Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhancing Moisture and Water Resistance in Perovskite Solar Cells by Encapsulation with Ultrathin Plasma Polymers
Idigoras, J; Aparicio, FJ; Contreras-Bemal, L; Ramos-Terron, S; Alcaire, M; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Anta, JAACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10 (2018) 11587-11594
Show abstract ▽
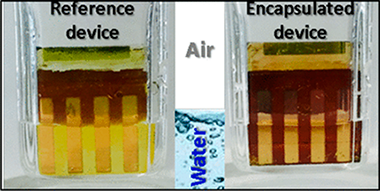
A compromise between high power conversion efficiency and long-term stability of hybrid organic inorganic metal halide perovskite solar cells is necessary for their outdoor photovoltaic application and commercialization. Herein, a method to improve the stability of perovskite solar cells under water and moisture exposure consisting of the encapsulation of the cell with an ultrathin plasma polymer is reported. The deposition of the polymer is carried out at room temperature by the remote plasma vacuum deposition of adamantane powder. This encapsulation method does not affect the photovoltaic performance of the tested devices and is virtually compatible with any device configuration independent of the chemical composition. After 30 days under ambient conditions with a relative humidity (RH) in the range of 35-60%, the absorbance of encapsulated perovskite films remains practically unaltered. The deterioration in the photovoltaic performance of the corresponding encapsulated devices also becomes significantly delayed with respect to devices without encapsulation when vented continuously with very humid air (RH > 85%). More impressively, when encapsulated solar devices were immersed in liquid water, the photovoltaic performance was not affected at least within the first 60 s. In fact, it has been possible to measure the power conversion efficiency of encapsulated devices under operation in water. The proposed method opens up a new promising strategy to develop stable photovoltaic and photocatalytic perovskite devices.
Abril, 2018 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b17824
Materiales Avanzados
Synthesis of vaterite CaCO3 as submicron and nanosized particles using inorganic precursors and sucrose in aqueous medium
Perez-Villarejo, L; Takabait, F; Mahtout, L; Carrasco-Hurtado, B; Eliche-Quesada, D; Sanchez-Soto, PJCeramics International, 44 (2018) 5291-5296
Show abstract ▽
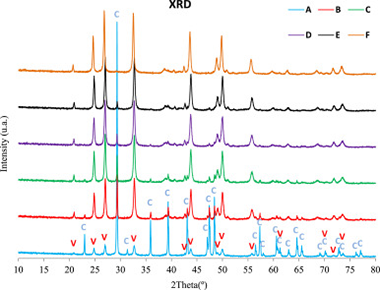
It is reported the synthesis of CaCO3 vaterite as stable nanoparticles and submicron-sized by a simple and relatively rapid procedure. XRD, SEM and FTIR techniques have been used to characterize the precipitated products. The synthesis is based on chemical precipitation of inorganic salt precursors, calcium nitrate tetra hydrate and sodium bicarbonate, and using the disaccharide sucrose as an additive in aqueous medium. The role of the disaccharide sucrose is to control the vaterite precipitation after nucleation and growth. It has been found that an increase in sugar concentration promotes the crystal precipitation of vaterite with spherulitic morphology, as revealed by SEM, and changed the surface of the precipitated particles. There is a significant difference between CaCO3 precipitation in the absence and presence of sucrose. Addition of 0% of sucrose leads to 83% of calcite as identified by XRD methods. In contrast, addition of 67% of sucrose in aqueous medium produces 100% vaterite. The present results may be useful to provide a quick, simple, inexpensive and novel method for the controlled synthesis of new advanced biomaterials based on vaterite particles without hazardous chemicals and inert atmosphere, with great possibilities for industrial scale production.
