Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales Coloidales
Revealing Structural Detail in the High Temperature La2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 Phase Diagram by Synchrotron Powder Diffraction and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Allix, M; Florian, P; Suchomel, MR; Becerro, AIJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 21523-21535
Show abstract ▽
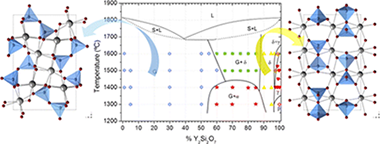
High resolution synchrotron powder XRD, 89Y CPMG NMR, and 139La MAS NMR spectroscopy have been applied to eventually draw the phase diagram of the La2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 system. The diagram presents a solid solubility region of G-(La,Y)2Si2O7, which extends to the La0.9Y1.1Si2O7 composition at any temperature of this study. Compositions richer in Y show two-phase domains, with G + α at T < 1450 °C and G + δ at T > 1450 °C. The Y-rich extreme is more complex, showing two solid solution regions of δ- and γ-(La,Y)2Si2O7 polymorphs which appear with increasing Y content, respectively. It is interesting to note that the La for Y substitution mechanism in the G-(La,Y)2Si2O7 polymorph is not homogeneous, but a preferential occupation of Y for the RE2 site is observed. Finally, the 89Y and 139La isotropic chemical shift values in G-(La,Y)2Si2O7 have been described here for the first time and assigned to the different RE crystallographic sites of the unit cell.
Octubre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp305777m
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
High-temperature plastic deformation mechanisms of ytterbium-doped barium cerate proton conductor
M. Jiménez-MelendoSolid State Ionics, 225 (2012) 286-290
Show abstract ▽
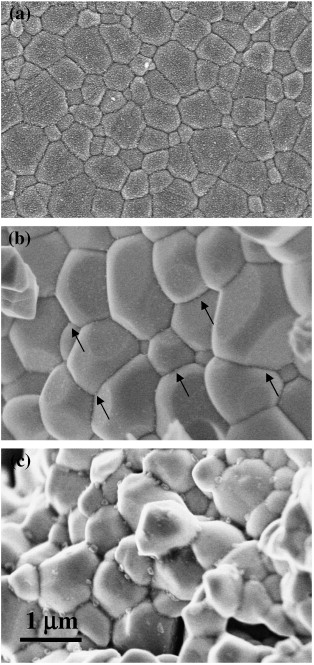
The enhanced proton conductivity exhibited by trivalent cation-doped barium cerate perovskites makes these materials excellent candidates for electrochemical applications, in particular as electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. These devices operate at elevated temperatures, where creep and other deformation processes influence the overall efficiency and lifetime. In this work, the high-temperature plastic deformation mechanisms of fine-grained 5 at.% Yb-doped BaCeO3 polycrystals produced by conventional solid-state reaction has been investigated by means of compressive tests at constant load between 1150 and 1250 °C in air. The creep curves show an unusual sigmoidal behavior, followed by extended steady states of deformation. Grain boundary sliding is the main deformation mechanism, characterized by a stress exponent n of 2, as found in other fine-grained superplastic ceramics and metals.
Octubre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2012.03.031
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Deactivation, reactivation and memory effect on Co–B catalyst for sodium borohydride hydrolysis operating in high conversion conditions
Arzac, GM; Hufschmidt, D; De Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, A; Sarmiento, B; Jimenez, MA; Jimenez, MMInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 37 (2012) 14373-14381
Show abstract ▽
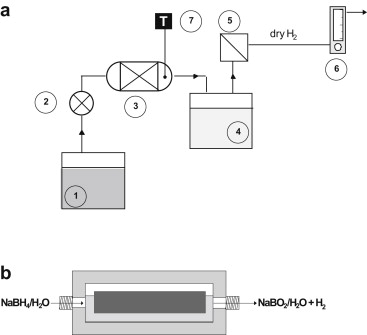
A system with a continuous reactor to produce hydrogen by sodium borohydride hydrolysis was designed and built. The purpose was to test a supported Co–B catalyst durability upon cycling and long life experiments in high conversion conditions. A Stainless Steel monolith was built and calcined to improve adherence. For comparison a Ru–B catalyst was tested upon cycling. Both Co–B and Ru–B catalysts are durable during 6 cycles and then deactivate. A known reactivation procedure has proven to be more effective for the Co–B than for the Ru–B catalyst. This is related to stronger adsorption of B–O based compounds on the Co–B catalyst which is reversible upon acid washing. For the Ru–B catalyst deactivation may be more related to particle agglomeration than to the adsorption of B–O based species. The continuous system enlarges the catalysts durability because of the continuous borate elimination at elevated temperatures.
