Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Growth of carbonaceous nanomaterials over stainless steel foams. Effect of activation temperature
Latorre, N; Cazana, F; Sebastian, V; Royo, C; Romeo, E; Centeno, MA; Monzon, ACatalysis Today, 273 (2016) 41-49
Show abstract ▽
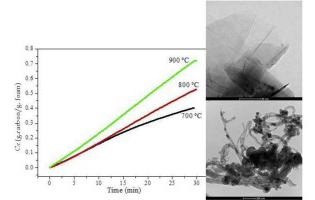
Some of the problems that occur during the operation of chemical reactors based of structured catalytic substrates, as monoliths, foams, membranes, cloths, fibres and other systems, are related to the preparation of long term stable coatings. Frequently, the deposition of the catalytic layer is carried out by washcoating, requiring this step a cautious attention, especially in the case of complex geometries, like of that of foams or cloths. In the case of the deposition of layers of carbonaceous materials (CNMs), an alternative route, avoiding the washcoating, it is their direct growth by catalytic decomposition light hydrocarbons (also called CCVD), over the surface of the metallic substrate. In this case, if the metallic substrate is of stainless steel, it already contains the catalytic active phases like Fe and Ni.
In order to optimize the process of CNMs growth over structured metallic substrates, we are studying the effect of the main operational variables of the ethane decomposition reaction on stainless steel foams. In this contribution we present a study of the influence of the temperature of the activation (oxidation and reduction) stage on the type and morphology of the carbonaceous materials formed. The results obtained allow us to determine the optimal operating conditions to maximize the amount and the selectivity of the process to obtain a given type of CNM.
Septiembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.02.063
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Impact of structured catalysts in amine oxidation under mild conditions
J.L. Santos; P. Navarro; J.A. Odriozola; M.A. Centeno; O.D. Pavel; B. Jurca; V.I. PàrvulescuCatalysis Today, 273 (2016) 266-272
Show abstract ▽
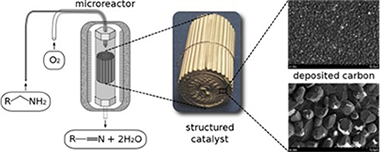
A structured graphene/graphite catalyst grown on a commercial austenitic stainless steel sheet providing a micromonolith was obtained by submitting the nude stainless steel structure to a carbon-rich atmosphere (first 300 mL/min of a reductive H-2/N-2 (1:1) flow, then to 180 mL/min of a CH4/H-2 (1:5)) at high temperature (900 degrees C) for 2 h. The preparation procedure resulted in a homogenous surface coated with a carbon-rich film as observed by EDX and SEM images. Further characterizations by Raman spectroscopy revealed characteristic Raman lines of graphene and crystalline graphite disposed in a hierarchical organization. The disposal of the obtained surface layers was also confirmed by grazing incidence X-ray diffraction. Besides this, XRD indicated the overlapping diffraction lines of graphite, cementite and M7C3 carbides. The graphene nature of the outermost layer was also confirmed by XPS. The catalytic behavior of the structured graphene/graphite catalyst was evaluated in the selective oxidation of heptylamine. At 200 degrees C it afforded a total conversion with a combined selectivity in heptanonitrile and N-heptylidene-heptylamine of 67% (10% heptanonitrile) that corresponds indeed to a very efficient system in the absence of any metal. Kinetic experiments with the scope to calculate the activation energies were also performed.
Septiembre, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.05.001
Materiales Coloidales
Luminescent Rare-earth-based Nanoparticles: A Summarized Overview of their Synthesis, Functionalization, and Applications
Escudero, A; Carrillo-Carrion, C; Zyuzin, MV; Parak, WJTopics in current chemistry, 374 (2016) Article number 48
Show abstract ▽
Rare-earth-based nanoparticles are currently attracting wide research interest in material science, physics, chemistry, medicine, and biology due to their optical properties, their stability, and novel applications. We present in this review a summarized overview of the general and recent developments in their synthesis and functionalization. Their luminescent properties are also discussed, including the latest advances in the enhancement of their emission luminescence. Some of their more relevant and novel biomedical, analytical, and optoelectronic applications are also commented on.
