed.
February, 2023 · DOI: 10.1002/jctb.7334
Materiales Avanzados
Sintering behaviour of a clay containing pyrophyllite, sericite and kaolinite as ceramic raw materials: Looking for the optimum firing conditions
Sanchez-Soto, PJ; Garzon, E; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, DBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Ceramica y Vidrio, 62 (2023) 26-39 DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.09.001
Abstract
The sintering behaviour of a pyrophyllite clay has been investigated. The mineralogical composition by X-ray diffraction (XRD) of this sample was -35 wt.% pyrophyllite, -25 wt.% sericite/illite, -15 wt.% kaolinite and -20 wt.% quartz. The chemical composition was consistent with these results, with a total flux content of 4.18 wt.%. Prismatic bars were prepared by dry pressing using this sample and fired in the range 800-1500 degrees C with 0.5-5 h of soaking times. Sintering diagrams were obtained using the results of linear firing shrinkage, water absorption capacity, bulk density and apparent porosity determined in the ceramic bodies as a function of firing temperatures. It was found a trend of slight variations of bulk density values firing in the range 1000-1150 degrees C, with marked decreases of these values for these bodies fired at 1200 degrees C and 1300 degrees C. The temperature of maximum bulk density was determined as -1200 degrees C and the vitrification temperature was -1300 degrees C where the apparent porosity becomes almost zero. The vitrification process of the pyrophyllite clay sample was investigated using a method previously described in the literature, which considered an Arrhenius approach under isothermal conditions and a first order kinetic. It was determined an activation energy (Ea) of -45 kJ/mol with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.998. The relative rates of vitrification were calculated. It was found that the contribution of vitrification due to the heating was relatively small compared to the vitrification during soaking. Mullite and quartz are forming the ceramic bodies besides a vitreous or glassy phase. The thermally treated pyrophyllite clay showed a dense network of rod-shaped and elongated needle-like crystals, being characteristic features of mullite as a dense felt. The vitrification rate equation, as deduced in this study by first time, can be a useful tool to estimate the optimum firing conditions of the pyrophyllite clays applied as ceramic raw materials.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.09.001
Reactividad de Sólidos
A novel, green, cost-effective and fluidizable SiO2-decorated calcium-based adsorbent recovered from eggshell waste for the CO2 capture process
Imani, M; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jim, P; Valverde, J; Garcia, VMSeparation and Purification Technology, 305 (2023) 122523 DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122523
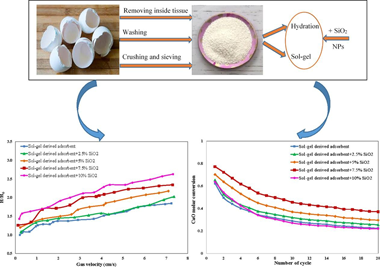
Abstract
The reduction, storage, and reuse of greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) is a crucial concern in modern society. Bio-waste adsorbents have recently aroused the investigator's attention as auspicious materials for CO2 capture. However, the adsorption capacity decaying and poor fluidizability during carbonation/calcination cycles of all natural adsorbents used in the calcium-looping process (CaL) are important challenges. The current study ex-plores the performance of a novel SiO2-decorated calcium-based adsorbent recovered from eggshell waste in terms of both CO2 capture capacity and fluidity. Two preparation methods of hydration and sol-gel were used to obtain Ca-based adsorbents with different pore configurations and volumes. Modification of the adsorbents was applied by dry physically mixing with different weight percentages of hydrophobic SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs), in order to maintain stability and fluidity. The adsorbent prepared by the sol-gel method exhibited a fluffier structure with smaller grain sizes and higher porosity than that of prepared by the hydration method, leading to a 6.9 % increase in conversion at the end of the 20th cycle. Also, with the optimal amount of SiO2 nanoparticles, i. e. 7.5 wt%, the amount of CaO conversion obtained by sol-gel derived adsorbent was 27.59 % higher than that by pristine eggshell at the end of the 20th carbonation/calcination cycles. The fluidizability tests showed that the highest bed expansion ratio (2.29) was achieved for sol-gel derived adsorbent in the presence of 7.5 wt% silica nanoparticles which was considerably higher than the amount of 1.8 and 1.6 belonged to sol-gel derived adsorbent and pristine eggshell without silica at the gas velocity of approximate to 6.5 cm/s, respectively. The high adsorption capacity and proper fluidity of this novel and green calcium-based adsorbent promise its wide application.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122523
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Engineering morphologies of yttrium oxide supported nickel catalysts for hydrogen production
Zhang, RB; Tu, ZA; Meng, S; Feng, G; Lu, ZH; Yu, YZ; Reina, TR; Hu, FY; Chen, XH; Ye, RPRare Metals, 42 (2023) 176-188 DOI: 10.1007/s12598-022-02136-5
Abstract
The catalytic performance is highly related to the catalyst structure. Herein, a series of Ni nanoparticles supported on Y2O3 with different morphologies were successfully synthesized via hydrothermal process screening different pH environments. These Ni/Y2O3 catalysts were applied to efficiently produce COx-free H-2 through ammonia decomposition. We identify a significant impact of Y2O3 supports on nickel nanoclusters sizes and dispersion. The experimental results show that Ni/Y11 catalyst achieves 100% ammonia decomposition conversion under a gas hour space velocity (GHSV) of 12,000 ml.h(-1).g(cat)(-1) and temperature of 650 degrees C. Such a high level of activity over Ni/Y11 catalyst was attributed to a large specific surface area, appropriate alkalinity, and small Ni nanoparticles diameter with high dispersion.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s12598-022-02136-5
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal arrest analysis of the reverse martensitic transformation in a Ni55Fe19Ga26 Heusler alloy obtained by melt-spinning
Vidal-Crespo, A; Manchon-Gordon, AF; Blazquez, JS; Ipus, JJ; Svec, P; Conde, CFJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, (2023) DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11889-1
Abstract
Ni55Fe19Ga26 ribbons obtained by melt-spinning technique exhibit a martensitic transformation from L2(1) cubic austenite phase to 14 M martensite phase above room temperature. We have taken advantage of the existence of thermal hysteresis of the martensitic phase transition (similar to 11 K) to analyze the effect of isothermal treatments on the reverse martensitic transformation, which has been analyzed by means of interrupted heating using differential scanning calorimetry. The experimental findings clearly indicate a time-depending effect in the martensitic transformation at temperatures between the austenite start and finish temperatures. Moreover, it has been observed that two successive martensitic transformations take place after the isothermal arrest was performed.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-022-11889-1
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Determination of the Primary Excitation Spectra in XPS and AES
Pauly, N; Yubero, F; Tougaard, SNanomaterials, 13 (2023) 339 DOI: 10.3390/nano13020339
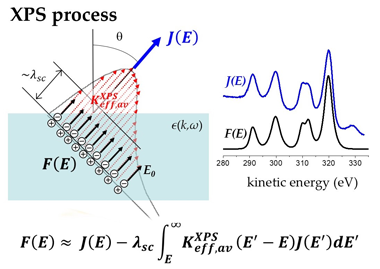
Abstract
This paper reviews a procedure that allows for extracting primary photoelectron or Auger electron emissions from homogeneous isotropic samples. It is based on a quantitative dielectric description of the energy losses of swift electrons travelling nearby surfaces in presence of stationary positive charges. The theory behind the modeling of the electron energy losses, implemented in a freely available QUEELS-XPS software package, takes into account intrinsic and extrinsic effects affecting the electron transport. The procedure allows for interpretation of shake-up and multiplet structures on a quantitative basis. We outline the basic theory behind it and illustrate its capabilities with several case examples. Thus, we report on the angular dependence of the intrinsic and extrinsic Al 2s photoelectron emission from aluminum, the shake-up structure of the Ag 3d, Cu 2p, and Ce 3d photoelectron emission from silver, CuO and CeO2, respectively, and the quantification of the two-hole final states contributing to the L3M45M45 Auger electron emission of copper. These examples illustrate the procedure, that can be applied to any homogeneous isotropic material.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/nano13020339
