Artículos SCI
2009
2009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Integration of methanol steam reforming and combustion in a microchannel reactor for H2 production: A CFD simulation study
Arzamendi, G; Dieguez, PM; Montes, M; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Gandia, LMCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 25-31 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.034

Abstract
A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of the thermal integration of the steam reforming of methanol (SRM) and the combustion of methanol in a catalytic microchannel reactor is presented. This issue is of interest for in situ H2 production for portable power units based on low-temperature PEM fuel cells. Three-dimensional simulations have been carried out under relevant conditions for the SRM reaction that have shown that microreactors allow achieving complete methanol reforming and combustion at space velocities as high as 50,000 h−1, with selectivities for H2 above 99% at relatively low temperatures in the 270–290 °C range.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.034
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Cationic (V, Mo, Nb, W) doping of TiO2–anatase: A real alternative for visible light-driven photocatalysts
Kubacka, A; Colon, G; Fernandez-Garcia, MCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 286-292 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.028

Abstract
In this article we investigate the structure–activity link of anatase-type Ti–M (M = V, Mo, Nb, and W) mixed oxides used for toluene photo-oxidation under sunlight-type excitation. An analysis of the local and long-range structural and electronic characteristics of the mixed oxides show that only structurally highly homogeneous anatase-type oxides with electronic properties exclusively leading to a band gap decrease drive to efficient visible light-driven photocatalysts. Within our microemulsion preparation method, this only occurs for Ti–V and Ti–W series of samples. The isoelectronic (V4+) substitution of Ti4+ ions at the anatase lattice is characterized by a low solubility limit (ca. 2.5 at. %), and drives to a limited modification of the band gap and to a moderate enhancement of the photo-activity with respect to bare titania reference systems. W presence at anatase cation positions occurs with concomitant presence of cation vacancies derived by the charge imbalance between the W6+ and Ti4+ species. A unique W-vacancy local arrangement is detected by the structural characterization, leading to both an important band gap decrease and enhancement of the photo-activity upon sunlight excitation.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.028
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Molding with nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals: a route to flexible and transferable Bragg mirrors of high dielectric contrast
Calvo, ME; Sobrado, OS; Lozano, G; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry, 19 (2009) 3144-3148 DOI: 10.1039/B902090J
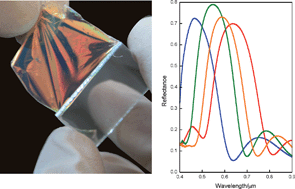
Abstract
Self-standing, flexible Bragg mirror films of high refractive index contrast and showing intense and wide Bragg peaks are herein presented. Nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals are used as templates to infiltrate a polymer, which provides the multilayer with mechanical stability while preserving the dielectric contrast existing in the mold. Such films can be lifted off the substrate and used to coat another surface of arbitrary shape.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1039/B902090J
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting angles and photocatalytic activities of illuminated TiO2 thin films
Rico, V; Romero, P; Hueso, JL; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARCatalysis Today, 143 (2009) 347-354 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.037

Abstract
TiO2 thin films have been prepared by physical vapour deposition (PVD) and plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD) to study the UV-induced photo-activity of this material. Wetting angle variations and photo-catalytic activity for the degradation of dyes upon UV illumination have been compared for thin films with different crystalline structure (amorphous, rutile and anatase), microstructure (columnar, compact, etc.) and porosities as estimated from the values of their refraction indices and their direct assessment with a quartz crystal monitor. The surface of the thin films became superhydrophilic upon UV light irradiation and then it recovered its original state by keeping the samples in the dark. Wetting angle decays follow very similar kinetics for amorphous and crystalline films, independently of their actual porosities. By contrast the photo-catalytic activity was very dependent on the crystalline structure of the films (anatase > rutile > amorphous) and on their porosities. The different behaviour depicted by the films with regard to these two properties suggests that they respond to different though related mechanisms and that they cannot be considered as equivalent when trying to prove the photo-activity of TiO2.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2008.09.037
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
High deposition rates of uniform films in tetramethylsilane-based plasmas generated by elementary microwave sources in matrix configuration
Latrasse, L; Lacoste, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Bes, A; Rayar, M; Pelletier, JSurface and Coatings Technology, 203 (2009) 2343-2349 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.02.121
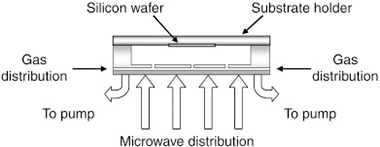
Abstract
Plasma scaling up can be achieved by distributing elementary microwave plasma sources on planar rectangular networks. These so-called matrix plasmas can generate uniform sheets of plasma over a wide argon pressure range, from 7.5 to 750 Pa, with densities between 1012 and 1013 cm− 3. In order to estimate the capabilities of matrix plasmas for PACVD processing in terms of deposition rate and uniformity, SiOCH and SiNCH films were deposited using TMS (tetramethylsilane), as the organic gas precursor of silicon, mixed with oxygen or nitrogen flows. Plasmas of O2 / TMS and N2 / TMS gas mixtures can be sustained between 5 and 25 Pa. Variations in the deposition rate as a function of microwave power and nitrogen partial pressure are reported. Thickness uniformity of SiOCH and SiNCH films was measured across a silicon wafer. The obtained deposition rates exceed 1.3 μm/min and the films present a uniformity better than 5% on 75 mm diameter silicon wafers. Composition of the films has also been analyzed by XPS as a function of process parameters: microwave input power, composition of gas mixture, and N2 partial pressure. In particular, these analyses have shown a very low yield of nitrogen incorporation when using N2 gas as nitrogen precursor and high Si and Si–Si bonding contents in the films, probably due to a strong fragmentation of the TMS precursor in the high density plasma.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.02.121
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Thermal Stability and Oxidation Resistance of Nanocomposite TiC/a-C Protective Coatings
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Gago, R; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCPlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) S462-S467 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931002

Abstract
Nanocomposite films composed by small crystallites of hard phases embedded in an amorphous lubricant matrix have been extensively studied as protective coatings. These kinds of coatings have often to work in extreme environments, exposed to high temperatures (above 800–900 °C), and/or oxidizing/corrosive atmospheres, which may resist. As a result, it is important to study the behavior of such coatings at high temperatures (thermal stability) and in the presence of oxygen (oxidation resistance). In this sense, we have selected a TiC/a-C nanocomposite coating with good mechanical and tribological properties in order to do several thermal tests under three different environments: high vacuum (10−6 mbar), low vacuum (10−1 mbar), and air. Our observations allow us to establish that the film microstructure is stable at least up to 1 000 °C in high vacuum. When oxygen is present, the practical temperature of use is reduced at 700 °C (low partial pressure) and 300 °C (air) by formation of Ti oxides and C removal.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200931002
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
AISI 304 Austenitic stainless steels monoliths for catalytic applications
Martinez, LM; Sanz, O; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 148 (2009) 191-200 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.030

Abstract
The thermal treatments of austenitic stainless steels monoliths were studied in order to generate a highly homogeneous and rough oxide scale strongly attached to the base alloy, which will subsequently ensure the good adherence of the catalysts. In this work it has been shown that the morphology, integrity and homogeneity of the scale are strongly influenced by the temperature and time of treatment. Washcoating method was used to deposit on the monolith surface a Au/CeO2 catalyst. The drying procedure turned out to be the most critical variable for the adherence and homogeneity of the catalytic ceria layer, while the ceria colloid concentrations in the starting aqueous dispersion seems to have only a threshold effect. The monolithic reactors containing Au/CeO2 layers are active in the oxidation of CO.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.12.030
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Molecular dynamics simulation of the effect of pH on the adsorption of rhodamine laser dyes on TiO2 hydroxylated surfaces
Hamad, S; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Barranco, A; Mejias, JA; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMolecular Simulation, 35 (2009) 1140-1151 DOI: 10.1080/08927020903108083
Abstract
We have carried out a study of adsorption, on the (1 0 1) surface of anatase TiO2, of two industrially relevant rhodamine molecules [rhodamine 6G (R6G) and rhodamine 800 (R800)] employing molecular dynamics. These theoretical studies have shown that R6G must adsorb on surfaces under basic conditions. Moreover, the adsorption of this molecule shows a strong dependence upon the pH of the system, i.e. under basic conditions the adsorption energy is quite high, under neutral conditions the adsorption energy is lower and under acidic conditions an even lower adsorption energy indicates that there must be very little adsorption under such conditions. By contrast, for R800, there is little dependence of the adsorption energy upon the pH, suggesting that the amount of adsorption of these molecules is little affected by this parameter. These theoretical results are in qualitative agreement with the experimental results consisting of the incorporation of these dye molecules into porous thin films.
Mayo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1080/08927020903108083
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Surface nanostructuring of TiO2 thin films by ion beam irradiation
Romero-Gomez, P; Palmero, A; Yubero, F; Vinnichenko, M; Kolitsch, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARScripta Materialia, 60 (2009) 574-577 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.12.014

