Artículos SCI
2018
2018
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Flexible and Adaptable Light-Emitting Coatings for Arbitrary Metal Surfaces based on Optical Tamm Mode Coupling
Jiménez-Solano, A.; Galisteo-López, J.; Míguez, H.Advanced Optical Materials, 6 (2018) 1700560
Show abstract ▽
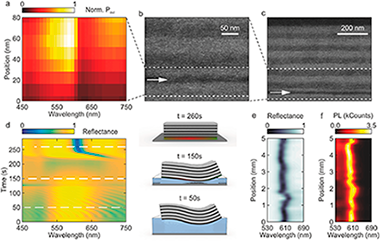
This study demonstrates a design that maximizes the power radiated into free space from a monolayer of nanoemitters embedded in a flexible distributed Bragg reflector conformably attached to a metal surface. This is achieved by positioning the light source at the precise depth within the multilayer for which optical Tamm states provide enhanced quantum yield and outcoupling efficiency, which are combined to optimize the luminous power radiated by the surface of the ensemble. This approach, based on the adhesion of flexible multilayer stacks onto metal surfaces with an arbitrary curvature, is versatile and permits the realization of spectrally narrow monodirectional or self-focusing light-emitting surfaces.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201700560
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Nanostructured hybrid device mimicking bone extracellular matrix as local and sustained antibiotic delivery system
Borrego-Gonzalez, S; Romero-Sanchez, LB; Blazquez, J; Diaz-Cuenca, AMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 256 (2018) 165-176
Show abstract ▽
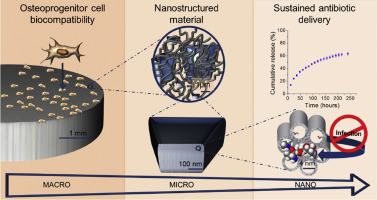
A fluidic permeable and stable in wet media, MBG-NfGel, device consisting of a mesoporous ceramic embodied in a nanofibrillar biodegradable polymer has been processed using appropriate thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processing variables of 5.4% (wt/v) gelatin in 50/50 water/ethanol (v/v) ratio. The device comprises high surface area mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) microparticles within a fibrous matrix of 170 nm average diameter nanofibers gelatin, forming a meshwork of 0.2-1.6 mu m range voids. Gentamicin sulphate (GS) antibiotic high loading capacity and sustained release ability, as well as in vitro bioactivity and osteoprogenitor cells biocompatibility supports long-term antibacterial and bone growth stimulation properties. Antibiotic local delivery functionality in vitro of this device has been analysed and discussed in relation to other systems previously reported. The presented device properties as well as its industrial scalability potential, in terms of process reliability and absence of toxic chemical agents, low raw material biopolymer cost and immunogenicity, are other important advantages. These advantages rank MBG-NfGel device as a potential candidate to further development for application as local antibiotic device in bone surgery and therapy.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.08.010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Phase-Contact Engineering in Mono- and Bimetallic Cu-Ni Co-catalysts for Hydrogen Photocatalytic Materials
Munoz-Batista, MJ; Meira, DM; Colon, G; Kubacka, A; Fernandez-Garcia, MAngewandte Chemie-International Edition, 57 (2018) 1199-1203
Show abstract ▽
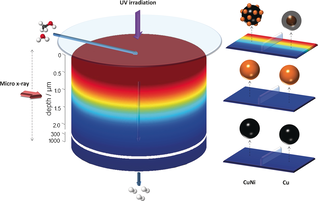
Understanding how a photocatalyst modulates its oxidation state, size, and structure during a photocatalytic reaction under operando conditions is strongly limited by the mismatch between (catalyst) volume sampled by light and, to date, the physicochemical techniques and probes employed to study them. A synchrotron micro-beam X-ray absorption spectroscopy study together with the computational simulation and analysis (at the X-ray cell) of the light-matter interaction occurring in powdered TiO2-based monometallic Cu, Ni and bimetallic CuNi catalysts for hydrogen production from renewables was carried out. The combined information unveils an unexpected key catalytic role involving the phase contact between the reduced and oxidized non-noble metal phases in all catalysts and, additionally, reveals the source of the synergistic Cu-Ni interaction in the bimetallic material. The experimental method is applicable to operando studies of a wide variety of photocatalytic materials.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1002/anie.201709552