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Is the RWGS a viable route for CO2 conversion to added value products? A techno-economic study to understand the optimal RWGS conditions
Portillo, E; Gandara-Loe, J; Reina, TR; Pastor-Perez, LScience of the Total Environment, 857 (2023) 159394 DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159394
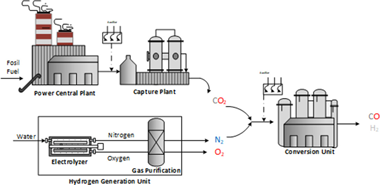
Abstract
Understanding the viability of the RWGS from a thermodynamic and techno-economic angle opens new horizons within CO2 conversion technologies. Unfortunately, profitability studies of this technology are scarce in literature and mainly focused on overall conversion and selectivity trends with tangential remarks on energy demands and pro-cess costs. To address this research gap, herein we present a comprehensive techno-economic study of the RWGS reac-tion when coupling with Fischer-Tropsch synthesis is envisaged to produced fuels and chemicals using CO2 as building block. We showcase a remarkable impact of operating conditions in the final syngas product and both CAPEX and OPEX. From a capital investment perspective, optimal situations involve RWGS unit running at low temperatures and high pressures as evidenced by our results. However, from the running cost angle, operating at 4 bar is the most favorable alternative within the studied scenarios. Our findings showcase that, no matter the selected temperature the RWGS unit should be preferentially run at intermediate pressures. Ultimately, our work maps out multiple operat-ing scenarios in terms of energy demand and process cost serving as guideline to set optimal reaction conditions to un-lock the potential of the RWGS for chemical CO2 recycling.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159394
Reactividad de Sólidos
Low Temperature Magnetic Transition of BiFeO3 Ceramics Sintered by Electric Field-Assisted Methods: Flash and Spark Plasma Sintering
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Perejon, A; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Kowalczyk, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAMaterials, 16 (2023) 189 DOI: 10.3390/ma16010189
Abstract
Low temperature magnetic properties of BiFeO3 powders sintered by flash and spark plasma sintering were studied. An anomaly observed in the magnetic measurements at 250 K proves the clear existence of a phase transition. This transformation, which becomes less well-defined as the grain sizes are reduced to nanometer scale, was described with regard to a magneto-elastic coupling. Furthermore, the samples exhibited enhanced ferromagnetic properties as compared with those of a pellet prepared by the conventional solid-state technique, with both a higher coercivity field and remnant magnetization, reaching a maximum value of 1.17 kOe and 8.5 10(-3) emu/g, respectively, for the specimen sintered by flash sintering, which possesses the smallest grains. The specimens also show more significant exchange bias, from 22 to 177 Oe for the specimen prepared by the solid-state method and flash sintering technique, respectively. The observed increase in this parameter is explained in terms of a stronger exchange interaction between ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic grains in the case of the pellet sintered by flash sintering.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16010189
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
A Holistic Solution to Icing by Acoustic Waves: De-Icing, Active Anti-Icing, Sensing with Piezoelectric Crystals, and Synergy with Thin Film Passive Anti-Icing Solutions
Del Moral, J; Montes, L; Rico-Gavira, VJ; Lopez-Santos, C; Jacob, S; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gil-Rostra, J; Fakhfouri, A; Pandey, S; Del Val, MG; Mora, J; García-Gallego, P; Ibanez-Ibanez, PF; Rodríguez Valverde, MA; Winkler, A; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARAdvanced Functional Materials, 33 (2023) 2209421 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202209421
Abstract
Icing has become a hot topic both in academia and in the industry given its implications in transport, wind turbines, photovoltaics, and telecommunications. Recently proposed de-icing solutions involving the propagation of acoustic waves (AWs) at suitable substrates may open the path for a sustainable alternative to standard de-icing or anti-icing procedures. Herein, the fundamental interactions are unraveled that contribute to the de-icing and/or hinder the icing on AW-activated substrates. The response toward icing of a reliable model system consisting of a piezoelectric plate activated by extended electrodes is characterized at a laboratory scale and in an icing wind tunnel under realistic conditions. Experiments show that surface modification with anti-icing functionalities provides a synergistic response when activated with AWs. A thoughtful analysis of the resonance frequency dependence on experimental variables such as temperature, ice formation, or wind velocity demonstrates the application of AW devices for real-time monitoring of icing processes.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202209421
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanocrystalline Skinnerite (Cu3SbS3) Prepared by High-Energy Milling in a Laboratory and an Industrial Mill and Its Optical and Optoelectrical Properties
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Fabian, M; Balaz, M; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Stahorsky, M; Achimovicova, M; Bujnakova, ZLMolecules, 28 (2023) 1 DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010326
Abstract
Copper, antimony and sulfur in elemental form were applied for one-pot solid-state mechanochemical synthesis of skinnerite (Cu3SbS3) in a laboratory mill and an industrial mill. This synthesis was completed after 30 min of milling in the laboratory mill and 120 min in the industrial mill, as corroborated by X-ray diffraction. XRD analysis confirmed the presence of pure monoclinic skinnerite prepared in the laboratory mill and around 76% monoclinic skinnerite, with the secondary phases famatinite (Cu3SbS4; 15%), and tetrahedrite (Cu11.4Sb4S13; 8%), synthesized in the industrial mill. The nanocrystals were agglomerated into micrometer-sized grains in both cases. Both samples were nanocrystalline, as was confirmed with HRTEM. The optical band gap of the Cu3SbS3 prepared in the laboratory mill was determined to be 1.7 eV with UV-Vis spectroscopy. Photocurrent responses verified with I-V measurements under dark and light illumination and Cu3SbS3 nanocrystals showed similar to 45% enhancement of the photoresponsive current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V. The optical and optoelectrical properties of the skinnerite (Cu3SbS3) prepared via laboratory milling are interesting for photovoltaic applications.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/molecules28010326
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over Ru- and Pd-Based Catalysts: Gas- vs. Liquid-Phase Reactions
Ruiz-Lopez, E; Pelaez, MR; Ruz, MB; Leal, MID; Tejada, MM; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MAMaterials, 16 (2023) 472 DOI: 10.3390/ma16020472
Abstract
Formic acid has recently been revealed to be an excellent hydrogen carrier, and interest in the development of efficient and selective catalysts towards its dehydrogenation has grown. This reaction has been widely explored using homogeneous catalysts; however, from a practical and scalable point of view, heterogeneous catalysts are usually preferred in industry. In this work, formic acid dehydrogenation reactions in both liquid- and vapor-phase conditions have been investigated using heterogeneous catalysts based on mono- or bimetallic Pd/Ru. In all of the explored conditions, the catalysts showed good catalytic activity and selectivity towards the dehydrogenation reaction, avoiding the formation of undesired CO.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16020472
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Methanation of CO2 over High Surface Nickel/Aluminates Compounds Prepared by a Self-Generated Carbon Template
Roudane, S; Bettahar, N; Caballero, A; Holgado, JPCatalysts, 13 (2023) 142 DOI: 10.3390/catal13010142
Abstract
Catalytic gas-phase hydrogenation of CO2 into CH4 was tested under three different nickel/aluminate catalysts obtained from precursors of hexaaluminate composition (MAl16O19, M = Mg, Ca, Ba). These catalysts were prepared using a carbon template method, where carbon is self-generated from a sol-gel that contains an excess of citric acid and the Al and M salts (Ba2+, Ca2+, Mg2+) by two-step calcination in an inert/oxidizing atmosphere. This procedure yielded Ni particles decorating the surface of a porous high surface area matrix, which presents a typical XRD pattern of aluminate structure. Ni particles are obtained with a homogeneous distribution over the surface and an average diameter of ca 25-30 nm. Obtained materials exhibit a high conversion of CO2 below 500 degrees C, yielding CH4 as a final product with selectivity >95%. The observed trend with the alkaline earth cation follows the order NiBaAlO-PRx > NiCaAlO-PRx > NiMgAlO-PRx. We propose that the high performance of the NiBaAlO sample is derived from both an appropriate distribution of Ni particle size and the presence of BaCO3, acting as a CO2 buffer in the process.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/catal13010142