Abstract
This work reports a procedure to modify the surface nanostructure of TiO2 anatase thin films through ion beam irradiation with energies in the keV range. Irradiation with N+ ions leads to the formation of a layer with voids at a depth similar to the ion-projected range. By setting the ion-projected range a few tens of nanometers below the surface of the film, well-ordered nanorods appear aligned with the angle of incidence of the ion beam. Slightly different results were obtained by using heavier (S+) and lighter (B+) ions under similar conditions.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.12.014
Sonication induced redox reactions of the Ojén (Andalucía, Spain) vermiculite
Poyato, J; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Ramirez-Valle, V; Lerf, A; Wagner, FEUltrasonics Sonochemistry, 16 (2009) 570-576 DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.12.009
Abstract
Sonication in a 1:1 mixture (volume ratio) of water and concentrated H2O2 (30%) is a soft method for particle size reduction of phyllosilicate minerals like vermiculites. Repeated sonication causes a particle size reduction to about 70 nm for the Santa Olalla and to 45 nm for the Ojén-vermiculite. In this context the question arises whether the strong oxidising effect of the hydrogen peroxide affects the oxidation state of the iron in the vermiculites. Therefore, the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio before and after sonication was determined by means of Mössbauer spectroscopy. Whereas this ratio was found to remain almost constant in the Santa Olalla vermiculite, it increased from 0.79 to 0.85 in case of the Ojén sample. In the latter case, the oxidation is accompanied by a decrease of the layer charge.
Surprisingly, sonication in pure water leads to a decrease of the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio in the case of the Ojén-vermiculite, i.e., to an increase of the Fe2+ fraction to roughly twice the value before sonication. Again the Fe3+/Fetotal ratio of the Santa Olalla vermiculite remains unchanged. The surface area SBET of the reduced Ojén-vermiculite amounts to 50 m2/g, which is close to the value obtained in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. The results presented should be taken as a warning that particle size reduction by sonication may be accompanied by a change of the redox state and the layer charge of the material.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.12.009
Comparison between micro-Raman and micro-FTIR spectroscopy techniques for the characterization of pigments from Southern Spain Cultural Heritage
Franquelo, ML; Duran, A; Herrera, LK; de Haro, MCJ; Perez-Rodriguez, JLJournal of Molecular Structure, 924-926 (2009) 404-412 DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.11.041
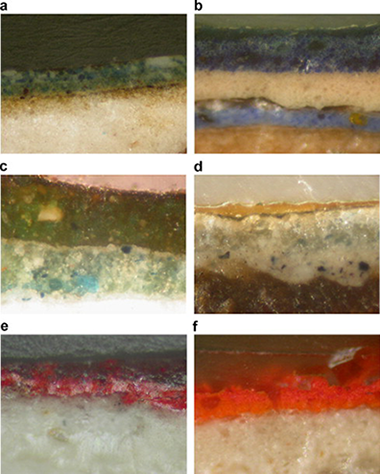
Abstract
An extensive overview of the complementary use of micro-FTIR and micro-Raman spectroscopy in the Cultural Heritage studies is described in this work.
The samples have been prepared using the cross-section technique. This technique allows the examination of a large portion of a single paint layer in its original condition. A variety of pigments from samples belonging principally to the Cultural Heritage of Southern Spain were characterized by micro-Raman spectroscopy using visible excitation sources and micro-FTIR spectroscopy. The pigments studied comprise blue (azurite, ultramarine blue, Prussian blue), red (vermilion, haematite, red ochre, red lead, etc.), ochre and yellow (goethite, orpiment, realgar, etc.), green (malachite, copper resinate), and white (calcite, gypsum, white lead, titanium white, barite, lithopone) pigments, among others. An orientation is given for their appropriate and unequivocal characterization. Characterization by micro-FTIR and micro-Raman presents difficulties with some pigments. In these cases, analysis by EDX solves most of these doubts. The combined use of both spectroscopic techniques, together with SEM–EDX microanalysis, provides one of the most useful methods in the characterization (and possible dating) of materials used in Cultural Heritage.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.11.041
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Co3O4 + CeO2/SiO2 Catalysts for n-Hexane and CO Oxidation
Todorova, S; Kadinov, G; Tenchev, K; Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Pereniguez, RCatalysis Letters, 129 (2009) 149-155 DOI: 10.1007/s10562-008-9805-x
Abstract
Two-component Co–Ce samples deposited onto SiO2 have been prepared, characterized and tested in the reaction of complete n-hexane and CO oxidation. It was established that cerium enhanced the catalytic activity of cobalt in the reaction of n-hexane oxidation, although this depended on the sequence of cobalt and cerium introduction. Co-impregnation of Co and Ce resulted in a close interaction between Co3O4 and CeO2 leading to more surface oxygen species available and, therefore, a better reactivity.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1007/s10562-008-9805-x
Study of ground and unground leached vermiculite
Maqueda, C; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Subrt, J; Murafa, NApplied Clay Science, 44 (2009) 178-184 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.01.019

Abstract
Grinding of clays modifies their surfaces and can significantly affect their leaching behaviour. The acid reaction of vermiculite from Santa Olalla (Huelva, Spain) with HCl at various concentrations was affected by grinding and acid concentration. The acid leaching of ground vermiculite for 3 min with 1 M HCl solution at 80 °C for 24 h removed MgO and Al2O3 almost completely, leaving a residue containing SiO2 and Fe2O3. X-ray diffraction analysis showed the presence of akaganeite (β-FeOOH) and an amorphous phase (silica). Porosity studies showed a very high specific surface area for ground samples compared with unground vermiculite samples, attributed to the presence of iron in the residue coming from structural iron. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) confirmed the presence of iron oxyhydroxides embedded in the silica material. The particle morphology of the iron oxides corresponded well to akaganeite microcrystals precipitated from solution. The leached vermiculite residue also contained Cl− and a small amount of Ti4+, which were accumulated into the akaganeite microcrystals.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.01.019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold/hydroxyapatite catalysts: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity to CO oxidation
Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B-Environmental, 87 (2009) 245-251 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.016
Abstract
This work reports the synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity for CO oxidation of gold catalysts supported on calcium hydroxyapatite. On both, the hydroxyapatite support and the gold-supported hydroxyapatite catalyst, the CO conversion shows a peak near 100% of conversion at room temperature. The generation of structural vacancies by interaction of CO with the solid provokes the formation of peroxide species in the presence of gaseous oxygen, which seems to be responsible of this high conversion of CO at room temperature. Moreover, the influence of the pre-treatment temperature on the activity has been observed and related with the elimination of carbonate species and the generation of structural defects in the apatite structure, which are able to modify the gold oxidation state.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.09.016
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological carbon-based coatings: An AFM and LFM study
Martinez-Martinez, D; Kolodziejczyk, L; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Fernandez, ASurface Science, 603 (2009) 973-979 DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2009.01.043

Abstract
In this work some carbon-based coatings were studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and lateral force microscopy (LFM) techniques in order to evaluate their microstructure and friction properties at the micro and nanoscale. With this aim, four samples were prepared by magnetron sputtering: an amorphous carbon film (a–C), two nanocomposites TiC/a–C with different phase ratio (∼1:1 and ∼1:3) and a nanocrystalline TiC sample. Additionally, a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and an amorphous hydrogenated carbon coating (a-C:H) were included to help in the evaluation of the influence of the roughness and the hydrogen presence respectively. The topography (roughness) of the samples was studied by AFM, whereas LFM was used to measure the friction properties at the nanoscale by two different approaches. Firstly, an evaluation of possible friction contrast on the samples was done. This task was performed by subtraction of forward and reverse images and lately confirmed by the study of lateral force profiles in both directions and the histograms of the subtraction images. Secondly, an estimation of the average friction coefficient over the analysed surface of each sample was carried out. To take into account the tip evolution/damaging, mica was used as a reference before and after each sample (hereafter called sandwich method), and samples-to-mica friction ratios were calculated. The LFM was shown to be a useful tool to characterise a mixture of phases with different friction coefficients. In general, the friction ratios seemed to be dominated by the amorphous carbon phase, as it was impossible to distinguish among samples with different proportions of the amorphous phase (friction ratios between 1.5 and 1.75). Nevertheless, it could be concluded that the differences in friction behaviour arose from the chemical aspects (nature of the phase and hydrogen content) rather than surface characteristics, since the roughness (Ra values up to 5.7 nm) does not follow the observed trend. Finally, the Ogletree method was employed in order to calibrate the lateral force and estimate the friction coefficient of our samples. A good agreement was found with macroscopic and literature values going from ∼0.3 for TiC to ∼0.1 for pure carbon.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2009.01.043
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Synthesis and Characterization of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 Mixed Oxides and Their Catalytic Activities for CO Oxidation
Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2012) 5629-5635 DOI: 10.1021/jp8092989

