Artículos SCI
2020
2020
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Binder-free supercapacitor electrodes: Optimization of monolithic graphitized carbons by reflux acid treatment
Gomez-Martin, A; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Ramirez-Rico, JFuel Processing Technology, 199 (2020) 106279
Show abstract ▽

The rational design of electrodes mimicking the cellular structure of natural bio-resources has been a matter of increasing interest for applications in energy storage. Due to their anisotropic and hierarchical porosity, monolithic carbon materials from natural wood precursors are appealing as electrodes for supercapacitor applications due to their interconnected channels, relatively low cost and environmentally friendly synthesis process. In this work, a liquid-phase oxidative treatment with refluxing nitric acid at 100 degrees C for 8 h was performed to enhance the surface properties of beech-derived graphitized carbons treated with an iron catalyst. Microstructural, textural and surface investigations revealed that this strategy was successful in removing amorphous carbon and in functionalizing their surfaces. The crystallinity, accessible surface area, micropore volume and surface functionality of beech-derived carbons were increased upon the reflux treatment. The resulting porous carbon materials were evaluated as binderless monolithic electrodes for supercapacitors applications in aqueous KOH electrolyte. A maximum specific capacitance of 179 F.g(-1) and a volumetric capacitance of 89 Fcm(-3) in galvanostatic charge/discharge experiments were reached. Monolithic electrodes exhibited good cycling stability, with a capacitance retention over 95% after 10,000 cycles.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106279
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical interference effects on the Casimir-Lifshitz force in multilayer structures
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HPhysical Review A, 101 (2020) 033815
Show abstract ▽
The Casimir-Lifshitz force F(C-L) between planar objects when one of them is stratified at the nanoscale is herein investigated. Layering results in optical interference effects that give rise to a modification of the optical losses, which, as stated by the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, should affect the Casimir-Lifshitz interaction. On these grounds, we demonstrate that, by nanostructuring the same volume of dielectric materials in diverse multilayer configurations, it is possible to access F(C-L) of attractive or repulsive nature, even getting canceled, at specific separation distances.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.033815
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Potentialization of bentonite properties as support in acid catalysts
Amaya, J; Bobadilla, L; Azancot, L; Centeno, M; Moreno, S; Molina, RMaterials Research Bulletin, 123 (2020) 110728
Show abstract ▽
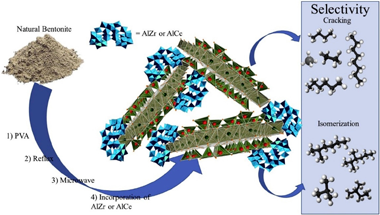
Enhancement of the main physicochemical properties of a natural bentonite was carried out by means of modifications using surfactant, reflux, microwave treatment and, subsequently, the incorporation of AlZr and AlCe species. The evolution of the main changes in each modification stage was evaluated by means of X-ray diffraction, N-2 sortometry, scanning microscopy (SEM), NH3-TPD, NH3-DRIFTS and CO adsorption at low temperature. For the evaluation of the catalytic behavior, the dehydration-dehydrogenation reactions of 2-propanol and hydro-conversion of decane were used; both of which generate, in addition, information regarding the acidic properties of the materials. The correlation of the number, type and acid strength with the catalytic behavior, allowed establishing the effect produced by both the delamination method and the nature of the incorporated cation. This generated tools that allow controlling the physicochemical properties, and more specifically, the enhancement of the acidity of new supports based on this type of natural clay mineral.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110728
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Test Configuration and Temperature on the Mechanical Behaviour of WC-Co
Gonzalez, LM; Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Llanes, L; Torres, YMetals, 10 (2020) 322
Show abstract ▽

In this work, the effect of the test configuration and temperature on the mechanical behaviour of cemented carbides (WC-Co) with different carbide grain sizes (d(WC)) and cobalt volume fractions (V-Co), implying different binder mean free paths (lambda (Co)), was studied. The mechanical strength was measured at 600 degrees C with bar-shaped specimens subjected to uniaxial four-point bending (4PB) tests and with disc specimens subjected to biaxial ball-on-three-balls (B3B) tests. The results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory and compared with strength measurements performed at room temperature under the same loading conditions. A mechanical degradation greater than 30% was observed when the samples were tested at 600 degrees C due to oxidation phenomena, but higher Weibull moduli were obtained as a result of narrower defect size distributions. A fractographic analysis was conducted with broken specimens from each test configuration. The number of fragments (N-f) and the macroscopic fracture surface were related to the flexural strength and fracture toughness of WC-Co. For a given number of fragments, higher mechanical strength values were always obtained for WC-Co grades with higher K-Ic. The observed differences were discussed based on a linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) model, taking into account the effect of the temperature and microstructure of the cemented carbides on the mechanical strength.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.3390/met10030322
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction as effective photocatalyst for the degradation of diclofenac and ketoprofen
Sacco, O.l; Murcia, J.J.; Lara, A.E.; Hernández-Laverde, M.; Rojas, H.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Vaiano, V.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 107 (2020) 104839
Show abstract ▽

Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction was synthetized and studied for the photocatalytic removal of diclofenac (DCF) and ketoprofen (KTF) under UV light irradiation. The physical-chemical properties of the prepared catalysts were analysed by different characterization techniques revealing that the lowest platinum nanoparticle size and the better metal distribution was observed in Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 sample. The Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction possessed the best photocatalytic activity toward both the photodegradation and mineralization of the two selected pollutants. The optimal photocatalyst showed a DCF and KTF mineralization rate of 0.0555 and 0.0746 min−1, respectively, which were higher than those of Pt–TiO2 (0.0321 min−1 for DCF and 0.0597 min−1 for KTF). The experiments driven to analyse the effects of free radical capture showed that ·OH, ·O2− and h+ have a primary role in reactive during the photocatalytic reaction. The improved photocatalytic performances of the Pt–TiO2–Nb2O5 heterojunction could be argue by a direct Z-scheme mechanism in which the Pt0 nanoparticles could act as a bridge between TiO2 and Nb2O5, improving the electron-hole separation and, ultimately, enhancing the photocatalytic removal rate of both DCF and KTF.
Marzo, 2020 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104839
- ‹ anterior
- 112 of 420
- siguiente ›