Agosto, 2016 | DOI: 10.1007/s41061-016-0049-8
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Optical analysis of CH3NH3SnxPb1−xI3 absorbers: a roadmap for perovskite-on-perovskite tandem solar cells
Anaya, M.; Correa-Baena, J.P.; Lozano, G.; Saliba, M.; Anguita, P.; Roose, B.; Abate, A.; Steiner, U.; Gratzel, M.; Calvo, M.E.; Hagfeldt, A.; Míguez, H.Journal lf Materials Chemistry A, 4 (2016) 11214-11221
Show abstract ▽
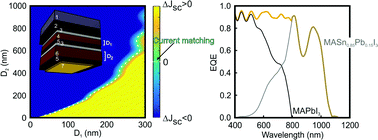
Organic–inorganic perovskite structures in which lead is substituted by tin are exceptional candidates for broadband light absorption. Herein we present a thorough analysis of the optical properties of CH3NH3SnxPb1−xI3 films, providing the field with definitive insights about the possibilities of these materials for perovskite solar cells of superior efficiency. We report a user's guide based on the first set of optical constants obtained for a series of tin/lead perovskite films, which was only possible to measure due to the preparation of optical quality thin layers. According to the Shockley–Queisser theory, CH3NH3xPb1−xI3 compounds promise a substantial enhancement of both short circuit photocurrent and power conversion efficiency in single junction solar cells. Moreover, we propose a novel tandem architecture design in which both top and bottom cells are made of perovskite absorbers. Our calculations indicate that such perovskite-on-perovskite tandem devices could reach efficiencies over 35%. Our analysis serves to establish the first roadmap for this type of cells based on actual optical characterization data. We foresee that this study will encourage the research on novel near-infrared perovskite materials for photovoltaic applications, which may have implications in the rapidly emerging field of tandem devices.
Agosto, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/C6TA04840D
Reactividad de Sólidos
Assessment of the performance of commonly used DFT functionals vs. MP2 in the study of IL-Water, IL-Ethanol and IL-(H2O)(3) clusters
López-López, A., Ayala, R.Journal of Molecular Liquids, 220 (2016)
Show abstract ▽
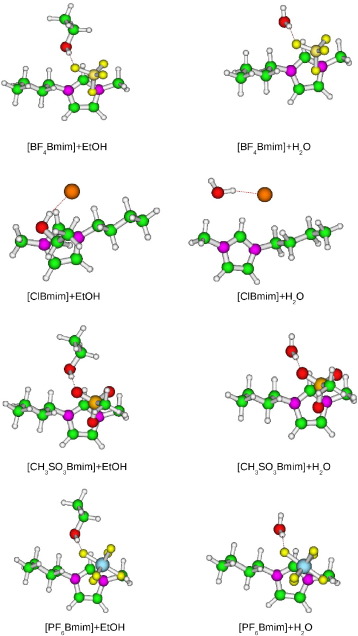
We present a comparative study of the accuracy of different DFT approaches vs. MP2 for evaluating ionic liquids (ILs) + cosolvent. Namely, we are interested in [XBmim] + cosolvent (X being Cl-, BF4-, PF6-, and CH3SO3- anions and cosolvent being water or ethanol) and [XBmim] + (H2O)(3) clusters. In this study the B3LYP, B3LYP-D3, M06, M06-2X and M06-HF functionals with Pople and Dunning basis sets are considered. We find that the influence of the basis sets is a factor to take into consideration. As already seen for weakly bonded systems when the basis set quality is low the uncorrected counterpoise (unCP) or averaging counterpoise (averCP) energies must be used due to cancellation errors. Besides, the inclusion of extra diffuse functions and polarization is also required specially in the case of ILs interacting with water clusters. The B3LYP functional does not reproduce either the structure or the interaction energies for ILs + H2O and ILs + EtOH aggregates, the energetic discrepancies being more significant than the structural ones. Among the dispersive corrected functionals, M06-2X results resemble to a great extent the reference data when the unCP interaction energies are considered for both water and ethanol. In turn, M06 and B3LYP-D3 functionals are the best option for ILs containing polar and non-polar anions, respectively, whether the averCP interactions energies are taking into consideration. From the structural point of view, B3LYP and M06 functionals describe more open structures whereas B3LYP-D3, M06-2X and M06-HF structures resemble quite well MP2 results. When the number of water molecules increases the H bonding motif gains importance and the effect depends on the underlying functional. Only M06-2X and M06-HF behaviour is similar to that observed for one water molecule. This is important because to describe ILs-cosolvent solutions is not only necessary to take into account the ILs-cosolvent interactions but also the cosolvent-cosolvent ones in the ensemble of the system.
Agosto, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.05.037
- ‹ anterior
- 215 of 420
- siguiente ›