Abstract
A series of Ce1−xEuxO2−x/2 mixed oxides was synthesized by coprecipitation. The solids were characterized by means of XRF, SBET, XRD, UV−vis, and Raman techniques, and their catalytic activities toward CO oxidation were tested. A solid solution, with CeO2 F-type structure, is formed for europium contents (measured as Eu2O3 by XRF) ≤20% wt. For higher contents, the solid solution is not formed, but a physical mixture is detected. The existence of oxygen vacancies in the solids with Eu2O3 contents between 3 and 17% wt was demonstrated by the presence of bands at 532 and 1275 cm−1 in their Raman spectra. The catalytic performances of the solids correlate with the amount of these punctual defects in the solid solution.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/jp8092989
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Reactividad de Sólidos
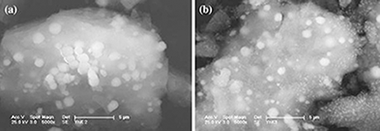
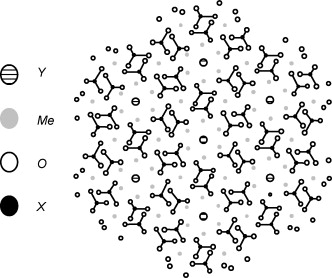
Properties of Ti(C,N) cermets synthesized by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Cordoba, JM; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Aviles, MA; Alcala, MD; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 29 (2012) 1173-1182 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.08.019
Abstract
The properties of TiCxN1−x/(Ni or Co) cermets sintered by a pressureless method from powder mixtures, and obtained for the first time by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction process (MSR), were studied. The hardness, toughness, friction and wear coefficients, and oxidation resistance were determined. It was shown that cermets obtained from powdered materials synthesized in one single MSR step possessed improved mechanical properties, similar to those obtained in cermets with more complex bulk compositions. Higher wear resistances were observed in cermets whose hard phase was richer in carbon. The oxidation resistance of the cermets depended primarily on the binder composition. This resistance was better for those cermets with cobalt as the binder. Superior oxidation resistance was displayed when small amounts of W or Mo were incorporated into the binder.
Abril, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.08.019
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study by grazing incident diffraction and surface spectroscopy of amalgams from ancient mirrors
Herrera, LK; Duran, A; Franquelo, ML; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Espinos, JP; Rubio-Zuazo, J; Castro, GR; Justo, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLCentral European Journal of Chemistry, 7 (2009) 47-53 DOI: 10.2478/s11532-008-0089-1

Abstract
Characterization of four amalgam surfaces, with different alteration degrees from Andalusia historical mirrors, has been carried out by grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD), and other spectroscopic techniques (SEM/EDX, XPS, and REELS). The combination of all these techniques allows determining the corrosion state of the amalgams. The results show that the amalgams are composed in all cases of a binary alloy of tin and mercury. As mercury has high vapour pressure at RT, it slowly segregates and eventually evaporates, it leaves finely divided particles of tin that easily can be oxidize, forming tin monoxide (SnO) and tin dioxide (SnO2). In one of the samples, most of the amalgam remains unoxidized, since Hg0.1Sn0.9 and metallic Sn phases are the major components; in two other samples, Hg0.1Sn0.9 and Sn phases are not detected while SnO2 and SnO phases appear. Finally, in the last studied sample, only SnO2 phase is detected. The surface analyses of these samples by XPS show that, for most of them an unique chemical species (Sn4+) is found.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.2478/s11532-008-0089-1
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Pillared clays with Al–Fe and Al–Ce–Fe in concentrated medium: Synthesis and catalytic activity
Sanabria, NR; Centeno, MA; Molina, R; Moreno, SApplied Catalysis A-General, 356 (2009) 243-249 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.01.013

Abstract
This paper proposes a new methodology for the modification of clays with the mixed Al–Fe and Al–Ce–Fe systems, which involves the synthesis of solid polymeric precursors and their use as pillaring agents in the modification of clays. The process of intercalation of clay with Al13, Al13 + Fe and Al13 + Ce + Fe nitrate was performed using ultrasound. The pillaring agents Al13, Al13 + Fe and Al13 + Ce + Fe were characterized by XRF, XRD, SEM and 27Al NMR techniques, and pillared clays were characterized by XRF, XRD and N2 adsorption to 77 K. The catalytic properties of pillared clays were evaluated using catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of phenol in dilute aqueous medium, demonstrating activity comparable to that of solids modified by the conventional method.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.01.013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Water plasmas for the revalorisation of heavy oils and cokes from petroleum refining
Hueso, JL; Rico, VJ; Cotrino, J; Jimenez-Mateos, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AREnvironmental Science & Technology, 43 (2009) 2557-2562 DOI: 10.1021/es900236b

Abstract
This work investigates the possibility of using plasmas to treat high boiling point and viscous liquids (HBPVL) and cokes resulting as secondary streams from the refining of oil. For their revalorisation, the use of microwave (MW) induced plasmas of water is proposed, as an alternative to more conventional processes (i.e., catalysis, pyrolysis, combustion, etc.). As a main result, this type of energetic cold plasma facilitates the conversion at room temperature of the heavy aromatic oils and cokes into linear hydrocarbons and synthesis gas, commonly defined as syngas (CO + H2 gas mixture). The exposure of the coke to this plasma also facilitates the removal of the sulfur present in the samples and leads to the formation on their surface of a sort of carbon fibers and rods network and new porous structures. Besides, optical emission measurements have provided direct evidence of the intermediates resulting from the fragmentation of the heavy oils and cokes during their exposure to the water plasma. Furthermore, the analysis of the mass spectra patterns suggests a major easiness to break the aromatic bonds mainly contained in the heavy oils. Therefore, an innovative method for the conversion of low value residues from oil-refining processes is addressed.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/es900236b
Materiales Avanzados
Effect of the grinding mechanical treatment on the pyrophilite textural properties
Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 48 (2009) 59-68 DOI: ---
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Wetting Angles on Illuminated Ta2O5 Thin Films with Controlled Nanostructure
Rico, V; Borras, A; Yubero, F; Espinos, JP; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 3775-3784 DOI: 10.1021/jp805708w

Abstract
Ta2O5 thin films with different nanostructure and surface roughness have been prepared by electron evaporation at different angles between the evaporation source and the substrates. Large variation of refraction indexes (n) from 1.40 to 1.80 were obtained by changing the geometry of evaporation and/or by annealing the evaporated films at increasing temperatures up to 1000 °C to make them crystalline. Very flat and compact thin films (n = 2.02) were also obtained by assisting the growth by bombardment with O2+ ions of 800 eV kinetic energy. A similar correlation has been found between the wetting contact angle of water and the roughness of the films for the evaporated and evaporated + annealed samples, irrespective of their procedure of preparation and other microstructural characteristics. When the films were illuminated with UV light of h > Eg = 4.2 eV (Eg, band gap energy of Ta2O5), their surface became superhydrophilic (contact angle < 10°) in a way quite similar to those reported for illuminated TiO2 thin films. The rate of transformation into the superhydrophilic state was smaller for the crystalline than for the amorphous films, suggesting that in Ta2O5 the size of crystal domains at the surface is an important parameter for the control of this kinetics. Changes in the water contact angle on films illuminated with visible light were also found when they were subjected to implantation with N2+ ions of 800 eV kinetic energy. The origin of this photoactivity is discussed in terms of the electronic band gap states associated with the nitrogen-implanted atoms. The possibility of preparing antireflective and self-cleaning coatings of Ta2O5 is discussed.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/jp805708w
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Duplex SiCN/DLC coating as a solution to improve fretting—Corrosion resistance of steel
Pech, D; Schupp, N; Steyer, P; Hack, T; Gachon, Y; Heau, C; Loir, AS; Sanchez-Lopez, JCWear, 266 (2009) 832-838 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.12.007

