Artículos SCI
2017
2017
Reactividad de Sólidos
Defect chemistry and electrical properties of BiFeO3
Schrade, M; Maso, N; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; West, ARJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 5 (2017) 10077-10086
Show abstract ▽
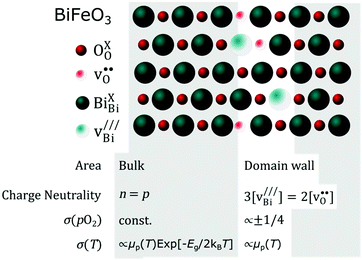
BiFeO3 attracts considerable attention for its rich functional properties, including room temperature coexistence of magnetic order and ferroelectricity and more recently, the discovery of conduction pathways along ferroelectric domain walls. Here, insights into the defect chemistry and electrical properties of BiFeO3 are obtained by in situ measurements of electrical conductivity, sigma, and Seebeck coefficient, a, of undoped, cation-stoichiometric BiFeO3 and acceptor-doped Bi1-xCaxFeO3-delta ceramics as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure pO(2). Bi1-xCaxFeO3-delta exhibits p-type conduction; the dependencies of s and a on pO(2) show that Ca dopants are compensated mainly by oxygen vacancies. By contrast, undoped BiFeO3 shows a simultaneous increase of s and a with increasing pO(2), indicating intrinsic behavior with electrons and holes as the main defect species in almost equal concentrations. The pO(2)-dependency of s and a cannot be described by a single point defect model but instead, is quantitatively described by a combination of intrinsic and acceptor-doped characteristics attributable to parallel conduction pathways through undoped grains and defect-containing domain walls; both contribute to the total charge transport in BiFeO3. Based on this model, we discuss the charge transport mechanism and carrier mobilities of BiFeO3 and show that several previous experimental findings can readily be explained within the proposed model.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1039/c7tc03345a
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Incorporation of Calcium Containing Mesoporous (MCM-41-Type) Particles in Electrospun PCL Fibers by Using Benign Solvents
Liverani, L.;Boccardi, E.; Beltrán, A.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.Polymers, 9 (2017) 487
Show abstract ▽
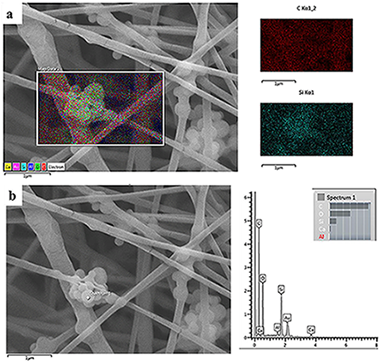
The electrospinning technique is a versatile method for the production of fibrous scaffolds able to resemble the morphology of the native extra cellular matrix. In the present paper, electrospinning is used to fabricate novel SiO2particles (type MCM-41) containing poly(epsilon-caprolactone) (PCL) fibers. The main aims of the present work are both the optimization of the particle synthesis and the fabrication of composite fibers, obtained using benign solvents, suitable as drug delivery systems and scaffolds for soft tissue engineering applications. The optimized synthesis and characterization of calcium-containing MCM-41 particles are reported. Homogeneous bead-free composite electrospun mats were obtained by using acetic acid and formic acid as solvents; neat PCL electrospun mats were used as control. Initially, an optimization of the electrospinning environmental parameters, like relative humidity, was performed. The obtained composite nanofibers were characterized from the morphological, chemical and mechanical points of view, the acellular bioactivity of the composite nanofibers was also investigated. Positive results were obtained in terms of mesoporous particle incorporation in the fibers and no significant differences in terms of average fiber diameter were detected between the neat and composite electrospun fibers. Even if the Ca-containing MCM-41 particles are bioactive, this property is not preserved in the composite fibers. In fact, during the bioactivity assessment, the particles were released confirming the potential application of the composite fibers as a drug delivery system. Preliminary in vitro tests with bone marrow stromal cells were performed to investigate cell adhesion on the fabricated composite mats, the positive obtained results confirmed the suitability of the composite fibers as scaffolds for soft tissue engineering.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.3390/polym9100487
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cellulose-polyhydroxylated fatty acid ester-based bioplastics with tuning properties: Acylation via a mixed anhydride system
