Scientific Papers in SCI
2020
2020
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tailoring materials by high-energy ball milling: TiO2 mixtures for catalyst support application
Rinaudo, MG; Beltran, AM; Fernandez, MA; Cadus, LE; Morales, MRMaterials Today Chemistry, 17 (2020) 100340
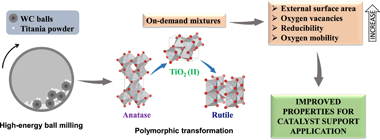
We carried out a rational design of catalyst supports by high-energy ball milling. Tailored mixtures of TiO2 crystalline phases were obtained using rotational speed and milling time as variable parameters. Polymorphic transformation from anatase to rutile through high-pressure TiO2 (II) as intermediate was confirmed by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Raman Spectroscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). Also, starting material doubled its specific surface area due to particle fragmentation, as confirmed by surface area of Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (S-BET) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). Defects introduced during milling process generated oxygen vacancies in the surface and bulk of supports, as evidenced by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR). Furthermore, longer milling time increased reducibility and oxygen mobility of supports, as observed by H-2 Temperature Programmed Reduction (H-2-TPR) and O-2 Temperature Programmed Desorption (O-2-TPD). Phase composition remained unchanged even under extreme conditions, highlighting the stability of unusual TiO2 (II) phase. Properties achieved in present materials could benefit metal-support interactions and play a major role in supported catalysts.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100340
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Elucidating esterification reaction during deposition of cutin monomers from classical molecular dynamics simulations
Bueno, OVM; Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MAJournal of Molecular Modeling, 26 (2020) 280
The structural behavior of some cutin monomers, when deposited on mica support, was extensively investigated by our research group. However, other events, such as esterification reaction (ER), are still a way to explore. In this paper, we explore possible ER that could occur when these monomers adsorb on support. Although classical molecular dynamics simulations are not able to capture reactive effects, here, we show that they become valuable strategies to analyze the initial structural configurations to predict the most favorable reaction routes. Thus, when depositing aleuritic acid (ALE), it is observed that the loss of capacity to form self-assembled (SA) systems favors different routes to occur ER. In pure ALE bilayers systems, an ER is given exclusively through the -COOH and primary -OH groups. In pure ALE monolayers systems, the ER does not happen when the system is self-assembled. However, for disorganized systems, it is able to occur by two possible routes: -COOH and primary -OH (route 1) and -COOH and secondary -OH (route 2). When palmitic acid (PAL) is added in small quantities, ALE SAMs can now form an ER. In this case, ER occurs mostly through the -COOH and secondary -OH groups. However, when the presence of PAL is dominant, ER can occur with either of both possibilities, that is, routes 1 and 2.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1007/s00894-020-04544-9
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Bimetallic PdAu catalysts for formic acid dehydrogenation
Santos, JL; Leon, C; Monnier, G; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 45 (2020) 23056-23068
A series of monometallic and bimetallic palladium gold catalyst were prepared and studied for the formic acid dehydrogenation reaction. Different Pd/Au compositions were employed (PdxAu100-x, where x = 25; 50 and 75) and their impact on alloy structure, particle size and dispersion was evaluated. Active phase composition and reaction parameters such as temperature, formic acid concentration or formate/formic acid ratio were adjusted to obtain active and selective catalyst for hydrogen production. An important particle size effect was observed and related to Pd/Au composition for all bimetallic catalysts.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.076
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Free-Carbon Surface for PtCu Nanoparticles: An In Situ Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study
Castillo, R; Navarro-Jaen, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Perez-Dieste, V; Escudero, C; Centeno, MA; Daturi, M; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2020) 19046-19056

