Scientific Papers in SCI
2019
2019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Noble Metal Supported on Activated Carbon for "Hydrogen Free" HDO Reactions: Exploring Economically Advantageous Routes for Biomass Valorisation
Jin, W; Santos, JL; Pastor-Perez, L; Gu, S; Centeno, MA; Reina, TRChemcatchem (2019) 4434-4441

An innovative route for bio‐compounds upgrading via “hydrogen‐free” hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) is proposed and evaluated using guaiacol as a model compound in a high‐pressure batch reactor. Experimental results showed that noble metal supported on activated carbon catalysts are able to conduct tandem multiple steps including water splitting and subsequent HDO. The activity of Ru/C catalyst is superior to other studied catalysts (i. e. Au/C, Pd/C and Rh/C) in our water‐only HDO reaction system. The greater dispersion and smaller metal particle size confirmed by the TEM micrographs accounts for the better performance of Ru/C. This material also presents excellent levels of stability as demonstrated in multiple recyclability runs. Overall, the proposed novel approach confirmed the viability of oxygenated bio‐compounds upgrading in a water‐only reaction system suppressing the need of external H2 supply and can be rendered as a fundamental finding for the economical biomass valorisation to produce added value bio‐fuels.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900841
Structural and compositional analysis of Co-based coatings after catalytic tests for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis
Beltran, AMMaterials Research Express, 6 (2019) art. 085511
The use of Co-based catalysts for the sodium borohydride hydrolysis for hydrogen production is a well-known process as a source of clean energy, although its mechanisms are still under discussion. With the aim of acquiring a deeper knowledge about this catalytic process, three different catalysts (Co, CoC and CoB) were deposited as a thin film layer by magnetron sputtering onto a polymeric membrane, used as a substrate and analyzed by advance transmission and scanning-transmission electron microscopy techniques (STEM). Structural and compositional characterizations, by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), have been performed on the coatings before and after their use as catalysts on the sodium borohydride reaction for 90 min, to check the production of hydrogen. Results have shown the formation of CoxB nanoflakes and other Co-based compounds over the catalysts and related to their catalytic activity. Knowing the changes in the structure and composition of the catalysts is key to understanding their catalytic behavior, activity and durability. Among the analyzed catalysts, the Co-C presents better activity during the first cycles, which is related to a larger formation of CoxB.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab1e27
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
MTA HP Repair stimulates in vitro an homogeneous calcium phosphate phase coating deposition
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e322-e326

Background: To study the mineralization capacity in vitro of the bioceramic endodontic material MTA HP Repair. Material and Methods: Bioactivity evaluation in vitro was carried out, by soaking processed cement disk in simulated body fluid (SBF) during 168 h. The cement surface was studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). Release to the SBF media of ionic degradation products was monitored using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Results: FT-IR showed increasing formation of phosphate phase bands at 1097, 960, 607 and 570 cm -1 with prolonged SBF soaking. FEG-SEM analysis reveals that HP produces a effectively surface covering consisting in homogeneous spherical phosphate phase aggregates with an average diameter of 0.5 -1 .0 μm. EDX analysis comparing un-treated (hydrated), 24 h and 72 h SBF treated surfaces of MTA HP Repair revealed phosphate deposition after 24 h, with high phosphorous/silicon element ratio signal measured after 24 h, indicating a very high phosphate phase deposition for this material. Conclusions: The study shows that MTA HP Repair produces a quick and effective bioactive response in vitro in terms of crystalline calcium phosphate surface coating formation. The high bioactive response of MTA HP Repair makes it an interesting candidate for endodontic use as repair cement.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.4317/jced.55661
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Physicochemical parameters - hydration performance relationship of the new endodontic cement MTA Repair HP
Jiménez-Sánchez, M.D.C.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Díaz-Cuenca, A.Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 11 (2019) e739-e744

