Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ionic liquid immobilization on carbon nanofibers and zeolites: Catalyst design for the liquid-phase toluene chlorination
Losch, Pit; Martinez Pascual, Antonio; Boltz, Marilyne; Ivanova, Svetlana; Louis, Benoit; Montilla, Francisco; Antonio Odriozola, JoseComptes Rendus Chimie, 18 (2015) 324-329 DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2014.06.006
Abstract
The environmental-friendly chlorination reaction of toluene by trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA, C3N3O3Cl3) was investigated applying immobilized ionic liquids (ILs) on different supports. Ionic liquids were grafted either on carbon nanofibers (CNF) or encapsulated in zeolites. Their influence on the chlorination activity as well as on the selectivity in different chlorinated products was studied. An unusually high selectivity toward meta-chlorotoluene was achieved, up to 36%. Hence, the selectivity could be tuned to produce either expected ortho-/para-chlorotoluene or meta-chlorotoluene with a proper support choice.
Marzo, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2014.06.006
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
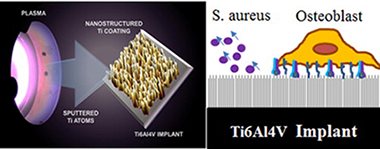
Nanocolumnar coatings with selective behavior towards osteoblast and Staphylococcus aureus proliferation
Izquierdo-Barba, Isabel; Miguel Garcia-Martin, Jose; Alvarez, Rafael; Palmero, Alberto; Esteban, Jaime; Perez-Jorge, Concepcion; Arcos, Daniel; Vallet-Regi, MariaActa Biomaterialia, 15 (2015) 20-28 DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.12.023
Abstract
Bacterial colonization and biofilm formation on orthopedic implants is one of the worst scenarios in orthopedic surgery, in terms of both patient prognosis and healthcare costs. Tailoring the surfaces of implants at the nanoscale to actively promote bone bonding while avoiding bacterial colonization represents an interesting challenge to achieving better clinical outcomes. Herein, a Ti6Al4V alloy of medical grade has been coated with Ti nanostructures employing the glancing angle deposition technique by magnetron sputtering. The resulting surfaces have a high density of nanocolumnar structures, which exhibit strongly impaired bacterial adhesion that inhibits biofilm formation, while osteoblasts exhibit good cell response with similar behavior to the initial substrates. These results are discussed on the basis of a "lotus leaf effect" induced by the surface nanostructures and the different sizes and biological characteristics of osteoblasts and Staphylococcus aureus.
Marzo, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.12.023
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
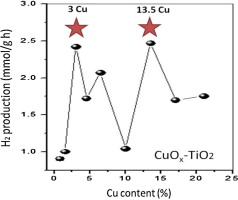
Evolution of H-2 photoproduction with Cu content on CuOx-TiO2 composite catalysts prepared by a microemulsion method
Kubacka, A; Munoz-Batista, MJ; Fernandez-Garcia, M; Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 163 (2015) 214-222 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.08.005
Abstract
Copper oxides in contact with anatase correspond to promising materials with high activity in the photo-production of hydrogen by aqueous reforming of alcohols. By a single pot microemulsion method we obtained a series of Cu-Ti composite systems with controlled copper content in the 0-25 wt.% range. The scanning of such a wide range of composition led to the discovery of two well differentiated maxima in the photo-reaction performance. These maxima present rather high and relatively similar reaction rates and photonic efficiencies but are ascribed to the presence of different copper species. A multi-technique analysis of the materials indicates that the maxima obtained comes from optimizing different steps of the reaction; while the first would be connected with a positive effect on anatase charge handling performance the second seems exclusively related to electron capture by surface copper species.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.08.005
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
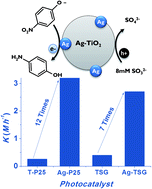
Effective photoreduction of a nitroaromatic environmental endocrine disruptor by AgNPs functionalized on nanocrystalline TiO2
Hernandez-Gordillo, A; Obregon, S; Paraguay-Delgado, F; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, VRSC Advances, 5 (2015) 15194-15197 DOI: 10.1039/c5ra00094g
Abstract
Unprecedented photoactivity of silver nanoparticles photodeposited on nanocrystalline TiO2 for the efficient reduction of 4-nitrophenol at room temperature is reported. The use of Na2SO3 as a harmless scavenger agent for the reduction of a nitroaromatic endocrine disruptor yields a valuable 4-aminophenol reagent.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/c5ra00094g
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Flexible Distributed Bragg Reflectors from Nanocolumnar Templates
Calvo, ME; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Barranco, A; Jimenez-Solano, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 3 (2015) 171-175 DOI: 10.1002/adom.201400338
Abstract
A flexible distributed Bragg reflector is made by the infiltration of a nanocolumnar array with polydimethyl siloxane oligomers. The high optical reflectance displayed by the final material is a direct consequence of the high refractive index contrast of the columnar layers whereas the structural stability is due to the polymer properties.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/adom.201400338
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Photocatalytic activity of bismuth vanadates under UV-A and visible light irradiation: Inactivation of Escherichia coli vs oxidation of methanol
Adan, C; Marugan, J; Obregon, S; Colon, GCatalysis Today, 240 (2015) 93-99 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.059
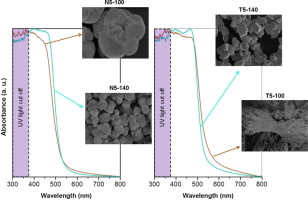
Abstract
Four bismuth vanadates have been synthesized by using two different precipitating agents (NH3 and triethylamine) following a hydrothermal treatment at 100 °C for 2 h and at 140 °C for 20 h. Then, solids were characterized by X-ray diffraction, BET surface area, UV–vis spectroscopy and scanning microscopy techniques. The characterization of the synthesized materials showed a well crystallized scheelite monoclinic structure with different morphologies. All materials display optimum light absorption properties for visible light photocatalytic applications. The photocatalytic activity of the catalysts was investigated for the inactivation of Escherichia coli bacteria and the oxidation of methanol under UV–vis and visible light irradiation sources. Main results demonstrate that BiVO4 are photocatalytically active in the oxidation of methanol and are able to inactivate bacteria below the detection level. The activity of the catalyst decreases when using visible light, especially for methanol oxidation, pointing out differences in the reaction mechanism. In contrast with bacteria, whose interaction with the catalyst is limited to the external surface, methanol molecules can access the whole material surface.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.059
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser Treatment of Ag@ZnO Nanorods as Long-Life-Span SERS Surfaces
Macias-Montero, M; Pelaez, RJ; Rico, VJ; Saghi, Z; Midgley, P; Afonso, CN; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 2331-2339 DOI: 10.1021/am506622x
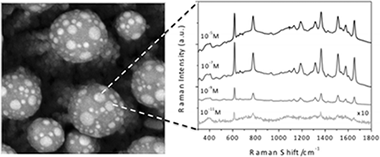
Abstract
UV nanosecond laser pulses have been used to produce a unique surface nanostructuration of Ag@ZnO supported nanorods (NRs). The NRs were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) at low temperature applying a silver layer as promoter. The irradiation of these structures with single nanosecond pulses of an ArF laser produces the melting and reshaping of the end of the NRs that aggregate in the form of bundles terminated by melted ZnO spherical particles. Well-defined silver nanoparticles (NPs), formed by phase separation at the surface of these melted ZnO particles, give rise to a broad plasmonic response consistent with their anisotropic shape. Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) in the as-prepared Ag@ZnO NRs arrays was proved by using a Rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) chromophore as standard analyte. The surface modifications induced by laser treatment improve the stability of this system as SERS substrate while preserving its activity.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/am506622x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Polyester Films Obtained by Noncatalyzed Melt-Condensation Polymerization of Aleuritic (9,10,16-Trihydroxyhexadecanoic) Acid in Air
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, AJournal of Applied Polymer, 132 (2015) Art. 41328 DOI: 10.1002/app.41328
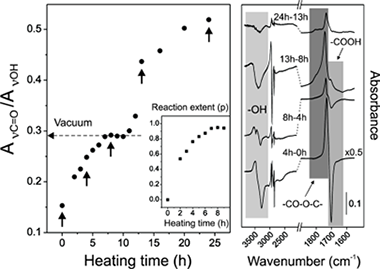
Abstract
To mimic nontoxic and fully biodegradable biopolymers like the plant cutin, polyester films from a natural occurring fatty polyhydroxyacid like aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxyhexadecanoic) acid have been prepared by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation at moderate temperature (150 degrees C) directly in air. The course of the reaction has been followed by infrared spectroscopy, C-13 magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction and well differentiated stages are observed. First, a high conversion esterification reaction leads to an amorphous rubbery, infusible, and insoluble material whose structure is made out of ester linkages mostly involving primary hydroxyls and partially branched by minor esterification with secondary ones. Following the esterification stage, the cleavage of vicinal secondary hydroxyls and further oxidation to carboxylic acid is observed at the near surface region of films. New carboxylic groups created also undergo esterification and generate cross-linking points within the polymer structure. Additionally, and despite the harsh preparation conditions used, very little additional side reaction like peroxidation and dehydration are observed. Results demonstrate the feasibility of polyester films fabrication from a reference fatty polyhydroxyacid like aleuritic acid by noncatalyzed melt-polycondensation directly in air. The methodology can potentially be extended to similar natural occurring hydroxyacids to obtain films and coatings to be used, for instance, as nontoxic and biodegradable food packaging material.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/app.41328
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribocorrosion behavior of TiBxCy/a-C nanocomposite coating in strong oxidant disinfectant solutions
Gracia-Escosa, E; Garcia, I; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Abad, MD; Mariscal, A; Arenas, MA; de Damborenea, J; Conde, ASurface & Coatings Technology, 263 (2015) 78-85 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.12.047
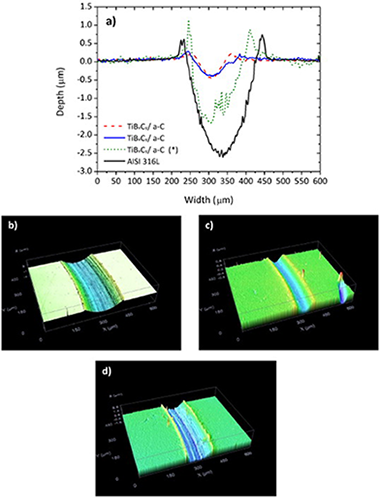
Abstract
Corrosion and tribocorrosion studies of a TiBxCy/a-C coating deposited on AISI 316L steel have been performed in an aqueous solution of 026 vol.% acetic, 0.16 vol.% peracetic and 0.18 vol.% hydrogen peroxide (commercial product Oxonia I vol.%). The corrosion current density of the TiBxCy/a-C coating ranges on the same order as bare steel but with a significantly decreasing friction (0.1 vs. 0.6) and wear rate (similar to 10 times lower). The compact microstructure of the coating hinders the access of the aggressive electrolyte to the substrate, preventing the onset of the corrosion attack, while maintaining an excellent tribological behavior in strong oxidant solutions.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.12.047
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Glycerol steam reforming on bimetallic NiSn/CeO2-MgO-Al2O3 catalysts: Influence of the support, reaction parameters and deactivation/regeneration processes
Bobadilla, LP; Penkova, A; Alvarez, A; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A: General, 492 (2015) 38-47 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.029
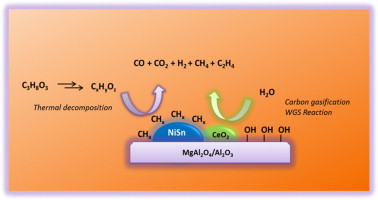
Abstract
NiSn bimetallic catalysts supported over Al2O3 modified with different promoter (Mg and/or Ce) were prepared and characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 sorptometry, and temperature programmed reduction (TPR). Hydrogen production by glycerol steam reforming over these catalysts was investigated. Among the catalysts, NiSn/AlMgCe catalyst shows the highest hydrogen yield as well as the best stability during the reaction. The effect of reaction temperature, water/glycerol molar ratio and space velocity on the glycerol steam reforming over NiSn/AlMgCe were also investigated. Finally, it was verified that the catalyst can be regenerated by oxidation of carbonaceous deposits.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.029
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Water splitting performance of Er3+-doped YVO4 prepared from a layered K3V5O14 precursor
Obregon, S; Colon, GChemical Engineering Journal, 262 (2015) 29-33 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.073
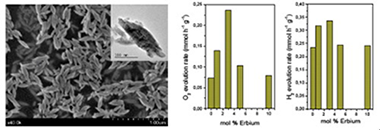
Abstract