Abril, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.142
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis of Pd-Al/biomorphic carbon catalysts using cellulose as carbon precursor
Cazana, F; Galetti, A; Meyer, C; Sebastian, V; Centeno, MA; Romeo, E; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 301 (2018) 226-238
Show abstract ▽

This work presents the results obtained with novel Pd and Pd-Al catalysts supported on carbon, which have been prepared using a biomorphic mineralization technique. The catalyst synthesis procedure includes a stage of thermal decomposition under reductive atmosphere of cellulose previously impregnated with the metallic precursors. We have studied the influence of the temperature and time of decomposition, and of the Al precursor addition, on the textural and catalytic properties. The characterisation results indicate that the preparation method used leads to the formation of carbonaceous supports with a high microporosity (up to 97% micropore volume) and values of the BET surface up to 470 m2/g while maintaining the original external structure. The use of low temperatures (ca. 600 °C) during the decomposition step allows the preparation of highly dispersed catalysts with narrow Pd particle size distributions. However, the thermal decomposition at elevated temperatures (ca. 800 °C) increases the Pd particle size due to the sintering of the metallic phase. This phenomenon is augmented with the decomposition time and is not affected by the presence of Al. Consequently, the catalytic activity of these materials in cyclohexene hydrogenation is strongly affected by the operational conditions used during the thermal decomposition step. Unexpectedly, the more sintered catalysts, i.e. those prepared at 800 °C, show the highest activity. According to the characterization results, this fact can be explained considering that the smaller Pd particles obtained after preparation at e.g. 600 °C are quite inactive because they are confined in the internal structure of the micropores of the support and/or embedded inside the carbon matrix. In contrast, after decomposition at 800 °C, the larger Pd particles formed are placed at the external surface of the catalyst, being accessible to the reactants. In addition, for the specific conditions under which the Pd is accessible, the presence of Al favours the cyclohexene conversion due to the enhancement of the adsorption on the Pd surface as a consequence of a charge transfer phenomenon. These results can serve as a guideline for the preparation of these catalysts based on raw lignocellulosic materials in order to maximize their catalytic performance.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.05.026
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold catalyst recycling study in base-free glucose oxidation reaction
Megias-Sayago, C.; Bobadilla, L. F.; Ivanova, S.; Penkova, A.; Centeno, M. A.; Odriozola, J. A.Catalysis Today, 301 (2018) 72-77
Show abstract ▽
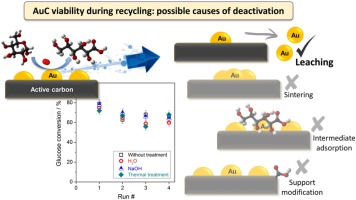
This work is devoted to the study of viability of immobilized gold colloids on carbon as catalysts for the base-free glucose oxidation reaction with a special emphasis made on catalysts' recycling, operational life and possible routes for deactivation/reactivation under batch conditions. The observed catalytic behavior is related to all possible manners of deactivation, like gold metal state changes (particle size agglomeration or leaching), support modifications or active sites blocking by intermediates. In an attempt to recover the initial catalytic activity, the samples are subjected to different treatments such as H2O and NaOH washings and calcination. The failure of the regeneration procedures to recover the initial activity and after detailed catalyst' characterization allows us to find out the main cause of deactivation
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2017.03.022
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and optical properties of environmentally benign and highly uniform NaCe(MoO4)(2) based yellow nanopigments
Laguna, M; Nuñez, NO; Fernandez, M; Ocaña, MJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 739 (2018) 542-548
Show abstract ▽
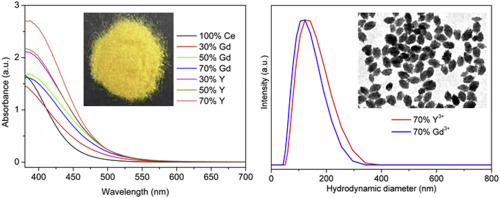
A method for the synthesis of uniform and aggregation free NaCeMoO4 based nanospheroids with tunable size is reported. The procedure is based on a precipitation reaction at 120 degrees C for 20 h from solutions containing Na2MoO4, sodium citrate and Ce(NO3)(3) and different amounts of Y(NO3)(3) or Gd(NO3)(3). The role played by the later compounds on the formation of the particles and their morphological and structural characteristics is analyzed through the analysis of the mechanism of particle formation. The chromaticity coordinates of the obtained samples are also evaluated showing that the here reported nanoparticles constitute an ecofriendly alternative to more toxic commercial yellow pigments. The synthesized nanoparticles are also free of aggregation in water suspensions and might be suitable for injet-printing technologies.
Marzo, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.158
- ‹ anterior
- 171 of 420
- siguiente ›