Abstract
Fretting corrosion damages are commonly observed when two metallic bodies, which are in contact with each other, are subjected to oscillatory motions of low amplitude. Such kind of degradation mode is often responsible for limited durability of aeronautical joints. In the present paper, a multifunctional duplex coating based on Si–C–N and diamond-like carbon (DLC) materials, combining corrosion resistance and good tribological properties is described. Amorphous hydrogenated SiC, SiCN, SiC/DLC and SiCN/DLC were deposited on steel substrates by a plasma assisted chemical vapour deposition (PACVD) technique, using tetramethylsilane (TMS), ammonia (NH3) or acetylene (C2H2) as gas precursors. Nitrogen incorporation has shown to improve the corrosion protection ability of SiC coatings. The corrosion behaviour and the tribological performance in aqueous media of SiCN/DLC coating have therefore been investigated. A test rig has been designed to validate the fretting resistance of this duplex coating for aeronautic applications. It was found that the combination of a SiCN-based PACVD sublayer with a DLC topcoat could provide an enhanced solution to withstand both fretting and corrosion.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.12.007
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth Mechanism and Chemical Structure of Amorphous Hydrogenated Silicon Carbide (a-SiC:H) Films Formed by Remote Hydrogen Microwave Plasma CVD From a Triethylsilane Precursor: Part 1
Wrobel, AM; Walkiewicz-Pietrzykowska, A; Ahola, M; Vayrynen, IJ; Ferrer-Fernandez, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARChemical Vapor Deposition, 15 (2009) 39-46 DOI: 10.1002/cvde.200806726
Abstract
Amorphous hydrogenated silicon carbide (a-SiC:H) films are produced by remote microwave hydrogen plasma (RHP)CVD using triethylsilane (TrES) as the single-source precursor. The reactivity of particular bonds of the precursor in the activation step is examined using tetraethylsilane as a model compound for the RHP-CVD experiments. The susceptibility of a TrES precursor towards film formation is characterized by determining the yield of RHP-CVD and comparing it with that of the trimethylsilane precursor. The effect of substrate temperature (Ts) on the rate of the RHP-CVD process, chemical composition, and chemical structure of the resulting a-SiC:H films is reported. The substrate temperature dependence of the film growth rate implies that film growth is independent of the temperature and RHP-CVD is a mass transport-limited process. The examination of the a-SiC:H films, performed by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), elastic recoil detection analysis (ERDA), and Fourier transform infrared absorption spectroscopy (FTIR), reveals that the increase in the substrate temperature from 30 °C to 400 °C causes the elimination of organic moieties from the film and the formation of a Si-carbidic network structure. On the basis of the results of the structural study, the chemistry involved in film formation is proposed.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1002/cvde.200806726
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Self-lubricating Ti–C–N nanocomposite coatings prepared by double magnetron sputtering
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Justo, A; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSolid State Sciences, 11 (2009) 660-670 DOI: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2008.10.017
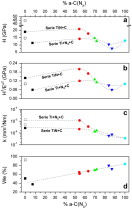
Abstract
This paper is devoted to the development of Ti(C,N)-based nanocomposite protective coatings consisting of nanocrystals of a hard phase (TiN or TiCxNy) embedded in an amorphous carbon-based matrix (a-C or a-CNx). The objective here is the achievement of a good compromise between the mechanical and tribological properties by the appropriate control of the hard/soft phase ratio and the microstructural characteristics of the film. To achieve this purpose, dual magnetron sputtering technique was employed following two different strategies. In the first one, we use Ti and graphite targets and Ar/N2 gas mixtures, while in the second case, TiN and graphite targets are sputtered in an Ar atmosphere. By changing the sputtering power applied to each magnetron, different sets of samples are prepared for each route. The effect of the bias voltage applied to the substrate is also studied in some selected cases. The mechanical and tribological properties of the films are characterized and correlated with the microstructure, crystallinity and phase composition. The establishment of correlations enables the development of advanced coatings with tailored mechanical and tribological properties for desired applications.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2008.10.017
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Cutin synthesis: A slippery paradigm
Heredia, A; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Dominguez, E; Benitez, JJBiointerphases, 4 (2009) P1-P3 DOI: 10.1116/1.3063816
Abstract
Despite its biological importance, the mechanism of construction of cutin, the polymer matrix of plant cuticles, has not yet been elucidated. Recently, progress on lipid barrier formation of polymers such as cutin and suberin has been recently reviewed by Pollard et al. In their review the authors state that the ubiquitous cutin is the least understood of the plant extracellular polymers and that major questions about cutin structure and its macromolecular assembly remain to be resolved. At the time this paper was being published our research group has developed a new hypothesis on plant cutin synthesis.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1116/1.3063816
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Redox chemistry of gold in a Au/FeOx/CeO2 CO oxidation catalyst
Penkova, A; Chakarova, K; Laguna, OH; Hadjiivanov, K; Saria, FR; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JACatalysis Communications, 10 (2009) 1196-1202 DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.01.014

