Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Mechanism of complete n-hexane oxidation on silica supported cobalt and manganese catalysts
Todorova, S; Naydenov, A; Kolev, H; Holgado, JP; Ivanov, G; Kadinov, G; Caballero, AApplied Catalysis A-General, 413-414 (2012) 43-51
Show abstract ▽
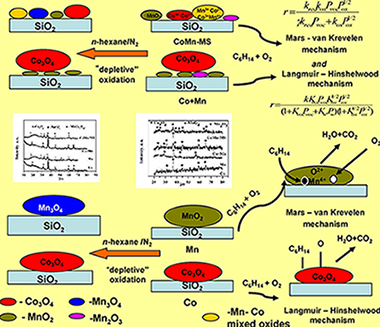
Mono- and bi-component cobalt and manganese samples were prepared by impregnation of silica with aqueous solutions of Co(NO3)2·6H2O and/or Mn(NO3)2·6H2O. The bi-component samples were obtained by a common solution of Co- and Mn nitrates (CoMn-MS) or by deposition of cobalt on calcined Mn sample (Co + Mn). The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), temperature programmed reduction (TPR), Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), elemental analysis and tested in reaction of complete n-hexane oxidation. It was observed that the well crystalline cobalt oxide partially covers poorly crystalline manganese oxide in the Co + Mn catalysts, while finely divided oxides (MnO2 and Mn2O3, Co3O4) are present on the surface of the (CoMn-MS) sample. Four Langmuir–Hinshelwood and two Mars–van Krevelen models were fitted with the experimental data from the catalytic tests. According to the model calculations and results from instrumental methods, the reaction pathway over single component manganese and bi-component Co-Mn catalysts proceeds through Mars–van Krevelen mechanism (the oxidation of the catalyst surface being the rate determining step), while Langmuir–Hinshelwood mechanism is more probable for the Co sample. A considerable increase in activity for the sample obtained from a mixed solution is explained by low crystallinity, simultaneous presence of Mn4+–Mn3+ and enrichment of the surface in oxygen species.
Enero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.10.041
Redox and catalytic properties of CuO/CeO2 under CO + O2 + NO: Promoting effect of NO on CO oxidation
Martinez-Arias, A.; Hungria, A. B.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Anderson, J. A.; Conesa, J. C.; Munuera, G.; Soria, J.Catalysis Today, 180 (2012) 81-87
Show abstract ▽
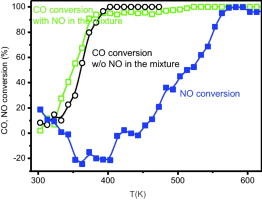
A CuO/CeO2 catalyst has been studied with respect to its catalytic activity for CO oxidation under stoichiometric conditions employing either O2 or O2–NO mixture as oxidants. The obtained results are rationalised on the basis of analysis of redox properties upon interaction with CO and O2–NO by EPR as well as by redox/catalytic analysis by operando-DRIFTS. These provide useful insight into the processes involved during NO reduction, for which two well differentiated steps associated to a change in the type of active centres during the course of the reaction are evidenced. Nevertheless, the most interesting result is related to observation of a novel promoting effect of NO on CO oxidation. This is explained mainly on the basis of DRIFTS results and appears to be associated with phenomena of adsorption/desorption of NOx species at interfacial positions which apparently activate such interfacial region allowing formation of greater amounts of active reduced copper centres in the presence of NO.
Enero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.02.014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Characterisation of ternary TixV1-xNy nitride prepared by mechanosynthesis
Roldan, MA; Alcala, MD; Real, CCeramics Intenational, 38 (2012) 687-693
Show abstract ▽
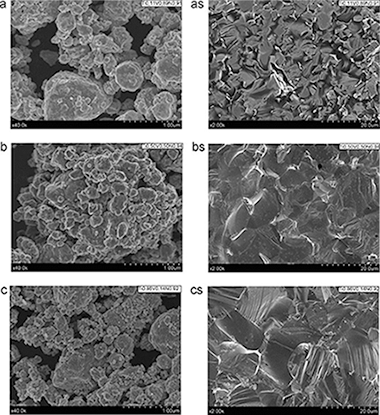
In the present manuscript the authors have systematically investigated the composition and microstructure of a series of ternary nitrides (TixV1-xNy) (0.0 <= x <= 1.0) prepared by mechanosynthesis, using XRD, SEM, EELS, XAS and TGA. The ternary titanium-vanadium nitride (TixV1-xNy) has been obtained in all range of compositions by the mechanical treatment of the two metals under nitrogen pressure in a planetary mill with a maximum milling time of 3 h and without any post-heating treatment. The materials' microhardnesses were measured after sinterisation and compared to those reported in the literature for these types of materials. When compared with the previously reported data for bulk samples, these values are similar or higher for compositions within the range x = 0.5 to x = 0.77 (TixV1-xN).
