Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Elucidation of Water Promoter Effect of Proton Conductor in WGS Reaction over Pt-Based Catalyst: An Operando DRIFTS Study
Jurado, L; Garcia-Moncada, N; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 10 (2020) 841
Show abstract ▽

A conventional Pt/CeO2/Al(2)O(3)catalyst physically mixed with an ionic conductor (Mo- or Eu-doped ZrO2) was tested at high space velocity (20,000 h(-1)and 80 L h(-1)g(cat)(-1)) under model conditions (only with CO and H2O) and industrial conditions, with a realistic feed. The promoted system with the ionic conductor physically mixed showed better catalytic activity associated with better water dissociation and mobility, considered as a rate-determining step. The water activation was assessed by operando diffuse reflectance infrared fourier transformed spectroscopy (DRIFTS) studies under reaction conditions and the Mo-containing ionic conductor exhibited the presence of both dissociated (3724 cm(-1)) and physisorbed (5239 cm(-1)) water on the Eu-doped ZrO(2)solid solution, which supports the appearance of proton conductivity by Grotthuss mechanism. Moreover, the band at 3633 cm(-1)ascribed to hydrated Mo oxide, which increases with the temperature, explains the increase of catalytic activity when the physical mixture was used in a water gas shift (WGS) reaction.
Agosto, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/catal10080841
Materiales Coloidales
Design of a nanoprobe for high field magnetic resonance imaging, dual energy X-ray computed tomography and luminescent imaging
Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Becerro, AI; Corral, A; Garcia-Embid, S; Balcerzyk, M; Garcia-Martin, ML; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 573 (2020) 278-286
Show abstract ▽
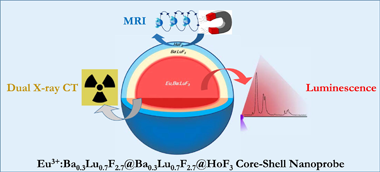
The combination of different bioimaging techniques, mainly in the field of oncology, allows circumventing the defects associated with the individual imaging modalities, thus providing a more reliable diagnosis. The development of multimodal endogenous probes that are simultaneously suitable for various imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), X-ray computed tomography (CT) and luminescent imaging (LI) is, therefore, highly recommended. Such probes should operate in the conditions imposed by the newest imaging equipment, such as MRI operating at high magnetic fields and dual-energy CT. They should show, as well, high photoluminescence emission intensity for their use in optical imaging and present good biocompatibility. In this context, we have designed a single nanoprobe, based on a core-shell architecture, composed of a luminescent Eu3+:Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 core surrounded by an external HoF3 shell that confers the probe with very high magnetic transverse relaxivity at high field. An intermediate, optically inert Ba0.3Lu0.7F2.7 layer was interposed between the core and the shell to hinder Eu3+-Ho3+ cross-relaxation and avoid luminescence quenching. The presence of Ba and Lu, with different K-edges, allows for good X-ray attenuation at high and low voltages. The core-shell nanoparticles synthesized are good potential candidates as trimodal bioprobes for MRI at high field, dual-energy CT and luminescent imaging.
Agosto, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.101
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Performance trends in wall-flow diesel particulate filters: Comparative analysis of their filtration efficiency and pressure drop
Orihuela, MP; Chacartegui, R; Gomez-Martin, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Villanueva, JABJournal of Cleaner Production, 60 (2020) 12063
Show abstract ▽
Soot and particulate emissions from the transport sector are a major concern worldwide, given their harmful effects on public health and the environment. On-road vehicles are the main contributing source to this kind of pollution. They are strictly regulated in many countries, with limitations on the number and concentration of released particles, and they must be equipped with particle abatement systems. Wall-flow particulate filters are the most popular and effective devices to reduce particulate emissions from diesel and gasoline vehicles. Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) have been a recurrent research topic since the last century. There are different research studies analysing different aspects of these systems, at different levels, using different methodologies and different approaches. Their results are not always comparable. This work analyses the latest advances and trends in this technology by comparing two relevant performance parameters: their filtration efficiency and pressure drop. The findings of this study suggest that, in order to be competitive, upcoming DPFs should have filtration efficiencies above 80%, and pressure drops below 10 kPa, for space velocities of 1.5.10(5) h(-1) or more at the clean state. They should reach similar to 100% efficiency after a short operation period, before the soot load reaches 0.2 g/L. Later, they should keep a low pressure drop for a longer time, with a reference of no more than 13 kPa for 6 g/L of soot load. Based on this analysis, this work proposes some test criteria and suggestions for the main parameters.