Erbium-doped YVO4 have been synthesized by means of a simple solution method having good photo activities under UV-like excitation for the water splitting half reactions. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces the promotion of luminescence. Moreover the incorporation of erbium clearly affects to the morphology YVO4 leading to 200 nm size well-defined spindle-like particles. The improved photocatalytic performance might be associated to a better electron–hole separation mechanism, probably due to the slight increase of band-gap value. The obtained photoactivities for H2 and O2 evolution reactions make this material a promising candidate for water splitting reactions.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.073
Química de Superficies y Catálisis - Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Synthesis and application of layered titanates in the photocatalytic degradation of phenol
Ivanova, S; Penkova, A; Hidalgo, MD; Navio, JA; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 163 (2015) 23-29 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.048
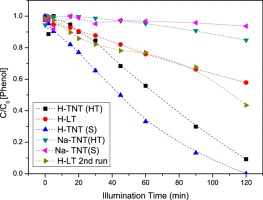
Abstract
This study proposes a direct synthetic route to single titanate sheets through the mild and versatile conditions of the “chimie douce”. The stages of the production include the complexation of the titanium alkoxide precursor by benzoic acid, the formation of titanium oxo-clusters and their controlled transformation into single sheet titanates during the hydrolysis stage. The resulted material appears to be an excellent precursor for self-organized TiO2 nanotubes formation which presents an excellent activity as photocatalyst in the photo-degradation of phenol.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.048
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the Processing Route on the Carbon Nanotubes Dispersion and Creep Resistance of 3YTZP/SWCNTs Nanocomposites
Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Munoz, A; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 98 (2015) 645-653 DOI: 10.1111/jace.13348
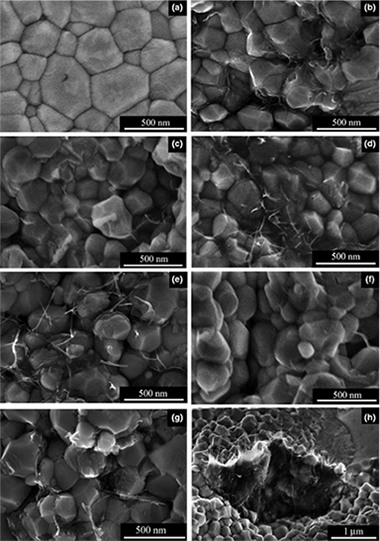
Abstract
3YTZP matrix composites containing 2.5 vol% of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) were fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) at 1250°C, following different processing routines with the aim of optimizing the SWCNTs dispersion throughout the ceramic matrix. Microstructural characterization of the as-fabricated samples has been performed by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The specimens have been crept at 1200°C to correlate creep resistance and SWCNTs distribution. There are no creep experimental results on these nanocomposites reported in literature. Mechanical results show that the incorporation of SWCNTs into a 3YTZP matrix produces an increase in the strain rate at high temperature with respect to monolithic zirconia. The creep resistance of these nanocomposites decreases with the improvement of the SWCNTs dispersion, where a smaller SWCNTs agglomerate size and consequently a higher concentration of carbon nanotubes surrounding the 3YTZP grain boundaries is found. This fact indicates that SWCNTs act as a lubricant making grain-boundary sliding easier during deformation of these composites.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.13348
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
STEM-EELS analysis reveals stable highdensity He in nanopores of amorphous silicon coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering
Schierholz, Roland; Lacroix, Bertrand; Godinho, Vanda; Caballero-Hernandez, Jaime; Duchamp, Martial; Fernandez, AsuncionNanotechnology, 26 (2015) 075703 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/7/075703
Abstract
A broad interest has been showed recently on the study of nanostructuring of thin films and surfaces obtained by low-energy He plasma treatments and He incorporation via magnetron sputtering. In this paper spatially resolved electron energy-loss spectroscopy in a scanning transmission electron microscope is used to locate and characterize the He state in nanoporous amorphous silicon coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering. A dedicated MATLAB program was developed to quantify the helium density inside individual pores based on the energy position shift or peak intensity of the He K-edge. A good agreement was observed between the high density (~35–60 at nm−3) and pressure (0.3–1.0 GPa) values obtained in nanoscale analysis and the values derived from macroscopic measurements (the composition obtained by proton backscattering spectroscopy coupled to the macroscopic porosity estimated from ellipsometry). This work provides new insights into these novel porous coatings, providing evidence of high-density He located inside the pores and validating the methodology applied here to characterize the formation of pores filled with the helium process gas during deposition. A similar stabilization of condensed He bubbles has been previously demonstrated by high-energy He ion implantation in metals and is newly demonstrated here using a widely employed methodology, magnetron sputtering, for achieving coatings with a high density of homogeneously distributed pores and He storage capacities as high as 21 at%.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/7/075703
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Active vacuum brazing of CNT films to metal substrates for superior electron field emission performance
Longtin, R; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Shorubalko, I; Furrer, R; Hack, E; Elsener, H; Groning, O; Greenwood, P; Rupesinghe, N; Teo, K; Leinenbach, C; Groning, PScience and Technology of Advanced Materials, 16 (2015) 015005 (11 pp) DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/16/1/015005
Abstract
The joining of macroscopic films of vertically aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to titanium substrates is demonstrated by active vacuum brazing at 820 degrees C with a Ag-Cu-Ti alloy and at 880 degrees C with a Cu-Sn-Ti-Zr alloy. The brazing methodology was elaborated in order to enable the production of highly electrically and thermally conductive CNT/metal substrate contacts. The interfacial electrical resistances of the joints were measured to be as low as 0.35 Omega. The improved interfacial transport properties in the brazed films lead to superior electron fieldemission properties when compared to the as-grown films. An emission current of 150 mu A was drawn from the brazed nanotubes at an applied electric field of 0.6 V mu m(-1). The improvement in electron field-emission is mainly attributed to the reduction of the contact resistance between the nanotubes and the substrate. The joints have high re-melting temperatures up to the solidus temperatures of the alloys; far greater than what is achievable with standard solders, thus expanding the application potential of CNT films to high-current and high-power applications where substantial frictional or resistive heating is expected.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/16/1/015005
Reactividad de Sólidos
Ca-looping for postcombustion CO2 capture: A comparative analysis on the performances of dolomite and limestone
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAApplied Energy, 138 (2015) 202-215 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.087

Abstract
The low cost and wide availability of natural limestone (CaCO3) is at the basis of the industrial competitiveness of the Ca-looping (CaL) technology for postcombustion CO2 capture as already demonstrated by similar to 1 Mw(t) scale pilot projects. A major focus of studies oriented towards further improving the efficiency of the CaL technology is how to prevent the gradual loss of capture capacity of limestone derived CaO as the number of carbonation/calcination cycles is increased. Natural dolomite (MgCa(CO3)(2)) has been proposed as an alternative sorbent precursor to limestone. Yet, carbonation of MgO is not thermodynamically favorable at CaL conditions, which may hinder the capture performance of dolomite. In the work described in this paper we carried out a thermogravimetric analysis on the multicyclic capture performance of natural dolomite under realistic regeneration conditions necessarily implying high calcination temperature, high CO2 concentration and fast transitions between the carbonation and calcination stages. Our study demonstrates that the sorbent derived from dolomite has a greater capture capacity as compared to limestone. SEM analysis shows that MgO grains in the decomposed dolomite are resistant to sintering under severe calcination conditions and segregate from CaO acting as a thermally stable support which mitigates the multicyclic loss of CaO conversion. Moreover, full decomposition of dolomite is achieved at significantly lower calcination temperatures as compared to limestone, which would help improving further the industrial competitiveness of the technology.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.10.087
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Ultra-fast and energy-efficient sintering of ceramics by electric current concentration
Zapata-Solvas, E; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Todd, RIScientific Reports, 5 (2015) art n. 8513 DOI: 10.1038/srep08513
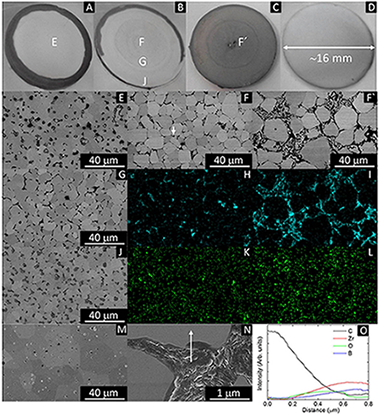
Abstract
Electric current activated/assisted sintering (ECAS) techniques, such as electrical discharge sintering (EDS) or resistive sintering (RS), have been intensively investigated for longer than 50 years. In this work, a novel system including an electrically insulated graphite die for Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is described, which allows the sintering of any refractory ceramic material in less than 1 minute starting from room temperature with heating rates higher than 2000°C/min and an energy consumption up to 100 times lower than with SPS. The system alternates or combines direct resistive sintering (DRS) and indirect resistive sintering (IRS). Electrical insulation of the die has been achieved through the insertion of a film made of alumina fibers between the graphite die and the graphite punches, which are protected from the alumina fiber film by a graphite foil. This system localized the electric current directly through the sample (conductive materials) as in DRS and EDS, or through the thin graphite foil (non-conductive materials) as in IRS, and is the first system capable of being used under EDS or RS conditions independently combining current concentration/localization phenomena.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1038/srep08513
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Structural and chemical reactivity modifications of a cobalt perovskite induced by Sr-substitution. An in situ XAS study
Hueso, JL; Holgado, JP; Pereniguez, R; Gonzalez-DelaCruz, VM; Caballero, AMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 151 (2015) 29-33 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.11.015
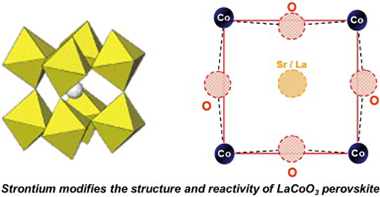
Abstract
LaCoO3 and La0.5Sr0.5O3O3-delta perovskites have been studied by in situ Co K-edge XAS. Although the partial substitution of La(III) by Sr(II) species induces an important increase in the catalytic oxidation activity and modifies the electronic state of the perovskite, no changes could be detected in the oxidation state of cobalt atoms. So, maintaining the electroneutrality of the perovskite requires the generation of oxygen vacancies in the network. The presence of these vacancies explains that the substituted perovskite is now much more reducible than the original LaCoO3 perovskite. As detected by in situ XAS, after a consecutive reduction and oxidation treatment, the original crystalline structure of the LaCoO3 perovskite is maintained, although in a more disordered state, which is not the case for the Sr doped perovskite. So, the La0.5Sr0.5CoO3-delta perovskite submitted to the same hydrogen reduction treatment produces metallic cobalt, while as determined by in situ XAS spectroscopy the subsequent oxidation treatment yields a Co(III) oxide phase with spinel structure. Surprisingly, no Co(II) species are detected in this new spinel phase.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.11.015
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis of a nanosilica supported CO2 sorbent in a fluidized bed reactor
Soria-Hoyo, C; Valverde, JM; van Ommen, JR; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sayagues, MJApplied Surface Science, 328 (2015) 548-553 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.106
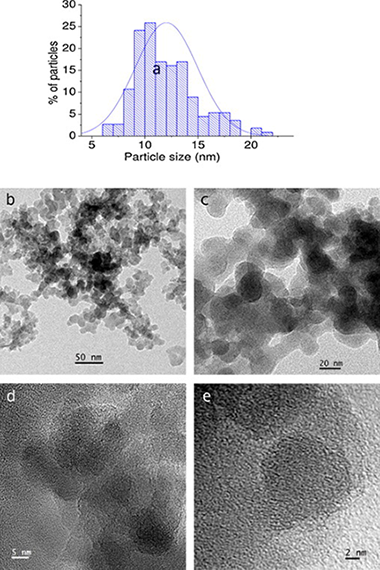
Abstract
CaO has been deposited on a nanosilica powder matrix by a procedure based on atomic layer deposition (ALD) in a fluidized bed reactor at atmospheric pressure following a potentially scalable process. In previous works ALD in gas fluidized bed has been mostly performed under reduced pressure, which hampers scaling-up the production technology. The material synthesized in the present work is tested as CO2 solid sorbent at calcium looping conditions. Multicyclic thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) shows that the nanosilica support stabilizes the capture capacity of CaO. EDX-STEM analysis illustrates the presence of Ca well distributed on the surface of the SiO2 nanoparticles.