Materiales Coloidales
Carboxylate functionalized NaDy(MoO4)(2) nanoparticles with tunable size and shape as high magnetic field MRI contrast agents
Gomez-Gonzalez, E; Nuñez, NO; Caro, C; Garcia-Martin, ML; Ocaña, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 629 (2023) 310-321 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.130
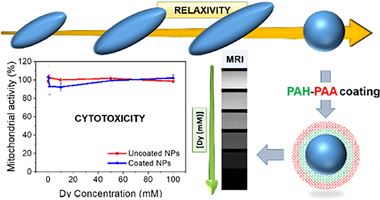
Abstract
Uniform sodium-dysprosium double molybdate (NaDy(MoO4)(2)) nanoparticles having different morphologies (spheres and ellipsoids) and tunable size have been synthesized for the first time in literature. The procedure is based on a homogeneous precipitation process at moderated temperatures (<= 220 ?) from solutions containing appropriated precursors dissolved in ethylene glycol-water mixtures, in the absence (spheres) or the presence (ellipsoids) of tartrate anions. The effects of the morphological characteristics (size and shape) of the nanoparticles on the magnetic relaxivity at high field (9.4 T) have been evaluated finding that the latter magnitude was higher for the spheres than for the ellipsoids, indicating their better suitability as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging. Such nanoparticles have been successfully coated with polymers bearing carboxylate functional groups through a layer-by -layer process, which improves the colloidal stability of the nanoparticles in physiological media. It has been also found that the coating layer had no significant effects on the nanoparticles relaxivity and that such coated nanoparticles exhibited a high biocompatibility and a high chemical stability. In summary, we have developed NaDy(MoO4)(2 )based bioprobes which meet the required criteria for their use as contrast agents for high-field magnetic resonance imaging.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.130
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructure and activity of Pd catalysts prepared on commercial carbon support for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid
Arzac, GM; Montes, O; Fernández, AInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 48 (2023) 2628-2639 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.10.149
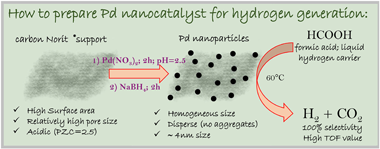
Abstract
In this work, a series of Pd catalysts supported on commercially available activated carbon (Norit (R)) were prepared by employing different metal precursors (Pd(NO3)2 and Na2PdCl4) by the impregnation-reduction method at different pH. Catalysts were tested for the liquid phase decomposition of formic acid to generate hydrogen. The best results, in terms of small particle size and high catalytic activity were achieved for the Pd/C sample prepared by using Pd(NO3)2 salt impregnated at pH = 2.5, and reduced with sodium borohydride. The particle size of the best Pd/C catalyst is (4.1 +/- 1.4) nm with initial TOFs of 2929 and 683 h-1 at 60 and 30 degrees C respectively and an apparent activation energy of 40 kJ mol-1. Samples prepared by using Na2PdCl4 precursor, consisted of particles with higher size and thus lower activity than the ones prepared with Pd(NO3)2. Regardless the Pd precursor employed, the best results in terms of particle size and activity were achieved at the point of zero charge of the support when the Pd species and the carbon surface were both neutral. The impregnation pH not only determines the particle size, but also the nature of the reducing agent does. The catalytic activity was shown to be size-dependent and it was shown that a mixture of surface Pd0 and PdII oxidation states is beneficial for the activity. When comparing with literature catalysts with similar composition, we found that our best catalyst is competitive enough and that Norit (R) support could be promising for future studies on this reaction.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.10.149
Reactividad de Sólidos
ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for analysis of thermal decomposition kinetics
Koga, N; Vyazovkin, S; Burnham, AK; Favergeon, L; Muravyev, NV; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Saggese, C; Sánchez-Jiménez, PEThermochimica Acta, 719 (2023) 179384 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2022.179384
Abstract
In this review article, the Kinetics Committee of the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC) delivers a collection of recommendations for the kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition processes. These recommendations specifically focus on the thermal decomposition processes in inorganic, organic, and polymeric materials, as well as biomass and solid fuels. A general introduction to the kinetic analysis of thermal decompositions studied by thermal analysis techniques is followed by individual sections that discuss thermal decomposition of specific classes of materials and respective kinetic approaches. In each section, various kinetic analysis procedures are introduced with regard to specific features of the reactions and explained pro-gressively from simple to complex reactions with examples of practical kinetic analysis. These recommendations are expected to provide a guidance for performing reliable and meaningful kinetic analysis in terms of practical usefulness and physico-chemical significance of the results.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2022.179384
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selective hydrodeoxygenation of levulinic acid to gamma-valerolactone over Ru supported on functionalized carbon nanofibers
Bounoukta, CE; Megias-Sayago, C; Rendon, N; Ammari, F; Penkova, A; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JASustainable Energy & Fuels, 7 (2023) 857-867 DOI: 10.1039/d2se01503j
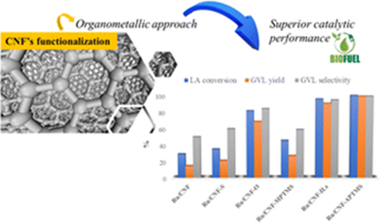
Abstract
In this work, carbon nanofibers (CNFs) have been successfully functionalized by using different approaches and finally used for the preparation of Ru based catalysts. The organometallic approach has been demonstrated to be suitable for CNF functionalization, leading to well-defined Ru NPs (by adding organosilane, amino or mercapto functionalities, among others) in comparison with mineral acid treatments conventionally used to activate and/or functionalize carbonaceous solids. All catalysts have been tested in levulinic acid hydrodeoxygenation to γ-valerolactone under mild conditions, with the impact of CNF functionalization on the catalysts' performance fully discussed in comparison with unmodified commercial CNFs.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d2se01503j
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Materiales Coloidales
Highly Nonstoichiometric YAG Ceramics with Modified Luminescence Properties
Cao, WW; Becerro, AI; Castaing, V; Fang, X; Florian, P; Fayon, F; Zanghi, D; Veron, E; Zandona, A; Genevois, C; Pitcher, MJ; Allix, MAdvanced Functional Materials DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202213418
Abstract
Y3Al5O12 (YAG) is a widely used phosphor host. Its optical properties are controlled by chemical substitution at its YO8 or AlO6/AlO4 sublattices, with emission wavelengths defined by rare-earth and transition-metal dopants that have been explored extensively. Nonstoichiometric compositions Y3+xAl5-xO12 (x not equal 0) may offer a route to new emission wavelengths by distributing dopants over two or more sublattices simultaneously, producing new local coordination environments for the activator ions. However, YAG typically behaves as a line phase, and such compositions are therefore challenging to synthesize. Here, a series of highly nonstoichiometric Y3+xAl5-xO12 with 0 <= x <= 0.40 is reported, corresponding to <= 20% of the AlO6 sublattice substituted by Y3+, synthesized by advanced melt-quenching techniques. This impacts the up-conversion luminescence of Yb3+/Er3+-doped systems, whose yellow-green emission differs from the red-orange emission of their stoichiometric counterparts. In contrast, the YAG:Ce3+ system has a different structural response to nonstoichiometry and its down-conversion emission is only weakly affected. Analogous highly nonstoichiometric systems should be obtainable for a range of garnet materials, demonstrated here by the synthesis of Gd3.2Al4.8O12 and Gd3.2Ga4.8O12. This opens pathways to property tuning by control of host stoichiometry, and the prospect of improved performance or new applications for garnet-type materials.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202213418