Abstract
Calcination and evacuation of a Au/FeOx/CeO2 catalyst at 573 K leads to reduction of the deposited gold to metal. This metal state is stable under oxygen and only at 573 K some metal atoms are oxidized to Auδ+ sites (Au+ cations situated on metal gold particles). However, even at room temperature, gold is readily oxidized in a CO + O2 mixture producing, in addition to the Auδ+ sites, some isolated Au+ cations.
Marzo, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2009.01.014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis, Rietveld Analysis, and Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of X2-Sc2SiO5
Alba, MD; Chain, P; Gonzalez-Carrascosa, TJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 92 (2009) 487-490 DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02877.x
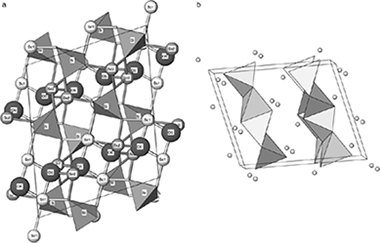
Abstract
Compounds containing rare earths are of increasing technological interest especially because of their unique mechanical, magnetic, electrical, and optical properties. Among them, rare earth oxyorthosilicates are attractive scintillators for γ- and X-ray spectroscopy and detection. However, there are many structural aspects of those compounds that are not clear. In this research, the structure parameters for Sc2Si2O5, X2-polymorph, have been refined from powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) data and the 29Si MAS NMR spectrum is reported for the first time. X2-Sc2SiO5 polymorph was synthesized by the sol–gel method and characterized by XRD and 29Si MAS NMR. The XRD pattern was indexed in a monoclinic unit cell with space group I2/c; the resulting unit cell parameters were a=9.9674(2) Å, b=6.4264(9) Å, c=12.0636(2) Å, and β=103.938(1)°. The 29Si MAS NMR spectrum showed a unique signal at −79.5 ppm, compatible with the unique Si crystallographic site in the unit cell. Finally, the band valence method has been applied to the calculation of a “shift parameter,” which is correlated with the NMR chemical shift.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02877.x
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Towards a full understanding of the growth dynamics and optical response of self-assembled photonic colloidal crystal films
Lozano, GS; Dorado, LA; Depine, RA; Miguez, HJournal of Materials Chemistry, 19 (2009) 185-190 DOI: 10.1039/b811955d
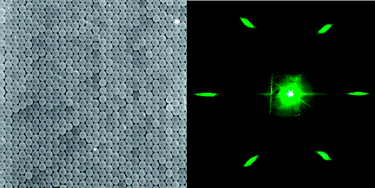
Abstract
Recent advances in the comprehension of the growth dynamics of colloidal crystal films opens the door to rational design of experiments aiming at fabricating lattices in which the density of intrinsic defects is minimized. Since such imperfections have a dramatic effect on scattered light of wavelength smaller than the lattice constant, the evaluation of the experimental optical response at those energy ranges, based on the comparison to rigorous calculations, is identified as the most sensitive guide to accurately evaluate the progress towards the actual realization of defect-free colloidal crystals.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1039/b811955d
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Phase separation of carboxylic acids on graphite surface at submonolayer regime
Alba, MD; Bickerstaffe, AK; Castro, MA; Clarke, SM; Medina, S; Millan, C; Orta, MM; Pavon, E; Perdigon, ACThe European Physical Journal Special Topics, 167 (2009) 151-156 DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2009-00951-6
Abstract
Mixing behaviour of solid crystalline monolayers adsorbed onto graphite from different mixtures of undecanoic and dodecanoic acids at submonolayer coverage has been investigated. X-ray diffraction measurements have been collected from a variety of compositions as a function of temperature. An extensive phase separation is found for all the compositions – the scattering patterns characteristic of the pure material crystalline structures being preserved across the entire composition range. The temperature dependence of the monolayer melting points and their depression is also clearly indicative of separation of the two surface components, in clear contrast to that expected if the two carboxylic acids mixed ideally in the monolayer.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2009-00951-6
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Preferential Adsorption from Binary Mixtures on Graphite: The n-Decane−n-Heptan-1-ol System
Alba, MD; Castro, MA; Clarke, S; Medina, S; Messe, L; Millan, C; Orta, MM; Perdigon, ACJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 3176-3180 DOI: 10.1021/jp8072014
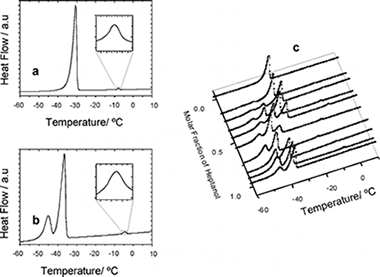
Abstract
The competitive adsorption of n-decane and n-heptan-1-ol adsorbed from the binary liquid mixture onto graphite has been studied using differential scanning calorimetry, incoherent quasielastic neutron scattering, and 1H and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance. A solid monolayer is identified at all bulk solution compositions with a melting temperature that varies with bulk composition in a manner resembling the bulk behavior. Incoherent elastic neutron scattering, IQNS, and nuclear magnetic resonance, NMR, data indicate that decane is preferentially adsorbed onto the surface over most of the composition range, heptanol being the principal surface component only at very high heptanol concentrations. NMR is proved, for the first time, to be an efficient tool to provide independent information on each component of the system.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/jp8072014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis of MCM-22 zeolites of different Si/Al ratio and their structural, morphological and textural characterisation
Delitala, C; Alba, MD; Becerro, AI; Delpiano, D; Meloni, D; Musu, E; Ferino, IMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118 (2009) 1-10 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.07.047
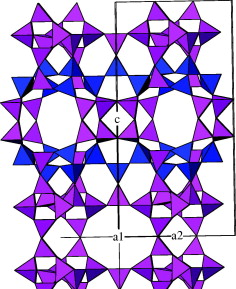
Abstract
MCM-22 zeolites with Si/Al in the 9–46 range were synthesised in rotating autoclave and characterised by X-ray diffraction, 1H, 29Si and 27Al magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance, scanning electron microscopy and nitrogen physisorption. For the Si/Al = 21, 30 and 46 samples both X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy revealed the crystallisation of pure MCM-22. Besides the latter, crystals of ferrierite also formed during the synthesis of the Si/Al = 9 sample. Based on the 1H MAS NMR spectra of dehydrated samples, the different proton species present on the MCM-22 samples were determined and quantified. Information about the incorporation of Al ions into the zeolite framework, as well as on the preferential crystallographic sites occupied in dependence on the Si/Al ratio of the sample, was obtained by 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy. From 29Si MAS NMR spectra, differences in the degree of crystallinity of the samples were assessed, the results being in agreement with the diffraction data. Nitrogen physisorption runs revealed the microporous nature of the adsorbents, with a supermicropore to ultramicropore volume ratio in good agreement, for the best crystallised samples, with the porous structure with supercages and sinusoidal channels of the ideal MCM-22 crystal.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.07.047
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Control over the Structural and Optical Features of Nanoparticle-Based One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals
Calvo, ME; Sanchez-Sobrado, O; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HLangmuir, 25 (2012) 2443-2448 DOI: 10.1021/la8030057
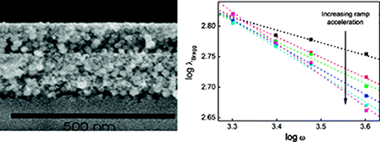
Abstract
Herein we present a detailed analysis of the effect of the spin-coating protocol over the optical properties of nanoparticle-based one-dimensional photonic crystals. Based on these results, we provide a reliable synthetic route to attain high-quality porous multilayers in which the effect of imperfections is minimized and whose Bragg diffraction can be precisely tuned over the entire visible and near-infrared spectrum. We present a systematic study of the effect of the acceleration ramp and final rotation speed over the structural and optical quality of these materials. This allows us to relate the structural variations observed with the different relative importance of fluid flow and solvent evaporation on the thinning of each layer in the stack for the different deposition conditions employed.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/la8030057
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Liquid-phase thiophene adsorption on MCM-22 zeolites. Acidity, adsorption behaviour and nature of the adsorbed products
Delitala, C; Cadoni, E; Delpiano, D; Meloni, D; Alba, MD; Becerro, AI; Ferino, IMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118 (2009) 11-20 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.08.008
Abstract
The liquid-phase adsorption of thiophene from thiophene/iso-octane solutions has been investigated in batch conditions at room temperature and atmospheric pressure on MCM-22 zeolites with Si/Al in the 9–46 range. Thiophene adsorption was found to occur in two steps whatever the Si/Al ratio of the adsorbent. The presence of ferrierite besides the MCM-22 phase caused a significant loss of the adsorption performance. For pure MCM-22 samples, the Si/Al ratio influenced the adsorption performance. Based on the acid properties of the samples, investigated by adsorption microcalorimetry of ammonia, the adsorption features were interpreted by assuming that positively charged species were originated during the first step; these species underwent successive reaction with weakly adsorbed species formed in the second step, leading to heavy molecular weight organosulphur compounds. Direct evidence for the occurrence of reactive adsorption of thiophene involving its transformation into heavy molecular weight organosulphur compounds was obtained by GC/MS investigation of the nature of the adsorbed material recovered after the adsorption experiments. The peculiar structure of MCM-22 zeolites made possible the formation of long-sized organosulphur compounds. Due to the mechanism by which thiophene is transformed (i.e. progressive addition of other thiophene molecules), the size of the resulting products was found to depend also on the concentration of the weakly adsorbed thiophene molecules able to interact with those already activated through protonation.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.08.008
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Fabrication of ordered crystalline zirconium nanoporous membranes by an one-step procedure
Marquez, F; Morant, C; Pirota, KR; Borras, A; Sanz, JM; Elizalde, ENano Today, 4 (2009) 21-26 DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2008.10.012
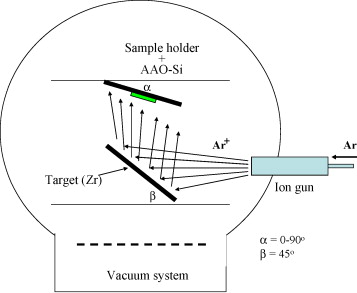
Abstract
Crystalline porous zirconium membranes were obtained by physical vapor deposition on AAO templates at room temperature. These membranes were found to have similar hexagonal nanohole arrays as the template and high crystallinity. The pore size of the synthesized metallic membranes could be controlled during the synthesis through appropriate parameters in the experimental procedure.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2008.10.012
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Porous One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals Improve the Power-Conversion Efficiency of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Colodrero, S; Mihi, A; Haggman, L; Ocana, M; Boschloo, G; Hagfeldt, A; Miguez, HAdvanced Materials, 21 (2009) 764-770 DOI: 10.1002/adma.200703115
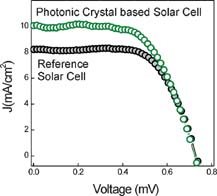
Abstract
A device for solar-energy conversion was introduced in which a porous and highly reflecting 1D photonic crystal (1D PC) was coupled to a dye-sensitized nanocrystals anatase (NC-TiO2) electrode. The results show that the transparency of the PC-based dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum is very similar to that of the reference cell. The multilayer whose photonic bandgap has a larger overlap with the absorption band of the ruthenium dye, gives rise to a larger enhancement of the photocurrent. It is also seen that the porous 0.5μm thick PC, whose deleterious effect is compensated by the large increment in photocurrent. The spectral photoelectric response of the cell clearly shows the effect that coupling to a PC has on the current photogenerated in the dye-sensitized electrode.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.200703115
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
WC/a-C nanocomposite thin films: Optical and electrical properties
Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cusnir, N; Sanjines, RJournal of Applied Physics, 105 (2009) 033510 DOI: 10.1063/1.3060717