Octubre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.06.117
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Chemical and microstructural characterization of (Y or Zr)-doped CrAlN coatings
Rojas, T. C.; El Mrabet, S.; Dominguez-Meister, S.; Brizuela, M.; Garcia-Luis, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, J. C.Surface and Coatings Technology, 211 (2012) 104-110
Show abstract ▽
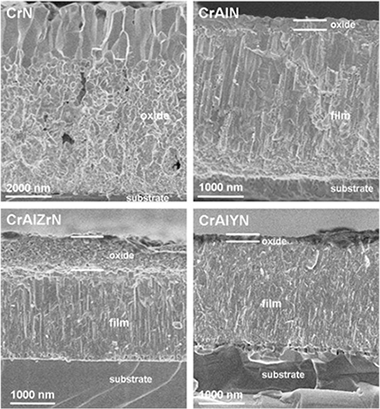
Magnetron sputtered chromium aluminium nitride films are excellent candidates for advanced machining and protection for high temperature applications. In this work CrAlN-based coatings including Y or Zr as dopants (≈ 2 at.%) are deposited by d.c. reactive magnetron sputtering on silicon substrates using metallic targets and Ar/N2 mixtures. The hardness properties are found in the range of 22–33 GPa with H/E ratios close to 0.1. The influence of the dopant element in terms of oxidation resistance after heating in air at 1000 °C is studied by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX). The microstructure and chemical bonding are investigated using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) and electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) respectively. The improvement in oxidation resistance as compared to pure CrN coating is manifested in the formation of a Al-rich outer layer that protects the underneath coating from oxygen diffusion. The best performance obtained with the CrAlYN film is investigated by in situ annealing of this sample inside the TEM in order to gain knowledge about the structural and chemical transformations induced during heating.
Octubre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.07.071
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Characterization of Mesoporous Thin Films by Specular Reflectance Porosimetry
Hidalgo, N; Lopez-Lopez, C; Lozano, G; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HLangmuir, 28 (2012) 13777-13782
Show abstract ▽
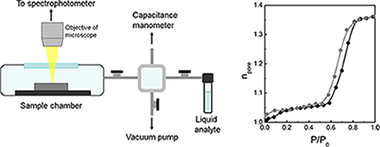
The pore size distribution of mesoporous thin films is herein investigated through a reliable and versatile technique coined specular reflectance porosimetry. This method is based on the analysis of the gradual shift of the optical response of a porous slab measured in quasi-normal reflection mode that occurs as the vapor pressure of a volatile liquid varies in a closed chamber. The fitting of the spectra collected at each vapor pressure is employed to calculate the volume of solvent contained in the interstitial sites and thus to obtain adsorption–desorption isotherms from which the pore size distribution and internal and external specific surface areas are extracted. This technique requires only a microscope operating in the visible range attached to a spectrophotometre. Its suitability to analyze films deposited onto arbitrary substrates, one of the main limitations of currently employed ellipsometric porosimetry and quartz balance techniques, is demonstrated. Two standard mesoporous materials, supramolecularly templated mesostructured films and packed nanoparticle layers, are employed to prove the concept proposed herein.
Octubre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/la3025793
- ‹ anterior
- 320 of 422
- siguiente ›














