Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Strong activation effect on a ru-co-c thin film catalyst for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride
Arzac, GM; Paladini, M; Godinho, V; Beltran, AM; de Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, AScientific Reports, 8 (2018) art. 9755
Show abstract ▽
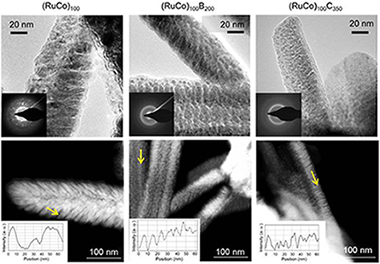
In this work, we prepared a series of Ni foam supported Ru-Co, Ru-Co-B and Ru-Co-C catalysts in the form of columnar thin films by magnetron sputtering for the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. We studied the activity and durability upon cycling. We found a strong activation effect for the Ru-Co-C sample which was the highest ever reported. This catalyst reached in the second cycle an activity 5 times higher than the initial (maximum activity 9310 ml.min(-1).g(CoRu)(-1) at 25 degrees C). Catalytic studies and characterization of the fresh and used samples permitted to attribute the strong activation effect to the following factors: (i) small column width and amorphous character (ii) the presence of Ru and (iii) dry state before each cycle. The presence of boron in the initial composition is detrimental to the durability. Our studies point out to the idea that after the first cycle the activity is controlled by surface Ru, which is the most active of the two metals. Apart from the activation effect, we found that catalysts deactivated in further cycles. We ascribed this effect to the loss of cobalt in the form of hydroxides, showing that deactivation was controlled by the chemistry of Co, the major surface metal component of the alloy. Alloying with Ru is beneficial for the activity but not for the durability, and this should be improved.
Junio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28032-6
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Understanding the differences in catalytic performance for hydrogen production of Ni and Co supported on mesoporous SBA-15
Rodriguez-Gomez, A; Pereniguez, R; Caballero, ACatalysts, 307 (2018) 224-230
Show abstract ▽
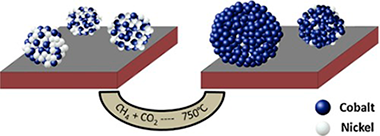
Three mono and bimetallic NixCo1-x/SBA-15 catalysts (x = 1, 0.5 and 0) with a total metallic content of 10 wt% have been prepared by a deposition-precipitation (DP) method. The catalytic performances on the dry reforming of methane reaction (DRM) have been determined and correlated with their physical and chemical state before and after the catalytic reaction. So, while the nickel monometallic system presents a high activity and stability in the DRM reaction, the Co/SBA-15 catalytic system turns out completely inactive. For its part, the Ni0.5Co0.5/SBA-15 has initially a catalytic performance similar to the Ni/SBA-15 monometallic system, but rapidly evolving to an inactive system, therefore resembling the behavior of the cobalt-based catalyst. The characterization by TEM and in situ XPS techniques has allowed us to ascribe these differences to the initial state of metallic particles after reduction and their different evolution under reaction conditions. So, while after reduction both nickel containing NixCo1-x/SBA-15 catalysts (x = 1 and 0.5) present a well dispersed metallic phase, the cobalt monometallic catalyst yields big metallic particles with a heterogeneous distribution of sizes. Additionally, unlike the Ni/SBA-15, the NiCo/SBA-15 system increases during reaction the metallic particle sizes.
Besides indicating that the particle size is a major reason determining the catalytic performances, these results suggest that in the Ni-Co system both metals form after reduction a bimetallic phase mainly located inside the mesoporous channels of SBA-15 support. Under DRM reaction conditions, the cobalt is segregated to the surface of the bimetallic particles, which seems to determine the interaction with the support surface SBA-15. This feature gives rise to a much less stable metallic phase which suffers an important sintering process under DRM catalytic conditions.
Junio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.02.020
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effects of milling time, sintering temperature, Al content on the chemical nature, microhardness and microstructure of mechanochemically synthesized FeCoNiCrMn high entropy alloy
Alcala, MD; Real, C; Fombella, I; Trigo, I; Cordoba, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 749 (2018) 834-843
Show abstract ▽
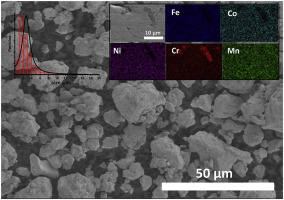
FeCoNiCrMn(Al)-based powdered high entropy alloys were synthesized by a short time mechanical alloying process in a high energy planetary ball milling from mixtures of elemental powders, and subsequently sintered by a pressureless procedure. The composition and microstructure of the HEA phases before and after the sintering process were studied by X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) and scanning electron microscopy. The microhardness and tensile strength values for Fe1,8Co1,8Ni1,8Cr1,8Mn1,8Al1,0 HEA sintered at 1400 degrees C sample were 3,7 GPa and 1011 MPa, respectively. Statistical Fisher-Pearson coefficient of skewness and kurtosis were played to determine the optimum synthesis milling time. The use of NaCl as additive led on to a reduction of the as-milled grain size. After sintering, SEM study confirmed a segregation of the initial HEA phase directly related to the melting temperature of the elements. Three melting temperature groups were described (Cr, FeCoNi and Mn) and they agree with the observation in the elemental mapping study. The presence of Al favored the segregation of Cr.
Junio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.358
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Heteroatom framework distribution and layer charge of sodium Taeniolite
Perdigon, AC; Pesquera, C; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 158 (2018) 246-251
Show abstract ▽
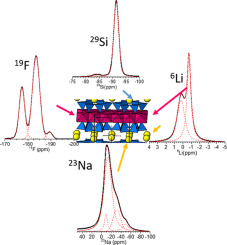
The most advanced applications of clays depend crucially on their hydration state and swelling is probably the most important feature of expandable 2:1 layered silicate. Sodium Taeniolite, Na-TAE, a swelling trioctahedral fluormica, has been synthesized and studied using thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and infrared and solid state NMR spectroscopies. The results indicated the formation of a swelling 2:1 phyllosilicate with actual layer charge lower than the nominal one. Herein, a new heteroatom distribution and more accurate composition could be deduced.
Junio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.036
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Unexpected Optical Blue Shift in Large Colloidal Quantum Dots by Anionic Migration and Exchange
Acebron, M; Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Lopez, C; Herrera, FC; Mizrahi, M; Requejo, FG; Palomares, FJ; Juarez, BHJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 9 (2018) 3124-3130
Show abstract ▽
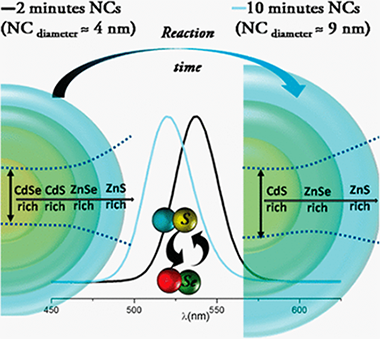
Compositional changes taking place during the synthesis of alloyed CdSeZnS nanocrystals (NCs) allow shifting of the optical features to higher energy as the NCs grow. Under certain synthetic conditions, the effect of those changes on the surface/interface chemistry competes with and dominates over the conventional quantum confinement effect in growing NCs. These changes, identified by means of complementary advanced spectroscopic techniques such as XPS (X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy) and XAS (X-ray absorption spectroscopy), are understood in the frame of an ion migration and exchange mechanism taking place during the synthesis. Control over the synthetic routes during NC growth represents an alternative tool to tune the optical properties of colloidal quantum dots, broadening the versatility of the wet chemical methods.
Junio, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b00741
- ‹ anterior
- 163 of 420
- siguiente ›