Usually, nanoparticle synthesis methodologies require the use of organic molecules (capping agent, solvent molecules, etc.), which results in carbon deposits on the nanoparticle surface. These residues modify the surface properties mainly affecting the catalytic behavior. In this work, unsupported poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP)-stabilized PtCu (1:3 molar ratio) bimetallic alloy nanoparticles were synthetized and characterized. An alternative surface cleaning method has been designed, which successfully removes the presence of organic fragments. To address this key issue, we have combined a first nanoparticle washing step with a near ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (NAPXPS) study in order to obtain a clean active site and the total understanding of the carbon elimination mechanism. The dynamic evolution of the surface organic species composition under different gas mixtures at 750 mTorr and 350 degrees C has been studied, and only under CO2 exposure, NAPXPS analysis revealed a total availability of the active site by the removal of the organic nanoparticle coating.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c04713
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The wrinkling concept applied to plasma-deposited polymer-like thin films: A promising method for the fabrication of flexible electrodes
Thiry, Damien; Vinx, Nathan; Damman, Pascal; Aparicio, Francisco F.J.; Tessier, Pierre-Yves; Moerman, David; Leclere, Philippe; Godfroid, Thomas; Deprez, Sylvain; Snyders, RonyPlasma Processes and Polymers, 17 (2020) e2000119
In this communication, we report on an innovative solvent-free method that allows for the design of nano-/micropatterns with tuneable dimensions. Our approach is based on the spontaneous wrinkling phenomenon taking place in a bilayer system formed by a mechanically responsive bottom plasma polymer layer and a top aluminum thin film. The dimensions of the wrinkles can be adjusted in a wide range (i.e., from nanometer to micrometer range) by modulating the cross-linking density as well as the thickness of the plasma polymer layer. Finally, it is demonstrated that these wrinkled surfaces could efficiently be used as flexible electrodes. The whole set of our data unambiguously reveals the attractiveness of our method for the fabrication of the micro-/nanopattern with dimensions on demand.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.202000119
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 directionally solidified eutectics: Hardness dependence modelled through an array of screw dislocations
Moshtaghioun, BM; Gomez-Garcia, D; Pena, JIJournal of The European Ceramic Society, 40 (2020) 4171-4176
Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics have been fabricated by means of the laser floating zone (LFZ) technique. The microstructure has revealed as an unusual one at lower growth rate, composed of broken lamellae of MgAl2O4 distributed randomly along one matrix, composed of Mg2SiO4. At higher growth rates, a cell structure with intra-cell lamella structure is dominant. Contrary to most eutectic systems, hardness is not dependent upon the inter-spacing, but it does depend on one characteristic length of lamellae: their perimeter. One simple model based upon the dislocation is proposed, which successfully accounts for such extraordinary hardness law. Accordingly, Mg2SiO4-MgAl2O4 eutectic ceramics fabricated at 50 mm/h growth rate with the smallest MgAl2O4 lamella perimeter favorably showed more elevated hardness (13.4 GPa from Vickers indentation and 15.3 GPa from nanoindentation) and strength (430 MPa) than those found in the monolithic Mg2SiO4 matrix.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.015
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of all equiatomic five-transition metals High Entropy Carbides of the IVB (Ti, Zr, Hf) and VB (V, Nb, Ta) groups by a low temperature route
Chicardi, E; Garcia-Garrido, C; Hernandez-Saz, J; Gotor, FJCeramics International, 46 (2020) 21421-21430
The six possible equiatomic five-transition metal High Entropy Carbides (HECs) of the IVB (Ti, Zr, Hf) and VB (V, Nb, Ta) groups of the periodic table, i.e., TiZrHfVNbC5, TiZrHfVTaC5, TiZrHfNbTaC5, TiZrVNbTaC5, TiHfVNbTaC5 and ZrHfVNbTaC5, were successfully obtained via a powder metallurgy route at room temperature, specifically, by one-step diffusion mechanosynthesis starting from the elemental constituents (using graphite as the carbon source). Three of those HECs, TiZrHfVTaC5, TiZrVNbTaC5 and ZrHfVNbTaC5, were developed for the first time. Their development was possible without any subsequent thermal treatment, in contrast to the usual way (reactive sintering at 1800-2200 degrees C), and in a powder form, make them potential advanced raw ceramics for hard, refractory and oxidation resistance coatings or matrix phase composites.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.05.240
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Novel procedure for laboratory scale production of composite functional filaments for additive manufacturing
Diaz-Garcia, A; Law, JY; Cota, A; Bellido-Correa, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Schafer, R; Franco, VMaterials Today Communications, 24 (2020) 101049
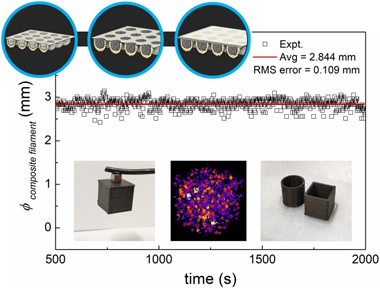
