Artículos SCI
2016
2016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Active metal brazing of silicon nitride ceramics using a Cu-based alloy and refractory metal interlayers
Fernandez, JM; Asthana, R; Singh, M; Valera, FMCeramics International, 42 (2016) 5447-5454
Show abstract ▽
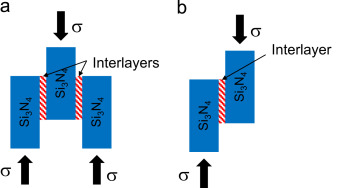
Silicon nitride/silicon nitride joints with refractory metal (W and Mo) interlayers were vacuum brazed using an active braze, Cu-ABA (Cu-3Si-2Al-2.25Ti, wt%), and two interlayer arrangements in a double-lap offset configuration: Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 and Si3N4/Cu-ABA /Si3N4. Titanium segregated at the Si3N4/Cu-ABA and Mo/Cu-ABA interfaces, but not at the W/Cu-ABA interface. The room-temperature compression-shear strength values of Si3N4/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 and Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints were 118 +/- 24 MPa and 22 +/- 5 MPa, respectively. Elevated-temperature compression tests showed that Si3N4/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints had strength of 31 +/- 6 MPa at 1023 K and 17 +/- 3 MPa at 1073 K. Likewise, Si3N4/Cu-ABA/W/Cu-ABA/Mo/Cu-ABA/Si3N4 joints had strength of 19 +/- 4 MPa at 1023 K and 13 +/- 3 MPa at 1073 K. Knoop microhardness profiles revealed hardness gradients across the joints. The effect of joint microstructure and test configuration on the mechanical behavior is discussed.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.12.087
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
TiO2-clay based nanoarchitectures for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production
Perez-Carvajal, J; Aranda, P; Obregon, S; Colon, G; Ruiz-Hitzky, EMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 222 (2016) 120-127
Show abstract ▽
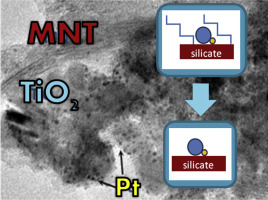
New functional TiO2-clay nanoarchitectures based on layered and fibrous silicates and incorporating Pd and Pt noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) have been synthesized by applying a sol–gel methodology that involves the use of commercial organoclays. The incorporation of the noble metal NPs can be done using two different approaches: i) direct addition to the synthesis medium of a noble metal precursor (typically acetylacetonate) during the generation of the nanoarchitecture, and ii) selective photodeposition of the noble metal NPs in a post-treatment of the TiO2-clay nanoarchitecture. The resulting materials have been characterized by means of XRD, FTIR, Raman, 29Si-NMR, FE-SEM, TEM and N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms. The efficiency of these nanoarchitectures in the photocatalytic hydrogen production has been tested in the photoreforming of methanol. The higher rate in the hydrogen production corresponds to the nanoarchitectures containing Pt and TiO2 NPs derived from sepiolite.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.10.007
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Reactividad de Sólidos
Intensification of hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming
Sanz, O; Velasco, I; Perez-Miqueo, I; Poyato, R; Odriozola, JA; Montes, MInternational Journal Hydrogen Energy, 41 (2016) 5250-5259
Show abstract ▽
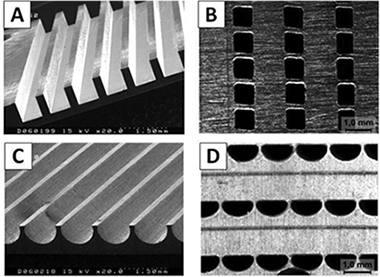
This paper studies the methanol steam reforming intensification to enhance the hydrogen production in a multi-channel block type micro-reformer. The effects of operating parameters such as reforming temperature, space velocity and catalyst layer thickness on reforming performance are investigated. For optimized design and operating conditions, the 8 cm(3) reformer unit produced 170 LH2/h containing on dry basis 75.0% H-2, 23.5% CO2, 0.06% CH3OH and 1.44% CO at 648 K allowing the production of 218-255 Win a commercial PEMFC with 80% hydrogen utilization. This study shows that high methanol conversion can be achieved with high Pd/ZnO catalyst loading at 648 K with very low CO content (<1.5%) in the outlet stream.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.01.084
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Characterization and application of a new pH sensor based on magnetron sputtered porous WO3 thin films deposited at oblique angles
Salazar, P; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Yubero, F; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARElectrochimica Acta, 193 (2016) 24-31
Show abstract ▽
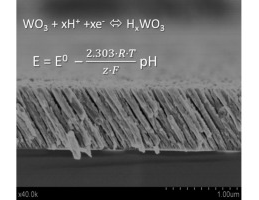
In this communication we report about an outstanding solid-state pH sensor based on amorphous nanocolumnar porous thin film electrodes. Transparent WO3 thin films were deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering in an oblique angle configuration to enhance their porosity onto indium tin oxide (ITO) and screen printed electrodes (SPE). The potentiometric pH response of the nanoporous WO3-modified ITO electrode revealed a quasi-Nernstian behaviour, i.e. a linear working range from pH 1 to 12 with a slope of about -57.7 mV/pH. pH detection with this electrode was quite reproducible, displayed excellent anti-interference properties and a high stable response that remained unaltered over at least 3 months. Finally, a pH sensor was developed using nanoporous WO3-modified screen printed electrode (SPE) using a polypyrrole-modified Ag/AgCl electrode as internal reference electrode. This full solid state pH sensor presented a Nernstian behaviour with a slope of about -59 mV/pH and offered important analytical and operation advantages for decentralized pH measurements in different applications.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.02.040
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
High-Throughput Fabrication of Resonant Metamaterials with Ultrasmall Coaxial Apertures via Atomic Layer Lithography
Yoo, D; Nguyen, NC; Martin-Moreno, L; Mohr, DA; Carretero-Palacios, S; Shaver, J; Peraire, J; Ebbesen, TW; Oh, SHNano Letters, 16 (2016) 2040-2046
Show abstract ▽
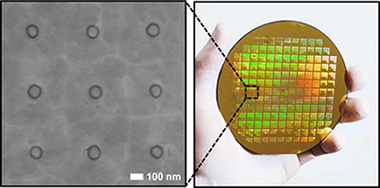
We combine atomic layer lithography and glancing angle ion polishing to create wafer-scale metamaterials composed of dense arrays of ultrasmall coaxial nanocavities in gold films. This new fabrication scheme makes it possible to shrink the diameter and increase the packing density of 2 nm-gap coaxial resonators, an extreme subwavelength structure first manufactured via atomic layer lithography, both by a factor of 100 with respect to previous studies. We demonstrate that the nonpropagating zeroth-order Fabry-Perot mode, which possesses slow light-like properties at the cutoff resonance, traps infrared light inside 2 nm gaps (gap volume similar to lambda(3)/10(6)). Notably, the annular gaps cover only 3% or less of the metal surface, while open-area normalized transmission is as high as 1700% at the epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) condition. The resulting energy accumulation alongside extraordinary optical transmission can benefit applications in nonlinear optics, optical trapping, and surface-enhanced spectroscopies. Furthermore, because the resonance wavelength is independent of the cavity length and dramatically red shifts as the gap size is reduced, large-area arrays can be constructed with lambda(resonance) >> period, making this fabrication method ideal for manufacturing resonant metamaterials.
Marzo, 2016 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00024
- ‹ anterior
- 228 of 420
- siguiente ›














