Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Strength and microplasticity of biocarbons prepared by carbonization in the presence of a catalyst
Shpeizman, VV; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 58 (2016) 703-710
Show abstract ▽
The microdeformation has been investigated under uniaxial compression of beech-derived biocarbons partially graphitized during carbonization in the presence of a Ni- or Fe-containing catalyst. The strength and ultimate fracture strain have been determined at different temperatures of carbonization of the samples in the absence or in the presence of a catalyst. It has been shown using high-precision interferometry that the deformation of biocarbon samples under uniaxial loading occurs through jumps (in magnitude and rate of deformation) with axial displacements in the nanometer and micrometer ranges. The use of a catalyst leads to a decrease in the size of nanometer-scale jumps and in the number of micrometer-scale jumps. The standard deviations of the strain rate on loading steps from the smooth average dependence of the strain rate on the displacement have been calculated for micrometer-scale jumps. A similar characteristic for nanometer- scale jumps has been determined from the distortion of the shape of beats in the primary interferogram. It has been shown that the variation in the standard deviation of the strain rate with a change in the carbonization temperature is similar to the corresponding dependence of the ultimate fracture strain.
Abril, 2016 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783416040223
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Pre-prosthetic use of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma and TiO2 nanocomposite particles for guided bone regeneration processes
Castillo-Dali, G; Castillo-Oyague, R; Terriza, A; Saffar, JL; Batista-Cruzado, A; Lynch, CD; Sloan, AJ; Gutierrez-Perez, JL; Torres-Lagares, DJournal of Dentistry, 47 (2016) 71-79
Show abstract ▽
Objectives: Guided bone regeneration (GBR) processes are frequently necessary to achieve appropriate substrates before the restoration of edentulous areas. This study aimed to evaluate the bone regeneration reliability of a new poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) membrane after treatment with oxygen plasma (PO2) and titanium dioxide (TiO2) composite nanoparticles.
Methods: Circumferential bone defects (diameter: 10 mm; depth: 3 mm) were created on the parietal bones of eight experimentation rabbits and were randomly covered with control membranes (Group 1: PLGA) or experimental membranes (Group 2: PLGA/PO2/TiO2). The animals were euthanized two months afterwards, and a morphologic study was then performed under microscope using ROI (region of interest) colour analysis. Percentage of new bone formation, length of mineralised bone formed in the grown defects, concentration of osteoclasts, and intensity of osteosynthetic activity were assessed. Comparisons among the groups and with the original bone tissue were made using the Kruskal-Wallis test. The level of significance was set in advance at a = 0.05.
Results: The experimental group recorded higher values for new bone formation, mineralised bone length, and osteoclast concentration; this group also registered the highest osteosynthetic activity. Bone layers in advanced formation stages and low proportions of immature tissue were observed in the study group.
Abril, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2016.01.015
Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Structure, electrochemical properties and functionalization of amorphous CN films deposited by femtosecond pulsed laser ablation
Maddi, C; Bourquard, F; Tite, T; Loir, AS; Donnet, C; Garrelie, F; Barnier, V; Wolski, K; Fortgang, P; Zehani, N; Braiek, M; Lagarde, F; Chaix, C; Jaffrezic-Renault, N; Rojas, TC; Sanchez-Lopez, JCDiamond and Related Materials,65 (2016) 17-25
Show abstract ▽
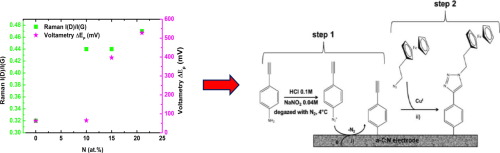
Amorphous carbon nitride (a-C:N) material has attracted much attention in research and development Recently, it has become a more promising electrode material than conventional carbon based electrodes in electrochemical and biosensor applications. Nitrogen containing amorphous carbon (a-C:N) thin films have been synthesized by femtosecond pulsed laser deposition (fs-PLD) coupled with plasma assistance through Direct Current (DC) bias power supply. During the deposition process, various nitrogen pressures (0 to 10 Pa) and DC bias (0 to -350 V) were used in order to explore a wide range of nitrogen content into the films. The structure and chemical composition of the films have been studied by using Raman spectroscopy, electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Increasing the nitrogen pressure or adding a DC bias induced an increase of the N content, up to 21 at%. Nitrogen content increase induces a higher sp(2) character of the film. However DC bias has been found to increase the film structural disorder, which was detrimental to the electrochemical properties. Indeed the electrochemical measurements, investigated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), demonstrated that a-C:N film with moderate nitrogen content (10 at.%) exhibited the best behavior, in terms of reversibility and electron transfer kinetics. Electrochemical grafting from diazonium salts was successfully achieved on this film, with a surface coverage of covalently bonded molecules close to the dense packed monolayer of ferrocene molecules. Such a film may be a promising electrode material in electrochemical detection of electroactive pollutants on bare film, and of biopathogen molecules after surface grafting of the specific affinity receptor.
Abril, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.01.001
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Light management: porous 1-dimensional nanocolumnar structures as effective photonic crystals for perovskite solar cells
Ramos, FJ; Oliva-Ramirez, M; Nazeeruddin, MK; Graetzel, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 4 (2016) 4962-4970
Show abstract ▽
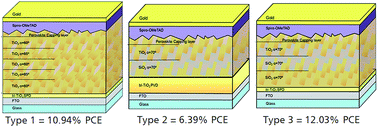
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite solar cells are a topic of increasing interest, as in a short time span they are able to lead in the third generation photovoltaics. Organohalide perovskites possess exceptional optoelectronic and physical properties, thus making their implementation possible in many diverse configurations of photovoltaic devices. In this work, we present three different configurations of porous 1-dimensional photonic crystals (1-DPCs) based on alternated nanocolumnar layers of oxides with different refractive indices (n) that were deposited by Physical Vapor Deposition at Oblique Angle Deposition (PVD-OAD). They are then implemented as the photoanode in CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells to improve the management of light into the device. These configurations improved the performance of the photovoltaic system by designing a light interference structure capable of enhancing the absorption capability of the perovskite. A device fabricated using these photonic crystal structures presented an efficiency >12% in contrast with only 10.22% for a reference device based on non-photonic crystal TiO2 layers deposited under analogous conditions.
Abril, 2016 | DOI: 10.1039/c5ta08743k
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Effect of temperature variations on equilibrium distances in levitating parallel dielectric plates interacting through Casimir forces
Esteso, V; Carretero-Palacios, S; Miguez, HJournal of Applied Physics, 119 (2016) 144301
Show abstract ▽
We study at thermal equilibrium the effect of temperature deviations around room temperature on the equilibrium distance (d(eq)) at which thin films made of Teflon, silica, or polystyrene immersed in glycerol levitate over a silicon substrate due to the balance of Casimir, gravity, and buoyancy forces. We find that the equilibrium nature (stable or unstable) of d(eq) is preserved under temperature changes, and provide simple rules to predict whether the new equilibrium position will occur closer to or further from the substrate at the new temperature. These rules depend on the static permittivities of all materials comprised in the system (epsilon((m))(0)) and the equilibrium nature of d(eq). Our designed dielectric configuration is excellent for experimental observation of thermal effects on the Casimir force indirectly detected through the tunable equilibrium distances (with slab thickness and material properties) in levitation mode.
Abril, 2016 | DOI: 10.1063/1.4945428
- ‹ anterior
- 226 of 420
- siguiente ›