Successful 3D printing by material extrusion of functional parts for new devices requires high quality filaments. Uniform homogeneity and good dispersion of particles embedded in filaments typically takes several cycles of extrusion or well-prepared feedstock by injection molding, industrial kneaders or twin-screw compounding. These methods need specific production devices that are not available in many laboratories non-specialized in polymer research, such as those working on different material science and technology topics that try to connect with additive manufacturing. Therefore, laboratory studies are usually limited to compositions and filler concentrations provided by commercial companies. Here, we present an original laboratory scale methodology to custom-prepare the feedstock for extruding magnetic composite filaments for fused filament fabrication (FFF), which is attainable by a desktop single-screw extruder. It consists in encapsulating the fillers in custom made capsules that are used as feedstock and reach the melting area of the extruder maintaining the same concentration of fillers. Results have shown that our approach can create smooth and continuous composite filaments with good homogeneity and printability with fine level of dimensional control. We further show the good dispersion of the particles in the composite filament using X-Ray Tomography, which enabled a 3D reconstruction of the spacial distribution of the embedded magnetic particles. The major advantage of this new way of preparing the composite feedstock is that it avoids the hassle of multiple extrusion runs and industrial machinery, yet providing uniform filaments of well controlled filler concentration, which is predictable and reproducible. The proposed methodology is suitable for different polymer matrices and applicable to other functional particle types, not just limited to magnetic ones. This opens an avenue for further laboratory scale development of novel functional composite filaments, useful for any community. This democratization of complex filament preparation, including consumers preparing their own desired uniform novel filaments, will facilitate to unify efforts nearing 3D printing of new functional devices.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101049
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Experimental evidence of HCO species as intermediate in the fischer tropsch reaction using operando techniques
Diaz-Sanchez, RM; de-Paz-Carrion, A; Serrera-Figallo, MA; Torres-Lagares, D; Barranco, A; Leon-Ramos, JR; Gutierrez-Perez, JLApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 272 (2020) 119032
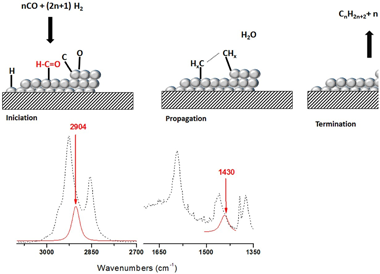
Fischer Tropsch's reaction, known from 1925, receives special attention nowadays due to its key role in the CO2 or biomass valorization to liquid fuels and chemicals. Several aspects on the exact mechanism or the role of water in this reaction are not yet completely clear. Formyl species, HCO, have been proposed as the most probable reaction intermediate, but they have never been observed under operation conditions closed to the real ones. In this work, using DRIFTS-MS operando techniques, HCO intermediates are detected under a H2/CO flow and 200 °C. IR bands at 2900 cm−1 and 1440 cm−1 attributed to ν(C–H) and δ(HCO) vibrations modes characterize these species. Evolution of these bands with the reaction time evidences its high reactivity with OH groups, which explains the positive effect of water on the CO conversion previously observed.
September, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119032
Materiales Coloidales
Design of a nanoprobe for high field magnetic resonance imaging, dual energy X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Garcia-Embid, S; Balcerzyk, M; Garcia-Martin, ML; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 573 (2020) 278-286
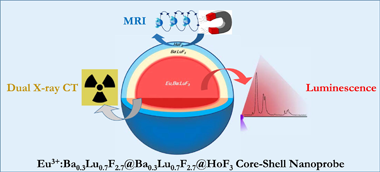
The combination of different bioimaging techniques, mainly in the field of oncology, allows circumventing the defects associated with the individual imaging modalities, thus providing a more reliable diagnosis. The development of multimodal endogenous probes that are simultaneously suitable for various imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray computed tomography (CT) and luminescent imaging (LI) is, therefore, highly recommended. Such probes should operate in the conditions imposed by the newest imaging equipment, such as MRI operating at high magnetic fields and dual-energy CT. They should show, as well, high photoluminescence emission intensity for their use in optical imaging and present good biocompatibility. In this context, we have designed a single nanoprobe, based on a core-shell architecture, composed of a luminescent Eu3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 core surrounded by an external HoF3 shell that confers the probe with very high magnetic transverse relaxivity at high field. An intermediate, optically inert Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 layer was interposed between the core and the shell to hinder Eu3+-Ho3+ cross-relaxation and avoid luminescence quenching. The presence of Ba and Lu, with different K-edges, allows for good X-ray attenuation at high and low voltages. The core-shell nanoparticles synthesized are good potential candidates as trimodal bioprobes for MRI at high field, dual-energy CT and luminescent imaging.
August, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
- ‹ previous
- 56 of 214
- next ›














