Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Reactividad de Sólidos
Morphological changes on graphene nanoplatelets induced during dispersion into an epoxy resin by different methods
Moriche, R; Prolongo, SG; Sanchez, M; Jimenez-Suarez, A; Sayagues, MJ; Urena, AComposites Part B-Engineering, 72 (2015) 199-205
Show abstract ▽
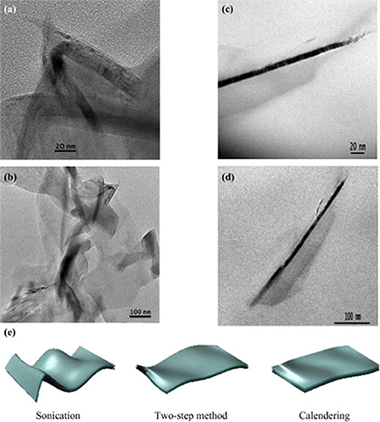
A structural analysis demonstrating how the manufacturing method of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) into a polymer matrix can strongly modify the GNPs morphology and, consequently, their properties, was carried out. Three different methods based on sonication and high shear forces were used to elucidate defects induction and possible size diminution. Manufacturing methods including high shear forces caused the extension of the GNPs while sonication induces wrinkling of the sheets. Residual stresses are induced in the nanoplatelets structure showing an increase in the Raman intensities ratios I-D/I-G and I-D/I-G when a major cycles number of calendering are applied.
Abril, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.12.012
Materiales Coloidales
Biosynthesis of silver fine particles and particles decorated with nanoparticles using the extract of Illicium verum (star anise) seeds
Luna, Carlos; Chavez, V. H. G.; Diaz Barriga-Castro, Enrique; Nunez, Nuria O.; Mendoza-Resendez, RaquelSpectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 141 (2015) 43-50
Show abstract ▽
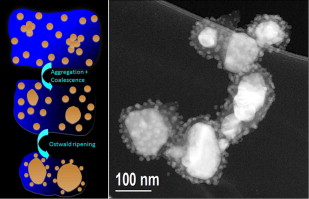
Given the upsurge of new technologies based on nanomaterials, the development of sustainable methods to obtain functional nanostructures has become an imperative task. In this matter, several recent researches have shown that the biodegradable natural antioxidants of several plant extracts can be used simultaneously as reducing and stabilizing agents in the wet chemical synthesis of metallic nanoparticles, opening new opportunities to design greener synthesis. However, the challenge of these new techniques is to produce stable colloidal nanoparticles with controlled particle uniformity, size, shape and aggregation state, in similar manner than the well-established synthetic methods. In the present work, colloidal metallic silver nanoparticles have been synthesized using silver nitrate and extracts of Illicium verum (star anise) seeds at room temperature in a facile one-step procedure. The resulting products were colloidal suspensions of two populations of silver nanoparticles, one of them with particle sizes of few nanometers and the other with particles of tens of nm. Strikingly, the variation of the AgNO3/extract weight ratio in the reaction medium yielded to the variation of the spatial distribution of the nanoparticles: high AgNO3/extract concentration ratios yielded to randomly dispersed particles, whereas for lower AgNO3/extract ratios, the biggest particles appeared coated with the finest nanoparticles.-This biosynthesized colloidal system, with controlled particle aggregation states, presents plasmonic and SERS properties with potential applications in molecular sensors and nanophotonic devices.
Abril, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.12.076
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanically induced self-propagating reaction of vanadium carbonitride
Roldan, MA; Alcala, MD; Real, CCeramics International, 41 (2015) 4688-4695
Show abstract ▽
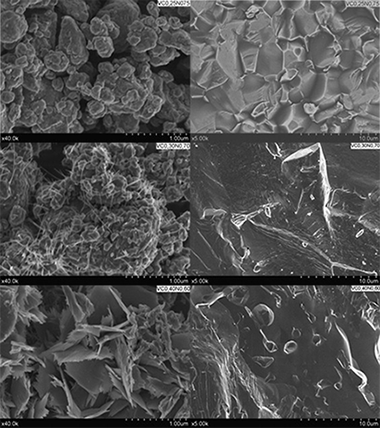
Vanadium carbonitrides (VCxN1-x) were prepared via mechanosynthesis from mixtures of elemental vanadium and carbon with different V/C atomic ratios under a nitrogen atmosphere using a high-energy ball mill. We obtained the full composition range of carbonitrides at room temperature. The products were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy. The results showed particle-sized products with high sinterability and very high microhardness.
Abril, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.12.016
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Self-Assembling of Tetradecylammonium Chain on Swelling High Charge Micas (Na-Mica-3 and Na-Mica-2): Effect of Alkylammonium Concentration and Mica Layer Charge
Pazos, MC; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pavon, E; Alba, MDLangmuir, 31 (2015) 4394-4401
Show abstract ▽
A family of tetradecylammonium micas is synthesized using synthetic swelling micas with high layer charge (NanSi8-nAln,Mg6F4O20 center dot XH2O, where n = 2 and 3) exchanged with tetradecylammonium cations. The molecular arrangement of the surfactant is,elucidated on the basis of XRD patterns and DTA. The ordering conformation of the surfactant molecules into the interlayer space of Micas is investigated by IR/FT, C-13, Al-27, and Si-29 MAS NMR. The structural arrangement of the tetradecylammonium cation in the interlayer space of high-charge micas is more sensitive to the effect of the mica layer charge at high concentration. The surfactant arrangement is found to follow the bilayer-paraffin model for all values of layer charge and surfactant concentration. However, at initial concentration below the mica CEC, a lateral monolayer is also observed. The amount of ordered conformation all-trans is directly proportional to the layer charge and surfactant concentration.
Abril, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b00224
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Pectin-Lipid Self-Assembly: Influence on the Formation of Polyhydroxy Fatty Acids Nanoparticles
Guzman-Puyol, Susana; Jesus Benitez, Jose; Dominguez, Eva; Bayer, Ilker Sefik; Cingolani, Roberto; Athanassiou, Athanassia; Heredia, Antonio; Heredia-Guerrero, Jose AlejandroPLoS One, 10 (2015) e0124639
Show abstract ▽
Nanoparticles, named cutinsomes, have been prepared from aleuritic (9,10,16-trihidroxipalmitic) acid and tomato fruit cutin monomers (a mixture of mainly 9(10), 16-dihydroxypalmitic acid (85%, w/w) and 16-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid (7.5%, w/w)) with pectin in aqueous solution. The process of formation of the nanoparticles of aleuritic acid plus pectin has been monitored by UV-Vis spectrophotometry, while their chemical and morphological characterization was analyzed by ATR-FTIR, TEM, and non-contact AFM. The structure of these nanoparticles can be described as a lipid core with a pectin shell. Pectin facilitated the formation of nanoparticles, by inducing their aggregation in branched chains and favoring the condensation between lipid monomers. Also, pectin determined the self-assembly of cutinsomes on highly ordered pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) surfaces, causing their opening and forming interconnected structures. In the case of cutin monomers, the nanoparticles are fused, and the condensation of the hydroxy fatty acids is strongly affected by the presence of the polysaccharide. The interaction of pectin with polyhydroxylated fatty acids could be related to an initial step in the formation of the plant biopolyester cutin.
Abril, 2015 | DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124639
- ‹ anterior
- 251 of 420
- siguiente ›