Febrero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.106
Materiales Coloidales
Quick synthesis, functionalization and properties of uniform, luminescent LuPO4-based nanoparticles
Becerro, AI; Ocana, MRSC Advances, 44 (2015) 34517-34524 DOI: 10.1039/C5RA05305F
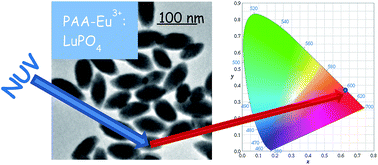
Abstract
The aim of this study was to find a surfactant-free method for the synthesis of uniform Eu:LuPO4nanophosphors which are able to form stable colloidal suspensions in aqueous media. Uniform, ovoid Eu-doped LuPO4 fluorescent nanoparticles were obtained after aging for 30 minutes at 180 °C a butylene glycol solution containing, exclusively, lutetium acetate, europium acetate and H3PO4. XRD and digital diffraction patterns of HRTEM images suggested that the particles were single crystalline in nature with the c-axis of the unit cell parallel to the long particle axis. The luminescence study revealed that the optimum doping level was 5 molar%. The latter particles (85 nm × 40 nm dimensions) were functionalized with polyacrylic acid and their colloidal stability in two different biological buffers was demonstrated to persist for at least 15 days.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1039/C5RA05305F
Materiales Coloidales
Template-free synthesis and luminescent properties of hollow Ln:YOF (Ln = Eu or Er plus Yb) microspheres
Martinez-Castro, E; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cusso, F; Ocana, MJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 619 (2015) 44-51 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.023
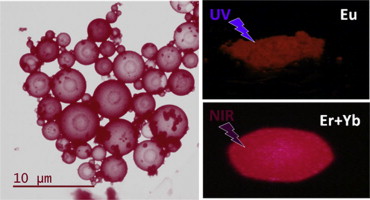
Abstract
A method for the synthesis of hollow lanthanide doped yttrium oxyfluoride (YOF) spheres in the micrometer size range with cubic structure based on the pyrolysis at 600 degrees C of liquid aerosols generated from aqueous solutions containing the corresponding rare earth chlorides and trifluoroacetic acid has been developed. This procedure, which has been used for the first time for the synthesis of YFO based materials, is simpler and advantageous when compared with other methods usually employed for the production of hollow spheres since it does not require the use of sacrificial templates. In addition, it is continuous, which is desirable because of practical reasons. The procedure is also suitable for doping the YOF spheres with europium cations resulting in down converting red phosphors when activated with UV light, or for co-doping with both Er3+ and Yb3+ giving rise to up-converting phosphors, which emit intense red light under near infrared (NIR) irradiation. Because of their optical properties and hollow architecture, the developed materials may find applications in optoelectronic devices and biotechnology.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.023
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Sonogashira Cross-Coupling and Homocoupling on a Silver Surface: Chlorobenzene and Phenylacetylene on Ag(100)
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Orozco, N; Holgado, JP; Beaumont, SK; Kyriakou, G; Watson, DJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Feria, L; Sanz, JF; Lambert, RMJournal of the American Chemical Society, 137 (2015) 940-947 DOI: 10.1021/ja5115584
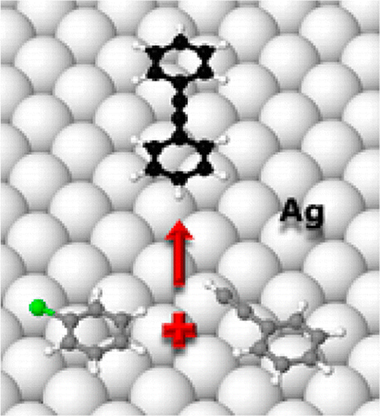
Abstract
Scanning tunneling microscopy, temperature-programmed reaction, near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations were used to study the adsorption and reactions of phenylacetylene and chlorobenzene on Ag(100). In the absence of solvent molecules and additives, these molecules underwent homocoupling and Sonogashira cross-coupling in an unambiguously heterogeneous mode. Of particular interest is the use of silver, previously unexplored, and chlorobenzene—normally regarded as relatively inert in such reactions. Both molecules adopt an essentially flat-lying conformation for which the observed and calculated adsorption energies are in reasonable agreement. Their magnitudes indicate that in both cases adsorption is predominantly due to dispersion forces for which interaction nevertheless leads to chemical activation and reaction. Both adsorbates exhibited pronounced island formation, thought to limit chemical activity under the conditions used and posited to occur at island boundaries, as was indeed observed in the case of phenylacetylene. The implications of these findings for the development of practical catalytic systems are considered.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/ja5115584
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Long-Chain Polyhydroxyesters from Natural Occurring Aleuritic Acid as Potential Material for Food Packaging
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, ASoft Materials, 13 (2015) 5-11 DOI: 10.1080/1539445X.2014.993476
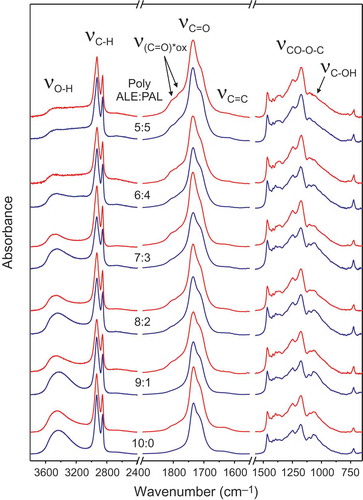
Abstract
Fatty polyhydroxyesters (C≥16) are present in nature as barrier polymers like cutin in some protective tissues of higher plants. The mimicry of these biopolymers is regarded as a strategy to design nontoxic and fully biodegradable food packaging films and coatings. To obtain cutin inspired materials we have used a natural occurring polyhydroxylated monomer like aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid and a direct and scalable synthesis route consisting in the noncatalyzed melt-condensation polymerization in air. To reduce the number of hydroxyl groups and to increase hydrophobicity, palmitic acid has been used as a capping agent. Aleuritic-palmitic polyhydroxyesteres films have been obtained and characterized.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1080/1539445X.2014.993476
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
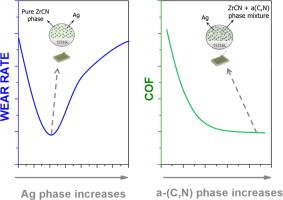
Biotribological behavior of Ag–ZrCxN1−x coatings against UHMWPE for joint prostheses devices
Calderon, SV; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cavaleiro, A; Carvalho, SJournal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 41 (2015) 83-91 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.09.028
Abstract
This study aims to evaluate the structural, mechanical and tribological properties of zirconium carbonitrides (ZrCxN1−x) coatings with embedded silver nanoparticles, produced with the intention of achieving a material with enhanced multi-functional properties, including mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, tribological performance and antibacterial behavior suitable for their use in joint prostheses. The coatings were deposited by direct current (DC) reactive magnetron sputtering onto 316 L stainless steel, changing the silver content from 0 to 20 at% by modifying the current density applied to the targets. Different nitrogen and acetylene gas fluxes were used as reactive gases. The coatings revealed different mixtures of crystalline ZrCxN1−x, silver nanoparticles and amorphous carbon phases. The hardness of the films was found to be mainly controlled by the ratio between the hard (ZrCxN1−x) and soft (Ag and amorphous carbon) phases in the films, fluctuating between 7.4 and 20.4 GPa. The coefficient of friction, measured against ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) in Hank’s balanced salt solution with 10 g L−1albumin, is governed by the surface roughness and hardness. The UHMWPE wear rates were in the same order of magnitude (between 1.4 and 2.0×10−6 mm3 N−1 m−1), justified by the effect of the protective layer of albumin formed during the tests. The small differences were due to the hydrophobic/hydrophilic character of the surface, as well as to the silver content.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.09.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
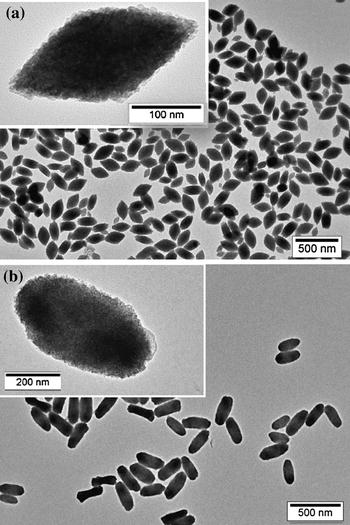
Uniform, luminescent Eu: LuF3 nanoparticles
Becerro, AI; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Ocana, MJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 17 (2015) 58 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-015-2874-z
Abstract
