Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of thickness and coatings morphology in the antimicrobial performance of zinc oxide coatings
Carvalho, P; Sampaio, P; Azevedo, S; Vaz, C; Espinos, JP; Teixeira, V; Carneiro, JOApplied Surface Science, 307 (2014) 548-557
Show abstract ▽
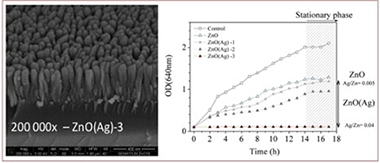
In this research work, the production of undoped and silver (Ag) doped zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films for food-packaging applications were developed. The main goal was to determine the influence of coatings morphology and thickness on the antimicrobial performance of the produced samples. The ZnO based thin films were deposited on PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) substrates by means of DC reactive magnetron sputtering. The thin films were characterized by optical spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The antimicrobial performance of the undoped and Ag-doped ZnO thin films was also evaluated. The results attained have shown that all the deposited zinc oxide and Ag-doped ZnO coatings present columnar morphology with V-shaped columns. The increase of ZnO coatings thickness until 200 nm increases the active surface area of the columns. The thinner samples (50 and 100 nm) present a less pronounced antibacterial activity than the thickest ones (200–600 nm). Regarding Ag-doped ZnO thin films, it was verified that increasing the silver content decreases the growth rate of Escherichia coli and decreases the amount of bacteria cells present at the end of the experiment
Julio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.04.072
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved O-2 evolution from a water splitting reaction over Er3+ and Y3+ co-doped tetragonal BiVO4
Obregon, S; Colon, GCatalysis Science & Technology, 4 (2014) 2042-2050
Show abstract ▽
Erbium–yttrium co-doped BiVO4 with a tetragonal structure is synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method. The studied photocatalyst shows good photoactivity under sun-like excitation for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) and for O2 evolution. From structural and morphological characterization, it has been stated that the presence of lanthanides induces the stabilization of the tetragonal phase. This is probably due to the substitutional occupation that occurs in the BiVO4 lattice. The photocatalytic performance under visible-NIR radiation clearly evidences the occurrence of an up-conversion process involved in the overall photo-electronic mechanism. The tetragonal phase Er0.0075,Y0.03–Bi0.9625VO4 system gives the highest O2 evolution rate (425 μmol g−1 h−1) under sun-like excitation, being 8 times higher than that attained for m-BiVO4 (53 μmol g−1 h−1).
Julio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/C4CY00050A
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar growth of thin films deposited at oblique angles: Beyond the tangent rule
Alvarez, R; Lopez-Santos, C; Parra-Barranco, J; Rico, V; Barranco, A; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 32 (2014) 041802
Show abstract ▽
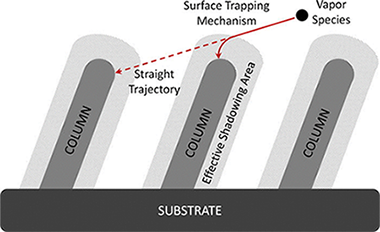
The growth of nanostructured physical vapor deposited thin films at oblique angles is becoming a hot topic for the development of a large variety of applications. Up to now, empirical relations, such as the so-called tangent rule, have been uncritically applied to account for the development of the nanostructure of these thin films even when they do not accurately reproduce most experimental results. In the present paper, the growth of thin films at oblique angles is analyzed under the premises of a recently proposed surface trapping mechanism. The authors demonstrate that this process mediates the effective shadowing area and determines the relation between the incident angle of the deposition flux and the tilt angle of the columnar thin film nanostructures. The analysis of experimental data for a large variety of materials obtained in our laboratory and taken from the literature supports the existence of a connection between the surface trapping efficiency and the metallic character of the deposited materials. The implications of these predictive conclusions for the development of new applications based on oblique angle deposited thin films are discussed.
Julio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1116/1.4882877
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of crystal structure on CO2 capture by limestone derived CaO subjected to carbonation/recarbonation/calcination cycles at Ca-looping conditions
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Quintanilla, MAS; Perez-Vaquero, JApplied Energy, 125 (2014) 264-275
Show abstract ▽
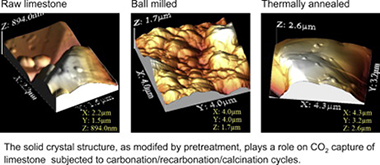
Large scale pilot plants are currently demonstrating the feasibility of the Calcium-looping (CaL) technology built on the multicyclic calcination/carbonation of natural limestone for post-combustion and precombustion CO2 capture. Yet, limestone derived CaO exhibits a drop of conversion when subjected to multiple carbonation/calcination cycles, which lessens the efficiency of the technology. In this paper we analyze a novel CaL concept recently proposed to mitigate this drawback based on the introduction of an intermediate stage wherein carbonation is intensified at high temperature and high CO2 partial pressure. It is shown that carbonation in this stage is mainly driven by solid-state diffusion, which is determined by the solid's crystal structure. Accordingly, a reduction of crystallinity by ball milling, which favors diffusion, serves to promote recarbonation. Conversely, thermal annealing, which enhances crystallinity, hinders recarbonation. An initial fast phase has been identified in the recarbonation stage along which the rate of carbonation is also a function of the crystal structure indicating a relevant role of surface diffusion. This is consistent with a recently proposed mechanism for nucleation of CaCO3 on the CaO surface in islands with a critical size determined by surface diffusion. A further issue analyzed has been the effects of pretreatment and cycling on the mechanical strength of the material, whose fragility hampers the CaL process efficiency. Particle size distribution of samples dispersed in a liquid and subjected to high energy ultrasonic irradiation indicate that milling promotes friability whereas thermal annealing enhances the resistance of the particles to fragmentation even though pretreatment effects become blurred after cycling. Our study demonstrates that recarbonation conditions and crystal-structure controlled diffusion are important parameters to be considered in order to assess the efficiency of CO2 capture in the novel CaL concept.
Julio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.065
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced oxidation resistance of Ti(C,N)-based cermets containing Ta
Chicardi, E; Gotor, FJ; Cordoba, JMCorrosion Science, 84 (2014) 11-20
Show abstract ▽
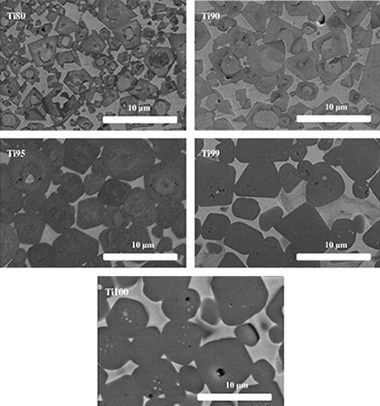
(TixTa1−x)(C0.5N0.5)–Co-based cermets with various Ta contents (x = 0, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2) were oxidized at 900 °C for 48 h in static air. A parabolic rate law, which is indicative of the formation of a protective oxide layer, was observed for all samples. The multi-layered oxide scale and the internal oxidation region that formed as the oxidation progressed toward the interior of the cermet specimens were characterized using XRD, SEM and EDS. The enhanced oxidation resistance achieved in cermets composed by a hard component with stoichiometry Ti0.95Ta0.05C0.5N0.5 may satisfy the optimal requirements for many applications in the field of cutting tools.
Julio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.03.007
- ‹ anterior
- 271 of 420
- siguiente ›