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Goldoni, L; Benitez, JJ; Davis, A; Ceseracciu, L; Cingolani, R; Bayer, IS; Heinze, T; Koschella, A; Heredia, A; Athanassiou, ACarbohydrate Polymers, 173 (2017) 312-320
Show abstract ▽
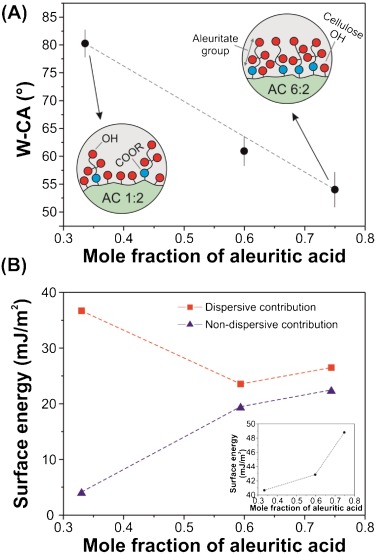
The synthesis of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and 9,10,16-hydroxyhexadecanoic (aleuritic) acid ester-based bioplastics was investigated through acylation in a mixed anhydride (trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/trifluoroacetic acid anhydride (TFAA)), chloroform co-solvent system. The effects of chemical interactions and the molar ratio of aleuritic acid to the anhydroglucose unit (AGU) of cellulose were investigated. The degree of substitution (DS) of new polymers were characterized by two-dimensional solution-state NMR and ranged from 0.51 to 2.60. The chemical analysis by attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) confirmed the presence of aleuritate groups in the structure induces the formation of new H-bond networks. The tensile analysis and the contact angle measurement confirmed the ductile behavior and the hydrophobicity of the prepared bioplastics. By increasing the aleuritate amounts, the glass transition temperature decreased and the solubility of bioplastic films in most common solvents was improved. Furthermore, this new polymer exhibits similar properties compared to commercial cellulose derivatives.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.068
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis and characterization of Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO-PrOx reaction
Martinez, TLM; Laguna, OH; Lopez-Cartes, C; Centeno, MAMolecular Catalysis, 440 (2017) 9-18
Show abstract ▽
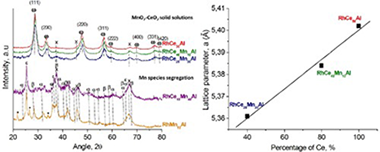
Rh/MnO2-CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts with different manganese-to-ceria ratios have been synthesized, characterized and tested in CO-PrOx reaction. The physicochemical properties of the solids were studied by XRD, Raman spectroscopy, BET surface area, H-2-TPR, TGA-DTG and TEM. The differences observed in the textural, structural and redox properties were related to the Mn-to-ceria ratio of the samples. The segregation of Mn species was observed at high Mn-to-Ce ratios. In opposite way, MnO2-CeO2 solid solutions were obtained at low Mn to Ce ones. In this last case, the physicochemical properties of the solids were favored by the intimate Rh-Ce-Mn contact. The effect of the Mn-Ce presence on Rh catalysts which promotes the catalytic behavior towards selective CO oxidation was observed to be better at low temperatures. At higher temperatures, Mn species promote the Reverse Water Gas Shift reaction, whilst ceria promotes the H-2 oxidation in the whole range of working temperatures.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.06.018
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Towards Extending Solar Cell Lifetimes: Addition of a Fluorous Cation to Triple Cation-Based Perovskite Films
Salado, M; Fernandez, MA; Holgado, JP; Kazim, S; Nazeeruddin, MK; Dyson, PJ; Ahmad, SChemsuschem, 10 (2017) 3846-3853
Show abstract ▽
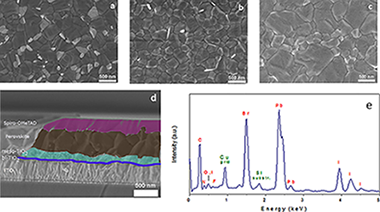
Organohalide perovskites have emerged as highly promising replacements for thin-film solar cells. However, their poor stability under ambient conditions remains problematic, hindering commercial exploitation. The addition of a fluorous-functionalized imidazolium cation during the preparation of a highly stable cesium-based mixed perovskite material Cs-0.05(MA(0.15)FA(0.85))(0.95)Pb(I0.85Br0.15)(3) (MA= methylammonium; FA= formamidinium) has been shown to influence its stability. The resulting materials, which vary according to the amount of the fluorous-functionalized imidazolium cation present during fabrication, display a prolonged tolerance to atmospheric humidity (> 100 days) along with power conversion efficiencies exceeding 16%. This work provides a general route that can be implemented in a variety of perovskites and highlights a promising way to increase perovskite solar cell stability.
Octubre, 2017 | DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201700797
- ‹ anterior
- 184 of 420
- siguiente ›














