Artículos SCI
2019
2019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin film as efficient anodic catalysts for anion exchange membrane water electrolysers
Lopez-Fernandez, E; Gil-Rostra, J; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, F; de Lucas-Consuegra, AJournal of Power Sources, 415 (2019) 136-144
Show abstract ▽
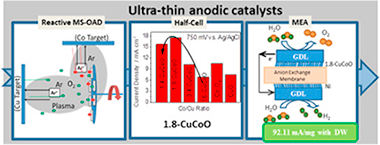
CuxCo3-xO4 ultra-thin films, deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles have been used as anodic catalysts in anion exchange membrane water electrolysers. It has been demonstrated that the used deposition procedure provides porous and amorphous samples with a strict control of the total catalyst load and Co/Cu ratio. Electrocatalytic tests showed a maximum performance for the oxygen evolution reaction at Co/Cu atomic ratio around 1.8. The optimized anodic catalyst presented a long-term stability confirmed by accelerated lifetime tests together with the chemical surface analysis of the used samples. The effect of the crystallization of a single layer CuxCo3-xO4 and a multilayer (CuO/Co3O4)(n) anodic catalyst samples was also investigated. The observed loss of catalytic performance found in both cases may prove that a particular local chemical environment around the Co and Cu sites acts as an efficient catalytic site for the oxygen evolution reaction. A catalyst film with the optimum Co/Cu atomic ratio was incorporated into a Membrane Electrode Assembly, using a sputtered Ni film as cathode. Current density values up to 100 mA cm(-2) at 2.0 V were obtained in 1.0 M KOH electrolyte. Upon normalization by the amount of catalyst, this performance is one of the highest reported in literature.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.01.056
Technological evolution of ceramic glazes in the renaissance: In situ analysis of tiles in the Alcazar (Seville, Spain)
de Viguerie, Laurence; Robador, Maria D.; Castaing, Jacques; Perez-Rodriguez, Jose L.; Walter, Philippe; Bouquillon, AnneJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 102 (2019) 1402-1413
Show abstract ▽
The Alcazar Palace (Seville, Spain) is famous for its ceramic decorations; 16th century wall tiles of different typologies have been analyzed in order to relate the manufacturing process of their colored glazes to the evolving technologies of the Renaissance. Chemical and mineralogical compositions have been determined in situ by nondestructive X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction on arista ceramics in the Cenador de Carlos Quinto, and majolica ceramics in the Palacio Gotico and the Royal oratory. The arista style belongs to the local Hispano-Moresque ceramic tradition. Majolica tiles have the complex microstructures of glazes from Italy. The two types are clearly differentiated by their typology, morphology (curved vs flat surface), and also microstructure (single vs multi-layers), glaze chemistry, and use of different coloring agents. Moreover, we found different glaze chemistries in the investigated majolicas, which correspond to different artists and/or practices.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.15955
Reactividad de Sólidos
A theoretical study of the bonding capabilities of the zinc-zinc double bond
Ayala, R; Galindo, AInternational Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 119 (2019) e25823
Show abstract ▽
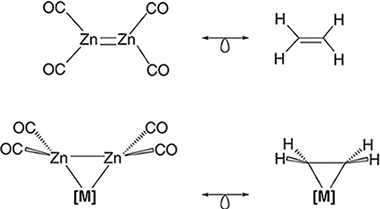
The theoretical knowledge about the zinc-zinc bond has been recently expanded after the proposal of a zinc-zinc double bond in several [Zn-2(L)(4)] compounds (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.2017, 56, 10151-10155). Prompted by these results, we have selected the [Zn-2(CO)(4)] species, isolobally related to ethylene, and theoretically investigated the possible (2)-Zn-2-coordination to several first-row transition metal fragments. The [Zn-2(CO)(4)] coordination to the metal fragment produces an elongation of the dizinc bond and a concomitant pyramidalization of the [Zn(CO)(2)] unit. These structural parameters are indicative of -backdonation from the metal to the coordinated dizinc moiety, as occurred with ethylene ligand. A quantum theory of atoms in molecules study of the ZnZn bond shows a decrease of (BCP), delta(2)(BCP) (ZnZn) and delocalization indexes (Zn,Zn), relative to corresponding values in the parent [Zn-2(CO)(4)] molecule. The ZnZn and MZn bonds in these [((2)-Zn-2(CO)(4))M(L)(n)] complexes can be described as shared interactions with an important covalent component where the ZnZn bond is preserved, albeit weakened, upon coordination.
Marzo, 2019 | DOI: 10.1002/qua.25823
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Catalytic Efficiency of Cu-Supported Pyrophyllite in Heterogeneous Catalytic Oxidation of Phenol
El Gaidoumi, A.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M.; Pulido Melián, E.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío, J.A.; El Bali, B.; Kherbeche, A.Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, (2019) 1-13
Show abstract ▽
The copper-impregnated pyrophyllite (Cu/RC) was prepared and used as catalyst in catalytic wet peroxide oxidation (CWPO) of phenol. The catalyst was prepared by impregnation of copper (2.5 wt%) into pyrophyllite-type clay and characterized by X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The optimum operation conditions for CWPO of phenol over Cu/RC were determined by investigating the effects of pH, temperature, catalyst amount, and hydrogen peroxide concentration. Stability of the Cu/RC catalyst and toxicity of treated solution were studied, by measuring the copper concentration leached out from the catalyst and the inhibition of Vibrio fischeri bacteria bioluminescence, respectively. The probable degradation mechanism of phenol over Cu/RC was considered by HPLC analysis. The obtained results showed that Cu/RC achieved highest activity (total phenol degradation and 80% TOC reduction) and detoxification with remarkable low copper leaching concentration (0.006 mg\,L−1)mg\,L−1) at optimized conditions (pH == 3, T=50∘T=50∘C, 2 g\,L−1g\,L−1 catalyst amount, 50 mg L−1L−1phenol concentration and 7.45 mmol\,L−1mmol\,L−1 hydrogen peroxide concentration during 4 h). Meanwhile, few intermediates with low concentration were observed by the HPLC analysis for the CWPO of phenol. The Cu/RC catalyst showed a good activity after five successive runs (88% of degradation and 73% mineralization) at optimized conditions.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.1007/s13369-019-03757-2
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Immobilization of Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles on Various Ceria-Based Oxides: Influence of the Protecting Agent on the Glucose Oxidation Reaction
Chenouf, M; Megias-Sayago, C; Ammari, F; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysts, 9 (2019) 125
Show abstract ▽
The influence of the protecting agent's nature on gold particle size and dispersion was studied in this work over a series of gold-based catalysts. CO and glucose oxidation were chosen as catalytic reactions to determine the catalyst's structure-activity relationship. The nature of the support appeared to be the predominant factor for the increase in activity, as the oxygen mobility was decisive for the CO oxidation in the same way that the Lewis acidity was decisive for the glucose oxidation. For the same catalyst composition, the use of montmorillonite as the stabilizing agent resulted in better catalytic performance.
Febrero, 2019 | DOI: 10.3390/catal9020125
- ‹ anterior
- 140 of 420
- siguiente ›