A simple procedure for the synthesis of orthorhombic, uniform, LuF3 particles with two different morphologies (rhombus- and cocoon-like) and nanometer and sub-micrometer size, respectively, is reported. The method consists in the aging, at 120 °C for 2 h, a solution containing [BMIM]BF4 ionic liquid (0.5 mL) and lutetium acetate (in the case of the rhombi) or lutetium nitrate (in the case of the cocoons) (0.02 M) in ethylene glycol (total volume 10 mL). This synthesis method was also adequate for the synthesis of Eu3+-doped LuF3 particles of both morphologies, whose luminescence properties were investigated in detail. The experimental observations reported herein suggest that these materials are suitable phosphors for optoelectronic as well as in vitro biotechnological applications.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1007/s11051-015-2874-z
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Effect of magnesium and titanium on the cathodic behaviour of aluminium in nitric acid
Garcia-Garcia, FJ, Chiu, TY, Skeldon, P, Thompson, GESurface and Interface Analysis, 47 (2015) 30-36 DOI: 10.1002/sia.5640
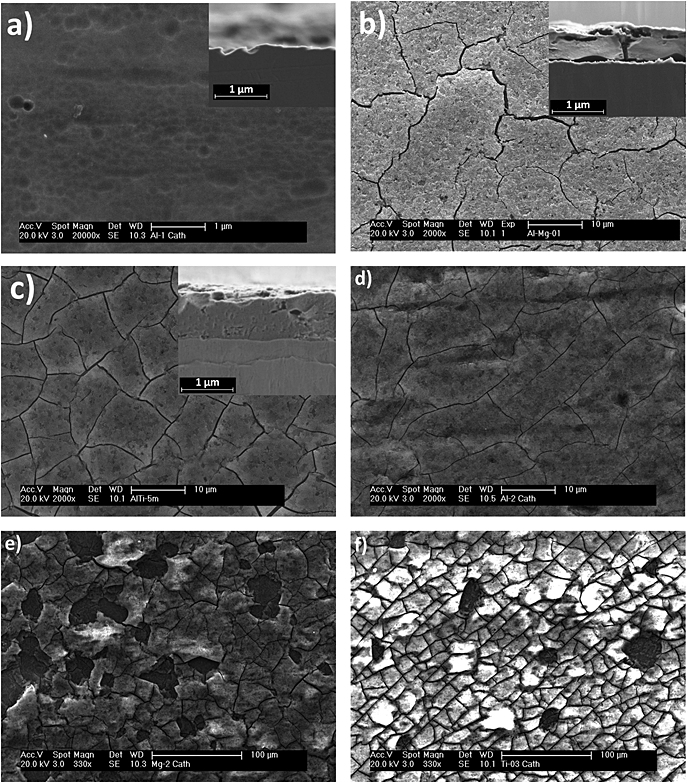

Abstract
Cathodic polarization of aluminium and Al-0.18wt.%Mg and Al-0.08wt.% Ti alloys in 0.24moldm(-3) nitric acid solution at 38 degrees C has been employed to assist understanding of the roles of alloying elements in electrograining. The findings indicate that additions of magnesium and titanium to aluminium accelerate the corrosion of the substrate under the alkalization caused by the cathodic reactions. The accelerated dissolution and the consequent formation of hydrated alumina result in a decreased net cathodic current density in potentiostatic and potentiodynamic polarization conditions relative to the behaviour of aluminium.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.5640
Reactividad de Sólidos
New Insights on the Kinetic Analysis of Isothermal Data: The Independence of the Activation Energy from the Assumed Kinetic Model
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMEnergy & Fuels, 29 (2015) 392-397 DOI: 10.1021/ef502269r
Abstract
Isothermal experiments are widely employed to study the kinetics of solid-state reactions or processes to extract essential kinetic information needed for modeling the processes at an industrial scale. The kinetic analysis of isothermal data requires finding or assuming a kinetic function that can properly fit the evolution of the reaction rate with time, so that the resulting parameters, i.e., the activation energy and pre-exponential factor, can be considered reliable. In the present work, we demonstrate using both simulated and experimental data that the kinetic analysis of a set of isothermal plots obtained at different temperatures, considering a single-step solid-state reaction, necessarily leads to the real activation energy, regardless the mathematical function selected for performing the kinetic analysis. This makes irrelevant the election of the kinetic function used to fit the experimental data and greatly facilitates the estimation of the activation energy for any single process.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/ef502269r
Reactividad de Sólidos
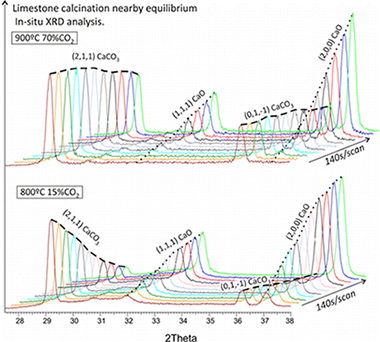
Limestone Calcination Nearby Equilibrium: Kinetics, CaO Crystal Structure, Sintering and Reactivity
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 119 (2015) 1523-1541 DOI: 10.1021/jp508745u
Abstract
In this work, we analyze limestone calcination kinetics at environmental conditions involving a CO2 partial pressure P close to the equilibrium pressure Peq by means of in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermogravimetric (TG) analyses. In contrast with previous empirical observations carried out mostly at conditions far from equilibrium (P/Peq ≪ 1), our results show that the decarbonation rate decreases as the temperature in increased while P/Peq is kept constant, which is explained from a reaction mechanism including desorption of CO2 and the exothermic structural transformation from metastable CaO* nanocrystals to the stable CaO form. The crystal structure and sintering of nascent CaO during calcination has been investigated from in situ XRD analysis, physisorption analysis, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which shows that the ratio of the size of polycrystalline CaO grains to crystallite size increases linearly with the CO2 partial pressure in the calcination atmosphere. For high CO2 partial pressures, the size of CaO grains reaches a maximum value of around 1 μm, which leads to a residual surface area of about 1 m2/g, whereas in the limit P → 0 grain size and crystallite size (of the order of 10 nm) would coincide. Accordingly, sintering in the presence of CO2 would be triggered by the agglomeration of CaO crystals enhanced by CO2adsorption, which increases the surface energy. The carbonation reactivity of CaO resulting from calcination scales proportionally to its surface area and is not determined by a growth of the CaO exposed surface along a preferred crystallographic direction wherein carbonation would be unfavorable as suggested in recent works.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/jp508745u
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
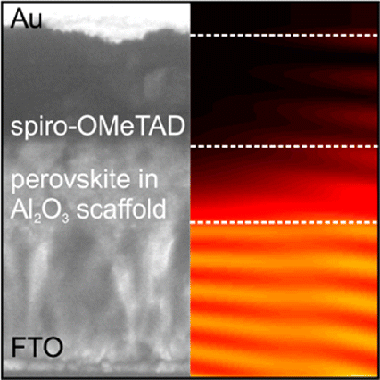
Optical Description of Mesostructured Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskite Solar Cells
Anaya, M; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Zhang, W; Johnston, MB; Snaith, HJ; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 6 (2015) 48-53 DOI: 10.1021/jz502351s
Abstract
Herein we describe both theoretically and experimentally the optical response of solution-processed organic–inorganic halide perovskite solar cells based on mesostructured scaffolds. We develop a rigorous theoretical model using a method based on the propagation of waves in layered media, which allows visualizing the way in which light is spatially distributed across the device and serves to quantify the fraction of light absorbed by each medium comprising the cell. The discrimination between productive and parasitic absorption yields an accurate determination of the internal quantum efficiency. State-of-the-art devices integrating mesoporous scaffolds infiltrated with perovskite are manufactured and characterized to support the calculations. This combined experimental and theoretical analysis provides a rational understanding of the optical behavior of perovskite cells and can be beneficial for the judicious design of devices with improved performance. Notably, our model justifies the presence of a solid perovskite capping layer in all of the highest efficiency perovskite solar cells based on thinner mesoporous scaffolds.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1021/jz502351s
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Catalytic screening of Au/CeO2-MOx/Al2O3 catalysts (M = La, Ni, Cu, Fe, Cr, Y) in the CO-PrOx reaction
Reina, TR; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40 (2015) 1782-1788 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.11.141
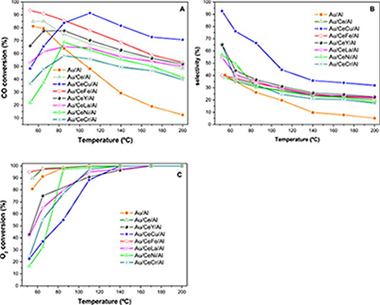
Abstract
In this work, a series of Au/CeO2-MOx/Al2O3 catalysts has been prepared and evaluated in the PrOx reaction. Within the series of dopants Fe and Cu containing samples enhanced the catalytic performance of the parent Au/CeO2/Al2O3 catalyst being copper the most efficient promoter. For both samples an enhanced oxygen storage capacity (OSC) is registered and accounts for the high CO oxidation activity. More particularly, the Au/CeO2-CuOx/Al2O3 catalyst successfully withstands the inclusion of water in the PrOx stream and presents good results in terms of CO elimination. However to achieve a good selectivity toward, CO2 formation properly adjusting of the reaction parameters, such as oxygen concentration and space velocity is needed. Within the whole screened series the Cu-containing catalyst can be considered as the most interesting alternative for H-2 clean-up applications.