Reactividad de Sólidos
A national data-based energy modelling to identify optimal heat storage capacity to support heating electrification
Lizana, J; Halloran, CE; Wheeler, S; Amghar, N; Renaldi, R; Killendahl, M; Perez-Maqueda, LA; McCulloch, M; Chacartegui, REnergy, 262 (2023) 125298 DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125298
Abstract
Heating decarbonisation through electrification is a difficult challenge due to the considerable increase in peak power demand. This research proposes a novel modelling approach that utilises easily accessible national-level data to identify the required heat storage volume in buildings to decrease peak power demand and maximises carbon reductions associated with electrified heating technologies through smart demand-side response. The approach assesses the optimal shifting of heat pump operation to meet thermal heating demand according to different heat storage capacities in buildings, which are defined in relation to the time (in hours) in which the heating demand can be provided directly from the heat battery, without heat pump operation. Ten scenarios (S) are analysed: two baselines (S1-S2) and eight load shifting strategies (S3-S10) based on hourly and daily demand-side responses. Moreover, they are compared with a reference scenario (S0), with heating currently based on fossil fuels. The approach was demonstrated in two different regions, Spain and the United Kingdom. The optimal heat storage capacity was found on the order of 12 and 24 h of heating demand in both countries, reducing additional power capacity by 30-37% and 40-46%, respectively. However, the environmental benefits of heat storage alternatives were similar to the baseline scenario due to higher energy consumption and marginal power generation based on fossil fuels. It was also found that load shifting capability below 4 h presents limited benefits, reducing additional power capacity by 10% at the national scale. The results highlight the importance of integrated heat storage technologies with the electrification of heat in highly gas-dependent regions. They can mitigate the need for an additional fossil-based dispatchable generation to meet high peak demand. The modelling approach provides a high-level strategy with regional specificity that, due to common datasets, can be easily replicated globally. For reproducibility, the code base and datasets are found on GitHub.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125298
Materiales Avanzados
New Types and Dosages for the Manufacture of Low-Energy Cements from Raw Materials and Industrial Waste under the Principles of the Circular Economy and Low-Carbon Economy
Martinez-Martinez, S; Perez-Villarejo, L; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJMaterials, 16 (2023) 802 DOI: 10.3390/ma16020802
Abstract
The cement manufacturing industry is one of the main greenhouse gas emission producers and also consumes a large quantity of raw materials. It is essential to reduce these emissions in order to comply with the Paris Agreement and the principles of the circular economy. The objective of this research was to develop different types of cement clinker blends using industrial waste and innovative design to produce low-energy cement. Several types of waste have been studied as alternative raw materials. Their main characteristics have been analyzed via X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Attenuated total reflectance Fourier trans-form infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), thermal analysis (TG-DTG-DSC) and scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis (SEM-EDS). The results obtained from the experimental work carried out in this research focused on the study of crude blends for low-energy cement created from industrial waste. The effect of the addition of different industrial waste types, as a substitution for raw materials, in the production of low-energy cement with high dicalcium silicate content has been investigated. Thus, the dosage design has been performed using modified Bogue equations and quality indexes (LSF, AM, and SM). The calculations of both the modified Bogue equations and quality indexes necessitate knowledge of the weight percentages of CaO, SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3, determined via XRF. In this theoretical design of the different blends, it has been established that a dicalcium silicate ratio of 60-65 wt % and an LSF of 78-83% as the limit are values common to all of them. The calculation basis for the crude blends has been based on calcined materials. Therefore, the chemical composition was established, following this premise. Thus, it was possible to develop cement clinker blends with compositions of 50 wt % and 100 wt % using industrial wastes. This research has shown that the clinkerization process is one of the main options for the valorization of waste and its consideration for inclusion as a raw material within the circularity of the cement industry's production process. Thus, waste is used as a raw material for the production of a more useful substance, taking into account the fundamental principles of the circular economy.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.3390/ma16020802
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Collective plasmonic resonances enhance the photoluminescence of rare-earth nanocrystal films processed by ultrafast annealing
Cabello-Olmo, E; Higashino, M; Murai, S; Tanaka, K; Lozano, G; Miguez, HChemical Communications, 59 (2023) 1289-1292 DOI: 10.1039/d2cc04779a
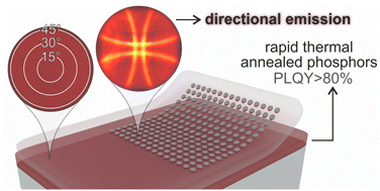
Abstract
Herein, we demonstrate that rapid thermal annealing allows achieving close-to-one photoluminescence quantum yield while preserving the transparency of rare-earth nanocrystal films, which further enables their integration with nanophotonics. The combination with periodic arrays of aluminum nanodisks that support collective plasmonic resonances leads to enhanced directional emission.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d2cc04779a
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Highly dispersed Rh single atoms over graphitic carbon nitride as a robust catalyst for the hydroformylation reaction
Jurado, L; Esvan, J; Luque-Alvarez, LA; Bobadilla, LF; Odriozola, JA; Posada-Perez, S; Poater, A; Comas-Vives, A; Axet, MRCatalysis Science & Tecnology, 13 (2022) 1425-1436 DOI: 10.1039/d2cy02094g
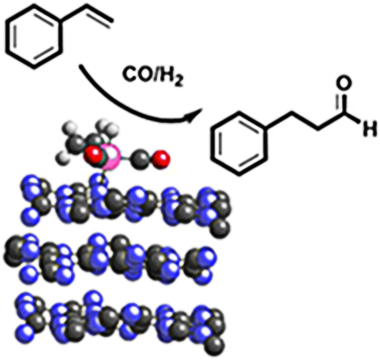
Abstract
Rhodium-catalysed hydroformylation, effective tool in bulk and fine-chemical synthesis, predominantly uses soluble metal complexes. For that reason, the metal leaching and the catalyst recycling are still the major drawbacks of this process. Single-atom catalysts have emerged as a powerful tool to combine the advantages of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts. Since using an appropriate support material is key to create stable, finely dispersed, single-atom catalysts, here we show that Rh atoms anchored on graphitic carbon nitride are robust catalysts for the hydroformylation reaction of styrene.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1039/d2cy02094g
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Responsive Optical Materials Based on Ligand-Free Perovskite Quantum Dots Embedded in Mesoporous Scaffolds
Romero-Perez, C; Zanetta, A; Fernandez-Delgado, N; Herrera-Collado, M; Hernandez-Saz, J; Molina, SI; Calio, L; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 15 (2023) 1808-1816 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c16867
Abstract
Herein we show that dispersing inorganic cesium lead bromide (CsPbBr3) perovskite quantum dots (QDs) in optical quality films, possessing an accessible and controlled pore size distribution, gives rise to fluorescent materials with a controlled and highly sensi t i v e response to ambient changes. A scaffold-based synthesis approach is employed to obtain ligand-free QDs, whose pristine surface endows them with high sensit i v i t y to the presence of different vapors in their vici n i t y . At the same time, the void network of the host offers a means to gradually expose the embedded QDs to such vapors. Under these conditions, the luminescent response of the QDs is mediated by the mesostructure of the matri x , which determines the rate at which vapor molecules will adsorb onto the pore walls and, eventually, condensate, filling the void space. With luminescence quantum yields as high as 60%, scaffold-supported ligand-free perovskite nanocrystals display intense photoemission signals over the whole process, as well as high photo-and chemical stabi l i t y , which allows illuminating them for long periods of time and recovering the original response upon desorption of the condensed phase. The results herein presented open a new route to explore the application of perovskite QD-based materials in sensing.