Abstract
WC/amorphous carbon (a-C) thin films were deposited by dual magnetron sputtering from individual WC and graphite targets. The influence of film composition and microstructure on the optical and electrical properties was investigated. As evidenced by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and grazing angle x-ray diffraction measurements, the WC/a-C films are composite materials made of hexagonal W2C and/or cubic β-WC1−X nanocrystallites embedded in (a-C) matrix. The optical properties were studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry and the electrical resistivity was measured by the van der Pauw method between 20 and 300 K. Both the optical and the electrical properties of the WC/a-C films are correlated with the chemical composition and microstructure evolution caused by a-C addition. The optical properties of W2C/a-C and β-WC1−x/a-C films with a-C content ≤ 10 at. % are explained by modeling their dielectric functions by a set of Drude–Lorentz oscillators. Further increase in a-C content leads only to the formation of β-WC1−x/a-C nanocomposite structures and their optical properties progressively evolve to those of a-C single phase. The electrical resistivity as a function of the temperature of all the films exhibits a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity. Theoretical fitting using the grain-boundary scattering model shows that the transport properties are mainly limited by the grain size and electron mean free path parameters.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1063/1.3060717
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Porosity and microstructure of plasma deposited TiO2 thin films
Borras, A; Sanchez-Valencia, JR; Garrido-Molinero, J; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 118 (2009) 314-324 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.09.002

Abstract
The microstructure of TiO2 thin films prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition has been assessed by using water adsorption–desorption isotherms measured by means of a quartz crystal monitor (QCM). Thin films have been deposited by using titanium tetraisopropoxide as a precursor and by changing different experimental parameters of the deposition procedure such as temperature of the substrate, pressure, and gas composition in the plasma. The films were characteristic of different microstructures that, according to their scanning electron micrographs, have been categorized as columnar, homogeneous and crystalline. They also have different refraction indices with values between 1.95 and 2.41. Water and toluene adsorption isotherms have been measured by means of a QCM monitor for the films heated in vacuum to remove the water previously adsorbed in their pores. The analysis of the adsorption-desorption isotherms by means of the so called “t-plots” and the determination of the pore size distribution curves rendered that the three kinds of microstructures presented different kinds of isotherms and water adsorption behaviours. Columnar films consisted of micro- and meso-pores had a very high adsorption hystheresis at low pressures. Homogeneous films only had micropores and presented no adsorption hystheresis. Crystalline films consisted of both micro- and meso-pores but had no adsorption hystheresis at low pressures. A zone scheme has been proposed to account for the microstructure of the films depending on the plasma conditions utilized. The implications of the different water adsorption behaviours of the films for the determination of their refraction indices are discussed.
Febrero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.09.002
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of the microstructure on the mechanical and tribological behavior of TiC/a-C nanocomposite coatings
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCThin Solid Films, 517 (2009) 1662-1671 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2008.09.091
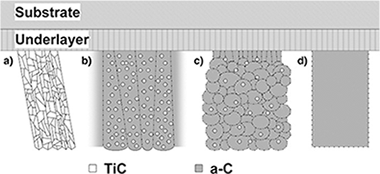
Abstract
The performance of protective thin films is clearly influenced by their microstructure. The objective of this work is to study the influence of the structure of TiC/a-C nanocomposite coatings with a-C contents ranging from ~ 0% to 100% on their mechanical and tribological properties measured by ultramicroindentation and pin-on-disks tests at ambient air, respectively. The microstructure evolves from a polycrystalline columnar structure consisting of TiC crystals to an amorphous and dense TiC/a-C nanocomposite structure when the amount of a-C is increased. The former samples show high hardness, moderate friction and high wear rates, while the latter ones show a decrease in hardness but an improvement in tribological performance. No apparent direct correlation is found between hardness and wear rate, which is controlled by the friction coefficient. These results are compared to the literature and explained according to the different film microstructures and chemical bonding nature. The film stress has also been measured at the macro and micro levels by the curvature and Williamson–Hall methods respectively. Other mechanical properties of the coating such as resilience and toughness were evaluated by estimating the H3/E⁎2 and H/E⁎ ratios and the percentage of elastic work (We). None of these parameters showed a tendency that could explain the observed tribological results, indicating that for self-lubricant nanocomposite systems this correlation is not so simple and that the assembly of different factors must be taken into account.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2008.09.091
Materiales Avanzados
Application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the search for and characterization of raw materials of interest in ceramics and glass
Garzon, E; Garcia, IG; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 48 (2009) 39-44 DOI: ---
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Experimental Demonstration of the Mechanism of Light Harvesting Enhancement in Photonic-Crystal-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Colodrero, S; Mihi, A; Anta, JA; Ocaña, M; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2012) 1150-1154 DOI: 10.1021/jp809789s
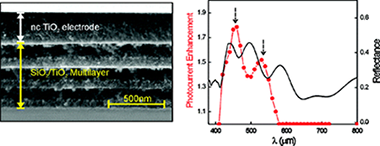
Abstract
Herein, we report an experimental analysis of the photogenerated current of very thin and uniform dye-sensitized nanocrytalline titanium oxide (nc-TiO2) electrodes coupled to high-quality one-dimensional photonic crystals. The effect of well-defined optical absorption resonances are detected both in optical spectroscopy and photogenerated current experiments, a clear correspondence between them being established. Our study demonstrates that light trapping within absorbing electrodes is responsible for the absorption enhancement that has previously been reported and unveils the mechanism behind it. We prove that this effect improves significantly the power conversion efficiency of very thin electrodes.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/jp809789s
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optically Active Luminescent Perylene Thin Films Deposited by Plasma Polymerization
Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Aparicio, FJ; Borras, A; Barranco, A; Alvarez-Herrero, A; Fernandez-Rodriguez, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 113 (2009) 12840-12847 DOI: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp807634j

Abstract
This work reports about the preparation of plasma polymerized thin films of perylene with thicknesses 30−150 nm and their characterization by different methods and the analysis of their optical properties. Highly absorbent and fluorescent films have been obtained by this method that combines the sublimation of the perylene molecules and their controlled polymerization by the interaction with remote Ar plasma. The polymeric films are very flat with a root mean square (rms) roughness in the range 0.3−0.4 nm. In contrast with the sublimated layers of perylene that present a high scattering of light, the polymerized films depict the well-defined absorption bands in the region 400−450 nm and fluorescence spectra of the perylene molecule at 475 nm. The films are formed by a matrix formed by cross-linked fragments of perylene and intact molecules that confer the observed optical properties to this material. The optical and microstructural characteristics of this type of thin films and the possibility to perform their deposition by using lithographic procedures make them suitable for their integration into photonic components for various applications. A preliminary study of the use of these films as an optical sensor of NO2 is also presented.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp807634j
General Quantum-Mechanical Study on the Hydrolysis Equilibria for a Tetravalent Aquaion: The Extreme Case of the Po(IV) in Water
Ayala, R; Martinez, JM; Pappalardo, RR; Paez, AM; Marcos, ESJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 113 (2009) 487-496 DOI: 10.1021/jp804957s
Abstract
A systematic study of the different hydrolyzed species derived from the hydrated Po(IV) in water, [Po(H2O)n(OH)m](4−m) for 1 m 4, and 4 m + n 9, has been carried out by means of quantum mechanical computations. The effects of outer solvation shells have been included using a polarizable continuum dielectric model. For a fixed number of hydroxyl groups, the preferred hydration number for the Po(IV) can be determined in terms of Gibbs energy. It is shown that the hydration number (n) systematically decreases with the increase in the number of hydroxyl groups (m) in such a way the total coordination number (n + m) becomes smaller, being 9 in the aquocomplex and 4 in the neutral hydroxo-complex. Free energies for the hydrolysis processes involving Po(IV) complexes and a different number of hydroxyl groups have been computed, revealing the strong tendency toward hydrolysis exhibited by these complexes. The predominant species of Po(IV) in aqueous solutions are ruled by a dynamical equilibrium involving aggregates containing in the first coordination shell OH− groups and water molecules. Although there is not experimental information to check the theoretical predictions, theoretical computations in solution seem to suggest that the most likely clusters are [Po(H2O)5(OH)2]2+ and [Po(H2O)4(OH)2]2+. The geometry of the different clusters is ruled by the trend of hydroxyl groups to be mutually orthogonal and to promote a strong perturbation of the water molecule in trans-position by lengthening the Po−H2O distances and tilting the corresponding bond angle. A general thermodynamic cycle is defined to compute the Gibbs free energy associated to the formation of the different hydrolyzed forms in solution. From it, the estimates of pKa values associated to the different protolytic equilibria are provided and discussed. Comparison of the relative values of pKa along a hydrolysis series with the experimental values for other tetravalent cations supports its consistency.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1021/jp804957s
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold nanoparticles on silica monospheres modified by amino groups
Penkova, A; Blanes, JMM; Cruz, SA; Centeno, MA; Hadjiivanov, K; Odriozola, JAMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 117 (2009) 530-534 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.07.041