Enero, 2015 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.11.141
2014
2014
Materiales Coloidales
One-Step Synthesis and Polyacrylic Acid Functionalization of Multifunctional Europium-Doped NaGdF4 Nanoparticles with Selected Size for Optical and MRI Imaging
Nunez, NO; Garcia, M; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 35 (2014) 6075-6084 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201402690
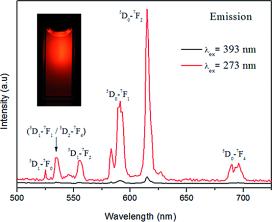
Abstract
Multifunctional Eu:NaGdF4 nanospheres functionalized with polyacrylic acid (PAA) polymer have been prepared for the first time by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction at 120 °C. The size of the nanospheres, which were polycrystalline and crystallized into a hexagonal structure, could be altered in the 60–95 nm range by adjusting the amount of polyacrylic acid added. The effects of Eu content and particle size of these nanomaterials on their optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) as well as on their relaxivity (r1 and r2) values were also analyzed to find the optimum system for optical bioimaging and as a positive contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications. Finally, such optimum nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells for concentrations up to 0.5 mg mL–1 and a high colloidal stability in 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid solutions, thereby satisfying the most important requirements for their use in biotechnological applications.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201402690
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
LMM Auger primary excitation spectra of copper
Pauly, N; Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface Science, 630 (2014) 294-299 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.08.029
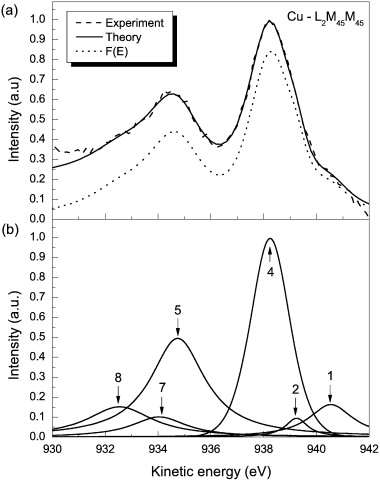
Abstract
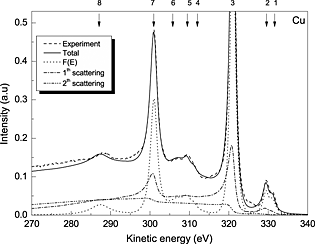
The shape and intensity of measured Auger peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface and to intrinsic excitations induced by the sudden creation of the two static core holes. Following a method developed for XPS in a previous work [N. Pauly, S. Tougaard, F. Yubero, Surf. Sci. 620 (2014) 17], we have calculated the effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross-sections, including the effects of the surface and of the two core holes, within the dielectric response theory by means of the QUEELS-XPS software (QUantitative analysis of Electron Energy Losses at Surfaces for XPS). The Auger spectra are then modeled by convoluting this energy loss cross section with the primary excitation spectrum that accounts for all effects which are part of the initial Auger process, i.e. L–S coupling and vacancy satellite effects. The shape of this primary excitation spectrum is fitted to get close agreement between the theoretical and the experimental spectra obtained from X-ray excited Auger electron spectroscopy (XAES). We have performed these calculations of XAES spectra for various LMM Auger transitions of pure Cu (L3M45M45, L3M23M45, L3M23M23 and L2M45M45 transitions). We compare the resulting primary excitation spectra with theoretical results published in the literature and obtain reasonable quantitative agreement. In particular, we extract from experimental spectra quantitative intensities due to Coster–Kronig, shake-off and shake-up processes relative to the intensity from the “normal” Auger process.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.08.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quinone-Rich Poly(dopamine) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biosensor Applications
Martin, M; Orive, AG; Lorenzo-Luis, P; Creus, AH; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Salazar, PChemPhysChem, 15 (2014) 3742-3752 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201402417
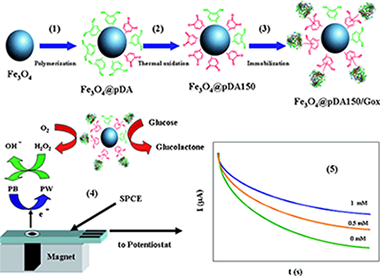
Abstract
Novel core-shell quinone-rich poly(dopamine)–magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were prepared by using an in situ polymerization method. Catechol groups were oxidized to quinone by using a thermal treatment. MNPs were characterized by using X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, magnetic force microscopy, UV/Vis, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and electrochemical techniques. The hybrid nanomaterial showed an average core diameter of 17 nm and a polymer-film thickness of 2 nm. The core-shell nanoparticles showed high reactivity and were used as solid supports for the covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase (Gox) through Schiff base formation and Michael addition. The amount of Gox immobilized onto the nanoparticle surface was almost twice that of the nonoxidized film. The resulting biofunctionalized MNPs were used to construct an amperometric biosensor for glucose. The enzyme biosensor has a sensitivity of 8.7 mA m−1 cm−2, a low limit of detection (0.02 mm), and high stability for 45 days. Finally, the biosensor was used to determine glucose in blood samples and was checked against a commercial glucometer.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201402417
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High temperature internal friction measurements of 3YTZP zirconia polycrystals. High temperature background and creep
Simas, P; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; No, ML; De-Bernardi, S; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Juan, JSJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 3859-3863 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.016

Abstract
This work focuses on the high-temperature mechanic properties of a 3 mol% yttria zirconia polycrystals (3YTZP), fabricated by hot-pressureless sintering. Systematic measurements of mechanical loss as a function of temperature and frequency were performed. An analytical method, based on the generalized Maxwell rheological model, has been used to analyze the high temperature internal friction background (HTB). This method has been previously applied to intermetallic compounds but never to ceramics, except in a preliminary study performed on fine grain and nanocrystalline zirconia. The HTB increases exponentially and its analysis provides an apparent activation enthalpy which correlates well with that obtained from creep experiments. This fact shows on the one hand the plausibility of applying the generalized Maxwell model to ceramics, and on the other hand indicates the possibility of using mechanical spectroscopy as a complementary helpful technique to investigate the high temperature deformation mechanism of materials.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Transmission electron microscopy of unstained hybrid Au nanoparticles capped with PPAA (plasma-poly-allylamine): Structure and electron irradiation effects
Gontard, LC; Fernandez, A; Dunin-Borkowski, RE; Kasama, T; Lozano-Perez, S; Lucas, SMicron, 67 (2014) 1-9 DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2014.06.004
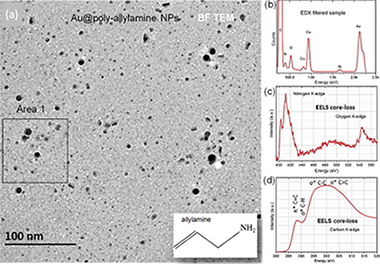
Abstract
Hybrid (organic shell–inorganic core) nanoparticles have important applications in nanomedicine. Although the inorganic components of hybrid nanoparticles can be characterized readily using conventional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques, the structural and chemical arrangement of the organic molecular components remains largely unknown. Here, we apply TEM to the physico-chemical characterization of Au nanoparticles that are coated with plasma-polymerized-allylamine, an organic compound with the formula C3H5NH2. We discuss the use of energy-filtered TEM in the low-energy-loss range as a contrast enhancement mechanism for imaging the organic shells of such particles. We also study electron-beam-induced crystallization and amorphization of the shells and the formation of graphitic-like layers that contain both C and N. The resistance of the samples to irradiation by high-energy electrons, which is relevant for optical tuning and for understanding the degree to which such hybrid nanostructures are stable in the presence of biomedical radiation, is also discussed.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micron.2014.06.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Heterogeneous selective oxidation of fatty alcohols: Oxidation of 1-tetradecanol as a model substrate
Corberan, VC; Gomez-Aviles, A; Martinez-Gonzalez, S; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Gonzalez-Perez, MECatalysis Today, 238 (2014) 49-53 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.033
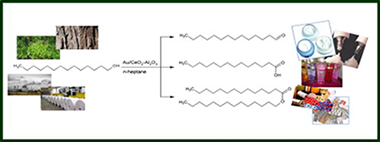
Abstract
Selective oxidation of fatty alcohols, i.e., linear long-chain alkanols, has been scarcely investigated to date, despite its potential application in high value chemical's production. We report for the first time the liquid phase heterogeneous oxidation of 1-tetradecanol, used as a model molecule for fatty alcohols, according to green chemistry principles by using a Au/CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst and O-2 as oxidant at normal pressure. High selectivity to tetradecanal (ca. 80%) or to tetradecanoic acid (60-70%) are reached at medium conversion (up to 38%), depending on the reaction conditions used. Comparison with similar tests of 1-octanol oxidation shows that the increase of the carbon chain length decreases the alcohol conversion and the formation of ester, probably due to a greater steric effect.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2014.03.033
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of precalcination and regeneration conditions on postcombustion CO2 capture in the Ca-looping technology
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAApplied Energy, 136 (2014) 347-356 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.09.052

Abstract
The Ca-looping (CaL) technology is already recognized as a potentially viable method to capture CO2 from postcombustion gas in coal fired power plants. In this process, CO2 is chemisorbed by CaO solid particles derived from precalcination of cheap and widely available natural limestone. The partially carbonated solids are regenerated by calcination under high CO2 concentration. Novel CaL concepts are proposed to further improve the efficiency of the technology such as the introduction of a recarbonation reactor in between the carbonation and calcination stages to mitigate the progressive deactivation of the regenerated CaO. Process simulations aimed at retrieving optimum design parameters and operating conditions to scale-up the technology yield results critically dependent on the multicyclic sorbent performance. Nevertheless, technical limitations usually preclude lab-scale tests from mimicking realistic CaL conditions necessarily involving high CO2 concentration for sorbent regeneration and quick transitions between carbonation and calcination. In this work, a lab-scale experimental analysis is reported on the CaO multicyclic conversion at CaL conditions closely resembling those to be expected in practice. The results presented evidence a relevant role of precalcination conditions. Precalcination in air leads to a strongly adverse effect on the activity of the sorbent regenerated under high CO2 concentration, which is further hindered if a recarbonation stage is introduced. On the other hand, sorbent deactivation is mitigated if precalcination is carried out at conditions similar to those used for sorbent regeneration. In this case, recarbonation helps lessening the loss of multicyclic conversion, which is further enhanced by the synergistic combination with heat pretreatment. Moreover, the present study shows that the kinetics of carbonation is strongly dependent on precalcination and regeneration conditions. The diffusion controlled carbonation phase and recarbonation are intensified if the sorbent is precalcined and regenerated under high CO2 concentration whereas the reaction controlled carbonation phase is notably hampered.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.09.052
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement of Vickers hardness measurement on SWNT/Al2O3 composites consolidated by spark plasma sintering
Rodriguez, AM; Lopez, AG; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Poyato, R; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 3801-3809 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.048
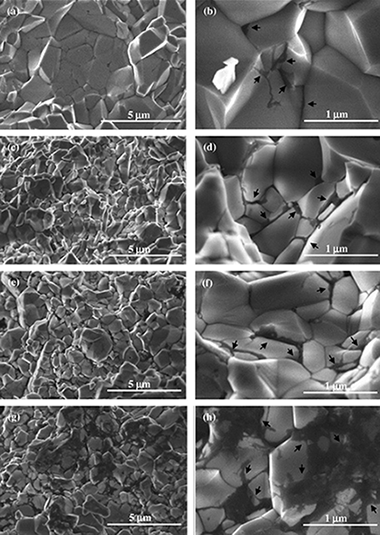
Abstract
Dense alumina composites with different carbon nanotube content were prepared by colloidal processing and consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) were distributed at grain boundaries and also into agglomerates homogeneously dispersed. Carrying out Vickers hardness tests on the cross-section surfaces instead of top (or bottom) surfaces has shown a noticeable increase in the reliability of the hardness measurements. This improvement has been mainly attributed to the different morphology of carbon nanotube agglomerates, which however does not seem to affect the Vickers hardness value. Composites with lower SWNT content maintain the Vickers hardness of monolithic alumina, whereas it significantly decreases for the rest of compositions. The decreasing trend with increasing SWNT content has been explained by the presence of higher SWNT quantities at grain boundaries. Based on the results obtained, a method for optimizing Vickers hardness tests performance on SWNT/Al2O3 composites sintered by SPS is proposed.
Diciembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.048
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Chemistry, nanostructure and magnetic properties of Co-Ru-B-O nanoalloys
Arzac, GM; Rojas, TC; Gontard, LC; Chinchilla, LE; Otal, E; Crespo, P; Fernandez, ARSC Advances, 4 (2014) 46576-46586 DOI:
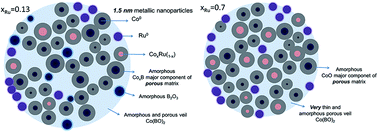
Abstract
In our previous works, Co–B–O and Co–Ru–B–O ultrafine powders with variable Ru content (xRu) were studied as catalysts for hydrogen generation through sodium borohydride hydrolysis. These materials have shown a complex nanostructure in which small Co–Ru metallic nanoparticles are embedded in an amorphous matrix formed by Co–Ru–B–O based phases and B2O3. Catalytic activity was correlated to nanostructure, surface and bulk composition. However, some questions related to these materials remain unanswered and are studied in this work. Aspects such as: 3D morphology, metal nanoparticle size, chemical and electronic information on the nanoscale (composition and oxidation states), and the study of the formation or not of a CoxRu1−x alloy or solid solution are investigated and discussed using XAS (X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy) and Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) techniques. Also magnetic behavior of the series is studied for the first time and the structure–performance relationships discussed. All Co-containing samples exhibited ferromagnetic behavior up to room temperature while the Ru–B–O sample is diamagnetic. For the xRu = 0.13 sample, an enhancement in the Hc (coercitive field) and Ms (saturation magnetization) is produced with respect to the monometallic Co–B–O material. However this effect is not observed for samples with higher Ru content. The presence of the CoxB-rich (cobalt boride) amorphous ferromagnetic matrix, very small metal nanoparticles (Co and CoxRu(1−x)) embedded in the matrix, and the antiferromagnetic CoO phase (for the higher Ru content sample, xRu = 0.7), explain the magnetic behavior of the series.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI:
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Ceramic Barrier Layers for Flexible Thin Film Solar Cells on Metallic Substrates: A Laboratory Scale Study for Process Optimization and Barrier Layer Properties
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Guilera, N; Francesch, L; Alba, MD; Lopez, L; Sanchez, EACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6 (2014) 18543-18549 DOI: 10.1021/am504923z
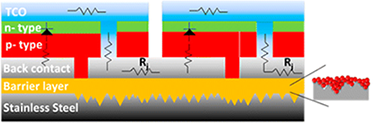
Abstract
Flexible thin film solar cells are an alternative to both utility-scale and building integrated photovoltaic installations. The fabrication of these devices over electrically conducting low-cost foils requires the deposition of dielectric barrier layers to flatten the substrate surface, provide electrical isolation between the substrate and the device, and avoid the diffusion of metal impurities during the relatively high temperatures required to deposit the rest of the solar cell device layers. The typical roughness of low-cost stainless-steel foils is in the hundred-nanometer range, which is comparable or larger than the thin film layers comprising the device and this may result in electrical shunts that decrease solar cell performance. This manuscript assesses the properties of different single-layer and bilayer structures containing ceramics inks formulations based on Al2O3, AlN, or Si3N4 nanoparticles and deposited over stainless-steel foils using a rotogravure printing process. The best control of the substrate roughness was achieved for bilayers of Al2O3 or AlN with mixed particle size, which reduced the roughness and prevented the diffusion of metals impurities but AlN bilayers exhibited as well the best electrical insulation properties.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/am504923z
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Enhanced activity of clays and its crucial role for the activity in ethylene polymerization
Camejo-Abreu, C; Tabernero, V; Alba, MD; Cuenca, T; Terreros, PJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 393 (2014) 96-104 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.030
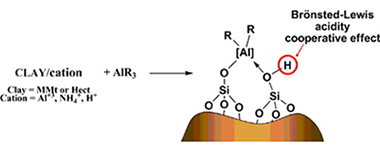
Abstract
This paper presents a study of the effects of different treatments on the polymerization activity of modified clays as cocatalysts. To achieve this goal, an intercalating cation was introduced into two smectites and these clays were then modified with trimethyl aluminium. The results for ethylene polymerization, when a zirconocene complex was used as catalyst, and the structure analysis, allow us to obtain interesting deductions about the generation mode of the active species. All active materials employed as support activators presented aluminium in a pentahedral environment together with acidic hydrogen atoms. These two features were detected only after TMA treatment and they seem to be crucial elements in active cocatalyst generation. Moreover, a material without structural aluminium displayed the best activity pointing to the new aluminium species generated in the solid matrix as the determining factor for the activity. We proposed a synergic effect between Lewis acid aluminium centres and acidic Bronsted protons that generate the SiOHAl groups that activate the zirconium compound.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.030
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Quantification and comparison of the reaction properties of FEBEX and MX-80 clays with saponite: Europium immobilisers under subcritical conditions
Villa-Alfageme, M; Hurtado, S; Castro, MA; El Mrabet, S; Orta, MM; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 101 (2014) 10-15 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.08.012
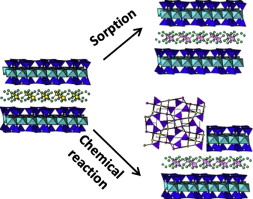
Abstract
The evaluation of the retention mechanisms in FEBEX and MX-80 bentonites, selected as reference materials to construct engineered barriers, carries major implications in the safe storage of immobilisation capacity through a recently discovered chemical retention mechanism and the structural analysis of the reaction products. Hydrothermal treatments were accomplished with immobilisation capacity through a recently discovered chemical retention mechanism and the structural analysis of the reaction products. Hydrothermal treatments were accomplished with Eu(NO3)3 (151Eu and 153Eu, with 52.2% 153Eu) and spiked with radioactive 152Eu for the quantification of the reactions. Results were compared with saponite as the reference smectite. The strong dependence of the reaction parameters with temperature and time was quantified and the reaction velocity was evaluated. The velocity follows these trends: 240 days are needed for the total retention of europium for temperatures over 200 °C; below 150 °C, significantly longer reaction times, on the order of three years, are required to complete the reaction. Clays do not influence velocity rates, but the retention capacity of bentonites remains lower than for saponite. At 300 °C, the milliequivalents retained by the three clays are consistently over CEC. The structural analyses reveal not only adsorption of europium but also the presence of Eu(OH)3 precipitation and Eu2SiO3 confirming the existence of a chemical reaction.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.08.012
Reactividad de Sólidos
Properties of mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline Bi2S3 particles
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Real, C; Balaz, P; Satka, A; Kovac, JMaterials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 27 (2014) 267-272 DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2014.05.057
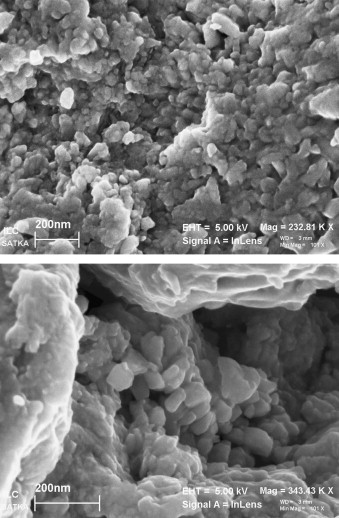
Abstract
Nanocrystalline Bi2S3 particles have been synthesized from Bi and S powders by high-energy milling in a planetary mill. Structural and microstructural characterization of the prepared particles, including phase identification, specific surface area measurement and particle size analysis has been carried out. The optical properties were measured by spectroscopic methods and the structural stability up to 500 °C was studied by thermal analysis. The production of orthorhombic Bi2S3 with crystallite size of about 26 nm was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The nanocrystals tend to agglomerate due to their large specific surface area. Accordingly, the average hydrodynamic diameter of the mechanochemically synthesized particles is 198 nm. EDS analysis shows that the synthesized material is pure Bi2S3. The band gap of the Bi2S3 nanoparticles is 4.5 eV which is wider than that in bulk materials. The nanoparticles exhibit good luminescent properties with a peak centered at 490 and 390 nm. Differential scanning calorimetry curves exhibit a broad exothermic peak between 200 and 300 °C, suggesting recovery processes. This interpretation is supported by X-ray diffraction measurements that indicate a 10-fold increase of the crystallite size to about 230 nm. The controlled mechanochemical synthesis of Bi2S3 nanoparticles at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure remains a great challenge.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2014.05.057
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal Stability of Multiferroic BiFeO3: Kinetic Nature of the beta-gamma Transition and Peritectic Decomposition
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 26387-26395 DOI: 10.1021/jp507831j
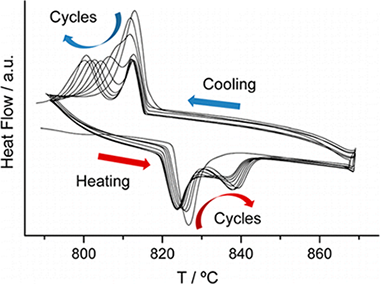
Abstract
The thermal stability of BiFeO3 prepared by mechanosynthesis and sintered at 850 °C has been studied by DSC as a function of the atmosphere and temperature. It has been found that neither the phase transitions nor the thermal stability of BiFeO3 is affected by the atmosphere in which the heating process is performed. The material is unstable above the α–β transition (TC) and slowly decomposes to produce Bi2O3 and Bi2Fe4O9. The kinetics of this slow process has been studied by performing heating–cooling DSC cycles, concluding it follows an Avrami–Erofeev nucleation and growth kinetic model. The β–γ transition and the peritectic decomposition of BiFeO3 overlap and are kinetically controlled. The kinetics of this complex process has been studied for the first time employing a new kinetic analysis procedure implying the deconvolution and subsequent analysis of the individual contributing stages. Thus, it has been demonstrated that the decomposition of BiFeO3 is accelerated when the sample is heated above the β–γ transition and both processes also follow Avrami–Erofeev kinetic models.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp507831j
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Characterization of porous graphitic monoliths from pyrolyzed wood
Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; de Arellano-Lopez, AR; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of Materials Science, 49 (2014) 7688-7696 DOI: 0.1007/s10853-014-8477-8
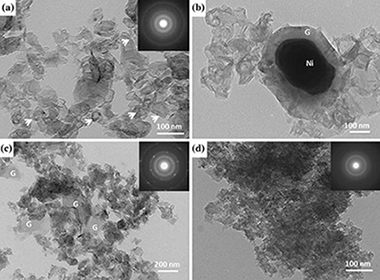
Abstract
Porous graphitic carbons were obtained from wood precursors using Ni as a graphitization catalyst during pyrolysis. The structure of the resulting material retains that of the original wood precursors with highly aligned, hierarchical porosity. Thermal characterization was performed by means of thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry, and the onset temperature for graphitization was determined to be similar to 900 A degrees C. Structural and microstructural characterization was performed by means of electron microscopy, electron and x-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. The effect of maximum pyrolysis temperature on the degree of graphitization was assessed. No significant temperature effect was detected by means of Raman scattering in the range of 1000-1400 A degrees C, but at temperatures over the melting point of the catalyst, the formation of graphite grains with long-range order was detected.