January, 2023 · DOI: 10.1021/acsami.2c16867
2022
2022
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Pd supported on defective TiO2 polymorphic mixtures: Effect of metal-support interactions upon glycerol selective oxidation
Rinaudo, MG; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, A; Cadus, LE; Morales, MRResults in Engineering, 16 (2022) 100737 DOI: 10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100737
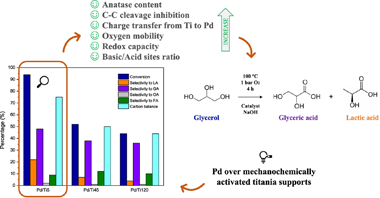
Abstract
Palladium catalysts supported on defective mixes of anatase, TiO2 (II) and rutile crystalline phases, previously obtained by high-energy ball milling, were synthesized and tested for glycerol selective oxidation. A deep characterization of these unusual materials was carried out to elucidate catalytic and physicochemical features. Electron density transfer from support to metal or vice versa, depending on the polymorphs present, could not only alter palladium particle sizes and its surface oxidation state but also reducibility and oxygen mobility of catalysts. Furthermore, acid-base properties achieved also influenced catalytic activity under mild conditions of liquid-phase glycerol oxidation. A conversion of 94% and a selectivity to glyceric and lactic acids of 48% and 22% respectively were obtained for the Pd catalyst supported on mechanochemically activated anatase. The presence of several polymorphs in a metal oxide support could therefore benefit or handicap catalytic cycle for a particular reaction. Metal-support interactions play a key role in heterogenous catalysts and thus the rational design of supports comes on the scene.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100737
Reactividad de Sólidos
Theoretical Analysis of Polynuclear Zinc Complexes Isolobally Related to Hydrocarbons
Ayala, R; Galindo, AInternational Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (2022) 14858 DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314858
Abstract
Based on the isolobal analogy of ZnCp (Cp = eta(5)-C5H5) and ZnR (R = alkyl or aryl group) fragments with hydrogen atom and fragment [Zn(CO)(2)] with a CH2 carbene, the following complexes [(ZnCp)(2){mu-Zn(CO)(2)}], 1, [(ZnPh)(2){mu-Zn(CO)(2)}], 2, [(ZnPh){mu-Zn(CO)(2)}(ZnCp)], 3, [(ZnCp)(2){mu-Zn-2(CO)(4)}], 4, [(ZnPh)(2){mu-Zn-2(CO)(4)}], 5, [(ZnPh){mu-Zn(CO)(2)}(2)(ZnCp)], 6, [Zn-3(CO)(6)], 7 and [Zn-5(CO)(10)], 8, were built. These polynuclear zinc compounds are isolobally related to simple hydrocarbons (methane, ethane, cyclopropane and cyclopentane). They have been studied by density functional theory (DFT) and quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) to compare the nature and topology of the Zn-Zn bond with previous studies. There are bond critical points (BCPs) between each pair of adjacent Zn centers in complexes 1-8 with Zn-Zn distances within the range 2.37-2.50 angstrom. The nature of the Zn-Zn bond in these complexes can be described as polar rather than pure covalent bonds. Although in a subtle way, the presence of different ligands and zinc oxidation states introduces asymmetry and polarity in the Zn-Zn bond. In addition, the Zn-Zn bond is delocalized in nature in complex 7 whereas it can be described as a localized bond for the remaining zinc complexes here studied.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314858
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Materials challenges and opportunities to address growing micro/ nanoplastics pollution: a review of thermochemical upcycling
Parrilla-Lahoz, S; Mahebadevan, S; Kauta, M; Zambrano, MC; Pawlak, JJ; Venditti, RA; Reina, TR; Duyar, MSMaterials Today Sustainability, 20 (2022) 100200 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100200
Abstract
Micro/nanoplastics have sparked attention in recent years due to their widespread presence in the environment. Currently, several waste valorization approaches are under development in order to upcycle micro/nanoplastics. Thermal conversion technologies such as pyrolysis, gasification, liquefaction, or hydrothermal carbonization can yield high-value solid products, oil, and gases from plastics waste. The common thermal conversion technologies investigated focus on maximizing the production of oil and gases (such as H2 and CH4) for use as fuel. Except for hydrogen, when these products are used to generate energy, the carbon emissions generated are comparable to those produced by traditional fossil fuels. Herein, we present a review of the current efforts to capture and convert plastic waste into valuable products with an emphasis on identifying the need to develop processes specifically for micro/nano-plastics while also preventing the release of CO2 emissions. We identify the development of efficient catalytic materials as a critical research need for achieving economically viable thermochemical con-version of micro/nanoplastics.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100200
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Development of Power-to-X Catalytic Processes for CO2 Valorisation: From the Molecular Level to the Reactor Architecture
Bobadilla, LF; Azancot, L; Luque-Alvarez, LA; Torres-Sempere, G; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Pastor-Perez, L; Ramírez-Reina, T; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemistry, 4 (2022) 1250-1280 DOI: 10.3390/chemistry4040083
Abstract
Nowadays, global climate change is likely the most compelling problem mankind is facing. In this scenario, decarbonisation of the chemical industry is one of the global challenges that the scientific community needs to address in the immediate future. Catalysis and catalytic processes are called to play a decisive role in the transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon future. This critical review analyses the unique advantages of structured reactors (isothermicity, a wide range of residence times availability, complex geometries) with the multifunctional design of efficient catalysts to synthesise chemicals using CO2 and renewable H-2 in a Power-to-X (PTX) strategy. Fine-chemistry synthetic methods and advanced in situ/operando techniques are essential to elucidate the changes of the catalysts during the studied reaction, thus gathering fundamental information about the active species and reaction mechanisms. Such information becomes crucial to refine the catalyst's formulation and boost the reaction's performance. On the other hand, reactors architecture allows flow pattern and temperature control, the management of strong thermal effects and the incorporation of specifically designed materials as catalytically active phases are expected to significantly contribute to the advance in the valorisation of CO2 in the form of high added-value products. From a general perspective, this paper aims to update the state of the art in Carbon Capture and Utilisation (CCU) and PTX concepts with emphasis on processes involving the transformation of CO2 into targeted fuels and platform chemicals, combining innovation from the point of view of both structured reactor design and multifunctional catalysts development.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/chemistry4040083
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO2 methanation on Ni/YMn1-xAlxO3 perovskite catalysts
Safdar, M; Gonzalez-Castano, M; Penkova, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Arellano-Garcia, HApplied Materials Today, 29 (2022) 101577 DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101577
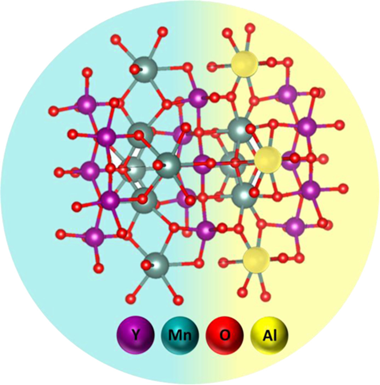
Abstract
Seeking for advanced catalytic systems for the CO2 methanation reaction, the use of Ni supported catalysts over redox materials is often proposed. Profiting the superior redox properties described for layered perovskite systems, this work has investigated a series Ni supported YMn1-xAlxO3 (x = 0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1) perovskite catalysts. The obtained results evidenced the impact of the support nature on the systems redox properties and Ni-support interactions. Within the catalysts series, the greater methanation rates displayed by Ni/YMn0.5Al0.5O3 catalyst (0.748 mmol(CO2,conv.)s(-1) g(Ni)(-1) at 400 ? and 60 L/gh) were associated to the interplay between the support redox properties and superior Ni dispersion. The improved redox behavior attained through the Al-incorporation (up to x = 0.5) was associated to the layered perovskite structures which, being distorted and constituted by smaller crystal sizes, facilitated the behavior of Mn redox couples as surface species readily interconverted. Exhibiting catalytic performances comparable to precious metals based catalysts, this work proposes the Ni/YMn0.5Al0.5O3 catalyst as an effective system for the CO2 methanation reaction.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101577
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
High-Quality SiO2/O-Terminated Diamond Interface: Band-Gap, Band-Offset and Interfacial Chemistry
Canas, J; Reyes, DF; Zakhtser, A; Dussarrat, C; Teramoto, T; Gutierrez, M; Gheeraert, ENanomaterials, 12 (2022) 4125 DOI: 10.3390/nano12234125