Abstract
Silica monospheres with a diameter of 330 nm modified with aminosilane compounds of three different basicities have been prepared. Surface coverage of the silica with an organic compound leads to an increase of the point of zero charge (PZC) of the silica surface from 2.1 to 5.1, 6.5 and 7.2 values, depending on the amine used. From these silicas, gold-containing catalysts have been prepared by a deposition–precipitation method at the same pH as the PZC of the support. The best results have been obtained using 3-(Diethoxymethylsilyl) propylamine as a modifying agent, which has allowed obtaining a good dispersion of the gold particles with an average size of 3.8 nm.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.07.041
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Luminescent and Optical Properties of Nanocomposite Thin Films Deposited by Remote Plasma Polymerization of Rhodamine 6G
Aparicio, FJ; Borras, A; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I; Groning, P; Alvarez-Herrero, A; Fernandez-Rodriguez, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Barranco, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 6 (2009) 17-26 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200800092

Abstract
Mechanically stable and insoluble fluorescent thin films have been deposited by sublimating Rhodamine 6G laser dye in the downstream region of a low-power microwave ECR plasma using an experimental set-up designed to control the interaction of the dye molecule with the glow discharge. The use of reactive organosilane plasmas allows to control the dye distribution inside the matrix, leading to solid nanocomposite thin films containing non-aggregated dye molecules. The suppression of aggregates is a key issue to avoid fluorescence quenching. The obtained nanocomposite films are interesting because of their strong absorption and high fluorescence emission. In addition, they can be patterned using in situ plasma treatments in order to produce optically functional devices.
Enero, 2009 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.200800092
2008
2008
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Fabrication, chemical etching, and compressive strength of porous biomimetic SiC for medical implants
Torres-Raya, C; Hernandez-Maldonado, D; Ramirez-Rico, J; Garcia-Ganan, C; de Arellano-Lopez, AR; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of Materials Research, 23 (2008) 3247-3254 DOI: 10.1557/JMR.2008.0392
Abstract
BioSiC is a biomimetic SiC-based ceramic material fabricated by Si melt infiltration of carbon preforms obtained from wood. The microstructure of bioSiC mimics that of the wood precursor. which can be chosen for tailored properties. When the remaining g unreacted Si is removed. a SiC Material with interconnected porosity is obtained. This porous bioSiC is Under study for its use as a medical Implant material. We have successfully fabricated bioSiC from Sipo wood and Studied the kinetics of Si removal by wet etching. The results suggest that the reaction is diffusion-limited, and the etch rate follows a t(-0.5) law. The etching rate is found to be anisotropic, which can be explained attending to the anisotropy of the pore distribution. The compressive strength was studied as a function of etching, time. and the results show a quadratic dependence with density. In the attainable ran-e of densities, the strength is similar or better than that of human bone.
Diciembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1557/JMR.2008.0392
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth and characterization of the ZnO/ZnS bilayer obtained by chemical spray pyrolysis
Lopez, MC; Espinos, JP; Leinen, D; Martin, F; Centeno, SP; Romero, R; Ramos-Barrado, JRApplied Surface Science, 255 (2008) 2118-2124 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.06.195
Abstract
ZnO/ZnS bilayer antireflection coatings have been prepared by spray pyrolysis using aqueous solutions of zinc acetate and thiourea or zinc chloride and thiourea. The structure, surface morphology, chemical composition and optical transmittance of the bilayer have been examined as a function of the composition of the initial solution. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis and Ar ion-beam sputter etching was carried out to obtain a depth profile of bilayer. Neither carbon nor other by-products, which could alter the optical transmittance of the bilayer were found in either the interface or bulk. The differences between the bilayers arise from the annealing of the ZnS underlayer, as well as the precursor used to prepare it.
Diciembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.06.195
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis of Supported Single-Crystalline Organic Nanowires by Physical Vapor Deposition
Borras, A; Aguirre, M; Groening, O; Lopez-Cartes, C; Groening, PChemistry of Materials, 20 (2008) 7371-7373 DOI: 10.1021/cm802172p
Characterization of iron oxide-based pigments by synchrotron-based micro X-ray diffraction
Herrera, LK; Cotte, M; de Haro, MCJ; Duran, A; Justo, A; Perez-Rodriguez, JLApplied Clay Science, 42 (2008) 57-62 DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2008.01.021
Abstract
The characterization of iron in microsamples by conventional X-ray diffraction is difficult due to its low concentration in thin layers and its low reflecting power relative to other phases. Synchrotron radiation can provide unique information because of high intensity, sample penetration, small beam diameter and fast data collection. In this study, micro X-ray diffraction (mu-XRD) data were obtained of two samples taken from wall paintings at San Agustin's Church in Cordoba. Crystalline iron phases such as goethite, lepidocrocite and hematite in the cross-section of the painting thin layers were identified. with a good spatial resolution. Conventional XRD only detected hydrocerussite and cerussite rather than the full range of iron phases found in the mu-XRD experiments.
Diciembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2008.01.021
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Comparative performance of nanocomposite coatings of TiC or TiN dispersed in a-C matrixes
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCSurface & Coatings Technology, 203 (2008) 756-760 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.08.064
Abstract
Titanium carbide (TiC) and nitride (TiN) are two of the most used materials in the field of protective coatings, due to their optimal mechanical and tribological properties. The addition of the second phase can provide extra benefits to the coating, like improved hardness, reduced friction and/or oxidation resistance. In this work, we present two series of coatings in which hard crystalline TiC and TiN phases are mixed at the nanometric level with a soft lubricant phase like amorphous carbon (a-C). Both series of TiC/a-C and TiN/a-C nanocomposite coatings were prepared by double magnetron sputtering of C and Ti(N) targets in a Ar atmosphere (P = 5 x 10(-3) Torr) by changing the power ratio applied to each magnetron. The chemical composition has been measured by electron energy loss spectroscopy, and the phase composition changes gradually from pure C to pure TiC or TiN through nanocomposite structures with variable phase contents. These structures are confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and diffraction techniques. like X-ray diffraction and electron diffraction. The mechanical and tribological properties are found to be mainly controlled by the hard/soft phase ratio present in the coating. The changes in hardness values follow similar trends in both types of nanocomposite samples. Introducing a small amount of TiN or TiC into a-C matrix causes a hardness reduction, but further addition of crystalline phase makes increase the hardness. The best tribological properties are found for nanocomposite coatings (both TiN/a-C and TiC/a-C) with high amount of a-C (> 65%), showing low friction values (f similar to 0.1) and high wear resistance (k about 10(-7) mm(3) N-1 m(-1)). However, coatings with 50-60% a-C show a good compromise between tribological and mechanical properties.
Diciembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.08.064
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Photocatalytic Degradation of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Over ZrO2, Cu/ZrO2 and Fe/ZrO2 Photocatalysts Synthesized by Sol Gel Method
Alvarez, M; Lopez, T; Odriozola, JA; Gonzalez, RDJournal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 8 (2008) 6414-6418 DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2008.003
Abstract
Photocatalytic oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid was performed over ZrO2, Cu/ZrO2 and Fe/ZrO2 catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method. The samples were annealed at 400 degrees C. Textural and electronic characterization was carried out using BET and UV-Vis in order to establish the relationship between surface, pore volume and E. with the photoactivity of the materials. The degradation of the acid was followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy. The disappearance of the herbicide in solution follows approximately pseudo-first order kinetics. The apparent rate constants were calculated for the three catalysts. The results reveal that Fe/ZrO2 exhibits the best photoactivity for the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
Diciembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2008.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kissinger kinetic analysis of data obtained under different heating schedules
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 94 (2008) 427-432 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-008-9200-2
Abstract
The dynamic heating rate method developed by TA Instruments (Hi-ResTM) is a kind of sample controlled thermal analysis in which a linear relationship between the logarithm of the heating rate and the rate of mass change is imposed. It is shown in this paper that the reacted fraction at the maximum reaction rate strongly depends on the parameters selected for the Hi-Res heating algorithm, what invalidates the use of the Kissinger method for analysing Hi-Res data unless that the reaction fits a first order kinetic law. Only in this latter case, it has been demonstrated that it is not required that a constant value of the reacted fraction at the maximum reaction rate is fulfilled for determining the activation energy from the Kissinger method. In such a case the Kissinger plot gives the real activation energy, independently of both the heating schedule used and the value of the reacted fraction, alpha(m), at the maximum.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-008-9200-2
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Catalytic growth of carbon nanotubes on stainless steel: Characterization and frictional properties