Reactividad de Sólidos
The dizinc bond as a ligand: A computational study of elongated dizinc bonds
Ayala, R; Carmona, E; Galindo, AInorganic Chimica Acta, 470 (2018) 197-205
Show abstract ▽
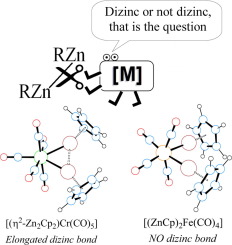
Following the synthesis of [Zn-2(eta(2)-C5Me5)(2)] (in short [Zn2Cp*(2)]) many complexes of the directly bonded Zn-Zn unit were prepared and characterized, leading to the recognition of an isolobal analogy between the Zn-Zn bond and the molecule of dihydrogen. Prompted by these results, we have investigated eta(2)-eta(2)-coordination of [Zn2Cp2] and [Zn2Ph2] (Cp = C5H5, Ph = C6H5) to several selected transition metal fragments and report herein the results of a QTAIM study of complexes [(ZnR)(2)Fe(CO)(4)], [(eta(2)-Zn2R2)M(CO)(5)]] and [(eta(2)-Zn2R2)Pd(PR'(3))(2)] (for R = Cp, Ph; M = Cr, Mo, W; and R' = F, H, Me). A decrease of rho(BCP), Delta(2) rho(BCP) and delocalization indexes delta(Zn, Zn), relative to corresponding values in the parent molecules of [Zn2Cp2] and [Zn2Ph2], accompanied dizinc coordination. In most cases the computed d(Zn, Zn) parameters were indicative of significant electron density sharing between the two Zn atoms. Nevertheless, the interaction with [Fe(CO)(4)] resulted in oxidative cleavage of the coordinated Zn-Zn bond, due to high pi backdonation to the sigma* Zn-2 MO as deduced from the delta(M, O-CO) index. The Zn-Zn bond critical points identified in our study are discussed. The computed Zn-Zn contacts concentrate in the range 2.44-2.58 angstrom, and we propose that this interval corresponds to elongated dizinc bonds.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2017.06.008
Reactividad de Sólidos
Low-cost Ca-based composites synthesized by biotemplate method for thermochemical energy storage of concentrated solar power
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Valverde, JM; Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maquecla, LAApplied Energy, 210 (2018) 108-116
Show abstract ▽
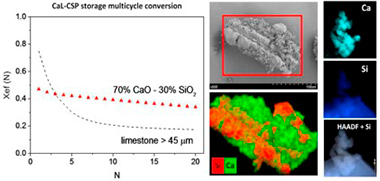
An ever more environmentally conscious society demands the use of green, sustainable and high-efficiency renewable energy resources. However, large-scale energy storage remains a challenge for a deep penetration of power produced from renewables into the grid. The Calcium-Looping (CaL) process, based on the reversible carbonation/calcination of CaO, is a promising technology for thermochemical energy storage (TCES) in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants. Natural limestone to be used as CaO precursor is cheap, non-toxic and abundant. Nevertheless, recent works have shown that carbonation of CaO derived limestone at optimum conditions for TCES is limited by pore-plugging, which leads to severe deactivation for large enough particles to be employed in practice. In our work, we have synthesized inexpensive CaO/SiO2 composites by means of a biotemplate method using rice husk as support. The morphological and compositional features of the biomorphic materials synthesized help improve the CaO multicycle activity under optimum CSP storage conditions and for particles sufficiently large to be managed in practical processes.
Enero, 2018 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.109
- ‹ anterior
- 176 of 420
- siguiente ›