Background: To characterize the chemical composition and textural parameters of the MTA Repair HP precursor powder and their influence to hydration performance. Material and Methods: Un-hydrated precursor material was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), laser diffraction (LD), N2 physisorption and field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM). Setting time was assessed according to ASTM specification C 266. Hydrated material was analysed by XRD, FT-IR, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis and FEG-SEM. Results: Ca3SiO5 and Ca2SiO4, in addition to CaWO4 as radiopacifier are the main compositional phases. Other measured parameters indicate high specific surface area of 4.8 m2 g-1, high aluminium content of 1.7 wt.% and low initial and final setting times of 12 and 199 min, respectively. Singular microstructural features consisting of high aspect ratio nanoparticles are main constituents of un-hydrated precursor. Besides, FEM-SEM observation shows notably growth of hexagonal shaped plate-like morphologies homogeneously distributed along the sample during hydration process. Conclusions: The short setting time measured for HP Repair, is correlated with high surface area of precursor powder, high Al content and the absence of compositional sulphate phases.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.4317/jced.56013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Bio-based composite fibers from pine essential oil and PLA/PBAT polymer blend. Morphological, physicochemical, thermal and mechanical characterization
Hernandez-Lopez, M; Correa-Pacheco, ZN; Bautista-Banos, S; Zavaleta-Avejar, L; Benitez-Jimenez, JJ; Sabino-Gutierrez, MA; Ortega-Gudino, PMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 234 (2019) 345-353
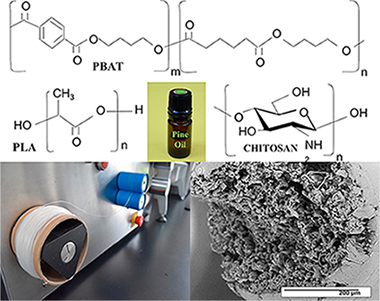
Biodegradable aliphatic polyesters are an alternative to reduce the use of synthetic plastic materials that cause severe damage to the environment. Formulations based on poly (lactic acid) (PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), were mixed in a 60:40 ratio, adding different concentrations of pine essential oil through the use of extrusion technology to obtain biodegradable polymer fibers. Some formulations were coated with chitosan. All the elaborated fibers were characterized by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy-Attenuated Total Reflection (FTIR-ATR), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and mechanical properties. The SEM studies showed that the PBAT improves the tenacity and provides greater elasticity promoting the interaction between the blends phases with fibril formation. In the FTIR-ATR analysis, compatibility between the blends was observed due to a possible interaction of the carbonyl group of PBAT with PLA. The DSC and the mechanical properties showed partial miscibility of the blends, indicating, that the plasticizing action of the essential oil gave greater mobility, flexibility, less rigidity and crystallization in the blends. A lower Young's modulus and greater elongation at break was also observed.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.034
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Support effects on NiO-based catalysts for the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of ethane
Delgado, D; Sanchis, R; Cecilia, JA; Rodriguez-Castellon, E; Caballero, A; Solsona, B; Nieto, JMLCatalysis Today, 333 (2019) 10-16

We report on the effect of NiO-support interactions on the chemical nature of Ni species in a series of supported NiO catalysts for the ODH of ethane. SiO2, TiO2-anatase, a high surface area TiO2 and a porous clay hetero-structure (PCH) with TiO2 and SiO2 pillars were used as supports, which led to a selectivity to ethylene in the range 30-90% over supported NiO catalysts. The catalysts were characterized by means of XRD, N-2-Adsorption, H-2-TPR, XPS and in situ (under H-2 reductive atmosphere) and ex situ XAS spectroscopy. The catalytic performance of supported materials is discussed in terms of their reducibility and specific reduction kinetics, but also taking into account the specific chemical nature of Ni species on each catalyst. The influence of the particle size and the presence of Ni and O vacancies on the catalytic performance in the ODH of ethane is inferred.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.07.010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au/Al2O3 - Efficient catalyst for 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid
Megias-Sayago, C; Lolli, A; Ivanova, S; Albonetti, S; Cavani, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 333 (2019) 169-175