Abad, MD; Srichez-Lopez, JC; Berenguer-Murcia, A; Golovko, VB; Cantoro, M; Wheatley, AEH; Fernandez, A; Johnson, BFG; Robertson, JDiamond and Related Materials, 17 (2008) 1853-1857 DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2008.03.021
Abstract
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been grown both on a sample of stainless steel (317-2R) and on the same steel coated with cobalt colloid nanoparticles. Both materials are suitable supports for the growth of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes, although a more sparse growth of significantly thicker carbon nanotubes is observed in the case of the bare steel. We find that carbon nanotubes grown directly on the stainless steel support show very poor tribological behaviour whereas the support using nanoparticles for carbon nanotube growth displayed interesting tribological properties with friction coefficients of approximately 0.1-0.2. The modified CNT material (studied by Raman spectroscopy) adheres to both mating surfaces avoiding direct contact between asperities and plough so the friction and wear processes decrease greatly.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2008.03.021
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasmas and atom beam activation of the surface of polymers
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 41 (2008) 225209 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/22/225209
Abstract
Wetting properties of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and low-density polyethylene polymers have been investigated after treatment with a microwave (MW) plasma discharge at low pressure and a dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Experiments have also been carried out in situ with an atom source installed in an x- ray photoemission spectrometer (XPS). The water contact angle measured on both polymers experienced a significant decrease after activation, but a progressive recovery up to different values after ageing. Standard chemical analysis by XPS showed that the plasma and oxygen beam treatments produced an increase in the concentration of -C(O) x functional groups at the outermost surface layers of the treated polymers. Besides, the oxygen distribution between the topmost surface layer and the bulk has been obtained by non- destructive XPS peak shape analysis. Atomic force microscopy analysis of the surface topography showed that, except for PET treated with the MW plasma and the atom beam, the surface roughness increased after the plasma treatments. Wetting angle variations, oxygen content and distribution, surface roughness and evolution of these properties with time are comparatively discussed by taking into account the basic processes that each type of activation procedure induces in the outmost surface layers of the treated polymers.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/22/225209
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Pt/TiO2 brain biocompatible nanoparticles: GBM treatment using the C6 model in Wistar rats
Lopez, T; Recillas, S; Guevara, P; Sotelo, J; Alvarez, M; Odriozola, JAActa Biomaterialia, 4 (2008) 2037-2044 DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.05.027
Abstract
In the present work we synthesized inorganic oxide nanoparticle carriers of platinum compounds and tested their therapeutic effect on animal models in which C6 glioma cells have been inoculated. TiO2-containing Pt(NH3)(4)Cl-2 complexes were synthesized using sol-gel methods. The platinum species are chemically bonded to the TiO2 carrier, as shown by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of probe molecules. Treatment with TiO2-Pt nanoparticles reduces tumour growth rate by up to 56%, showing that a synergistic effect exists between the TiO2 carrier and the platinum drug.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.05.027
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Optical properties of Zr and ZrO2 films deposited by laser ablation
Prieto-Lopez, LO; Yubero, F; Machorro, R; De La Cruz, WMicroelectronics Journal, 39 (2008) 1371-1373 DOI: 10.1016/j.mejo.2008.01.048
Abstract
Optical properties of Zr and ZrO2 films in the energy range from 1.5 to 100eV were obtained by quantitative analysis of reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS) and ellipsometry. The films were prepared oil (I 1 1) silicon substrates by reactive laser ablation using a zirconium target. For the growth of ZrO2 films a pressure of 5 m Torr of oxygen in the growth chamber was used. The substrate temperature during deposition was 400 degrees C. The deposits were Studied ex situ by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and in situ by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and REELS. The ZrO2 films were found to be polycrystalline With monoclinic structure. The XPS results showed that the oxygen pressure used is the optimal control to produce ZrO2 films by laser ablation. A gap of 5eV for the ZrO2 film W IS measured by REELS.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mejo.2008.01.048
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Influence of the Capping Molecule on the Magnetic Behavior of Thiol-Capped Gold Nanoparticles
Crespo, Patricia; Guerrero, Estefania; Angel Munoz-Marquez, Miguel; Hernando, Antonio; Fernandez, AsuncionIEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 44 (2008) 2768-2771 DOI: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2001990
Abstract
Gold nanoparticles with an average particle size below 3 nm have been synthesized and stabilized with different thiol-derivatized molecules for studying the influence of the capping molecule on the magnetic behavior. Thiolated-alkane chains with different lengths as well as a thiol-containing biomolecule (tiopronin) have been selected as protecting shells for the synthesized NPs. Magnetic characterization indicates that the appearance of a ferromagnetic-like behavior is related not only with the formation of Au-S bonds linking the protective molecules to the nanoparticle surface but also with the formation of the nanoparticle itself as well as with the geometry of the capping molecule. The later seems to determine whether the protective monolayer shell is ordered or not. The simultaneous presence of Au-Au and Au-S bonds together with a reduced particle diameter, and the formation of an ordered monolayer protective shell, have been proved to be key parameters for the ferromagnetic-like behavior exhibited by thiol-functionalized gold NPs.
Noviembre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1109/TMAG.2008.2001990
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Crystallographic texture in Al2O3-ZrO2 (Y2O3) directionally solidified eutectics
Ramirez-Rico, J; de Arellano-Lopez, AR; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Pena, JI; Larrea, AJournal of The European Ceramic Society, 28 (2008) 2681-2686 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.04.015
Abstract
Directionally solidified Al2O3-based eutectics are in situ composites grown from the melt. The directional nature of the solidification process makes these materials highly anisotropic and therefore the measurement and quantification of their crystallographic texture is necessary to understand their physical properties. We studied the texture of Al2O3-ZrO2 (12 mol% Y2O3) eutectic rods by means of X-ray and electron backscattering diffraction. The phases grow according to the relationship (10 (1) over bar2}(Al2O3) //{110}(ZrO2) and Al2O3 is oriented with its c-axis approximately parallel to the growth direction. We observed that the c-axis orientation is not constant throughout the sample, but instead changes according to the distance from the growth axis. The c-axis orientation spread was found to be 10 degrees. This spread is a consequence of the curvature of the liquid-solid interface during solidification, whose shape we reconstructed using EBSD data.
Octubre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2008.04.015
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
The Role of Hydroxyl Groups in the Self-Assembly of Long Chain Alkylhydroxyl Carboxylic Acids on Mica
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Serrano, FM; Heredia, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 124 (2008) 16391-16401 DOI: 10.1021/jp805445z
Abstract
The adsorption and self-assembly of hydroxylated long chain fatty acids on mica has been studied by AFM. The presence of secondary midchain hydroxyl groups is found to strongly affect the self-assembly process via the reinforcement of lateral interactions between molecules by -OH center dot center dot center dot HO- hydrogen bonding. On the other side, the availability of an exposed terminal hydroxyl group in the acid molecule triggers the formation of a second layer due to the strength of tile -OH center dot center dot center dot HOOC- tail-to-head interaction. Surface coverage (theta) data follow a Langmuir-type relationship vs solution concentration (c). The analysis of the slope of 1/theta vs 1/c plots provides a relative estimation of the adsorption enthalpy for the formation of the first and second monolayers. Based on that, both the contribution of molecule-substrate and lateral molecule-molecule energy terms are found to be relevant in the self-assembly of this type of molecule oil mica.
Octubre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1021/jp805445z
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis of Spherical Down- and Up-Conversion NaYF4-Based Nanophosphors with Tunable Size in Ethylene Glycol without Surfactants or Capping Additives
Nunez, NO; Miguez, H; Quintanilla, M; Cantelar, E; Cusso, F; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 29 (2008) 4517-4524 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.200800363
Abstract
A very simple route for the synthesis of spherical down-conversion (DC) and up-conversion (UC) NaYF4-based nanophosphors is described which consists of a precipitation reaction at rather low temperature (max. 120 degrees C) from solutions containing sodium fluoride and appropriate Ln precursors in a common solvent (ethylene glycol/water mixtures), without the use of any other additive (complexing agent or surfactant). The role played by the nature of the yttrium precursor and the solvent on the morphological characteristics of the nanoparticles is discussed. The size of the nanospheres, which crystallized in the cubic alpha-NaYF4 phase, could be tuned within the 45-155 nm range by adjusting the reaction parameters (temperature and ethylene glycol/water ratio). The applicability of this method is illustrated for the synthesis of Eu-III-doped (DC), Tb-III-doped (DC) and Yb-III/Er-III codoped (UC) NaYF4 nanophosphors, whose luminescent properties were also analysed.
Octubre, 2008 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.200800363
- ‹ anterior
- 35 of 36
- siguiente ›