Abstract
Silicon oxide atomic layer deposition synthesis development over the last few years has open the route to its use as a dielectric within diamond electronics. Its great band-gap makes it a promising material for the fabrication of diamond-metal-oxide field effects transistor gates. Having a sufficiently high barrier both for holes and electrons is mandatory to work in accumulation and inversion regimes without leakage currents, and no other oxide can fulfil this requisite due to the wide diamond band-gap. In this work, the heterojunction of atomic-layer-deposited silicon oxide and (100)-oriented p-type oxygen-terminated diamond is studied using scanning transmission electron microscopy in its energy loss spectroscopy mode and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The amorphous phase of silicon oxide was successfully synthesized with a homogeneous band-gap of 9.4 eV. The interface between the oxide and diamond consisted mainly of single- and double-carbon-oxygen bonds with a low density of interface states and a straddling band setting with a 2.0 eV valence band-offset and 1.9 eV conduction band-offset.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/nano12234125
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Assessment of pilot-plant scale solar photocatalytic hydrogen generation with multiple approaches: Valorization, water decontamination and disinfection
Ruiz-Aguirre, A; Villachica-Llamosas, JG; Polo-Lopez, MI; Cabrera-Reina, A; Colon, G; Peral, J; Malato, SEnergy, 260 (2022) e10272 DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125199
Abstract
The main goal of the present study was to explore pilot-scale combination of H-2 generation with simultaneous water disinfection or decontamination. Performance of a TiO2-CuO mixture for solar-to-hydrogen (STH) con-version was studied, focusing on treatment optimization (catalyst dose, proportion of semiconductors in the mixture and concentration of the sacrificial agent). Experiments were performed in a 25-L compound parabolic collector (2 m(2)) solar pilot plant specifically designed for photocatalytic hydrogen generation. The best operating conditions were 100 mg L-1 TiO2-CuO (10:1) with 0.075 M glycerol as the sacrificial agent. The best STH conversion attained was 0.9%. 25 mg L-1 imidacloprid was completely degraded (over 99%). The synergetic effect of anoxic conditions, TiO2:CuO and solar radiation caused a significant reduction (> 5 Log) in concen-tration of E. coli, used as a model waterborne pathogen, in less than 10 min.
December, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125199
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanoantennas Patterned by Colloidal Lithography for Enhanced Nanophosphor Light Emission
Viana, JM; Romero, M; Lozano, G; Míguez, HACS Applied Nano Materials, 5(11) (2022) 16242-16249 DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.2c03258
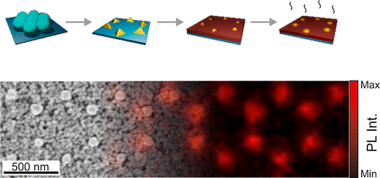
Abstract
Transparent coatings made of rare-earth doped nanocrystals, also known as nanophosphors, feature efficient photoluminescence and excellent thermal and optical stabi l i t y . Herein, we demonstrate that the optical antennas prepared by colloidal lithography render thin nanophosphor films with a brighter emission. In particular, we fabricate gold nanostructures in the proximity of GdVO4:Eu3+ nanophosphors by metal evaporation using a mask made of a monolayer of polymer beads arranged in a triangular lattice. Optical modes supported by the antennas can be controlled by tuning the diameter of the polymer spheres in the colloidal mask, which determines the shape of the gold nanostructure, as confirmed by numerical simulations. Confocal microscopy reveals that metallic antennas induce brighter photoluminescence at specific spatial regions of the nanophosphor film at targeted frequencies as a result of the coupling between gold nanostructures and nanophosphors. Patterning of nanophosphor thin layers with arrays of metallic antennas offers an inexpensive nanophotonic solution to develop bright emitting coatings of interest for color conversion, labeling , or anti-counterfeiting.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.2c03258
Reactividad de Sólidos
Reactive flash sintering of SrFe12O19 ceramic permanent magnets
Manchon-Gordon, AF; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Blazquez, JS; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 922 (2022) 166203 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166203
Abstract
Reactive flash-sintering technique has been used in order to obtain strontium ferrite magnets from a mixture of SrCO3 and Fe2O3 commercial powders. This technique allows preparing sintered SrFe12O19 at a furnace temperature of just 973 K during just 2 min by applying a modest field of 40 V cm(-1), instead of the conventional sintering process employed in ferrite magnet manufacturing that demands high temperature and long dwell times. Analysis of structural and magnetic properties were performed as a function of time in which the flash event was held. Mossbauer spectra show the existence of five different kinds of local environments, confirming the formation of strontium hexaferrite. The resulting samples exhibit comparable magnetic properties to the state-of-the-art ferrite magnets. In particular, produced samples reach a coercivity of 0.4 T and a specific saturation magnetization of 70 Am-2 kg(-1).
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166203
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Exploring the local environment of the engineered nanoclay Mica-4 under hydrothermal conditions using Eu(3+)as a luminescent probe
Martin-Rodriguez, R; Aguado, F; Alba, MD; Valiente, R; Pavon, E; Perdigon, ACJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 921 (2022) 166086 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166086
Abstract
High charge mica Na4Al4Si4Mg6O20F4 , Mica-4, is a promising candidate as a filling material to immobilize high-level radioactive waste in deep geological repositories due to its extraordinary adsorption capacity. In contrast to traditional clay materials, the structural composition of this mica, with a high content of alu-minum in the tetrahedral sheet, enhances its chemical reactivity, favoring the formation of new crystalline phases under mild hydrothermal conditions, and thus providing a definitive isolation of the radionuclides in the engineered barrier. Moreover, this synthetic clay has some features that allow its use as an optical sensor by doping with luminescent rare earth cations such as Eu3+. In this paper we discuss the local structure of the nanoclay Mica-4 using Eu3+ as a local probe to track the physical and chemical modifica-tions under hydrothermal conditions. For that purpose, a set of hydrothermal experiments has been carried out heating Mica-4 and an aqueous Eu(NO3)(3) solution in a stainless steel reactor at different temperatures and times. Optical properties of the as-treated samples were characterized by spectroscopic measurements. The fine peak structure of emission and the relative intensity of different Eu3+ transitions as well as the luminescence lifetime have been correlated with the structure and composition of this nanoclay, and the interaction mechanisms between the lanthanide ions and the clay mineral at different temperatures and times. Special attention has been paid to understanding the role of the aluminum content, which may act as either an aggregating or dispersing agent, in the optical features and reactivity of the system.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166086
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Insights into the Impact of Activators on the 'Catalytic' Graphitization to Design Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries
Hanhart, V; Frankenstein, L; Ramirez-Rico, J; Diozios, V; Winter, M; Gomez-Martin, A; Placke, TChemelectrochem, 9 (2022) e202200819 DOI: 10.1002/celc.202200819
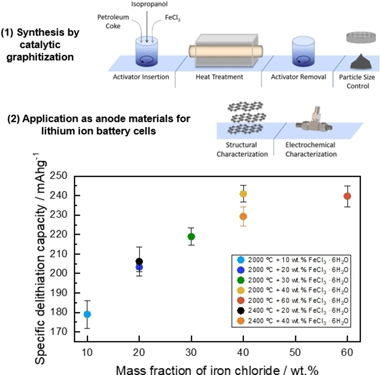
Abstract
In this work, we systematically investigate the 'catalytic' graphitization of a biomass precursor (coffee ground) using 10-60 wt.% of the activator iron (III) chloride hexahydrate in a temperature range of 1000 degrees C-2400 degrees C. Special focus is put on the correlation of synthesis conditions, e.g., heat treatment temperature and mass fraction of iron chloride, with the electrochemical performance in carbon vertical bar vertical bar Li metal cells. The structural investigations of the materials reveal a positive impact of an increasing heat treatment temperature and/or mass fraction of inserted activator on the degree of graphitization and the delithiation capacity. However, a saturation point regarding the maximum degree of graphitization at 2000 degrees C and reversible capacity by the 'catalytic' graphitization approach using iron (III) chloride has been found. A maximum degree of graphitization of approximate to 69% could be reached by applying 2000 degrees C and 40 wt.% FeCl3 center dot 6H(2)O, resulting in a reversible capacity of 235 mAh g(-1).