The catalytic activity of a simple Au/Al2O3 catalytic system prepared by the direct anionic exchange (DAE) method was evaluated in the selective 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) oxidation under mild conditions, using molecular oxygen as the oxidant. The influence of the HMF/NaOH ratio and reaction time on product yield and distribution were studied and discussed in detail. Extremely high activity and selectivity were observed in mild conditions, with 99% of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) production at full HMF conversion after 4 h with the use of only 4 equivalents of NaOH at 70 degrees C. Catalyst viability and stability were verified by repeating the cycle up to five times. Changes in the nature of the support were also contemplated by introducing some ceria fraction, i.e. 20 wt%.
August, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.04.024
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On‐Surface Synthesis and Characterization of Acene‐Based Nanoribbons Incorporating Four‐Membered Rings
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Dienel, T; Nicolai, A; Kharche, N; Liang, LB; Daniels, C; Meunier, V; Liu, JZ; Feng, XL; Mullen, K; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Groning, O; Ruffieux, P; Fasel, RChemistry-A European Journal
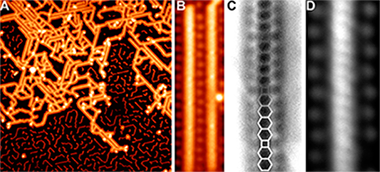
A bottom up method for the synthesis of unique tetracene-based nanoribbons, which incorporate cyclobutadiene moieties as linkers between the acene segments, is reported. These structures were achieved through the formal [2+2] cycloaddition reaction of ortho-functionalized tetracene precursor monomers. The formation mechanism and the electronic and magnetic properties of these nanoribbons were comprehensively studied by means of a multitechnique approach. Ultra-high vacuum scanning tunneling microscopy showed the occurrence of metal-coordinated nanostructures at room temperature and their evolution into nanoribbons through formal [2+2] cycloaddition at 475 K. Frequency-shift non-contact atomic force microscopy images clearly proved the presence of bridging cyclobutadiene moieties upon covalent coupling of activated tetracene molecules. Insight into the electronic and vibrational properties of the so-formed ribbons was obtained by scanning tunneling microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and theoretical calculations. Magnetic properties were addressed from a computational point of view, allowing us to propose promising candidates to magnetic acene-based ribbons incorporating four-membered rings. The reported findings will increase the understanding and availability of new graphene-based nanoribbons with high potential in future spintronics.
July, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/chem.201901410
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Size-tailored Ru nanoparticles deposited over gamma-Al2O3 for the CO2 methanation reaction
Navarro-Jaen, S; Navarro, JC; Bobadilla, LF; Centeno, MA; Laguna, OH; Odriozola, JAApplied Surface Science, 483 (2019) 750-761
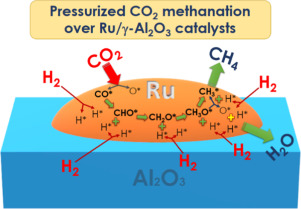
By means of the polyol method, a series of 5 wt% Ru/Al2O3 catalysts was synthesized controlling the particle size of the ruthenium species. The physico-chemical characterization demonstrated the successful particle size control of the Ru species, in such a way that higher the Ru/PVP ratio, higher the Ru particle size. Moreover, there are evidences that suggest preferential growth of the RuO2 clusters depending on the Ru/PVP ratio. Regarding the catalytic activity during the CO2 methanation, the total conversion and the CH4 yield increased with the particle size of Ru. Nevertheless, a considerable enhancement of the catalytic performance of the most active system was evidenced at 4 bar, demonstrating the improvement of the thermodynamics (superior total conversion) and kinetics (superior reaction rate) of the CO2 methanation at pressures above the atmospheric one. Finally, the in situ DRIFTS study allowed to establish that CO2 was dissociated to CO* and O* species on the metallic Ru particles, followed by the consecutive hydrogenation of CO* towards CHO*, CH2O*, CH3O*, and finally CH4 molecules, which were further desorbed from the catalyst. Thus from the mechanistic point of view, a suitable particle size of the Ru nanoparticles along with the high-pressure effects results in the enhancement of the availability of hydrogen and consequently in the formation of CHxO species that enhance the cleavage of the C-O bond, which is the rate-determining step of the overall CO2 methanation process.
July, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.248
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the preparation method in the metal-support interaction and reducibility of Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts for methane steam reforming
Azancot, L; Bobadilla, LF; Santos, JL; Cordoba, JM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 44 (2019) 19827-19840
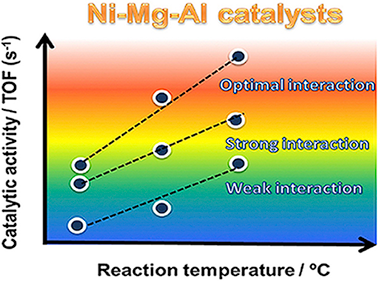
Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts were prepared using different preparation methods (impregnation, impregnation-coprecipitation and coprecipitation) and tested in steam reforming of methane. The differences observed in catalytic activity were directly correlated to the physicochemical properties and the different degree of Ni-Mg-Al interaction. The reducibility results showed that the catalyst prepared by the impregnation-coprecipitation method presented the most optimal metal-support interaction to reduce the NiO preserving the Ni-0 particles highly dispersed on the support surface. These results demonstrate that the structure and catalytic performance of Ni-Mg-Al based catalysts can be tuned by controlling the metal-support interaction through of the preparation method.
July, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.167
- ‹ previous
- 69 of 214
- next ›