Enero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.07.057
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Effect of hydrothermal treatment on structural and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 synthesized by sol-gel method
Melian, EP; Diaz, OG; Rodriguez, JMD; Colon, G; Navio, JA; Pena, JPApplied Catalysis A-General, 411 (2012) 153-159
Show abstract ▽
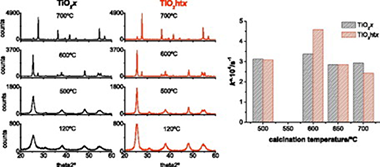
TiO 2 nanoparticles have been prepared by sol-gel precipitation and further hydrothermal treatment. In this way, the effect of the hydrothermal treatment on the structural properties and photocatalytic activity of sol-gel synthesized catalysts has been investigated. These catalysts have been produced by hydrolysis of a mixture of isopropanol-titanium tetraisopropoxide (iPrOH-TiiP). The prepared photocatalysts were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD), surface area analysis (BET), transmission microscopy (TEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TG), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, diffuse reflectance, sedimentability analysis and aggregate size study. Besides, the structural evolution with the temperature of the photocatalysts treated or not hydrothermally was studied. It was observed that the calcination produces approaching between the characteristics of both sets of photocatalysts. The photocatalytic activity of the obtained photocatalysts was investigated, using phenol as a model pollutant. The calcination temperature is the most remarkable factor that can affect the ultimate photocatalytic activity of the prepared photocatalysts. However, the hydrothermal treatment previous to calcination led to obtain photocatalysts which exhibit larger photocatalytic activity than their homologous photocatalysts without hydrothermal treatment. The obtained photocatalyst TiO 2ht600 exhibits the same photocatalytic activity per surface area than the commercial TiO 2 Degussa P25 but with much faster sedimentability.
Enero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2011.10.033
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Aluminum incorporation in alpha-PbO2 type TiO2 at pressures up to 20 GPa
Escudero, A; Langenhorst, FPhysics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 190 (2012) 87-94
Show abstract ▽
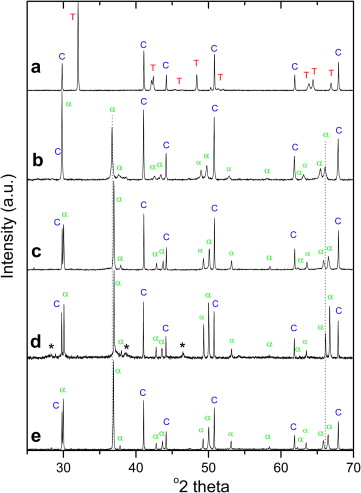
Aluminum incorporation into the high pressure polymorph of TiO2 with the structure of alpha-PbO2 has been studied from 10 to 20 GPa and 1300 degrees C by XRD, high-resolution Al-27 MAS-NMR and TEM. Al-doped alpha-PbO2 type TiO2 can be recovered at atmospheric pressure. Al2O3 solubility in alpha-PbO2 type TiO2 increases with increasing the synthesis pressure. The alpha-PbO2 type TiO2 polymorph is able to incorporate up to 35 wt.% Al2O3 at 13.6 GPa and 1300 degrees C, being the substitution of Ti4+ by Al3+ on normal octahedral sites and the formation of oxygen vacancies the mechanism of solubility. The transition to the higher pressure TiO2 polymorph with the ZrO2 baddeleyite structure, akaogiite, has not been observed in the quenched samples at room pressure. The microstructure of the recovered sample synthesized at 16 GPa and 1300 degrees C points to the existence of an intermediate non-quenchable aluminum titanium oxide phase at these conditions.
Enero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.pepi.2011.11.002
- ‹ anterior
- 340 of 422
- siguiente ›