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1002/celc.202200819
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement in cyclic CO2 capture performance and fluidization behavior of eggshell-derived CaCO3 particles modified with acetic acid used in calcium looping process
Imani, M; Tahmasebpoor, M; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Valverde, JM; Moreno, VJournal of CO2 Utilization, 65 (2022) 102207 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102207
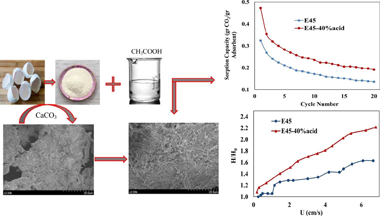
Abstract
Although calcium-based materials are the most promising adsorbents used in calcium looping process for carbon dioxide removing, their CO2 capture capacity decaying besides poor fluidization, still are the important challenges. In the present investigation, eggshell as a cheap, easily available and unpolluted source of calcium carbonate was used for CO2 capturing in calcium looping process. Eggshell particles were treated with various volume concentrations of acetic acid to improve its sorption capacity. According to the TGA results after 20 carbonation/calcination cycles, the effective carbonation conversion of modified eggshell with 5%, 20%, 30% and 40%. v/v acetic acid was 21.33%, 24.26%, 25.97% and 28.97%, respectively, which is considerable compared to 20.54% for untreated eggshell. The effect of initial eggshell particle size on the adsorption behavior of final adsorbent was also investigated by using two different sizes including dp < 45 mu m and dp > 320 mu m. The results showed that the effective conversion of the adsorbent containing 40%. v/v acetic acid derived from small particle size eggshells was 9.32% higher than that from larger particle size eggshells. In terms of fluidization behavior, surprisingly the addition of acetic acid to the eggshell particles also increased the bed expansion ratio as 8% and 36.2% at gas velocities of 0.27 and 6.67 cm/s, respectively. Further improvement in the fluidity of eggshell modified with 40% acid was performed by manually mixing of SiO2 nanoparticles at different weight percentages. According to the results, adding 7.5 wt% SiO2 leaded to the homogeneous and agglomerate particulate fluidization.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jcou.2022.102207
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Biopolymer-Based Films Reinforced with FexOy-Nanoparticles
Abdullah, JAA; Jimenez-Rosado, M; Benitez, JJ; Guerrero, A; Romero, APolymers, 14 (2022) 4487 DOI: 10.3390/polym14214487
Abstract
Nowadays, natural polymer-based films are considered potentially environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastic films, due to many advantageous properties, including their easy processability, high flexibility, non-toxicity, low cost, high availability, and environmental safety. However, they are limited in their application by a number of shortcomings, including their high water solubility and vapor permeability as well as their poor opacity and low mechanical resistance. Thus, nanoparticles, such as green FexOy-NPs, can be used to overcome the drawbacks associated with these materials. Therefore, the aim of this study was to develop three different polymer-based films (gelatin-based, cellulose acetate-based and chitosan-based films) containing green synthesized FexOy-NPs (1.0% w/w of the initial polymer weight) as an additive to improve film properties. This was accomplished by preparing the different films using the casting method and examining their physicochemical, mechanical, microstructural, and functional characteristics. The results show that the incorporation of FexOy-NPs into the different films significantly enhanced their physicochemical, mechanical, and morphological properties as well as their antioxidant characteristics. Consequently, it was possible to produce suitable natural polymer-based films with potential applications across a wide range of industries, including functional packaging for food, antioxidants, and antimicrobial additives for pharmaceutical and biomedical materials as well as pesticides for agriculture.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/polym14214487
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Transparency of polymeric food packaging materials
Guzman-Puyol, Susana; Benitez, Jose J; Heredia-Guerrero, Jose AFood Research International, 161 (2022) 111792 DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111792
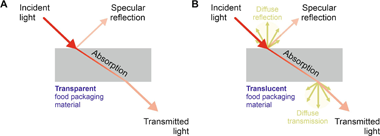
Abstract
Transparency is a very important technical parameter to evaluate and validate certain food packaging materials. In the recent scientific literature, several methods (i.e. transmittance, opacity, haze, and absorbance) have been used and such variety hinders a direct comparison of results from different authors. In this Review, we describe and discuss the most widely employed methods to measure transparency, with special emphasis on two main parameters: transmittance and opacity. Moreover, a comparison of the different techniques is addressed and the typical values of transmittance and opacity of common transparent food packaging materials are provided. Our current opinion is that transparency should be expressed as transmittance in the visible range due to both the quickness and easiness of the measurement and the standardization of data. This information should be accompanied by the thickness value and a graphical image of the analysed samples for a useful and complete characterization.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111792
Monitoring the Simultaneous Implantation of Ti and Tb Cations to a Sacrificial Template and the Sol-Gel Synthesis of Tb-Doped TiO2 (Anatase) Hollow Spheres and Their Transition to Rutile Phase
Colomer, MT; Vattier, FInternational Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23 (2022) 13162 DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113162
Abstract
Tb-doped TiO2 (anatase) micro-hollow spheres (HSs) with nano-shells, in the range 0.00-3.00 at.% Tb, were successfully synthesized by a simultaneous chemical implantation route of both Ti and Tb cations from chlorides to a poly-styrene (PST)-co-poly-divinyl benzene (PDVB) sacrificial template, followed by controlled hydrolysis and polycondensation reactions. After water addition to the mixture of the precursors with the template, a decrease in the intensity and a shift to lower wavenumbers of the C=O absorption band in the IR spectra can indicate not only the anchoring of Ti and Tb ions to the carbonyl group of the template but also the hydrolysis of the implanted precursors. This latter process can involve a proton attack on the Ti-Cl, Tb-Cl and C=O bonds, the occupation of a vacant site by a water molecule, and then the dissociation of the dangling Ti-Cl, Tb-Cl ligands and C=O bonds. It gives rise to Ti1-xTbx[(OH)(4-u)Cl-v]@PST-PDVB and Ti1-xTbx[(OH)(4-y)]@PST-PDVB complexes (x = 0.00, 0.0012, 0.0170 and 0.030). Finally, polycondensation of these species leads to Ti1-xTbxO2-w'@PST-PDVB compounds. After subsequent thermal removal at 550 degrees C of the template, the IR bands of the core (template) totally vanished and new bands were observed in the 400-900 cm(-1) region which can be attributed to the metalloxane bondings (M-O, M'-O, M-O-M, M-O-M' and/or M'-O-M', being M and M' = Ti and Tb, respectively, i.e., mainly vibration modes of anatase). Then, micron-sized HSs of TiO2 and Tb-doped-TiO2 (anatase) were obtained with nano-shells according to field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations. Furthermore, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements confirmed the presence of Tb4+ (38.5 and 41.2% for 1.70 and 3.00 at.% Tb, respectively) in addition to Tb3+ in the resulting HSs, with increasing Tb4+ content with both Tb doping and higher calcination temperatures. Then, these HSs can be considered as rare earth (RE) co-doped systems, at least for 1.70 and 3.00 at.% Tb contents being the transition to rutile phase favored by Tb doping for those compositions. Finally, diffusion of Tb from the inner parts to the surface of the HSs with the calcination treatments was also observed by XPS.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113162
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Effective photocatalytic conversion of formic acid using iron, copper and sulphate doped TiO2
Zouheir, M; Tanji, K; Navío, JA; Hidalgo, MC; Jaramillo-Paez, CA; Kherbeche, AJournal of Central South University, 29 (2022) 3592-3607 DOI: 10.1007/s11771-022-5172-9
Abstract