Noviembre, 2014 · DOI: 0.1007/s10853-014-8477-8
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Shape-defined nanodimers by tailored heterometallic epitaxy
Garcia-Negrete, Carlos A; Rojas, Teresa C; Knappett, Benjamin R; Jefferson, David A; Wheatley, Andrew E H; Fernandez, AsuncionNanoscale, 6 (2014) 11090-11097 DOI: 10.1039/C4NR01815J
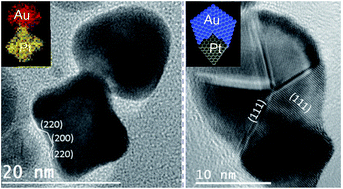
Abstract
The systematic construction of heterogeneous nanoparticles composed of two distinct metal domains (Au and Pt) and exhibiting a broad range of morphologically defined shapes is reported. It is demonstrated that careful Au overgrowth on Pt nanocrystal seeds with shapes mainly corresponding to cubeoctahedra, octahedra and octapods can lead to heterometallic systems whose intrinsic structures result from specific epitaxial relationships such as {111} + {111}, {200} + {200} and {220} + {220}. Comprehensive analysis shows also that nanoparticles grown from octahedral seeds can be seen as comprising of four Au tetrahedral subunits and one Pt octahedral unit in a cyclic arrangement that is similar to the corresponding one in decahedral gold nanoparticles. However, in the present case, the multi-component system is characterized by a broken five-fold rotational symmetry about the [011] axis. This set of bimetallic dimers could provide new platforms for fuel cell catalysts and plasmonic devices.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C4NR01815J
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Heterostructured Er3+ doped BiVO4 with exceptional photocatalytic performance by cooperative electronic and luminescence sensitization mechanism
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 158-159 (2014) 242-249 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.029
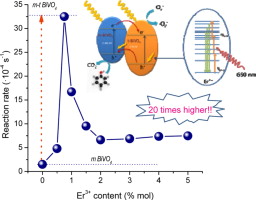
Abstract
Er-BiVO4 has been synthesized by means of mw-assisted hydrothermal method having good photoactivity under sun-like excitation. It is stated that the precursor addition sequence plays a critical role which determine the further structural feature of BiVO4. From the structural and morphological characterization, it can be demonstrated that the presence of Er3+ would induce the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to the formation of tetragonal-ErVO4 seeds previous to BiVO4 formation. The best photocatalytic performance is attained for the sample with 0.75 at% Er3+ content. At this dopant loading a mixture of tetragonal and monoclinic phase (70% tetragonal) is obtained. The dramatic increase in the photocatalytic activity for 0.75 at% Er-BiVO4 is related to the occurrence of such heterostructure. For this system, the MB degradation rate constant appears drastically higher as bare m-BiVO4. Furthermore, activities of photocatalysts for visible-light-driven O2 evolution have been evaluated, demonstrating that the photocatalytic activity of this Er-doped system (O2 evolution rate, 1014 μmol g−1 h−1) is 20 times as that of undoped m-BiVO4 (O2 evolution rate, 54 μmol g−1 h−1). From the obtained results, the cooperative conjunction of electronic and luminescence mechanism involved in the reaction is proposed to be the origin of the enhanced photocatalytic efficiencies of such systems.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.029
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Processing of CaCu3Ti4O12 with Giant Dielectric Properties
Espinoza-Gonzalez, R; Vega, E; Tamayo, R; Criado, JM; Dianez, MJMaterials and Manufacturing Processes, 29 (2014) 1179-1183 DOI: 10.1080/10426914.2014.921702
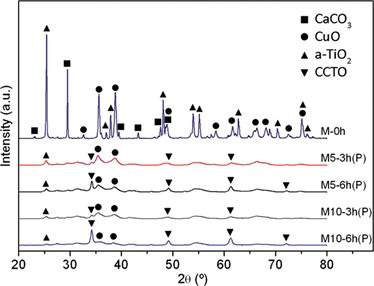
Abstract
The dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) ceramic prepared by mechanochemical synthesis (MCS) were investigated. The effect on dielectric properties of ball-to-powder weight ratio and milling time was investigated and compared to the behavior of CCTO prepared by conventional solid state reaction (CSSR). CCTO ceramic was partially obtained after 6h of the milling process, while complete transformation was obtained during the sintering step of milled powders. It was shown that the dielectric properties of CCTO processed by MCS are dramatically improved compared with samples prepared by CSSR.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1080/10426914.2014.921702
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological comparison of different C-based coatings in lubricated and unlubricated conditions
Ciarsolo, I; Fernandez, X; de Gopegui, UR; Zubizarreta, C; Abad, MD; Mariscal, A; Caretti, I; Jimenez, I; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSurface and Coatings Technology, 257 (2014) 278-285 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.07.068
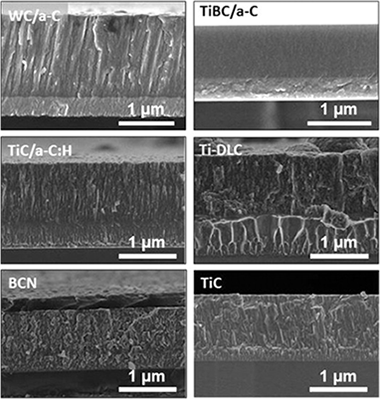
Abstract
The use of carbon-based coatings (hydrogenated and non-hydrogenated DLC, doped and alloyed-DLC) is of wide interest due to its applications in mechanical components submitted to friction and wear including sliding parts in automotive engines. A tribological comparative analysis using a reciprocating (SRV) tester in lubricated and unlubricated conditions with a 4-stroke motor oil has been carried out on six currently relevant state-of-the-art coatings (namely WC/a-C, TiBC/a-C and TiC/a-C:H nanocomposites, Ti-doped DLC, BCN film and a crystalline monolithic TiC film as reference). The quantification of the fraction of the sp(2)-bonded matrix has been done by fitting of C 1s XPS peak and the mechanical properties evaluated by nanoindentation. The comparative analysis has allowed us to identify the capabilities of each system depending on the testing conditions and the possible synergies as a function of the chemical composition and film nature. Under lubricated harsh conditions (max. contact pressure 1.7 GPa) only coatings displaying hardness superior to 20 GPa could stand the sliding motion without failure. At lower contact pressures, a significant fraction of sp(2) carbon (>= 75%) is advantageous for reducing wear in boundary lubrication. WC/a-C, BCN and Ti-DLC films showed the best tribological response in dry sliding conditions. This fundamental information would be of relevance for assisting engineers in selecting best partnership for lubrication systems.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.07.068
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The Use of Fluorocarbons to Mitigate the Oxygen Dependence of Glucose Microbiosensors for Neuroscience Applications
Martin, M; O'Neill, RD; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Salazar, PJournal of The Electrochemical Society, 161 (2014) H689-H695 DOI: 10.1149/2.1071410jes
Abstract
First-generation amperometric glucose biosensors are the most commonly used method for glucose monitoring in neuroscience. Nevertheless, biosensors of this genre suffer from the so-called "oxygen deficit". This problem is particularly acute when the oxygen concentration is low, as is the case in brain extracellular fluid. In the present work we use different fluorocarbons, such as Nafion and H700, to mitigate the oxygen deficit. These fluorocarbon-derived materials display a remarkable solubility for oxygen, and are able to act as oxygen reservoirs supporting the enzymatic reaction. Different biosensor configurations are presented, evaluating their sensitivity, linear range and oxygen dependence. Optimized Nafion- and H700-modified biosensors displayed a remarkable oxygen tolerance, with K-M(O-2) values as low as 11 and 4 mu mol L-1, respectively, and an appropriate sensitivity for in-vivo applications. Finally, in-vivo data are reported in order to illustrate the application of such devices in neuroscience applications.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1149/2.1071410jes
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Active Site Considerations on the Photocatalytic H-2 Evolution Performance of Cu-Doped TiO2 Obtained by Different Doping Methods
Valero, JM; Obregon, S; Colon, GACS Catalysis, 4 (2014) 3320-3329 DOI: 10.1021/cs500865y
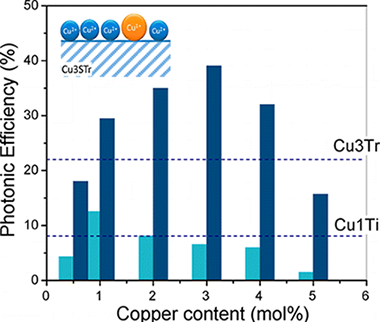
Abstract
A photocatalytic H2 evolution reaction was performed over copper doped TiO2. The influence of sulfate pretreatment over fresh TiO2 support and the Cu doping method has been evaluated. Wide structural and surface characterization of catalysts was carried out in order to establish a correlation between the effect of sulfuric acid treatment and the further Cu-TiO2photocatalytic properties. Notably a different copper dispersion and oxidation state is obtained by different metal decoration methods. From the structural and surface analysis of the catalysts we have stated that the occurrence of highly disperse and reducible Cu2+ species is directly related to the photocatalytic activity for the H2 production reaction. Highly active materials have been obtained from a chemical reduction method leading to 18 mmol·h–1·g–1for 3 mol % copper loading.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/cs500865y
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the early stages of growth of Co oxides on oxide substrates
Diaz-Fernandez, D; Mendez, J; Yubero, F; Dominguez-Canizares, G; Gutierrez, A; Soriano, LSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 975-979 DOI: 10.1002/sia.5366
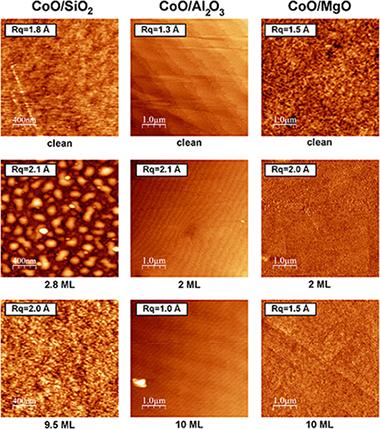
Abstract
The growth of Cobalt oxides by reactive thermal evaporation of metallic Cobalt in an oxygen atmosphere on a series of oxide substrates, namely SiO2, Al2O3 and MgO, has been chemically and morphologically studied by means of XPS and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The XPS results reveal that cobalt oxide grows as CoO (Co2+) for coverages up to some tens of equivalent monolayers on all substrates. For larger coverages, the formation of the spinel oxide Co3O4 has been observed. AFM and XPS quantification allowed us to determine the way of growth of CoO on all substrates, being of Volmer-Weber (i.e. islands) mode for SiO2, whereas for Al2O3 and MgO, the growth follows the Frank-van der Merwe (i.e. layer-by-layer) mode. The results are discussed in terms of the mismatch of the lattice parameters of the CoO adsorbates with the substrates
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.5366
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Real, C; Zorkovska, A; Balaz, P; Satka, A; Kovac, J; Ficeriova, JActa Physica Polonica A, 126 (2014) 943-946 DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.126.943
Abstract
Nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles have been synthesized from Sb and S powders by high-energy milling in a planetary mill using argon protective atmosphere. X-ray diffraction, particle size analysis, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, high resolution transmission electron microscopy, UV-VIS, and differential scanning calorimetry methods for characterization of the prepared particles were applied. The powder X-ray diffraction pattern shows that Sb2S3 nanocrystals belong to the orthorhombic phase with calculated crystallite size of about 36 nm. The nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles are constituted by randomly distributed crystalline nanodomains (20 nm) and then these particles are forming aggregates. The monomodal distribution of Sb2S3 particles with the average hydrodynamic parameter 210 nm was obtained. The quantification of energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis peaks give an atomic ratio of 2:3 for Sb:S. The optical band gap determined from the absorption spectrum is 4.9 eV, indicating a considerable blue shift relative to the bulk Sb2S3. Differential scanning calorimetry curves exhibit a broad exothermic peak between 200 and 300°C, suggesting recovery processes. This interpretation is supported by X-ray diffraction measurements that indicate a 23-fold increase of the crystallite size to about 827 nm as a consequence of application of high temperature process. The controlled mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3nanoparticles at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure remains a great challenge.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.126.943
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modeling of X-ray photoelectron spectra: surface and core hole effects
Pauly, N; Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 920-923 DOI: 10.1002/sia.5372
Abstract