Julio, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120863
Reactividad de Sólidos
Calcium-Looping Performance of Biomineralized CaCO3 for CO2 Capture and Thermochemical Energy Storage
Arcenegui-Troya, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Valverde, JM; Chacartegui, R; Perez-Maqueda, LAIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 59 (2020) 12924-12933
Show abstract ▽
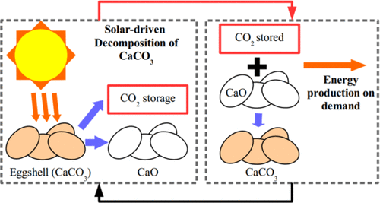
The commercial deployment of calcium-looping (CaL)-based technologies relies on the availability of nontoxic, widely available and cheap CaCO3 rich materials. Biomineralized CaCO3 from waste amply fulfills the aforementioned requirements. In the present work, we study the performance of eggshell and snail shell from food waste as CaO precursors for CaL applications. The results obtained suggest the feasible use of these waste materials. The multicyclic conversion exhibited by biomineralized CaCO3 was comparable to that demonstrated by limestone, which is a commonly proposed material for CaL applications. In addition, the temperature needed to completely calcine biomineralized CaCO3 in short residence times is lower than that required to fully calcine limestone. This would mitigate the energy cost of the technology.
Julio, 2020 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05997
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of Sr-doping on structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of synthesized Ca3(PO4)2
Y.Naciri; A.Hsini; Z.Ajmal; A.Bouddouch; B.Bakiz; J.A.Navío; A.Albourine; J-C.Valmalette; M.Ezahri; A.BenlhachemiJournal of Colloid and Interface Science, 572 (2020) 269-280
Show abstract ▽
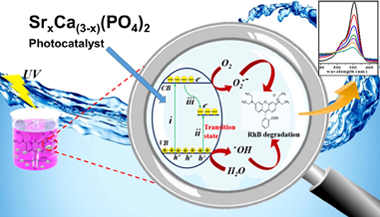
Well-crystallized Ca3(PO4)2 doped and un-doped nano-particles with the maximum strontium content (40 wt% Sr) followed by calcination at 800 °C for 3 h were synthesized via facile co-precipitation method. DTA/TGA, X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive scanning electron microscopy (SEM/EDX), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectrum (UV–vis DRS), Raman spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) techniques were used for material characterization. The (XRD) patterns of as-synthesized Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution samples exhibited a systematic shift toward lower angles by possessing a single rhombohedral crystal structure without any secondary phases. The UV light driven photocatalytic activity was assessed for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. As a result, ultrafast photodegradation activity was observed after Sr doping. Moreover, the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 sample showed the highest photocatalytic degradation among the Sr-doped Ca3(PO4)2 samples toward RhB. It was further suggested that as-synthesized 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 superior photocatalytic performance is ascribed to the more proficient partition of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Furthermore, the involved mechanism of superior photocatalytic performance of the 30 wt% Sr-Ca3(PO4)2 solid solution was also investigated. In addition, regeneration cycles indicated the higher stability of the photocatalyst to be effectively recycled up to four times without any considerable reduction in photocatalytic performance. Thus, these informations further provides us a scalable pathway to fabricate Sr doped Ca3(PO4)2 and its consequent use as an efficient photocatalyst for rhodamine B (RhB) contaminated wastewater treatment.
Julio, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.03.105
- ‹ anterior
- 105 of 420
- siguiente ›