In this paper, the combined addition of copper or iron and sulphate ions onto TiO2 prepared by a simple sol-gel method is studied for formic acid photocatalytic conversion. A wide structural and morphological characterization of the different photocatalysts was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2-physisorption for BET surface area measurements, scanning and transmission electronic microscopies (SEM and TEM), UV-Vis diffuse spectroscopy (DRS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), in order to correlate the physico-chemical properties of the materials to their photocatalytic efficiencies for formic acid oxidation. Results have shown important differences among the catalysts depending on the metal added. Sulphated TiO2/Cu (1%Cu) was the best photocatalyst obtaining about 100% formic acid conversion in only 5 min. The appropriate physico-chemical features of this photocatalyst, given by the addition of combined copper and sulphate ions, explain its excellence in photocatalytic reaction.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1007/s11771-022-5172-9
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Morphologically diverse CaCO3 microparticles and their incorporation into recycled cellulose for circular economy
Guerra-Garces, J; Garcia-Negrete, CA; Pastor-Sierra, K; Arteaga, GC; Barrera-Vargas, M; de Haro, MJ; Fernandez, AMaterials Today Sustainability, 19 (2022) 100166 DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100166
Abstract
The main raw material for manufacture of paper is cellulose fibers that can be virgin or recycled. Globally, 70% of the Tetra Pak packages sold are not recycled and remain as unused wastes. Therefore, the development of alternatives to promote greater recycling and sustainable use of these packages is of great interest. In this study, the formation of precipitated calcium carbonates (PCC) in the presence of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is studied at different temperatures, and the morphologically diverse particles obtained are explored as filler for composites based on cellulosic fibers recovered from Tetra Pak containers. It was found that the addition of filler does not lead to deterioration of either tensile strength or thermal and stability of the obtained composite samples. Results also suggest that the morphological diversity of the filler contributes to a more efficient filling of the interfibrillar spaces of cellulosic fibers and, in turn, to the fiber and filler compatibility.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100166
Reactividad de Sólidos
Supercooled sodium acetate aqueous solution for long-term heat storage to support heating decarbonisation
Lizana, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Chacartegui, R; Becerra, JA; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Energy Storage, 55 (2022) 105584 DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.105584
Abstract
Heating decarbonisation through electrification requires the development of novel heat batteries. They should be suitable for the specific application and match the operation conditions of domestic renewable energy sources. Supercooled liquids, often considered a drawback of phase change materials, are among the most promising technologies supporting heating decarbonisation. Although some studies have shed light on stable supercooling, the fundamentals and stability remain open problems not always accompanied by relevant experimental in-vestigations. This research critically analyses the physic and chemistry of sodium acetate (SA, NaCH3COO) aqueous solution, a low-cost, non-toxic, and abundant compound with stable supercooling for long-term heat storage. It has an appropriate phase change temperature for high-density heat storage using heat pumps or solar thermal technologies in residential applications. The existing discrepancies in literature are critically discussed through a systematic experimental evaluation, providing novel insights into efficient material design and appropriate boundary conditions for reliable material use in long-term heat batteries. Despite previous studies showing that the thermal reliability and stability of sodium acetate aqueous solution as a supercooled liquid for heat storage cannot be guaranteed, this study demonstrates that through an appropriate encapsulation and sealing method, the peritectic composition of sodium acetate solution (p-SA 58 wt%) can be used as a super-cooled liquid for long-term heat storage with a stable melting temperature of 57 degrees C, appropriate for domestic heat technologies. It is demonstrated that energy storage efficiency can be maintained under cycling, with a constant latent heat storage capacity of 245 kJ/kg and a volumetric storage density of 314 MJ/m3. It was confirmed that the material should achieve a fully-melted state for stable supercooling. Finally, local cooling and retaining seed crystals through high pressure were highlighted as the most suitable basic principles for successful crystallization and heat release. This promising material can store energy for long periods without latent heat losses due to its stable subcooling. Latent heat can be released when required at any selected time and tem-perature just by a simple activation process.
November, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.105584
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Enhanced red-UC luminescence through Ce3+ co-doping in NaBiF4:Yb3+/Ho3+(Er3+)/Ce3+ phosphors prepared by ultrafast coprecipitation approach
Giordano, L; Du, H; Castaing, V; Luan, F; Guo, D; Viana, BOptical Materials X, 16 (2022) 100199 DOI: 10.1016/j.omx.2022.100199
Abstract
Series of Yb3+/Ho3+(Er3+)/Ce3+ co-doped NaBiF4 phosphors were synthesized through an ultrafast co-precipitation reaction technique at room temperature. The effect of the Ce3+ ions on the crystal structure and upconversion (UC) luminescence properties of the studied samples were investigated in detail. FTIR and XPS demonstrated the pre-formation of NaBiF4 and the introduction of Yb3+, Ho3+, Er3+ and Ce3+ all as dopants in the host materials. Under 980 nm excitation, NaBiF4:Yb3+,Ho3+(Er3+),Ce3+performed the characteristic emission of the activator ion, and the introduction of Ce3+ did not change the emission wavelengths, only the relative intensities. Due to partial good energy overlap when 2F7/2 Ce3+ manifold is populated, raising Ce3+ ions concentration enhanced the red UC emission versus green UC emission but also lead to significant decrease in the average lifetimes of all monitored emissions for Ho3+ and Er3+. These lifetime decreases are explained by the energy loss in non-radiative pathways after the introduction of Ce3+. In addition, the green to yellow color emission change through addition of Ce3+ was explored in NaBiF4: Yb3+,Ho3+,Ce3+ to propose a novel application in two-level anti-counterfeiting.
October, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.omx.2022.100199
Reactividad de Sólidos
Highly efficient electrical discharge machining of yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics with graphene nanostructures as fillers
Muñoz-Ferreiro, C; Lopez-Pernia, C; Moriche, R; Gommeringer, A; Kern, F; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 42 (2022) 5943-5952 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.06.037
Abstract
Electrical-discharge machining (EDM) of advanced ceramics allows the miniaturization of parts with complex shapes. Since electrical conductivity is required, non-conductive ceramics need a conductive second phase. This work assesses the feasibility of industrial EDM in advanced yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia (3YTZP) composites with 20 vol% graphene nanostructures with different morphology using different EDM energies. The structural integrity of the graphene nanostructures, the roughness of the machined surfaces and the geometrical tolerances have been evaluated by Raman spectroscopy, confocal microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, showing that it is possible to obtain a stable and efficient EDM process in these composites using low electrode energies. The use of the largest and thickest graphene nanostructures led to the best performance in terms of EDM machinability, the smallest nanostructures produced the best surface finish for low electrode energy and the thinnest nanostructures allowed the highest material removal rate at medium energy in the composites.
October, 2022 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.06.037
- ‹ previous
- 6 of 37
- next ›