The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface and by intrinsic excitations induced by the sudden creation of the static core hole. Besides, elastic electron scattering may also be important. These effects should be included in the theoretical description of the emitted photoelectron peaks. To investigate the importance of surface and core hole effects relative to elastic scattering effect, we have calculated full XPS spectra for the Cu 2p emissions of Cu and CuO with the simulation of electron spectra for surface analysis (SESSA) software and with a convolution procedure using the differential inelastic electron scattering cross-section obtained with the quantitative analysis of electron energy loss in XPS (QUEELS-XPS) software. Surface and core hole effects are included in QUEELS-XPS but absent in SESSA while elastic electron scattering effects are included in SESSA but absent in QUEELS-XPS. Our results show that the shape of the XPS spectra are strongly modified because of surface and core hole effects, especially for energy losses smaller than about 20eV.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.5372
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Pyridine adsorption on NiSn/MgO-Al2O3: An FTIR spectroscopic study of surface acidity
Penkova, A; Bobadilla, LF; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Surface Science, 317 (2014) 241-251 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.093
Abstract
The acid-base properties of MgO-Al2O3 supports and NiSn/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts were evaluated by IR spectroscopy using pyridine as a probe molecule. The results indicate that only Lewis acid sites were detected on the surface of the supports as well as on the catalysts. Nevertheless, Bronsted acid sites were not detected. In the support without MgO three kinds of coordinatively unsaturated acid sites were detected: Al3+ cations occupying octahedral, tetrahedral and tetrahedral with cationic vacancy in the neighbourhood. The last sites appear as the strongest. Moreover, they are able to activate the pyridine molecules leading to the formation of an intermediate ce-pyridone complex. When MgO or NiO were added to the alumina, the number and strength of the Lewis acid sites decreased and significant changes were observed in the tetrahedral sites with adjoining cation vacancies. The incorporation of the Mg2+ cations into the alumina's structure takes place on the vacant tetrahedral positions, forming spinel MgAl2O4. As a result, the fraction of tetrahedral sites with adjoining cationic vacancy diminished and the intermediate ce-pyridone complex in the support with the highest MgO loading was hardly detected. The addition of Ni2+ cations leads to the filling of the free octahedral positions, resulting in the formation of a NiAl2O4 spinel structure and the thermal stability of the ce-pyridone species decreases. In the catalysts, the progressive reduction of the number and strength of the Lewis acid sites is due to a competitive formation of the two types of MgAl2O4 and NiAl2O4 spinels. In the catalyst NiSn/30MgO-Al2O3 no cationic vacancies were detected and the surface reaction with ce-pyridone formation did not occur.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.093
Reactividad de Sólidos
The Mitigation Effect of Synthetic Polymers on Initiation Reactivity of CL-20: Physical Models and Chemical Pathways of Thermolysis
Yan, QL; Zeman, S; Jimenez, PES; Zhang, TL; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Elbeih, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 22881-22895 DOI: 10.1021/jp505955n
Abstract
In this paper, the thermal decomposition physical models of different CL-20 polymorph crystals and their polymer bonded explosives (PBXs) bonded by polymeric matrices using polyisobutylene (PIB), acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), Viton A, and Fluorel binders are obtained and used to predict the temperature profiles of constant rate decomposition. The physical models are further supported by the detailed decomposition pathways simulated by a reactive molecular dynamics (ReaxFF-lg) code. It has been shown that both ε-CL-20 and α-CL-20 decompose in the form of γ-CL-20, resulting in close activation energy (169 kJ mol–1) and physical model (first-order autoaccelerated model, AC1). Fluoropolymers could change the decomposition mechanism of ε-CL-20 from the “first-order autocatalytic” model to a “three-dimensional nucleation and growth” model (A3), while the polymer matrices of Formex P1, Semtex, and C4 could change ε-CL-20 decomposition from a single-step process to a multistep one with different activation energies and physical models. Compared to fluoropolymers, PIB, SBR and NBR may make ε-CL-20 undergo more complete N–NO2 scission before collapse of the cage structure. This is likely the main reason why those polymer bases could greatly mitigate the decomposition process of ε-CL-20 from a single step to a multistep, resulting in lower impact sensitivity, whereas fluoropolymers have only a little effect on that. For ε-CL-20 and its PBXs, the impact sensitivity depends not only on the heat built-up period of their decomposition, but also on the probability of hotspot generation (defects in solid crystals and interfaces) especially when it decomposes in a solid state.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp505955n
Reactividad de Sólidos
Single phase, electrically insulating, multiferroic La-substituted BiFeO3 prepared by mechanosynthesis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; de Paz, JR; Saez-Puche, R; Maso, N; West, ARJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 2 (2014) 8398-8411 DOI: 10.1039/C4TC01426J
Abstract
Single phase, electrically insulating samples of Bi1−xLaxFeO3 solid solutions have been prepared by mechanosynthesis over the whole compositional range for the first time. Lanthanum substitution influenced the kinetics of the mechanochemical reaction and crystallite size of the products. For 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15, an increase in the La content produced a significant decrease in the weight-normalized cumulative kinetic energy required to obtain the final product and an increase in the resulting crystallite size. Larger La contents did not affect either the reactivity or the crystallite size. The effect of x on the structure has been identified. Samples in the ranges x ≤ 0.15 and x ≥ 0.45 gave single phase solid solutions with R3c and Pnma space groups, respectively, while for the intermediate range, a non-centrosymetric Pn21a(00γ)s00 super structure was obtained. For 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.30, differential scanning calorimetry showed two endothermic effects corresponding to the Néel temperature (TN, antiferromagnetic–paramagnetic transition) and the Curie temperature (TC, ferroelectric–paraelectric transition), demonstrating their multiferroic character. Compositions with a larger La content only showedTN. Dilatometric and permittivity measurements confirmed the results obtained by DSC for the ferroelectric–paraelectric transition. The composition dependence of TN and TC showed that, at low x, TN < TC, but a cross-over, or isoferroic transition occurred at x [[similar]] 0.28, when TN = TC = 386 °C. Ceramics with 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15 were highly insulating at room temperature with a resistivity, extrapolated from the Arrhenius plots, of [[similar]] 7 × 1016 to 8 × 1014 Ω cm and an activation energy [[similar]] 1.14–1.20 eV. Magnetization of the samples improved with La substitution.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C4TC01426J
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hardness and flexural strength of single-walled carbon nanotube/alumina composites
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, R; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 20 (2014) 7116-7123 DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8419-5
Abstract
This work adds new experimental facts on room temperature hardness and flexural strength of alumina and composites with 1, 2, 5 and 10 vol% single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) with similar grain size. Monolithic Al2O3 and composites were spark plasma sintered (SPS) in identical conditions at 1300 A degrees C, achieving high density, submicrometric grain size and a reasonably homogeneous distribution of SWNT along grain boundaries for all compositions with residual agglomerates. Vickers hardness values comparable to monolithic alumina were obtained for composites with low (1 vol%) SWNT content, though they decreased for higher concentrations, attributed to the fact that SWNT constitute a softer phase. Three-point bending flexural strength also decreased with increasing SWNT content. Correlation between experimental results and microstructural analysis by electron microscopy indicates that although SWNT agglomerates have often been blamed for detrimental effects on the mechanical properties of these composites, they are not the main cause for the reported decay in flexural strength.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8419-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Supported Co catalysts prepared as thin films by magnetron sputtering for sodium borohydride and ammonia borane hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; De Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 158-159 (2014) 400-409 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.047
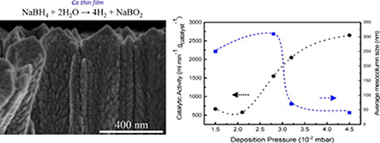
Abstract
Supported Co catalysts were prepared for sodium borohydride and ammonia borane hydrolysis by magnetron sputtering for the first time under different conditions. Ni foam was selected as support. Deposition conditions (time, pressure, and power) were varied to improve catalytic activity. A decrease in deposition power from 200 to 50 W, leads to a decrease in crystallite and column size and a higher activity of catalysts. The increase in deposition pressure from 1.5 × 10−2 to 4.5 × 10−2 mbar produces same effect but in this case the enhancement in activity is higher because amorphous materials were obtained. The highest activity for SB hydrolysis was 2650 ml min−1 gcat−1 for the 50 W Co 4.5 (4 h) sample (Ea = 60 ± 2 kJ mol−1). For AB hydrolysis activity for the 50 W Co 3.2 (4 h) sample was similar. Durability of the thin films was tested for both reactions upon cycling (14 cycles). Diluted acid washing was effective to recover the activity for sodium borohydride reaction but not for ammonia borane hydrolysis. The strong Co–NH3 interactions explain the non-efficiency of the acid washing.
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.047
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Interpretation of electron Rutherford backscattering spectrometry for hydrogen quantification
Alvarez, R; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 812-816 DOI: 10.1002/sia.5486
Abstract
In the last few years, several papers have appeared showing the capabilities of electron Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (eRBS) to quantify the H content at surfaces. The basis of the H detection in this technique relies on the difference in recoil energy of the incident electrons depending on the mass of the atoms located at the surface that act as scatter centers. In this paper, we address the interpretation of eRBS spectra of hydrogen containing surfaces. The aim is to compare the naive single elastic scattering approximation with a more realistic description of eRBS spectra including multiple elastic scattering using the HQ-eRBS (hydrogen quantification eRBS) software based on a Monte Carlo algorithm. It is concluded that multiple elastic scattering is a significant contribution to experimentally measured eRBS spectra of a polyethylene surface. It induces significant broadening of the distribution of the maximum elastic scattering angle along the electron trajectories contributing to the measured spectra. However, it has weak effect in the energy distribution of the collected electrons (about 10% overestimation of the H content in the particular case of a polyethylene surface with respect to the corresponding ratio of elastic scattering cross sections).
Octubre, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/sia.5486
- ‹ anterior
- 24 of 37
- siguiente ›














